Search results: 1466
The aim of Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy is to publish novel, original, peer-reviewed research manuscripts within relevant topics and research methods related to pharmaceutical research and development, and industrial pharmacy. All going to develop more information about the following topics in this semester
- Pilot Plant Scale up techniques
- Technology Development and Transfer
- Regulatory affairs and Regulatory requirements for drug approval
- Quality Management system and Regulatory Management Systems
- Indian Regulatory Requirements
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
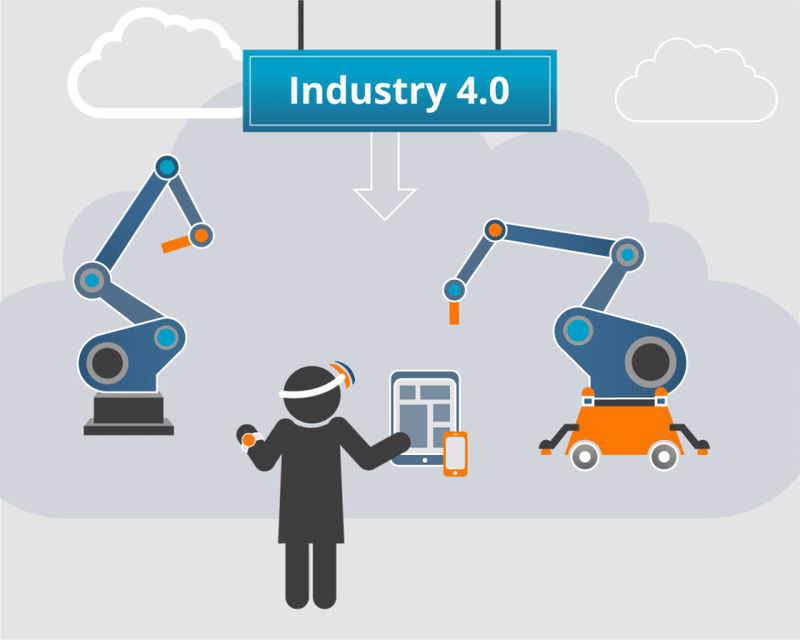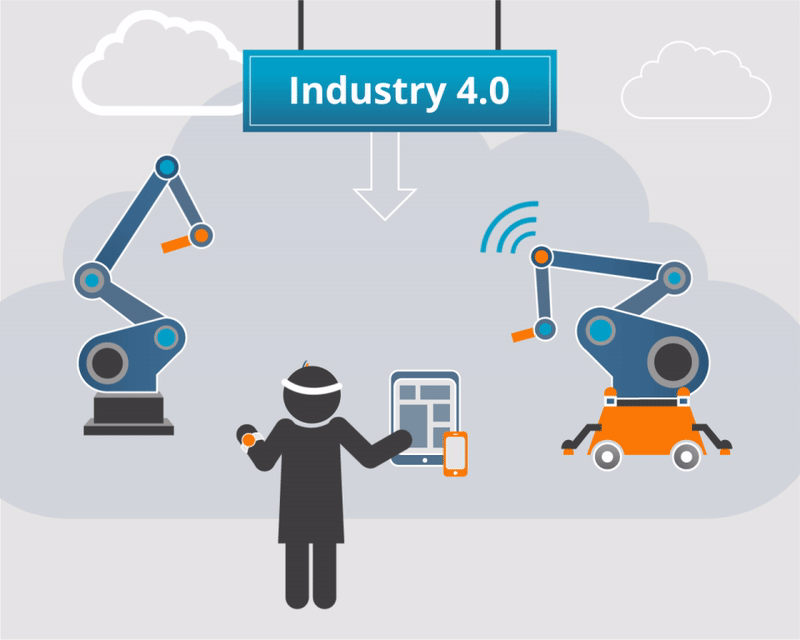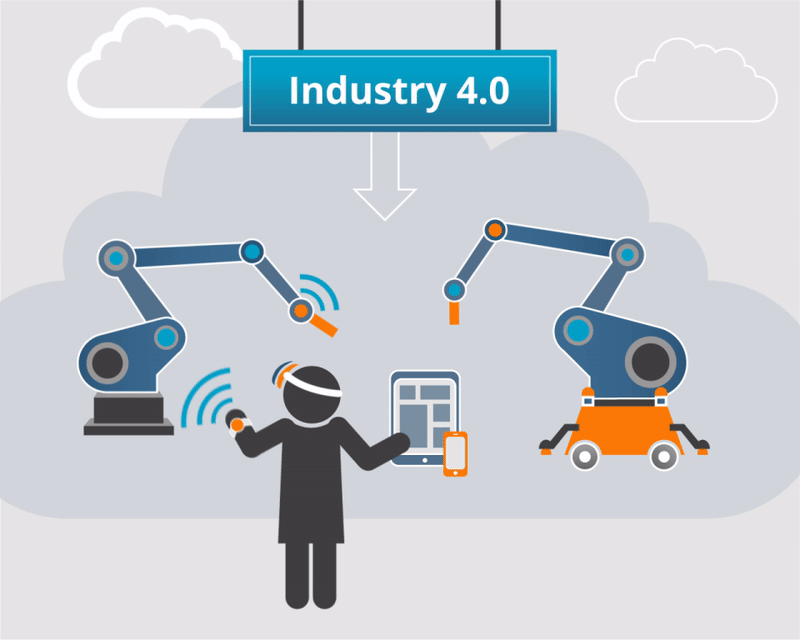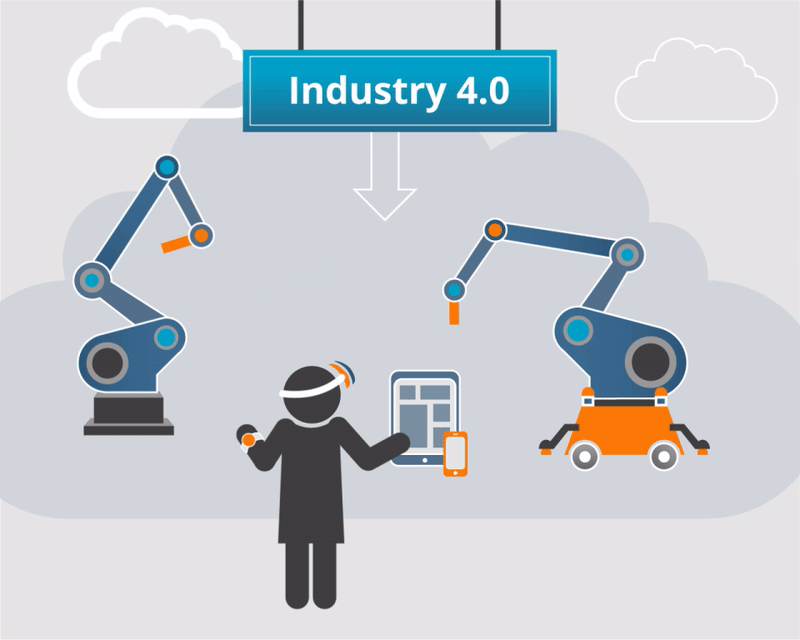
➢ To enable students understand the fundamentals and the contributing technologies of Industry 4.0.
➢ To make the students evaluate the suitability of Industry 4.0 technologies for the design and manufacturing sectors.
➢ To help the students implement the Industry 4.0 technologies to diverse applications.
UNIT 1 CONTRIBUTING TECHNOLOGIES 8 hrs
Brief introduction to the industrial revolutions. Contributing technologies to Industry 4.0: Additive manufacturing, Digital twin, Internet of things, Smart sensors, AR and VR, Artificial intelligence, Cloud computing, Block chain, Big data and analytics. Challenges and opportunities.
UNIT 2 ADVANCED CAD TECHNOLOGIES 8 hrs
Introduction to CAD. Enabling technologies: Digital twin, AR/VR, AI. Cloud computing, Touch/Voice/Motion enabled CAD, Customized CAD, Cloud based CAD, Digital twin and live simulation.
UNIT 3 SMART MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS 8 hrs
Enabling technologies: AI, Cloud computing, Robotics, IoT. Digital manufacturing: CNC, Cloud based manufacturing, IoT based manufacturing, Advanced CNC programming. Additive manufacturing. Micro electro mechanical systems. Robotics: Robotic automation, Collaborative robots, Autonomous robots, Swarm robots, and Modular robots.
UNIT 4 SMART FACTORY ENABLERS 8 hrs
Enabling technologies. Smart energy: Improving energy efficiency with data, Smart grids. Clean energy. Smart logistics. Smart Inspection. Smart decision making.
