Search results: 1466

- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
To understand the distinctive features of the major ancient literary genres as illustrated in various texts.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
UNIT 1 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
Nuclear radius, charge distribution, spin and magnetic moment – Determination of nuclear mass – Binding energy – Semiempirical mass formula – Nuclear stability – Mass parabolas – Nuclear shell model – Liquid drop model - Optical model – Collective model Nuclear Forces Exchange forces – Yukawa’s meson theory –Yukawa potential – Ground state of deuteron
UNIT 2 RADIOACTIVE DECAYS
Alpha decay – Gamow’s theory – Geiger Nuttal law - Neutrino hypothesis –Fermi’s theory of beta decay-Selection Rules – Non conservation of parity in beta decay – Gamma decay – Selection rules – International conversion – Nuclear isomerism. Detection of Nuclear Radiation Interaction of charged particles and X-rays with matter - Basic principles of particle detectors - Proportional counters and Geiger – Muller counters - Solid state and semiconductor detectors – Scintillation counters.
UNIT 3 NUCLEAR FISSION
Fission process – neutron released in the fission process - Characteristics of fission – Mass and energy distribution of nuclear fragments – Nuclear chain reactions – Four factor formula – Bohr-Wheeler’s theory of nuclear fission – Fission reactors – Power & breeder type reactors Nuclear Fusion Basic fusion processes – Solar fusion – Cold fusion- Controlled thermonuclear reactions – Pinch effects - Laser fusion techniques.
UNIT 4 NUCLEAR REACTIONS
Energetic of reactions – Q-equation - Level widths in nuclear reaction –Nuclear reaction cross sections – Partial wave analysis – Compound nucleus model – Resonance scattering – Breit –Wigner one level formula – Direct reactions – Stripping and pick-up reactions. Scattering Process, scattering cross-section – Scattering amplitude – Expression in terms of Green’s function – Born approximation and its validity – Screened Coulomb potential
UNIT 5 ELEMENTARY PARTICLES
Four types of interactions and classifications of elementary particles – Isospin - Isospin quantum numbers – Strangeness & hyper charge – Hadrons – Baryons – Leptons – Invariance principles and symmetries – Invariance under charge-parity(CP), Time(T) and CPT - CP violation in neutral K-meson decay - Quark model – Gell-Mann-Nishijma formula – Gauge theory of weak and strong interactions – Charm, bottom and top quarks.
- Teacher: Rameshkumar C
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Understand different metal casting processes, associated defects, merits, and demerits.
CO2 - Compare different metal joining processes.
CO3 - Summarize various hot working and cold working methods of metals.
CO4 - Study the various sheet metal-making processes. CO5 - Distinguish various methods of manufacturing plastic components.
CO6 - Understand the concept of molding process.
- Teacher: Jayaprakash Venugopal
This course would cover the legal aspects of activities like carriage of goods and persons by sea along with concepts of marine insurance and adjudication of marine disputes

- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
: To Impart the Knowledge to the students with MATLAB software to enhances programming knowledge in
Research and Development. To provide a working introduction to the Mat lab technical computing environment. To introduce
students the use of a high-level programming language, Matlab
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
- Teacher: Sathya Bama R
- Teacher: Subapriya V
PAPER I: CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
Examination, diagnosis and treatment plan
Occlusion as related to conservative dentistry, contact, contour, its significance.
Separation of teeth, matrices, used in conservative dentistry.
Dental caries – epidemiology, recent concept of etiological factors, pathophysiology.
Histopathology, diagnosis, caries activity tests, prevention of dental caries and management – recent methods.
Hand and rotary cutting instruments, development of rotary equipment, speed ranges, hazards.
Dental bur and other modalities of tooth reparation – recent developments (air abrasions, Lasers etc)
Infection control procedures in conservative dentistry, isolation equipments etc.
Direct concepts in tooth preparation for amalgam, composite, GIC and restorative techniques, failures and management.
Direct and indirective composite restorations.
Indirect tooth coloured restorations – ceramic, inlays and onlays, veneers, crowns, recent
Advances in fabrication and materials.
Tissue Management
Impression procedures used for indirect restorations.
