Search results: 406
The purpose of this course is to introduce to students a number of health issues and their challenges. This course also introduced a number of national health programmes. The roles of the pharmacist in these contexts are also discussed.

- Teacher: Magaline Breezy M.K
- Teacher: Harini R R
- Teacher: Monisha S
Students will be able to:
• Identify and describe distinct literary characteristics of British literature from beginnings to the 18th century
• Identify the distinct literary genres of the tragedies, comedies, and histories present in Shakespeare's work • Demonstrate greater reading fluency of Elizabethan English
• Analyze Shakespeare's plays for their structure and meaning, using correct terminology
• Write analytically about Shakespeare's works, using MLA guidelines
• Effectively communicate ideas related to Shakespeare's plays during class and group activities.

Course Objectives:
● To introduce the student to British poetry
● To immense drama from the age of Chaucer to Milton.
● To comprehend the development of trends in British drama and poetry. .
● To understand the theme, structure and style in British poetry, drama.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To focus on basics of semiconductor physics, Predominant CMOS technology.
- To study challenges of digital VLSI design.
- To get an idea about combinational logic circuit using CMOS logic style.
- To acquire the knowledge about sequential logic circuit and subsystem design.
- To extract the backend VLSI algorithms for ASIC.
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Remember the mathematical methods and circuit analysis models in analysis of CMOS transistors and inverters.
CO2 - Recognize the different styles of CMOS logic for combinational logic circuit circuits.
CO3 - Apply the performance issues and the inherent trade-offs involved in sequential logic design. CO4 - Analyze the design of CMOS subsystems, memory structures.
CO5 - Evaluate the design of programmable logic devices and FPGA.
CO6 - Create a significant VLSI system design project having a set of objectives criteria and design constraints of ASICs
along with algorithms of backend VLSI.

- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINE DESIGN LAB
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Design and drawing of piston.
2. Piston pin and piston rings and drawing of these components.
3. Design of connecting rod small end and big end, shank design, design of big end cap, bolts and drawing
of the connecting rodassembly
4. Design of crankshaft, balancing weight calculations.
5. Development of short and long crank arms, front end and rear end details, drawing of the crankshaft
assembly.
6. Design and drawing of flywheel.
7. Ring gear design, drawing of the flywheel including the development of ring gear teeth.
8. Design and drawing of the inlet and exhaust valves.
9. Design of cam and camshaft, cam profile generation, drawing of cam and camshaft.
10. Design of combustion chamber.
COMPUTER AIDED CHASSIS DESIGN LAB
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Design of heavy duty vehicle frame (Leyland, Tata etc.)
2. Design of light duty vehicle frame (Ambassador, Maruti van etc.)
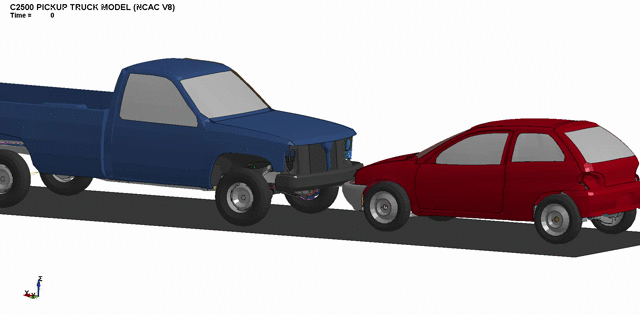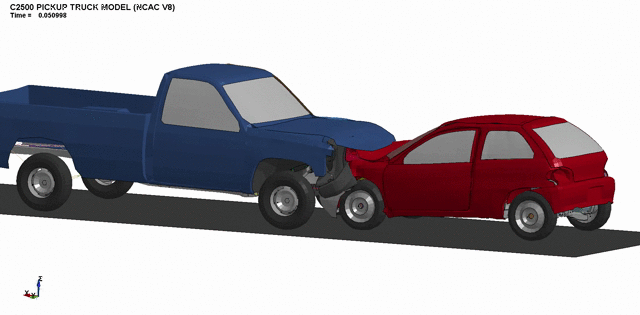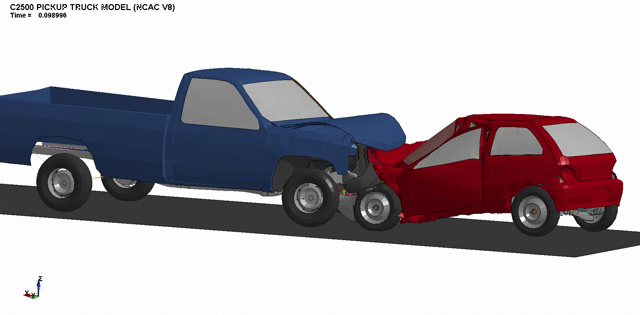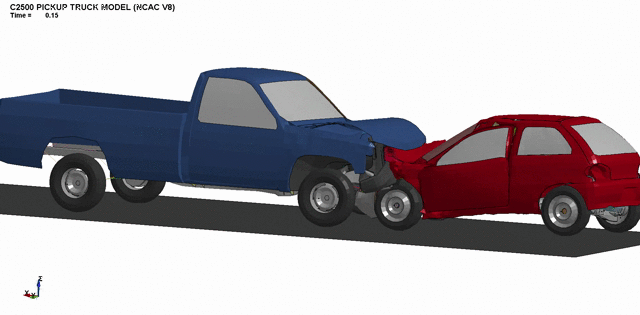
3. Front bumper crashworthiness optimization.
4. Simulation of full-scale passenger car impacts.
5. Design of front axle and rear axle
6. Automotive styling: sketching, modeling, surfacing and visualization.
7. Design of differential
8. Design of steering systems along with any two types of steering gear box
9. Design of braking systems – hydraulic servo vacuum, compressed air power brakes.
10. Design of leaf spring, coil spring, torsion bar spring, hydraulic shock absorber
11. Design of clutch assembly of different types
12. Design of gear Box
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
1.Display a working knowledge of the cultural and historical contexts of significant works prescribed for study
2. Identify and describe distinct literary characteristics of contemporary literature and demonstrate an understanding of how 21st century culture, trends, and historical events affect the literature produced today.
3. Analyze literary works from various genres for their structure and meaning, using correct terminology.
4. Write analytically about contemporary literature .
5. Effectively communicate ideas related to the literary works during class and group activities.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enrich the students in the field of Cryogenic Engineering and its Applications.
To learn the various Refrigeration processes, Equipment, Instruments, gas separation and Purification processes.
UNIT 1 CRYOGENIC FLUIDS AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 9 Hrs.
