Search results: 406
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the method of biasing transistors.
To familiarize the students with the analysis and design of basic transistor Amplifier
circuits.
To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits.
To understand the frequency response of amplifiers.
To provide foundation and confidence to the students to troubleshoot and fault
analysis of power supplies and power amplifiers.
To develop current mirrors and differential operations.
UNIT 1 BIASING OF BJT AND FET 9 Hrs.
BJT– Need for biasing – Various biasing methods of BJT- Bias Circuit Design- DC Load Line –
DC analysis of Transistor circuits-AC Load Line- AC analysis of Transistor Circuits- Quiescent Point
–
Thermal stability - Stability factors - Biasing of JFET - Various biasing methods of JFET - JFET Bias
Circuit Design - MOSFET Biasing-Two port network.
UNIT 2 EQUIVALENT MODEL OF BJT AND FET AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Hybrid model- Analysis of CE, CC and CB amplifiers using Hybrid equivalent circuits to obtain
gain, input impedance and output impedance--Small Signal Amplifiers – Analysis of CE, CC and CB
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits to obtain gain, input impedance and output
impedance. Small Signal equivalent circuit of FET and MOSFET - Analysis of CS, CD and CG JFET
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits- Analysis of CS, CD and CG MOSFET amplifiers
using small signal equivalent circuits.
UNIT 3 MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIERS AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF BJT AND FET
AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Multistage Amplifiers- Methods of Coupling- RC Coupled- Transformer Coupled – Direct
Coupled Amplifiers- Amplifier frequency response – Miller effect- Frequency response of transistor
amplifiers with circuit capacitors – BJT frequency response – Low and High frequency analysis of
CE, CB, CC -Frequency response of FET - Low and High frequency analysis of CS, CG, CD JFET
& MOSFET.
UNIT 4 POWER SUPPLIES AND POWER AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Linear mode power supply - Rectifiers - Half-Wave Rectifier - Full-Wave Rectifier - Filters-L, C,
LC, CLC Filter- Regulators - Zener Diode regulator- Linear series, shunt voltage Regulators -
Switched mode power supply (SMPS) – Large Signal Amplifiers – Class A, Class B, Class C, Class
D- Distortion in power amplifiers.
UNIT 5 CURRENT MIRRORS AND DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS. 9 Hrs.
Current sources for biasing – Current steering circuits – Current mirror with improved performance
(Cascode mirror, Wilson, Widlar). Large and small signal operation of Differential pair circuit
Differential pair with active load - Frequency response of the Differential amplifier
Max. 45 Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquire knowledge of simple BJT circuits design and implement circuits with transistor
biasing design.
CO2 - Draw the equivalent circuits of BJT and FET.
CO3 - Understand the working principles, Frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET.
CO4 - Compare the frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET amplifiers.
CO5 - Design and troubleshoot simple power supplies and analyse the performance parameters of
power supplies. Understand and identify the performance level in power amplifiers and checking its
distortion levels.
CO6 – Design the differential amplifier and study the performance of current mirrors
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Millman J and Halkias C., “Integrated Electronics”, TMH, 2nd Edition, 2017.
2. S. Salivahanan, N. Suresh Kumar and A. Vallavaraj, “Electronic Devices and Circuits”, TMH,
2 nd Edition, 2017.
3. Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C.Smith, “Microelectronic Circuits”, Oxford University Press, Sixth
Edition, 2009.
4. Behzad Razavi, “Fundamentals of Microelectronics”, 1st edition, wiley publication, 2008.
5. Donald. A. Neamen, “Electronic Circuits Analysis and Design”, McGraw Hill Education (India)
Private Ltd., 3rd Edition, 2010.
6. Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nasheresky, ”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Pearson
Education, 11th Edition, 2013.
7. Floyd, “Electronic Devices”, Pearson Education, 9th Edition, 2012.
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand operational principles and characteristics of semiconductor electronic devices.
➢ To learn about analog electronic circuits such as rectifiers, regulators and amplifiers.
➢ To learn about Boolean algebra and basic building blocks of digital systems.
➢ To learn about optimized implementation of combinational and sequential digital circuits and systems.
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
- Teacher: VINO T
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Discuss the fundamental concepts of wave propagation in Transmission Lines and Wave Guides.
CO2 - Analyze the line parameters and various losses in transmission lines.
CO3 - Apply smith chart for line parameter and impedance calculations.
CO4 - Evaluate the characteristics of parallel plane and rectangular wave guides.
CO5 - Evaluate the characteristics of Circular waveguides.
CO6 - Evaluate the characteristics of resonators.

- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes.

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To know the principles of sampling and quantization
- To understand the various base band signalling schemes
- To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of base band signals
- To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding
- To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- To learn the basic antenna parameters.
- To understand the radiation mechanism from the dipole antennas.
- To explore the various antenna arrays and calculate the maxima, minima and half power directions.
- To discuss the characteristics of travelling wave radiators and high frequency antennas.
- To study antenna measurements techniques.

- Teacher: Magthelin Therase
On completion of the course, student will be able to
Apply the knowledge of basic microwave components and understand the scattering parameters differences between low and high frequency processes.
Analyses the characteristics of various microwave sources and solid state devices.
Classify and analyze the various microwave measurements and EMI/EMC measurements
Demonstrate the qualitative knowledge of optical communication and types of optical fibers, its losses and signal degradation
Become Aware of the latest optical sources, launching and coupling of optical fibers
Examine the theoretical concepts of optical Networks.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
To understand the characteristics of diodes, transistors, LDRs, SCR, DIAC, Triac.
To understand the theorems for electrical circuit analysis.

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the micro level dataflow in various units of computer.
CO2 - Demonstrating the impact of control memory operations and multi-process or characteristics.
CO3 - Examining the different types of memory and experimenting the mapping techniques.
CO4 - Select the suitable process scheduling technique for optimized function of operating systems.
CO5 - Critically upraising the deadlock in CPU and other memory management techniques.
CO6 - Design and Developing optimized architecture for stand-alone applications.
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
Course Objectives
• To learn about wireless mobile communication standards and co-existence of 4G and 5G.
• To learn 5G network architecture, components, features and their benefits.
• To learn channel access methods, modulation and spectrum sensing techniques used in 5G wireless systems.
• To understand advanced wireless concepts such as Massive MIMO, Virtualized RAN and Network Slicing.
• To learn about mmWave communication systems and its use cases.
Course Outcomes:
On Completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 - Distinguish major mobile communication standards such as 3G, 4G and 5G
CO2 - Analyze various modulation and multiplexing techniques like OFDM, NOMA etc.
CO3 - Design system level architecture of 5G communication systems.
CO4 - Analyze spectrum sensing and sharing techniques in 5G systems.
CO5 - Assess the potential of mmWave spectrum for 5G applications.
CO6 - Apply the concepts of green communications in real life applications.