Cast metal restorations, indications, contraindications, tooth preparation for class 2 inlay, onlay full crown restoration
Restorative techniques, direct and indirect methods of fabrication including materials used for fabrication like inlay wax, investment materials and
Direct gold restorations.
Recent advances in restorative materials and procedures.
Management of non-carious lesion.
Advance knowledge of minimal intervention dentistry.
Recent advances in restoration of endodontically treated teeth and grossly mutilated teeth
Hypersensitivity, theories, causes and management
Lasers in Conservative Dentistry
CAD-CAM & CAD-CIM in restorative dentistry
Dental imaging and its applications in restorative dentistry (clinical photography)
Principles of esthetics
Color
Facial analysis
Smile design
Principles of esthetic integration
Treatment planning in esthetic dentistry
PAPER – II : ENDODONTICS
Rationale of endodontics
Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its implications in endodontic treatment.
Dentin and pulp complex.
Pulp and periapical pathology
Pathobiology of periapex
Diagnostic procedure – recent advances and various aids used for diagnosis –
Orofacial dental pain emergencies: endodontic diagnosis and management
Case selection and treatment planning
Infection control procedures used in Endodontics (aseptic techniques such as rubber dam, sterilization of instruments etc)
Access cavity preparation – objectives and principles
Endodontic instruments and instrumentation – recent developments, detailed description of hand, rotary, sonic, ultra sonic etc.,
Working length determination / cleaning and shaping of root canal system and recent development in techniques of canal preparation.
Root canal irrigants and intra canal medicaments used including non – surgical Endodontics by calcium hydroxide.
Endodontic microbiology.
Obturating materials, various obturation techniques and recent advances in obturation of root canal.
Traumatic injuries and management – endodontic treatment for young permanent teeth.
Pediatric Endodontics – treatment of immature apex.
Endodontic surgeries, recent developments in techniques and devices, endoosscous
Endodontic implants – biology of bone and wound healing.
Endoperio interrelationship, endo + Perio lesion and management
Drugs and chemicals used in Endodontics
Endo emergencies and management.
Restoration of endodontically treated teeth, recent advances.
Geriatric Endodontics
Endo emergencies and management
Biologic response of pulp to various restorative materials and operative procedures.
Lasers in Endodontics.
Multidisciplinary approach to endodontics situations.
Endodontics radiology – digital technology in endodontics practice.
Local anesthesia in endodontics.
Procedural errors in endodontics and their management.
Endodontics failures and retreatment.
Resorptions and its management.
Microscopes in endodontics.
Single visit endodontics, current concepts and controversies.
Paper III:
1. Descriptive and Analysing type question.

- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: PRIYANKA L.S
Part 2:
PAPER I: CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
- Examination, diagnosis and treatment plan
- Occlusion as related to conservative dentistry, contact, contour, its significance.
- Separation of teeth, matrices, used in conservative dentistry.
- Dental caries – epidemiology, recent concept of etiological factors, pathophysiology.
- Histopathology, diagnosis, caries activity tests, prevention of dental caries and management – recent methods.
- Hand and rotary cutting instruments, development of rotary equipment, speed ranges, hazards.
- Dental bur and other modalities of tooth reparation – recent developments (air abrasions, Lasers etc)
- Infection control procedures in conservative dentistry, isolation equipments etc.
- Direct concepts in tooth preparation for amalgam, composite, GIC and restorative techniques, failures and management.
- Direct and indirective composite restorations.
- Indirect tooth coloured restorations – ceramic, inlays and onlays, veneers, crowns, recent
- Advances in fabrication and materials.
- Tissue Management
- Impression procedures used for indirect restorations.
- Cast metal restorations, indications, contraindications, tooth preparation for class 2 inlay, onlay full crown restoration
- Restorative techniques, direct and indirect methods of fabrication including materials used for fabrication like inlay wax, investment materials and
- Direct gold restorations.
- Recent advances in restorative materials and procedures.
- Management of non-carious lesion.
- Advance knowledge of minimal intervention dentistry.
