SMEA1303 FLUID MECHANICS AND FLUID MACHINERY
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the fluid properties, flow characteristics and hydrostatic force on surfaces.
To study the equation of motions such as mass, momentum and energy equation and their practical applications.
To understand the functioning and characteristic curves of hydraulic machines.
UNIT 1 FLUID PROPERTIES 9 Hrs.
Fluid Properties: Density-Specific Weight-Specific Gravity-viscosity-surface tension-capillarity-Vapour pressure-compressibility. Fluid Static: Hydrostatic Law-Pressure Variation in static fluid-Hydrostatic force on a submerged plane surfaces-Location of hydrostatic force. Manometers-Simple, U tube and differential Manometers. Buoyancy-Meta centric height-determination of stability of floating bodies and submerged bodies.
UNIT 2 EQUATIONS OF MOTION 9 Hrs.
Types of fluid flow-Concept of Control Volume- Control Volume Analysis of mass, momentum and energy. Differential equation of continuity and momentum - Euler’s and Bernoulli’s Equation and its applications. Flow Measurement: Orifice meter, Venturi meter, Piezometer, Pitot tube.
UNIT 3 FLOW THROUGH ORIFICE, NOTCHES, WEIRS AND PIPES 9 Hrs.
Hydraulic co-efficient-Flow through orifice, Notches and weirs. Laminar and Turbulent flow-Reynolds experiment-laminar flow through circular pipe (Hagen poiseulle’s)-Major and minor losses in pipes-Darcy weisbach’s equation, chezy’s formula-friction factor- moody diagram-pipes in series and pipes in parallel-total energy line-hydraulic gradient line-Equivalent pipe. Concept of Boundary Layer-Types of boundary layer thickness-drag on flat plate.
UNIT 4 PUMPS 9 Hrs.
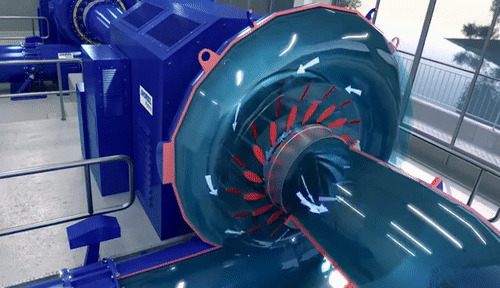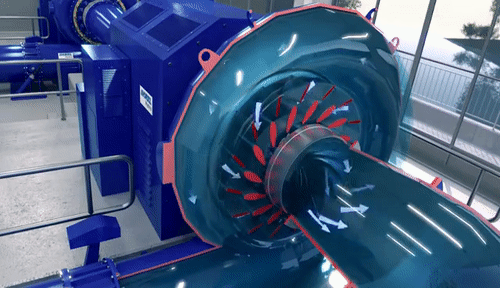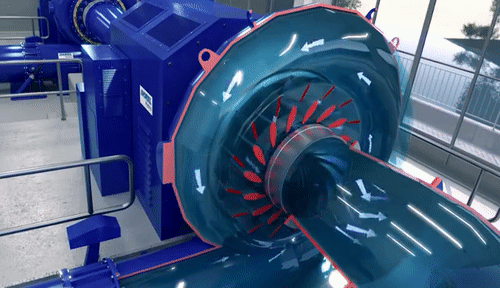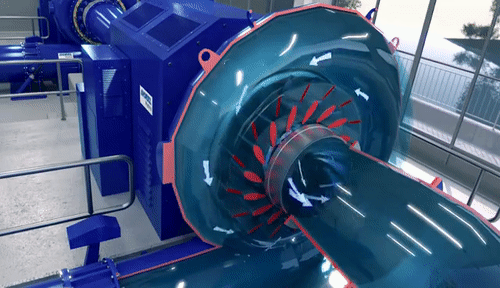
Centrifugal Pumps: Introduction-Definitions of heads and efficiencies-Operations-work done by the Impeller with Velocity triangles-Performance curves-Cavitations-Multi-staging: Pumps in Series and Parallel. Reciprocating Pumps: Operation–power required driving the pump-Slip-indicator Diagram–Separation-Air vessels.
UNIT 5 TURBINES AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 9 Hrs.
Hydraulic Turbines: Classification of hydraulic turbines-Working principle of Pelton wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines-velocity triangles-draft tube-hydraulic turbine characteristics. Governing of turbines. Dimensional Analysis: Needs and methods-Buckingham’s π Theorem, Non-Dimensional Numbers, Similarities of flow. Model studies. Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the different properties of fluids and compute the fluid pressure in a pipe & hydrostatic forces acting on different surfaces.
CO2 - Analyze the Bernoulli’s theorem and applies it in engineering application.
CO3 - Evaluate and compare (i) the hydraulic coefficients and (ii) the energy losses in pipes.
CO4 - Explain the principle, working and operating characteristic curves of different types of pumps and estimate the power required.
CO5 - Distinguish the principle, working and operating characteristic curves of different types of turbines and compute the power developed.
CO6 - Understand the methods of dimensional analysis and application in model analysis.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., "Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Machines", 9th Edition, Laxmi Publications, 2015.
2. Modi P.N., Seth S.M., "Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Including Hydraulic Machines", 21st Edition, Standard Book House, 2017.
3. Goyal, Manish Kumar, "Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines", PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 2015.
4. Kumar K.L., "Engineering Fluid Mechanics", 8th Edition, Eurasia Publication House (P) Ltd, 2014.
5. Rajput R.K., "Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Machines", 4th Edition, S. Chand Limited, 2008.
6. Yunus.A.Cengel, John.M.Cimbala, "Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Application", 3rd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2013.
7. Robert W. Fox, Alan T. McDonald, Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell, "Fluid Mechanics", 9th Edition, Wiley India, 2016.
8. Franck M. White, "Fluid Mechanics", 8th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publication, 2015.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
