தேடல் விளைவுகள்: 406
UNIT 1 CONCEPTOF SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS 9 Hrs. Concept of stress and strain, Hooke's law-Tension, Compression, and Shear, stress-strain diagram-Poisson's ratio, elastic constants and their relationship- Deformation of simple and compound bars. Principal plane, principal stress, maximum shearing stress - Uniaxial, biaxial state of stress-Mohr's circle for plane stresses.
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF BEAMS 9 Hrs. Types of beams and loads-shear force and bending moment diagrams for cantilevers, simply supported and overhanging beams. Theory of pure bending- assumptions in the simple bending theory, Flexure formula: its application to beams of rectangular, circular and channel, I&T Sections,: Combined direct and bending stresses in fore mentioned sections.
UNIT 3 DEFLECTION OF BEAMS 9 Hrs. Differential Equation of the Elastic Axis-Deflection and slope of beams-Double Integration, Area Moment and Macaulay’s methods for simply supported, Cantilever and overhanging beams.
UNIT 4 STRESSES IN SHAFTS, HELICAL SPRINGS AND THIN PRESSURE VESSELS 9 Hrs. Torsion of Circular Shafts–Shear Stresses and Twist in Solid and Hollow Shafts. Close and open Coil Helical springs. Stresses in Thin Walled Pressure Vessels.
UNIT 5 COLUMNS AND FAILURE THEORIES 9 Hrs. Columns- Member subjected to combined bending and axial loads, Euler's theory, Crippling load, Rankine's theory. Failure theories - Maximum Stress theory – Maximum Strain Theory – Maximum Shear Stress Theory – Distortion Theory – Maximum Strain energy theory. Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Analysis of different types of stresses and strains. CO2 - Analysis of different types of beams and loads acting on it. CO3 - Analysis of deflections in beams. CO4 - Analysis of stresses in shafts, helical springs and pressure vessels. CO5 - Analysis of Column structure and understanding of failure theories.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Malhotra,D.R.andGupta,H.C. ,“The Strength of Materials”, Satya PrakasanTech.India Publications, New Delhi, 2011.
2. Kazimi.S.M.A., “Solid Mechanics”, TataMcGrawHill,1976. Dym.C.L.and Shames I.H., Solid Mechanics”, McGraw hill,
Kogakusha, Tokyo, 2012.
3. Timoshenko.S.,Young,"Elements of Strength of Material", Vol. I & II, T.Van Nostrand CoInc, Princeton, N.J. 2012.
4. Ferdinand P.Beer, and Rusel l Johnston, E .,”Mechanics of Materials”, SI Metric Edition, McGrawHill, 2011.
5. Rajput. R.K.,”Strength of materials”, Fourth Edition,S.ChandLimited,2007

To impart knowledge to the students about advanced technology in food science and recent trends
adapted in food industry.

- ஆசிரியர்: Annam Renita A
- ஆசிரியர்: Karthikeyan M
➢ To focus on basics of semiconductor physics, Predominant CMOS technology.
➢ To study challenges of digital VLSI design.
➢ To get an idea about combinational logic circuit using CMOS logic style.
➢ To acquire the knowledge about sequential logic circuit and subsystem design.
➢ To extract the backend VLSI algorithms for ASIC.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Analyze the AC and DC characteristics of MOSFET.
CO2 Select the suitable style of CMOS logic for the design of combinational logic circuits.
CO3 Analyze the limitations and the inherent trade-offs involved in sequential logic design.
CO4 Analyze the performance of CMOS subsystems and memory structures.
CO5 Evaluate the performance of programmable logic devices and FPGA.
CO6 Create a significant VLSI system design project having a set of objectives criteria and design constraints of ASICs along with algorithms of backend VLSI.

- ஆசிரியர்: MUTHIAH M. A
Mechanical Engineering, as its name suggests, deals with the mechanics of operation of mechanical systems. It includes design, analysis, testing, manufacturing and maintenance of mechanical systems.

- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
- The ability to identify reflects upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements.
- Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject
COURSE OUTCOME:
· CO1: Apply laws of mechanics to determine efficiency of simple machines with consideration of friction.
· CO2: Understand interference of sound waves and longitudinal standing waves
· CO3: Describe basic definition and conception of materials and physical properties of materials
· CO4: Understand the nature of thermodynamic properties of matter like internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, temperature, pressure and specific volume
· CO5: Understand the properties of light like reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction etc
- ஆசிரியர்: VIJAI ANAND K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand importance of bioethics and biosafety. To understand legal social and economic impacts of biotechnology. To understand regulatory guidelines and their importance. To understand importance of patent.
Ø To understand procedure to apply for patent.
Ø To understand procedure of assessment of biosafety for biotech foods. To understand ethical implications of biotechnology.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSAFETY
Definition of ethics and Bioethics, Ethics in Biotechnology(positive and negative effects with classical examples – Rice with Vitamin A, No-till Agriculture, cotton without insecticide, reduced need for fertilizer, biological pest control , slow ripening fruits and controlled ripening, fast growing trees and fishes.
UNIT 2 GMO
Guidelines for research with transgenic organisms. Environmental impact of genetically modified organisms (beneficial and hazardous impact), Field trials with GMO, Containment levels. Biosafety protocol, Cartagena Biosafety protocol, Mechanism of implementation of biosafety guidelines. Biosafety and politics. Biosafety database.
UNIT 3 IMPLICATIONS OF BIOSAFETY
Awareness education on genetically engineered organism.-Transgene instability, gene flow, resistance/ tolerance of target organism, increase weedlessness, risks and uncertainty associated with Biotechnology. Containment levels and their impact on Environment- Containment- definition, types of containment, summary of recommended Biosafety levels for infectious agents, detail checklist–premises and lab equipment, Animal facilities, environment.
UNIT 4 GLP AND PATENTS
Gene technology laboratory. GLP and Bioethics- introduction, national Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), the GLP authority functions, Good Laboratory Practices- necessity, aspiration and responsibility. Procedure to apply patent, other intellectual properties viz copy rights, Rights, Plant breeder’s rights, trade secrets/ trade symbol etc. WTO, TRIPS, PCT and GATT. IPR problems and its hindrance.
UNIT 5 ETHICS.
Ethics in clinical trials and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) – Definition of clinical trials and GCP, general information about clinical trials, need to conduct clinical trials, faces ofclinical trials, institutional set ups for conducting clinical trials, ethics in clinical Biotechnology
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Safety Assessment by Thomas, J.A., Fuch, R.L. (2002), Academic Press.
2. Biological safety Principles and practices) by Fleming, D.A., Hunt, D.L., (2000). ASMPress.
3. Biotechnology - A comprehensive treatise. Legal economic and ethical dimensions VCH.Bioethics by Ben Mepham, Oxford University Press, 2005.
4. Bioethics & Biosafety by R Rallapalli & Geetha Bali, APH Publication, 2007
5. Bioethics & Biosaftey By Sateesh Mk (2008), Ik Publishers
6. Biosafety And Bioethics Rajmohan Joshi Publishers
Introduction to pharmacology, scope of pharmacology.
Routes of administration of drugs
General mechanism of drugs action
Drugs acting on the central Nervous system

COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To impart knowledge on Construction and principle operation of Asynchronous and Synchronous machines.
- To impart knowledge on not self-starting AC machines.
- To convey knowledge on speed control of three-phase induction motors.
- To analyze performance characteristics of Synchronous and Asynchronous machines.
- To convey knowledge on synchronized operation of an Alternator with an Infinite bus bar.