- Recent advances in restoration of endodontically treated teeth and grossly mutilated teeth
- Hypersensitivity, theories, causes and management
- Lasers in Conservative Dentistry
- CAD-CAM & CAD-CIM in restorative dentistry
- Dental imaging and its applications in restorative dentistry (clinical photography)
- Principles of esthetics
- Color
- Facial analysis
- Smile design
- Principles of esthetic integration
- Treatment planning in esthetic dentistry
PAPER – II : ENDODONTICS
- Rationale of endodontics
- Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its implications in endodontic treatment.
- Dentin and pulp complex.
- Pulp and periapical pathology
- Pathobiology of periapex
- Diagnostic procedure – recent advances and various aids used for diagnosis –
- Orofacial dental pain emergencies: endodontic diagnosis and management
- Case selection and treatment planning
- Infection control procedures used in Endodontics (aseptic techniques such as rubber dam, sterilization of instruments etc)
- Access cavity preparation – objectives and principles
- Endodontic instruments and instrumentation – recent developments, detailed description of hand, rotary, sonic, ultra sonic etc.,
- Working length determination / cleaning and shaping of root canal system and recent development in techniques of canal preparation.
- Root canal irrigants and intra canal medicaments used including non – surgical Endodontics by calcium hydroxide.
- Endodontic microbiology.
- Obturating materials, various obturation techniques and recent advances in obturation of root canal.
- Traumatic injuries and management – endodontic treatment for young permanent teeth.
- Pediatric Endodontics – treatment of immature apex.
- Endodontic surgeries, recent developments in techniques and devices, endoosscous
- Endodontic implants – biology of bone and wound healing.
- Endoperio interrelationship, endo + Perio lesion and management
- Drugs and chemicals used in Endodontics
- Endo emergencies and management.
- Restoration of endodontically treated teeth, recent advances.
- Geriatric Endodontics
- Endo emergencies and management
- Biologic response of pulp to various restorative materials and operative procedures.
- Lasers in Endodontics.
- Multidisciplinary approach to endodontics situations.
- Endodontics radiology – digital technology in endodontics practice.
- Local anesthesia in endodontics.
- Procedural errors in endodontics and their management.
- Endodontics failures and retreatment.
- Resorptions and its management.
- Microscopes in endodontics.
- Single visit endodontics, current concepts and controversies.
1. Descriptive and Analysing type question.
- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Megavarnan R
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
PART-I: Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy of Head and Neck:
• Development of face, paranasal sinuses and the associated structures and their anomalies, cranial and facial bones, TMJ anatomy and function, arterial and venous drainage of head and neck, muscles of face and neck including muscles of mastication and deglutition, brief consideration of structures and function of brain. Brief consideration of all cranial nerves and autonomic nervous system of head and neck. Salivary glands, Functional anatomy of mastication, deglutition and speech. Detailed anatomy of deciduous and permanent teeth, general consideration in physiology of permanent dentition, form, function, alignment, contact, occlusion.
• Internal anatomy of permanent teeth and its significance.
• Applied histology – histology of skin, oral mucosa, connective tissue, bone, cartilage,
blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves, muscles, tongue.
Anatomy and Development of Teeth:
• Enamel – development and composition, physical characteristics, chemical properties, structure.
• Age changes – clinical structure.
• Dentin – development, physical and chemical properties, structure type of dentin,
innervations, age and functional changes and clinical considerations.
• Pulp – development, histological structures, innervations, functions, regressive changes,
clinical considerations.
• Dentin and pulp complex.
• Cementum – composition, cementogenesis, structure, function, clinical considerations.
• Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its
implications in endodontic treatment.
• Periodontal ligament – development, structure, function and clinical considerations.
• Salivary glands – structure, function, clinical considerations.
Applied Physiology:
• Mastication, deglutition, digestion and assimilation, fluid and electrolyte balance.
• Blood composition, volume, function, blood groups, haemostasis, coagulation, blood transfusion, circulation, heart, pulse, blood pressure, shock, respiration-control, anoxia, hypoxia, asphyxia, artificial respiration, and endocrinology – general principles of endocrine activity and disorders relating to pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals
including pregnancy and lactation.
• Physiology of saliva – composition, function, clinical significance.
• Clinical significance of vitamins, diet and nutrition – balanced diet.
• Physiology of pain, sympathetic and Para sympathetic nervous system, pain pathways,
physiology of pulpal pain, Odontogenic and non Odontogenic pain, pain disorders –
typical and atypical.