- Teacher: Dr. KRUTI DEEPA
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: MATHAN N
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
Course Objectives:
- To Present the mathematical, statistical, and computational challenges of building neural networks
- To study the concepts of deep learning
- To introduce dimensionality reduction techniques
- To enable the students to know deep learning techniques to support real-time applications
- To examine the case studies of deep learning techniques
- Teacher: Ishwarya C
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Gomathi V
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the components of embedded system and different communication protocols.
CO2 - Describe the differences between the general computing system and embedded system, also recognize the classification of embedded systems.
CO3 - Attain expertise with embedded system development and debugging tools.
CO4 - Apply the interrupt service mechanism in the design of embedded system.
CO5 - Design of real time embedded systems using the concepts of RTOS.
CO6 - Articulate the role of embedded systems in industry and provide feasible design solutions for given problem
statement.
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
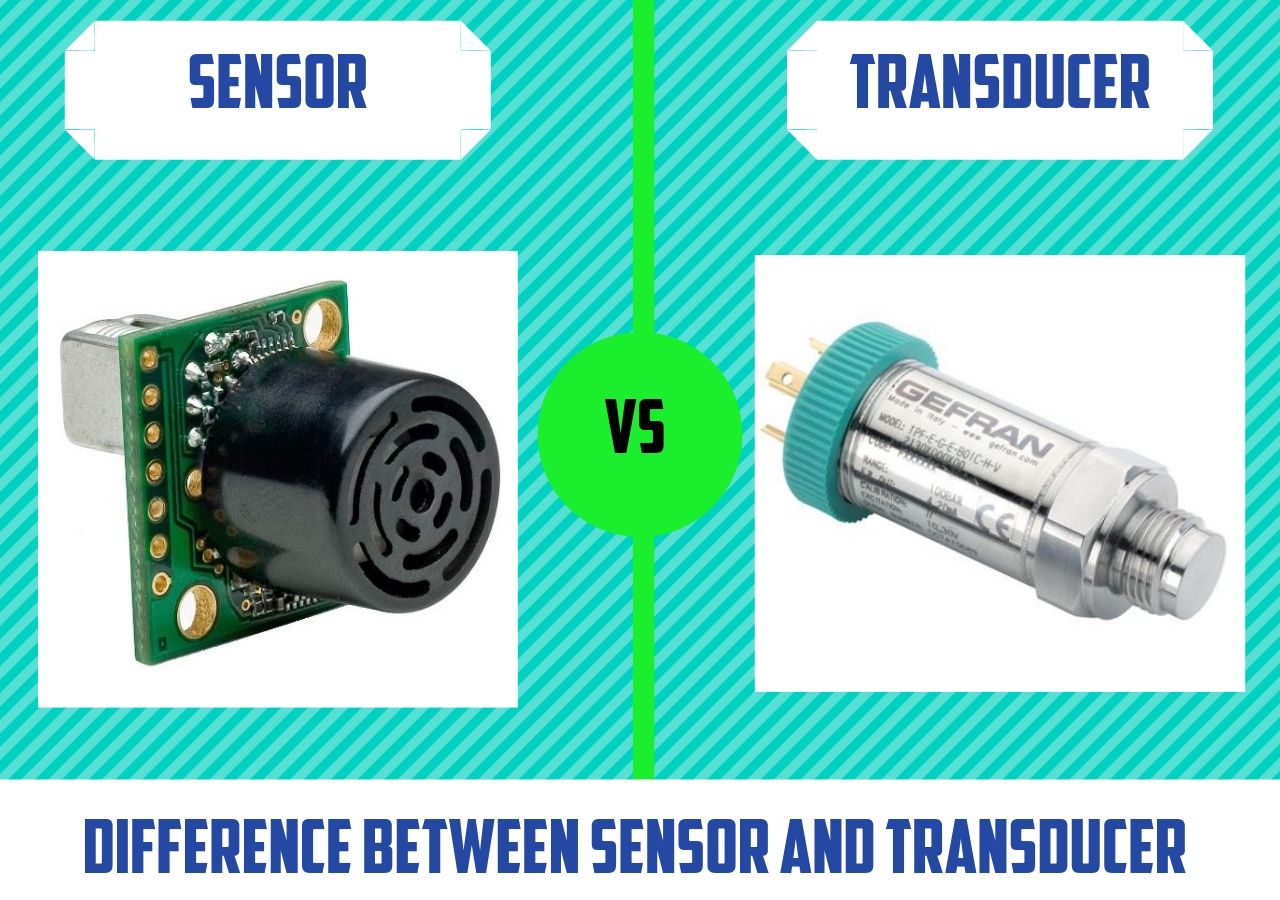
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To explain how digital circuit of large complexity can be built in a methodological way to acquire the knowledge about memory architectures.
- To illustrate how the concepts presented in the lectures are applied in practice, and how the need to accommodate different practically motivated trade-offs can lead to alternative implementations.
- To teach fundamental concepts of hardware description languages.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the steps for state table reduction and state assignment, ASM chart and ASM tables for the design of synchronous sequential design.
CO2 Determine the Real Time Challenges in the design of Asynchronous sequential circuits.
CO3 Elaborate the feasibility of sequential circuit design using PLA.
CO4 Evaluate the testing algorithms and perform the comparison study for digital circuits.
CO5 Design the Combinational logic circuits using VHDL.
CO6 Construct the low power sequential circuit using VHDL.

- Teacher: AISHWARYA K
- Teacher: EMIMAL M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: GEETHA P
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
COURSE OUTCOMES :
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Model various parameters in communication channels.
CO2 - Analyze the suitability of IEEE standards for specific applications.
CO3 - Correlate ISO-OSI and TCP/IP reference models.
CO4 - Develop suitable error detection and error correction techniques for reliable communication.
CO5 - Analyze various transport layer protocols for Real Time Applications.
CO6 - Develop suitable routing and congestion control algorithms for Real World Problems.