UNIT 5 AUTOMOMOUS VEHICLES 8 hrs
Introduction: Traditional mobility versus autonomous driving, Levels of automation, and challenges. Enabling technologies. Self-propelled vehicles, Drones, Unmanned aerial vehicles, Space crafts
UNIT 6 CASE STUDIES 5 hrs
Case studies related to Industry 4.0 applications, such as, transportation, energy, infrastructure, manufacturing, and product design sectors.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
At the end of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Justify how the digitalization technologies are advantageous to the design and manufacturing industries.
CO2: Use the advanced CAD technologies to create the CAD models.
CO3: Use the smart manufacturing technologies to produce the components and products.
CO4: Recommend the enabling technologies to make various factory operations smarter.
CO5: Choose the suitable sensors and technologies to the future autonomous vehicles, drones and space crafts.
CO6: Prepare a report with the challenges faced currently, the enabling technologies to become smarter, and the
steps needed for the effective implementation for the given case study.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Flavio Craveiro, Jose Pinto Duarte, Helena Bartolo and Paulo Jorge Bartolo, “Additive manufacturing as an enabling technology for digital construction: A perspective on Construction 4.0”, Automation in Construction, Vol. 103,pp. 251- 267, 2019.
2. Klaus Schwab, “Fourth Industrial Revolution”, Random House USA Inc, New York, USA, 2017.
3. Oliver Grunow, ”Smart Factory and Industry 4.0. The current state of Application Technologies”, Studylab Publications, 2016
4. Alasdair Gilchrist, “Industry 4.0: Industrial Internet of Things”, Apress, 2016
5. Sang C. Suh, U. John Tanik, John N Carbone, Abdullah Eroglu, “Applied Cyber-Physical Systems”, Springer Publications, New York, 2013.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
To develop an understanding of building services such as water supply, drainage and plumbing system.
To familiarize them with the advanced service integration system and their applications in building.
To choose appropriate systems and integrate the same in their design projects.
- Teacher: ANITHA M
- Teacher: Mohana Gopiraj N
This course aims at understanding the essential metabolic functions of the organism as well as consumption
and storage of energy intermediary metabolism of main biomolecules and its regulatory mechanisms
It seeks to acquaint the reader to the critical approaches that have significantly impacted the study of English Literature.
It attempts to facilitate a chronological overview of critical theories while simultaneously allowing for a quick survey of classical criticism along the way.

- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
Summary
There are several ways of collecting and understanding information and finding answers to your questions – research is one way. The difference between research and other ways of obtaining answers to your questions is that in a process that is classified as research, you work within a framework of a set of philosophies, use methods that have been tested for validity and reliability, and attempt to be unbiased and objective.
Research has many applications. You need to have research skills to be an effective service provider, administrator/manager or planner. As a professional who has a responsibility to enhance professional knowledge, research skills are essential.
The typology of research can be looked at from three perspectives: application, objectives and the enquiry process. From the point of view of the application of research, there is applied and pure research. Most of the research undertaken in the social sciences is
applied, the findings being designed either for use in understanding a phenomenon/issue or to bring change in a programme/situation.
Pure research is academic in nature and is undertaken in order to gain knowledge about phenomena that may or may not have applications in the near future, and to develop new techniques and procedures that form the body of research methodology. A research study can be carried out with four objectives: to describe a situation, phenomenon, problem or issue (descriptive research); to establish or explore a relationship between two or more variables (correlational research); to explain why certain things happen the way they do (explanatory research); and to examine the feasibility of conducting a study or exploring a subject area where nothing or little is known (exploratory research). From the point of view of the mode of enquiry, there are two types of research: quantitative (structured approach) and qualitative (unstructured approach). The main objective of a qualitative study is to describe the variation and diversity in a phenomenon, situation or attitude with a very flexible approach so as to identify as much variation and diversity as possible, whereas quantitative research, in addition, helps you to quantify the variation and diversity. There are many who strongly advocate a combined approach to social enquiries.
These are the two paradigms that form the basis of social science research. Though these may provide values, terminology, methods and techniques for you to apply to your research, it is the purpose of research rather than the paradigm that should determine the mode of enquiry.

- Teacher: Malliga P
- The lab course is designed to train the students in basic techniques of Biochemistry.

- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
Course Objectives
- To understand the origins, structure, and development of language
- To apply linguistics to other areas of humanistic and scientific knowledge.
- To interpret the basic principles of linguistic theories
- To analyze phonological sound system, word structure, and phrase and sentence patterns

- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Murugesan S
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M