Cryogenic Engineering – Properties of cryogenic fluids – Oxygen, Nitrogen, Argon, Neon, Flourine, Helium. Hydrogen, Properties of Solids – Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical-Super conductivity, Cryogenic applications.
UNIT 2 CRYOGENIC REFRIGERATION AND GAS LIQUEFACTION 9 Hrs.
Principle – Joule Thomson Expansion, Cascade processes, Ortho para hydrogen conversion, cold gas refrigerators, LindeHampson cycles, Claude and cascaded systems, magnetic cooling, Stirling Cycle, Pulse Tube refrigeration.
UNIT 3 CRYOGENIC EQUIPMENTS AND REQUIREMENTS 9 Hrs.
Cryogenics- Heat Exchangers, Compressors, Expanders, Effect of various parameters in performance and system optimization. Insulation and Storage equipment for cryogenic fluids, industrial storage and transfer of cryogenic fluids.
UNIT 4 GAS SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION 9 Hrs.
Ideal gas, Mixture characteristics – composition diagrams – gas separation – Principle of Rectification process– principle and working of air separation, principle and working of gas purification.
UNIT 5 CRYOGENIC INSTRUMENTATION 9 Hrs.
Grinding process; cylindrical grinding, surface grinding, center less grinding – honing, lapping, super finishing, polishing, buffing and hobbing. Metallic Coatings; electro plating, galvanizing, tin coating, anodizing. Organic Finishes; primers, oil paint, brushing, spraying and rubber base coatings.
Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Describe the basic concepts of various cryogenic fluids and materials.
CO2 - Understand the cryogenic refrigeration and gas liquefaction.
CO3 - Understanding the working principles of cryogenic equipment.
CO4 - Understanding the working of gas separation and purification.
CO5 - Understanding the instrumentation of cryogenic technology
CO6 - To design the cryogenic system based on the application.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Randal F. Barron, Cryogenic Systems, McGraw Hill, 2010.
2. Cryogenic Engineering, Van Nostrand Co. Inc. 2011.
3. Klaus D. Timmerhaus, Richard Palmer Reed, Cryogenic Engineering: 50 years of progress, Springer, 2011.
4. Hastlden, C., “Cryogenic Fundamentals”, Academic Press, 2001.
5. Walker, “Cryocoolers”, Plenum Press, 2000.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
Data Communication is exchange of information through a transmission medium may be wired or wireless. Network is a set of devices connected by a communication link. Hence the course focuses on how communication is managed in a network and its basic protocols.
This course comprises of totally five chapters including the basics of data communication and networking concepts and various protocols in Physical, Data link and Transport Layers.

- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: V.J.K.Kishor Sonti
Broad outline of theoretical, clinical and practical courses. 1, Study of Dental Anatomy, Oral Histology, Physiology and Embryology of oral tissues. 2. Oral biology of hard and soft tissues. Study of clinical changes and their significance to dental and oral diseases. 3. Tooth Carving Exercises. 4. Maintenance of records of all activities.

- Teacher: Khadijah Mohideen
- Teacher: Indu Bharkavi S K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide a clear understanding on the basic concepts, Building Blocks of Embedded Systems.
- To teach the fundamentals of Embedded processor Modeling, Bus Communication in processors, Input/output interfacing.
- To introduce processor-scheduling algorithms, Basics of Real time operating systems.
- To discuss on aspects required in developing a new embedded processor, different Phases& Modeling of embedded system.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the components of embedded system and different communication protocols.
CO2 - Describe the differences between the general computing system and embedded system, also recognize the
classification of embedded systems.
CO3 - Attain expertise with embedded system development and debugging tools.
CO4 - Apply the interrupt service mechanism in the design of embedded system.
CO5 - Design of real time embedded systems using the concepts of RTOS.
CO6 - Articulate the role of embedded systems in industry and provide feasible design solutions for given problem
statement.
After the completion of this course, Students will be able...
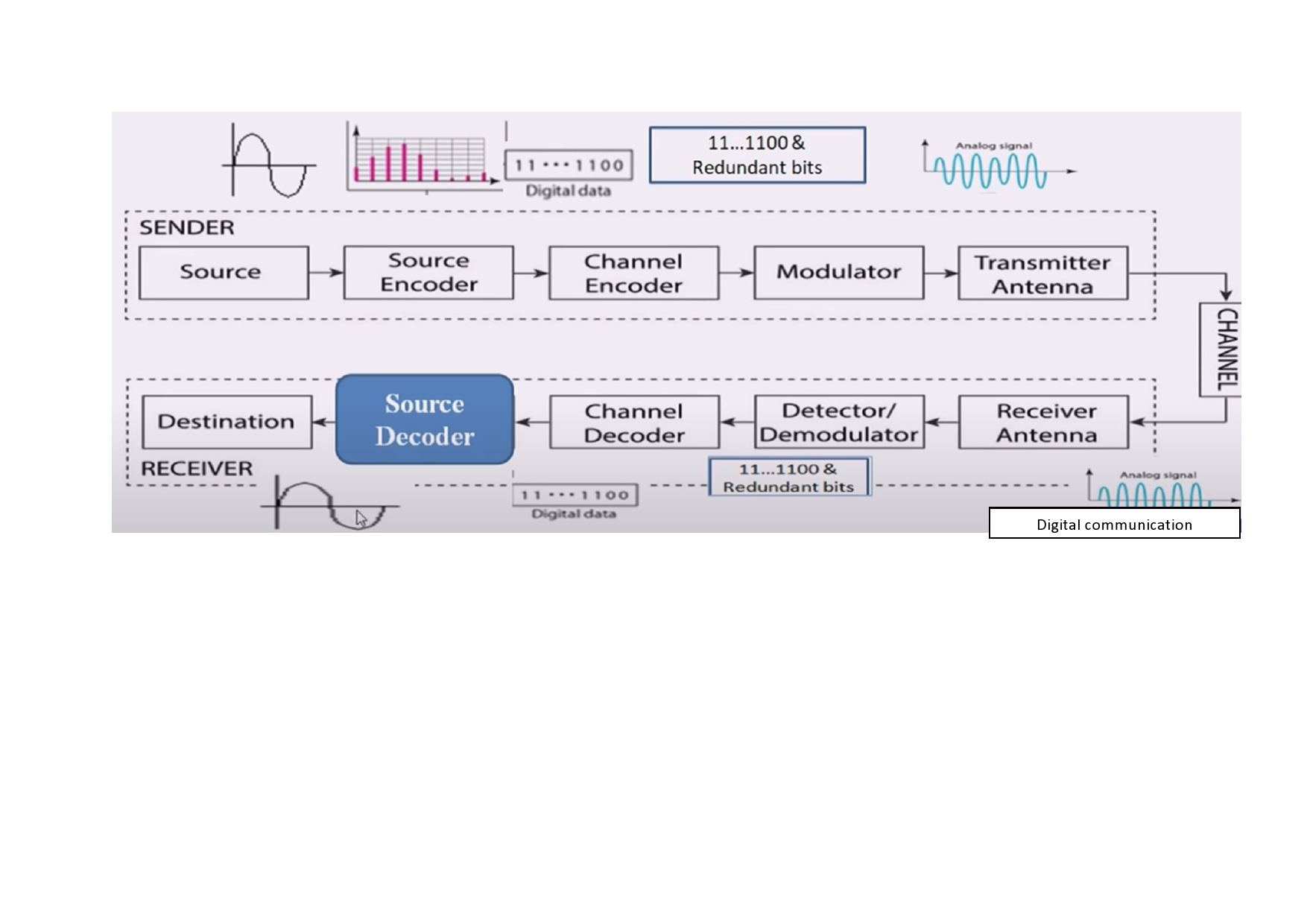
To know the principles of formatting (sampling , quantization and encoding)
To analyze the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To analyze various digital modulation techniques and compare with analog modulation techniques
To under stand the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To review the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: JEGAN G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Design PCM systems.
CO2 - Apply the knowledge of signals and system and evaluate the performance of digital communication system in the presence of noise.
CO3 - Design and implement band pass signaling schemes and analyze the spectral characteristics of band pass signaling schemes.
CO4 - Design encoder and decoder for the error control codes like block code, cyclic code. CO5 - Analyze the digital communication system with spread spectrum modulation.
CO6 - Examine the theoretical concepts through laboratory experiments, analyze and interpret the results to provide valid
conclusions.
- Teacher: JEGAN G
This course introduces students to documentary film production using digital video, with an emphasis on the practical challenges of working in the real world. While students learn the traditional methods of production, they are also encouraged to range widely in their thinking about how to document daily life.
After taking this course the students are expected to have familiarized
themselves with the art of socially engaged storytelling through documentary
film. Moreover, this module is an exercise in creative group work in the field
of social sciences that seeks to equip the students with increasingly sought
after skills of understanding, producing and using media in the digital age.

