COURSE OBJECTIVES
To study the aspects of Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
To gain knowledge of different types of stresses, strain and deformation induced in the components due to external loads.
To study the distribution of various stresses in the elements such as beams, shafts etc.
To study the effect of component dimensions and shapes on the stresses and deformations.
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 9 Hrs.
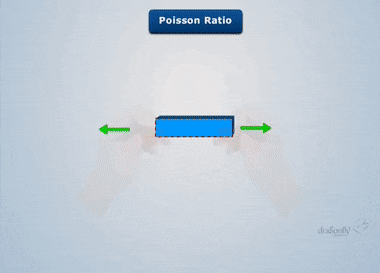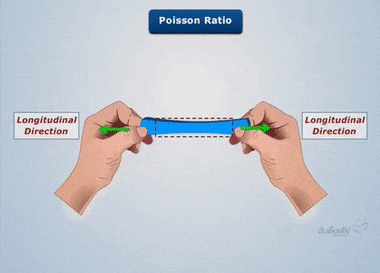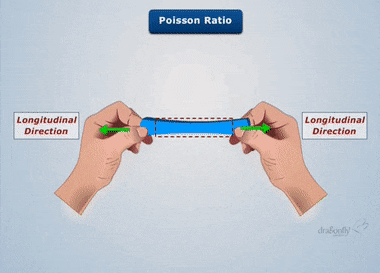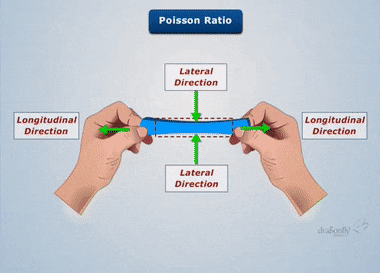
Rigid and Deformable bodies – Strength, Stiffness and Stability – Stresses; Tensile, Compressive and Shear – Deformation of simple and compound bars under axial load – Thermal stresses and strains. Elastic constants – Relation between Elastic constans- Strain energy and unit strain energy – Strain energy in uniaxial loads.
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN TWO DIMENSIONS 9 Hrs.
Principal planes and stresses – Mohr’s circle for biaxial stresses – Maximum shear stress - simple problems- Stresses on inclined planeBiaxial state of stresses – Thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Deformation in thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Efficiency of joint- Effect of Internal Pressure.
UNIT 3 BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES 9 Hrs.
Types of beams - Supports and Loads – Shear force and Bending Moment in beams – Cantilever, Simply supported and Overhanging beams – SFD and BMD for inclined loads and couples.Stresses in beams – Theory of simple bending – Stress variation along the length and in the beam section – Effect of shape of beam section on stress induced.
UNIT 4 TORSION 9 Hrs.
Analysis of torsion of circular bars – Shear stress distribution – Bars of Solid and hollow circular section – Stepped shaft – Twist and torsion stiffness – Composite shafts Springs - Laminated springs, axial load and twisting moment acting simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs– Deflection of helical coil springs under axial loads – stresses in helical coil springs under torsion.
UNIT 5 BEAM DEFLECTION 9 Hrs.
Columns – End conditions – Equivalent length of a column – Euler equation – Slenderness ratio – Rankine Gordon formula for columns. Elastic curve of Neutral axis of the beam under normal loads – Evaluation of beam deflection and slope: Double integration method, Macaulay Method, and Moment-area Method.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the fundamentals of Stress and Elastic Constants.
CO2 - Understand the concept of Principal stresses and thin shells.
CO3 - Create Shear force & Bending moment diagram and Bending stress.
CO4 - Apply the Concept of Torsion for Circular Shafts and Understand the concept of Springs.
CO5 - Understand the theory of Column and Beam deflection.
CO6 - Analyze overall deflection aspects related to Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., "Strength of Materials", Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd., 5th Edition, 2012.
2. Punmia B.C. & Jain A.K., Mechanics of Materials, Laxmi Publications, 2001.
3. Ryder G.H., "Strength of Materials", Macmillan India Ltd., 3rd Edition, 2002.
4. Ray Hulse, Keith Sherwin & Jack Cain, "Solid Mechanics", Palgrave ANE Books, 2004. 5. Allan F. Bower, "Applied Mechanics of Solids", CRC Press, 2009.
- ஆசிரியர்: Madhan Kumar G