- ஆசிரியர்: Abitha Memala W
- To know about the functioning of combinational and sequential logic circuits in detail.
- To analyse the behaviour of CSSN using different tables and diagrams.
- To model a CSSN and to understand its behaviour.
- To understand about Algorithmic State Machines (ASM) and to design digital circuits with the aid of ASM chart.
- To analyse the behaviour of Asynchronous Sequential Circuit (ASN) using different tables and diagrams.
- To implement the digital design using PLDs and FPGAs.
- ஆசிரியர்: Dr. SUMATHI M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ÿ To study the characteristics of advanced power semiconducting switches.
ÿ To analyse the on-state and switching losses involved in the operation of power semiconducting switches.
ÿ To study the firing and protection circuits of advanced power semiconducting switches.
- ஆசிரியர்: Bharathi M L
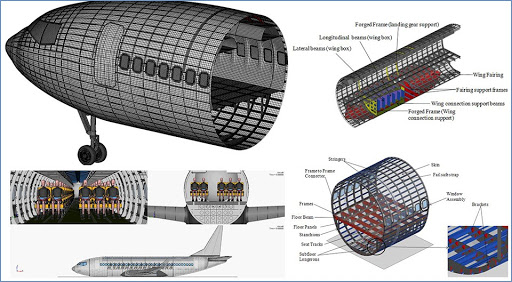
AIRCRAFT COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
L T P Credits Total Marks
3 0 0 3 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To study the mechanics of composites in micro level and macro level.
To study the plate, shell and sandwich theories of composites for various applications.
To understand the fabrication methods and design of composite structures.
UNIT 1 MICROMECHANICS 9 Hrs.
Introduction - advantages and application of composite materials – types of reinforcements and matrices - micro mechanics
– mechanics of materials approach, elasticity approach- bounding techniques – fiber volume ratio – mass fraction – density
of composites. Effect of voids in composites
UNIT 2 MACROMECHANICS 9 Hrs.
Generalized Hooke’s Law - elastic constants for anisotropic, orthotropic and isotropic materials - macro mechanics stressstrain relations with respect to natural axis, arbitrary axis – determination of in plane strengths of a lamina - experimental
characterization of lamina. Failure theories of a lamina. Hygrothermal effects on lamina.
UNIT 3 LAMINATED PLATE THEORY 9 Hrs.
Governing differential equation for a laminate. Stress – strain relations for a laminate. Different types of laminates. in plane
and flexural constants of a laminate. Hygrothermal stresses and strains in a laminate. failure analysis of a laminate. Impact
resistance and interlaminar stresses. netting analysis.
UNIT 4 SANDWICH CONSTRUCTIONS 9 Hrs.
Basic design concepts of sandwich construction - materials used for sandwich construction - failure modes of sandwich
panels - bending stress and shear flow in composite beams.
UNIT 5 FABRICATION PROCESS AND REPAIR METHODS 9 Hrs.
Various open and closed mould processes, manufacture of fibers, importance of repair and different types of repair
techniques in composites – autoclave and non-autoclave methods.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Understand different constituent materials of composites and properties.
CO2 - Analyze the mechanical behaviour of laminated composites based on fiber direction.
CO3 - Understand the design and failure modes of sandwich composites.
CO4 - Analyse the Hygrothermal property and interlaminar shear strength of composite.
CO5 - Understand fabrication methods based on various applications .
CO6 - Understand different types of repair techniques in composites.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Dam Ishai., "Mechanics of Composite Materials", 2010.
2. Autar K Kaw, ‘Mechanics of Composite Materials’, CRC Press, 2012.
3. Madhuji Mukhapadhyay, Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structures, University Press, 2012.
4. Agarwal, B.D., and Broutman, L.J., "Analysis and Performance of Fibre Composites," John Wiley and sons. Inc., New
York, 95.
5. Lubin, G., "Handbook on Advanced Plastics and Fibre Glass", Von Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1989.
6. Calcote, L R. “The Analysis of laminated Composite Structures”, Von – Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York 1998.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 Question of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concepts of applying Aero thermodynamics to air breathing propulsion. To familiarize the student's ability to analyze the concepts of compressor. To understand the basics of Axial Turbine. To understand the basics of Ramjet and Scramjet.
UNIT 1 THERMODYNAMICS OF AIR BREATHING PROPULSION 9 Hrs. History and classifications of Aero engines, Working of gas turbine engine – Thrust equation – Factors affecting thrust – Engine performance parameters – Efficiency, Specific fuel consumption, Methods of thrust augmentation – The propeller, turboprop, turbofan and turbojet engines characteristics.
UNIT 2 INLETS, COMBUSTION CHAMBER AND NOZZLES 9 Hrs. Introduction-Subsonic inlets-Supersonic inlets-Modes of Inlet operation- Gas turbine combustors-Types of combustion chamber-Fuel injector- Flame Tube cooling-Flame Stabilization-Flame holders- Theory of flow in isentropic nozzles – Losses in nozzles –Nozzle efficiency––nozzle choking –Over expanded and under expanded nozzles – Ejector and variable area nozzles.
UNIT 3 AIR COMPRESSOR 9 Hrs. Compressor and its classification- Centrifugal compressor - Work and compression ratio -Performance characteristicsCentrifugal compressor staging- Axial compressor-Work and compression ratio- Degree of reaction- Characteristic performance of a single stage axial compressor- Characteristic performance of a multistage axial compressor- Cascading of axial compressor-Compressor efficiency.
UNIT 4 AXIAL TURBINES 9 Hrs. Axial turbine stage -Velocity triangles and Power output - Elementary theory - Vortex theory- Limiting Factors of gas turbine design-Turbine performance- Turbine Blade cooling- Axial flow Turbine and compressor matching.
UNIT 5 RAMJET AND SCRAMJET 9 Hrs. Operating principle of RAMJET engine- RAMJET with afterburner- RAMJET performance- SCRAMJET working principleProblems faced in supersonic combustion.
Max 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOME On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Understand the working principles of gas turbine. CO2 - Comprehend the sound foundation in the design principles of inlets, combustion chambers, nozzles used in aircraft engines. CO3 - Learn the operation of compressors in aircraft engines. CO4 - Understand the concept of turbines in gas turbine propulsion systems. CO5 - Understand the principle and performance of ramjet and scramjet propulsion. CO6 - Applying the importance of Propulsion to Aircraft system.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Philip Hill and Carl Peterson, “Mechanics and thermodynamics of propulsion”, Pearson India, second edition 2010.
2. V.Ganesan., “Gas Turbines”, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, third edition, 2010.
3. Cohen.H, Rogers.G.F.C. and Saravanamuttoo.H.I.H, “Gas turbine theory”. Pearson education, fifth edition,2001.
4. Rathakrishnan E., “Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics”, Prentice-Hall India, 2012.
5. Saeed Farokhi, “Aircraft Propulsion”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc ., 2009.
6. Rolls Royce Jet Engine – 5thEdition – 1996.