• Biochemistry such as osmotic pressure, electrolytic dissociation, oxidation, reduction etc.
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and their metabolism, nucleoproteins, nucleic acid and their metabolism. Enzymes, vitamins and minerals, metabolism of inorganic elements, detoxification in the body, anti metabolites, chemistry of blood lymph and urine.
Pathology:
• Inflammation, repair, degeneration, necrosis and gangrene.
• Circulatory disturbances – ischemia, hyperemia, edema, thrombosis, embolism,
infarction, allergy and hypersensitivity reaction.
• Neoplasms – classifications of tumors, characteristics of benign and malignant tumors,
spread of tumors.
• Blood dyscrasias.
• Developmental disturbances of oral and Para oral structures, dental caries, regressive
changes of teeth, pulp, periapical pathology, pulp reaction to dental caries and dental
procedures.
• Bacterial, viral, mycotic infections of the oral cavity.
Microbiology:
• Pathways of pulpal infection, oral flora and micro organisms associated with endodontic diseases, pathogenesis, host defense, bacterial virulence factors, healing, theory of focal infections, microbes relevance to dentistry – strepto, staphylococci, lactobacilli, cornyebacterium, actinomycetes, clostridium, neisseria, vibrio, bacteriods, fusobacteria, spirochetes, mycobacterium, virus and fungi.
• Cross infection, infection control, infection control procedure, sterilization and disinfection.
• Immunology – antigen antibody reaction, allergy, hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis, auto immunity, grafts, viral hepatitis, HIV infections and aids. Identification and isolation of microorganisms from infected root canals. Culture medium and culturing technique
(Aerobic and anaerobic interpretation and antibiotic sensitivity test).
Pharmacology:
• Dosage and route of administration of drugs, actions and fate of drug in body, drug addiction, tolerance of hypersensitivity reactions.
• Local anesthesia – agents and chemistry, pharmacological actions, fate and metabolism of anaesthetic, ideal properties, techniques and complications.
• General anesthesia – pre medications, neuro muscular blocking agents, induction agents, inhalation anesthesia, and agents used, assessment of anesthetic problems in medically compromised patients.
• Anaesthetic emergencies
• Antihistamines, corticosteroids, chemotherapeutic and antibiotics, drug resistance,
haemostasis, and haemostatic agents, anticoagulants, sympathomimitic drugs, vitamins and minerals (A, B, C, D, E, K IRON), anti sialogogue, immunosupressants, drug interactions, antiseptics, disinfectants, anti viral agents, drugs acting on CNS.
Biostatistics:
• Introduction, Basic concepts, Sampling, Health information systems – collection, compilation, presentation of data. Elementary statistical methods – presentation of statistical data, Statistical averages – measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, Normal distribution. Tests of significance – parametric and non – parametric tests (Fisher extract test, Sign test, Median test, Mann Whitney test, Kruskal Wallis one way analysis, Friedmann two way analysis, ANOVA, Regression analysis), Correlation and regression,Use of computers.
Research Methodology:
• Essential features of a protocol for research in humans
• Experimental and non-experimental study designs
• Ethical considerations of research Applied Dental Materials:
• Physical and mechanical properties of dental materials, biocompatibility.
• Impression materials, detailed study of various restorative materials, restorative resin and recent advances in composite resins, bonding- recent developments, tarnish and
corrosion, dental amalgam, direct filling gold, casting alloys, inlay wax, die materials, investments, casting procedures, defects, dental cements for restoration and pulp protection (luting, liners, bases) cavity varnishes.
• Dental ceramics-recent advances, finishing and polishing materials.
• Dental burs – design and mechanics of cutting – other modalities of tooth preparation.
Methods of testing biocompatibility of materials used.