- Teacher: GOMATHI T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
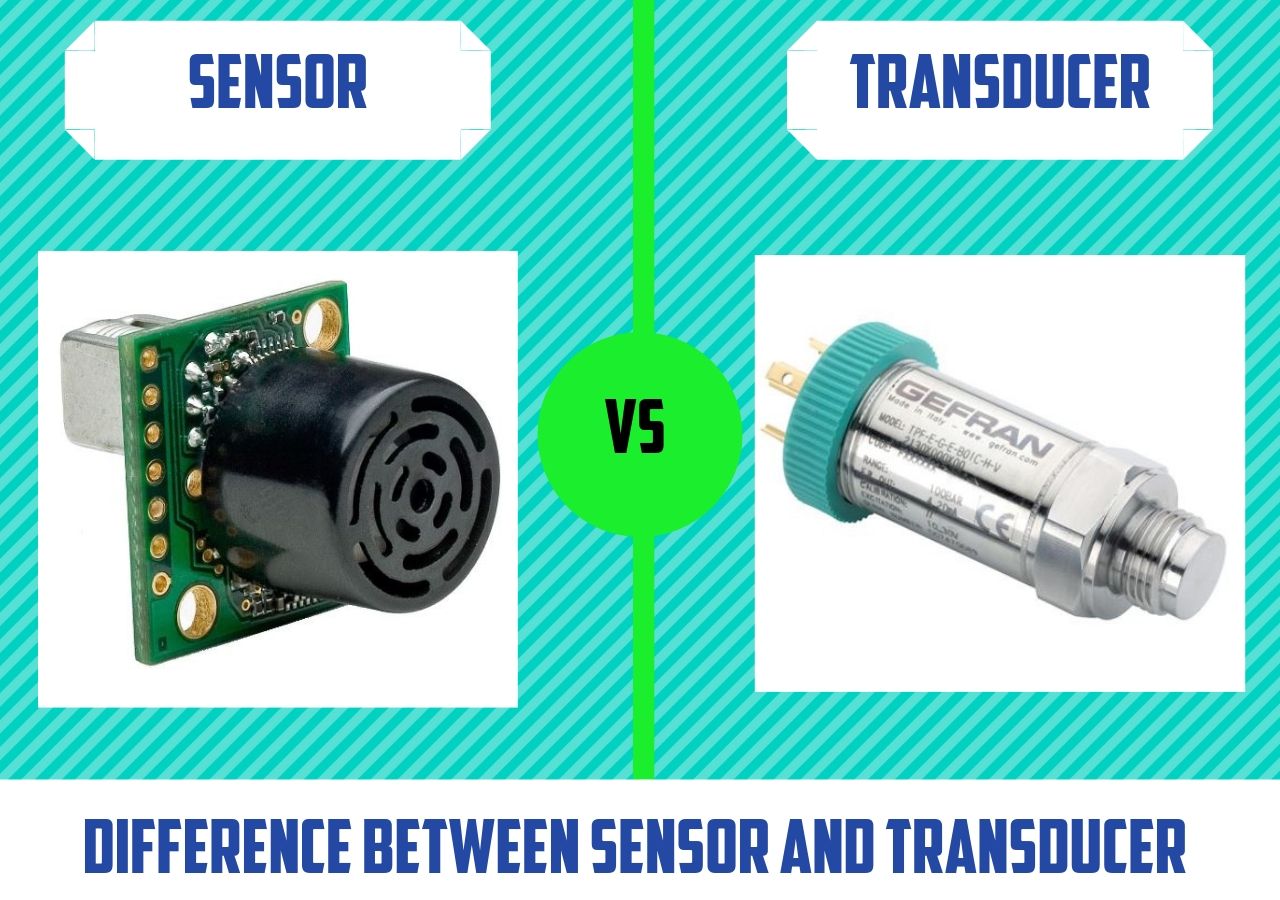
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
Course Outcomes
On
completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1-Apply the mathematical concepts to compare
different types of optical fibers, modes and configuration.
CO2-Analyze
the transmission characteristics of optical fibers.
CO3-Examine
the optical sources and detectors for use in optical communication system.
CO4-Construct
launching and coupling of optical fibers.
CO5-Design
high speed optical communication networks.
CO6-Design wireless
communication system using Li-Fi.
- Teacher: JEGAN G
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
COURSE OBJECTIVES :
To learn the basics of Semiconductor devices, MOS transistors.
To learn the fundamental concepts of CMOS devices and characteristics.
To learn the CMOS circuits and design with VLSI software tools.

- Teacher: Dr. SUMATHI M
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Identify the main challenges associated with machine-to-machine communications with respect to the status quo in networking today.
- CO2 - Describe the standards, protocols and algorithms that are used to address the challenges in M2M communications.
- CO3 - Develop an understanding of edge and fog computing for data aggregation, filtering and detecting anomalies
- CO4 - Design and build a network based on the client server, as well as how to publish/subscribe to connect, collect data, monitor and manage assets.
- CO5 - Develop device, gateway and server-side scripts and apps, enabling them to aggregate and analyze sensor data
- CO6 - Analyze and suggest suitable application-layer protocols and web services architectures for a seamless integration of various components within an IoT ecosystem.
- Teacher: MATHAN N