- ஆசிரியர்: MATHIYARASI M
COURSE OBJECTIVES To get clear cut idea about the stability of aircraft at various flight conditions.
UNIT 1 BASIC CONCEPTS 11 Hrs.
Aircraft Axis System, Coordinate Transformation, Aircraft Force Equations, Moment Equations, Basic Concept Of Stability And Control, Longitudinal And Lateral- Directional Equations, Kinematic Equation
UNIT 2 LONGITUDINAL DYNAMIC STABILITY AND CONTROL 12 Hrs.
Stick - fixed stability, control effectiveness, hinge moment, tabs, aerodynamic balancing, effects of freeing the stick. Control forces and force gradients. Critical conditions for stability and control.
UNIT 3 MANEUVERABILITY 11 Hrs.
Effect of maneuvers. Longitudinal dynamic stability, equations of motion of a disturbed aircraft, stability derivatives, characteristic equation for stick fixed case, modes and stability criterion, effect of freeing the stick.
UNIT 4 DYNAMIC STABILITY 11 Hrs.
Brief description of lateral and directional dynamic stability- spiral, divergence and Dutch roll. Response, automatic control, autorotation and spin. Determination Of Neutral Points And Maneuver Points In Flight Tests
UNIT5 MODERN CONTROL THEORY 15 Hrs.
Classical Vs modern control theory, introduction – state-space modeling, canonical transformation, controllability and observability, state-feedback design, application of modern control theory to aircraft autopilot design- stability augmentation, autopilot design, state observer, optimal control, problems . Introduction to aircraft autopilot design using classic control theory. Introduction to nonlinear problems in aircraft flight dynamics - Inertia coupling. - High angle of attack phenomena - Flexibility effects -Divergence.
Max.60 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Thomas R. Yechout, ‘An introduction to Aircraft Flight Mechanics’, AIAA educational Series; 2003.
2. Bernard Etkin, Lloyd Duff Reid, Dynamics of Flight, Stability & Control, 3rd ed, John Wiley & Sons, 1995
3. Malcom J Abzug, E E. Larrabee, Airplane Stability & Control , 2nd ed, Cambridge University Press,, 2002
4. Nelson. R.C., Flight Stability and Automatic Control, McGraw Hill, 1989.
5. Perkins, C, D.,and Hage, R,E., Airplane Performance, Stability and Control, Wiley Toppan, 1974.
(Computational problems can be given as assignments)

This course deals and integrates with the following concepts
- Differentiate baseband and passband transmissions & realize the needs for modulation.
- Explain the Functional blocks of a communication system & Classification of communications based on the type of modulation techniques and channels used.
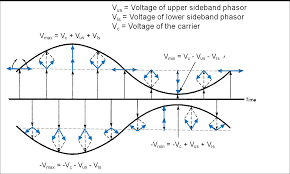
- Analyze Amplitude modulation and their types (DSB-SC, SSB-SC and VSB) using mathematical equations, Frequency Spectrum, Band Width, and Power relations.
- Demonstrate the generation of AM at the transmitter side and de-modulation process using appropriate circuits.
- Compare FM with AM. Analyze single tone and multi-tone FM using mathematical equations, Frequency Spectrum, and Band Width. Differentiate WBFM from NBFM.
- Relate FM (as Indirect PM) and PM (as indirect FM) using mathematical proof with a functional block diagram set-up.
- Demonstrate the FM modulator (direct and indirect methods) at the transmitter side and demodulator process with suitable circuits.
- Various noise sources and types
- Analyze, AM, PM, PAM, PDM, PPM, and PCM using mathematical equations and demonstrate their modulation and demodulation /techniques.
- Understand the importance of the sampling process in pulse modulation systems and explain various multiplexing techniques with many message inputs.
- Demonstrate the working of AM and FM transmitters, Receivers, and Communication Systems.
- Performance evaluation and selection of appropriate modulation techniques for real-time applications.
- Working with Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.
- ஆசிரியர்: JEGAN G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the basic principles and concepts of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science.
- To gain knowledge of various machine learning algorithms and their applications.
- To develop skills in data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model evaluation.
- To explore ethical considerations and challenges associated with AI and Data Science applications
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Analyze the software and hardware requirements to work with AI Algorithms.
CO2 - Simulate given problem scenario using appropriate AI libraries.
CO3 - Develop AI programming solutions for given problem scenario.
CO4 - Implement deep learning algorithms and solve real-world problems.
CO5 - Implement AI based edge computing solutions using GPUs.
CO6 - Analyze the performance of various ML algorithms for a specific application.