PART-I: Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics
A. Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy:
a. Prenatal growth of head:
Stages of embryonic development, origin of head, origin of face, origin of teeth.
b. Postnatal growth of head:
Bones of skull, the oral cavity, development of chin, the hyoid bone, general growth of head, growth of the face.
c. Bone growth:
Origin of bone, composition of bone, units of bone structure, schedule of Ossification, mechanical properties of bone, roentgen graphic appearance of bone
d. Assessment of growth and development:
Growth prediction, growth spurts, the concept of normality and growth increments of growth, differential growth, gradient of growth, methods of gathering growth data. Theories of growth and recent advances, factors affecting physical growth.
e. Muscles of mastication:
Development of muscles, muscle change during growth, muscle function and facial development, muscle function and malocclusion
f. Development of dentition and occlusion:
Dental development periods, order of tooth eruption, chronology of permanent tooth formation, periods of occlusal development, pattern of occlusion.
g. Assessment of skeletal age.
Physiology:
a. Endocrinology and its disorders:
Growth hormone, thyroid hormone, parathyroid hormone, ACTH.
b. Calcium and its metabolism:
c. Nutrition-metabolism and their disorders:
Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals
d. Muscle physiology:
e. Craniofacial Biology:
Adhesion molecules and mechanism of adhesion
f. Bleeding disorders in orthodontics: Hemophilia
Dental Materials:
a. Gypsum products:
Dental plaster, dental stone and their properties, setting reaction etc.
b. Impression materials:
Impression materials in general and particularly of alginate impression material.
c. Acrylics:
Chemistry, composition physical properties
d. Composites:
Composition types, properties, setting reaction
e. Banding and bonding cements:
f. Wrought metal alloys:
Deformation, strain hardening, annealing, recovery, recrystallization, grain growth,
properties of metal alloys
g. Orthodontic arch wires
h. Elastics:
Latex and non-latex elastics.
i. Applied physics, Bioengineering and metallurgy:
j. Specification and tests methods used for materials used in Orthodontics:
k. Survey of all contemporary literature and recent advances in above mentioned
materials:
Genetics:
a. Cell structure, DNA, RNA, protein synthesis, cell division
b. Chromosomal abnormalities
c. Principles of orofacial genetics
d. Genetics in malocclusion
e. Molecular basis of genetics
f. Studies related to malocclusion
g. Recent advances in genetics related to malocclusion
h. Genetic counseling
i. Bioethics and relationship to Orthodontic management of patients.
Physical Anthropology:
a. Evolutionary development of dentition
b. Evolutionary development of jaws.
Pathology:
a. Inflammation b. Necrosis
Biostatistics:
a. Statistical principles
• Data Collection
• Method of presentation
• Method of Summarizing
• Methods of analysis – different tests/errors
b. Sampling and Sampling technique
c. Experimental models, design and interpretation
d. Development of skills for preparing clear concise and cognent scientific abstracts and
publication
Applied Research Methodology In Orthodontics:
a. Experimental design
b. Animal experimental protocol
c. Principles in the development, execution and interpretation of
methodologies in Orthodontics
d. Critical Scientific appraisal of literature.
Applied Pharmacology
Definitions & terminologies used – Dosage and mode of administration of drugs. Action and fate of drugs in the body, Drug addiction, tolerance and hypersensitive reactions, Drugs acting on the central nervous system, general anesthetics hypnotics, analeptics and tranquilizers. Local anesthetics, Chemotherapeutics and antibiotics. Vitamins: A, D, B – complex group, C & K etc.
Part I Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry
A) Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy of Head and Neck:
• Anatomy of the scalp, temple and face
• Anatomy of the triangles of neck and deep structures of the neck
• Cranial and facial bones and its surrounding soft tissues with its applied aspects
• Muscles of head and neck
• Arterial supply, venous drainage and lymphatics of head and neck
• Congenital abnormalities of the head and neck
• Anatomy of the cranial nerves
• Anatomy of the tongue and its applied aspects
• Anatomy and its applied aspects of salivary glands, pharynx, thyroid and parathyroid
gland, larynx, trachea, esophagus
• Autonomous nervous system of head and neck
• Functional anatomy of mastication, deglutition, speech, respiration and circulation
• TMJ: anatomy and function
Applied Physiology:
Introduction, Mastication, deglutition, digestion and assimilation, Homeostasis, fluid and electrolyte balance. Blood composition, volume, function, blood groups and hemorrhage, Blood transfusion, circulation, Heart, Pulse, Blood pressure, Normal ECG,capillary and lymphatic circulation, shock, respiration, control, anoxia, hypoxia, asphyxia, artificial respiration. Endocrine glands in particular reference to pituitary, parathyroid and thyroid glands and sex hormones. Role of calcium and Vit D in growth and development of teeth, bone and jaws.Role of Vit.A, C and B complex in oral mucosal and periodontal health.Physiology and function of the masticatory system. Speech mechanism, swallowing and deglutition mechanism, salivary glands and Saliva
Applied Pathology:
Inflammation and chemical mediators, Thrombosis, Embolism, Necrosis, Repair, Degeneration , Shock, Hemorrhage , Blood dyscrasias, Pathogenesis of Dental Caries, Periodontal diseases, tumors, oral mucosal lesions etc. in children
Applied Microbiology:
Microbiology & Immunology as related to Oral Diseases in Children: Basic concepts, immune system in human body, Auto Immune diseases and Immunology of Dental caries.