- Teacher: Prasanna Lakshmi S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ÿ To Give a Introduction to Electrical machines.
ÿ To explain how electrical power is converted in to mechanical Power.
ÿ To explain how Mechanical power is converted in to Electrical Power.
ÿ To explain the importance of load test on the electrical machines.
- Teacher: Bharathi M L
ELEMENTS OF TEXTILES
Course Code -SFD1103
ObjectiveElements of Textiles is to understand the important characteristic of different fabrics used Commercially. Students will learn to identify various fabrics textile by their look, appearance and feel. The knowledge gained through this subject will enable to select the right fabric for a particular end-use. They will be introduced to Basic surface ornamentation like Embroidery .
UNIT I
Introduction to Fibers - Classification of Textile fibers - Natural and Manmade fibers. Primary and secondary characteristics
of textile fibers. Swatch file collection with different types of fibers - Cotton, Linen, Wool, Synthetic.
UNIT II
Manufacturing process, properties and uses of natural fibers and Manmade fibers. Natural Fibers – cotton, linen, jute, silk,
wool, and hair fibers. Manmade fibers – Rayon and its types, nylon, polyester and acrylic.
UNIT III
Spinning - Introduction, Spinning methods - Chemical Spinning and Mechanical Spinning. Chemical spinning – Wet, Melt &
Dry spinning of filament yarns. Mechanical Spinning – cotton system - sequence of process, objectives of blow room,
carding, drawing, combing, roving and ring spinning.
UNIT IV
Yarn – definition. Properties of Yarn - Yarn numbering systems – Direct and indirect system of yarn count. Yarn twist.
Classification of yarns – Simple yarn, Single yarn, Ply yarn, Novelty Yarns.
UNIT V
Basic fabric formation methods – Woven, Knitted and Nonwoven fabrics. Manmade Weaving process - Basic weaves used
in commercial fabric - End use of fabrics - different type of weaves. Introduction to knitting, Types of Knitting, Applications of
knitwear. Fabric Sourcing and market awareness - Fabric Analysis - Swatch file collection with various types of weaves and
fabrics.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Classify the various sources of fibers and
CO2: Elaborate the manufacturing process of fibers
CO3: Understand the process of spinning sequences.
CO4: Classify yarns and analyze its attributes.
CO5: Understand the different types of fabric formation methods
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Textiles, Sara J. Kadolph, Pearson publication, 2009.
2. Fabric Science -5th edition, Joseph J Pizzuto, Fairchild Publications, Newyork ,1980.
3. Handbook of Nonwovens- Edited by R J Russell, Woodhead Publishing Ltd, England, 2007.
4. Knitting Technology- B.Ajgoankar, Universal Publishing Corporation, Mumbai, 1998.
5. Fibre to Fabric, Bernard P Corbman, (6th edition), Tata McGraw - Hill Education, 2003

Introduce the students to the issues and challenges in developing software for embedded systems.
Educate the students in formal modeling, design and development methodologies.
Expose the students to software tools and techniques used in the development process.

To understand the concept of Statics.
To appreciate the concept of Equilibrium.
To recognise properties of surfaces and solids.
To learn the theory of Friction.
To acquire the concept of Dynamics.
- Teacher: RAM PRAKASH S
|
SPYA1202 |
Professional Elective II Environmental Psychology |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT I(15 hours)
Environmental Psychology: History – Scope - Research Methods: Questionnaire studies - Laboratory experiments - Computer simulation studies - Field studies -Case studies- Overconsumption: Our Ecological Footprint – Energy – Water – Food -Material Goods.
UNIT II(15 hours)
Climate Change as a Unique Environmental Problem: Public Understanding of Climate Change - Assessing the Risk of Climate Change - Environmental Stress: Conceptualizations of Stress - Effects of Environmental Stress
UNIT III (15 hours)
Measuring Environmental Behaviour Values and Pro - Environmental Behaviour -Theory of Planned Behaviour - Protection Motivation Theory - The Norm Activation Model - The Value‐Belief‐Norm Theory of Environmentalism - Goal‐Framing Theory
UNIT IV (15 hours)
Social Norms and Pro - Environmental Behaviour, Emotions and Pro - Environmental Behaviour, Symbolic Aspects of Environmental Behaviour-Restorative Environments Research: Stress Recovery Theory - Attention Restoration Theory
UNIT V (15 hours)
Informational Strategies to Promote Pro- Environmental Behaviour: Changing Knowledge, Awareness, and Attitudes - Encouraging Pro Environmental Behaviour with Rewards and Penalties - Persuasive Technology to Promote Pro - Environmental Behaviour
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
This course introduces you to the study of human-environment interactions from a geographic perspective, with a special emphasis on agriculture. ... These themes include: human population growth, consumption, biodiversity, climate change, and environmental health.

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
- Teacher: Krithika S