- ஆசிரியர்: MOHANA PRIYA G
- ஆசிரியர்: MUTHIAH M. A
COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the construction details of various types of automotive Frames and basic Chassis layouts
CO2 - Understand the basic function steering system and steering components
CO3 - Select the appropriate transmission system for various automobiles
CO4 - Comprehend the final drive system of a vehicle.
CO5 - Apply the knowledge for selection of suitable axles, wheels and tyres for a vehicle.
CO6 - Distinguish various types of suspension system, brake system.

COURSE OBJECTIVE:
- Gain knowledge of the context, concepts and process of entrepreneurship. Be better able to conceive and develop entrepreneurial opportunities. Be able to determine the feasibility of a new business concept.
Unit: I Project planning 12 Hrs
scope – problem statement – project goals – objectives – success criteria –
assumptions – risks – obstacles – approval process – projects and
strategic planning. Project implementation – project resource requirements –
types of resources – men –materials, finance. Case studies.
Unit: II Project monitoring 12 Hrs
Evaluation – control – project network technique –planning for monitoring and evaluation – project audits – project management information system – project scheduling – PERT & CPM –project communication – post project reviews and Case studies. Project team management – recruitment – organizing – human resources – team operating rules – project organization – various forms of project organizations. Closing the project – types of project termination – strategic implications – project in trouble – termination strategies – evaluation of termination possibilities.
Unit: III Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship 12 Hrs
Ideas to Reality, Proof of Concepts to Product realization, Strategic Management, Forms of Ownership and Franchising, Buying an existing Business, Business Models, Mobilization of Financial resources; Bank loans & Venture capitalism. Building a good Marketing Plan, Concepts in MSME. Accounting for planning, control, and motivation. Factors influencing capital acquisition and allocation. Financial decision making; Decision making under uncertainty; positive and normative models; Current issues in financial management. Case studies.
Unit: IV Industrial R&D and product development 12 Hrs
Product development and project management in Agri, Pharma, Health and other biotech industries. Overview of issues and techniques involved in conducting & outcome of research. The multidisciplinary nature of outcomes research: research design and methods, data collection measurement instruments and clinical endpoints, quality of life issues, behavior change, and cost-effectiveness. Analysis Transition from R&D to business units. Product development, market learning and transition from R&D. Management of radical innovation technologies vs. stage gate approach in product development. Case studies.
12 Hrs
Unit: V Rights and responsibilities of business
under the Indian Constitutional system.
Basic standards, rules, principles and issues relating to the law of
corporations; core issues affect the corporate governance of business;
relationship between management, boards and shareholders. Business laws
applied to Biotech industries. Regulatory issues in Biotech industries with
special reference to clinical trial of pharma products and field trials of
Agricultural products. Regulatory processes details. Intellectual property
in biotech. Business. Models around intellectual property, licensing issues.
Product development for commercial ventures. Bioethics and Current legal
issues. Ethics of new technology. Case studies.

- ஆசிரியர்: Dayanandan Anandan
This course provide the general introduction to different types of Immune cells, their function, cross talks and activation mechanism. Also gives over view about the primary and secondary immune organs, B-Cell, T-cell biology and their surface receptor. Immune responses, antigen nature, hypersensitivity, tumor immunology and autoimmune responses are covered in detail.
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to
- Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human body.
- Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
- Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of the human body.
- Perform the various experiments related to special senses and the nervous system.
- Appreciate coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system
- ஆசிரியர்: Harini R R
- ஆசிரியர்: SAI HARINI S