Applied Nutrition & Dietics:
• General principles, balanced diet, effect of dietary deficiencies and starvation, protein energy, malnutrition, Kwashiorkor, Marasmus.
• Fluid and Electrolytic balance in maintaining haemostasis
• Diet, digestion, absorption, transportation and utilization
Genetics:
• Introduction to genetics
• Cell structure, DNA, RNA, protein synthesis, cell division
• Modes of inheritance
• Chromosomal anomalies of oral tissues & single gene disorders
Growth & Development:
Prenatal and Postnatal development of cranium, face, jaws, teeth and supporting structures.Chronology of dental development and development of occlusion. Dimensional changes in dental arches. Cephalometric evaluation of growth.
- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: MALATHY BALARAMAN RAVINDRRAN
- Teacher: Dr.PRATHIBA GNANASEKARAN
- Teacher: PRIYANKA L.S
- Teacher: MANEESHWARI M
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Dr.Premjanu N
- Teacher: Venkatalakshmi Nagella
- Teacher: Tamil Selvi Palaniappan
- Teacher: Revathy Rajendran
- Teacher: REESHMA RUCKSCHANDA
- Teacher: MOHAMMED MEERA RIYAZ S
- Teacher: Srividya S
- Teacher: Priya Sathish
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
- Teacher: GOUSALYA V
This course is meant to provide learners conceptual knowledge about various electronic measuring instruments and how to choose a specific measuring instrument based on their requirement. There are two types of measuring instruments: one is the type of measuring instruments that show the values on the scale of the meter, and other are type of measuring instruments that displays the waveforms.

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
In chemical engineering and its related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process. For this reason they can be classified in different ways. The first category assigned to UOs is mechanical operations.Mechanical unit operations can be categorized into three:Operations involving particulate solids;Operations involving solid-fluid;Operations involving fluid systems;

- Teacher: Sathish S
|
SMEB1603 |
MECHANICS OF MACHINES |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
The aim of the course is to:
· Provide the insights of the fundamentals of Mechanisms and Cams.
· Understand the basics of Flywheels, Balancing of Rotating and Reciprocating unbalance systems.
· Enhance knowledge of Single degree - Free and Damped Vibrations.
· Provide the detailed overview of Forced Vibrations.
· Discuss the fundamentals of Gyroscopes and Governors.
UNIT I MECHANISMS AND CAMS 9 hrs
Mechanisms – Terminology and definitions – Kinematics inversions of 4 bars and slider crank chain – Kinematic analysis in simple mechanisms. Types of cams and followers - Terminology and definitions – Displacement diagrams – SHM, uniform velocity, uniform acceleration and retardation. Graphical constructions of cam profiles – Disc cam with knife edge follower, roller follower and flat-faced follower.
UNIT II FLY WHEELS AND BALANCING 9 Hrs
Turning moment diagrams – Fluctuation of Energy and speed – Energy stored in Flywheel – Mass of Flywheel – Dimensions of Flywheel. Balancing – Static and Dynamic Balancing of Rotating Masses - Balancing of several masses rotating in same plane and in different planes- Partial Balancing of locomotives – Variation of tractive force, Hammer blow and swaying couple.
UNIT III FUNDAMENTALS OF VIBRATION 9 Hrs
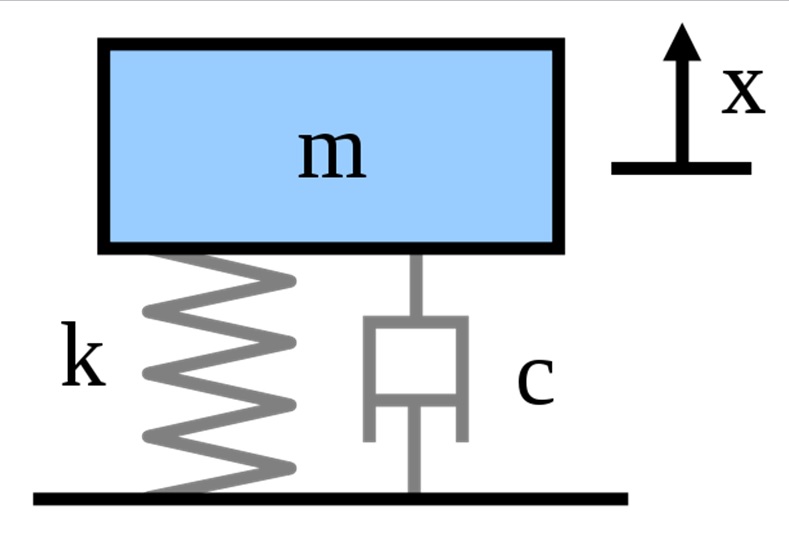
Basic features of vibratory systems - Lumped mass systems - Degrees of freedom - Free vibration of Longitudinal, Transverse and Torsional systems of Single degree of freedom - Equations of motion - Natural frequency – Whirling of shafts and critical speed - Dunkerley’s Method – Torsional vibration of Two and Three rotor system. Damped free vibration - Types of Damping –Critical damping coefficient - Damping Factor – Logarithmic Decrement.
UNIT IV FORCED VIBRATION 9 Hrs
Forced vibration of single degree freedom system with damping - Response to periodic forcing- Harmonic Forcing - Force transmissibility and amplitude transmissibility - Reciprocating and rotating unbalance - vibration isolation and transmissibility - Support motion - self excited vibration with examples
UNIT V GOVERNORS AND GYROSCOPES 9 Hrs
Gyroscopes and gyroscopic effects-Effect of precession motion on the stability of moving vehicles such as motor car, motor cycle, aero planes and ships gyroscopic couple, (Demonstration of models in video). Governors - types and applications - Watt, Porter and Proell governors - Spring loaded governors -Hartnell and Hartung with auxiliary springs. Sensitiveness- isochronisms and hunting.
Max Hours: 45 Hrs
COURSE OUTCOMES:
At the end of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Investigate the Mechanisms and Cams.
CO2: Determine the principle of Flywheel, Rotating and Reciprocating masses.
CO3: Analyze the Single degree - Free and Damped Vibrations.
CO4: Evaluate the force transmitted to the foundation for mechanical systems in Forced Vibrations.
CO5: Apply the fundamentals of Gyroscopes.
CO6: Apply the fundamentals of Governors.
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Khurmi R.S& Gupta J.S, “Theory of Machines”, 16th Edition, S.Chand & Company, 2005, Reprint 2016.
2. Singh V.P, “Mechanical Vibrations”, 3rd Edition, Dhanpatrai & Co., 2006.
3. Ghosh A. and Malik A.M, “Theory of Mechanism and Machines”, 4th Edition, Affiliated East West Press (P) Ltd. 2009.
4. Ashok G. Ambekar, “Mechanism and Machine Theory”, First Edition,PHI Learning Private limited, 2009.
5. Rattan S. S, Theory of Machines, 3rd Ed., Tata Mcgraw Hill, 2009.
6. Gordon R Pennock, Joseph E Shigley, “Theory of Machine and Mechanisms SI Edition, 4th Edition, Oxford University Press, 2014
|
END SEMESTER EXAM QUESTION PAPER PATTERN |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
- Teacher: LAKSHMI SANKAR S
The course makes the students to understand the ethics and the principles of Media. The course covers topics on the definition of ethics, values and principles. The learners will identify the relationship between ethics and society. This course will make them to analyze the ethical challenges in the media. Through various case studies, the learners can understand the prevailing laws and ethics especially in cyber space. The course also aims to introduce the concept of cyber crime .


