Search results: 406
Objectives:
• Understanding the origins, structure and development of language and its application to other areas of humanistic and scientific knowledge.
• Understanding the general characteristic of the structure of language, its phonological sound system, word structure, and phrase and sentence patterns.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Grasp the complexity of language as a communication system shaped by cognitive, biological, cultural, and social factors. Demonstrate understanding of the concepts, theories, and methodologies used by linguists in qualitative and quantitative analyses of linguistic structure, and patterns of language use. Demonstrate understanding of processes of language change and variation, the role of language in reflecting and constructing social identities, and the distinctive properties of human language. Acquire the technical vocabulary and theoretical tools of the field, necessary to read published linguistic research. Apply their understanding of linguistic concepts, methods and approaches to the construction and analysis of meanings in different modes of communication. Are ready for significant scholarly participation in the field of linguistics.

- Teacher: Amutha Monica
COURSE OBJECTIVE
• To enable the students to read and respond to specialized (scientific) materials and to subject
areas included for their study.
• To provide an opportunity for students to comprehend and react in oral and written forms to the
specialized texts that they read in their respective courses so as to summarise and paraphrase
the texts presented in the class.
• To provide opportunities for students to respond to listening and writing tasks by using digital
tools
• To enhance 21st century skills like communication, collaboration, critical thinking and creativity
through blended learning contexts
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Classify technical words to use them in sentences framing, compose problem solving paragraphs in semi formal letters, use rubrics to self evaluate, listening to take linear notes, reading to infer, predict and to differentiate facts from opinions, guess contextual meaning of words, modify the verbs in present tense, use learnt language in role plays with 80% accuracy
CO2: Categorize information based on global understanding of reading materials to prepare notes in graphic format like tables, use cohesive words related to comparing and contrasting by writing short paragraphs based on visual inputs in the form of bar diagrams, pie chart etc; describe process by composing paragraphs, recognize topic sentences and identifying verbal phrases while reading, use prepositions and prepositional phrases, modify the verbs from one form to the other in past and future tenses with 80% accuracy
CO 3: Generate specific information by using scanning and skimming reading materials, Construct questionnaire to conduct class survey by framing open ended questions to generate data on current issues to make oral presentations and report in written format by using template provided, arrange sentences in the right order by using sentence linkers as clues, revise the written materials by identifying elements of editing, edit errors related to subject verb agreement, punctuation and spelling besides coherence with 70 % accuracy, use reported speech in spoken and written form in class room in reporting contexts, list paired words, word associations by recalling and identifying by noticing them while reading CO 4: Paraphrase based on reading to discuss and design products thereby to create and design user manual, identify technical words related to compound nouns to expand and to paraphrase, enact role plays to present the product, discuss facts and opinions of the product in pair and team work, read current topics to summarise in note form , listen to current issues to deduct meaning from the context, choose the right option, define technical words related to the reading materials.
CO 5: Summarise reading materials, use the ideas while writing essays, take, and differentiate meaning of homonyms and homophones
CO 6: Demonstrate the ability to work cooperatively in a small group environment, in activities developed for language learning in the classroom/ online for formative assessment purposes, use and develop rubrics for self reflection, apply elements of reasoning skills for critical reading, identify facts and opinions and make judgements independently, develop intellectual courage and perseverance in pair and group work.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Classify technical words to use them in sentences framing, compose problem solving paragraphs in semi formal letters, use rubrics to self evaluate, listening to take linear notes, reading to infer, predict and to differentiate facts from opinions, guess contextual meaning of words, modify the verbs in present tense, use learnt language in role plays with 80% accuracy
CO2: Categorize information based on global understanding of reading materials to prepare notes in graphic format like tables, use cohesive words related to comparing and contrasting by writing short paragraphs based on visual inputs in the form of bar diagrams, pie chart etc; describe process by composing paragraphs, recognize topic sentences and identifying verbal phrases while reading, use prepositions and prepositional phrases, modify the verbs from one form to the other in past and future tenses with 80% accuracy
CO 3: Generate specific information by using scanning and skimming reading materials, Construct questionnaire to conduct class survey by framing open ended questions to generate data on current issues to make oral presentations and report in written format by using template provided, arrange sentences in the right order by using sentence linkers as clues, revise the written materials by identifying elements of editing, edit errors related to subject verb agreement, punctuation and spelling besides coherence with 70 % accuracy, use reported speech in spoken and written form in class room in reporting contexts, list paired words, word associations by recalling and identifying by noticing them while reading
CO 4: Paraphrase based on reading to discuss and design products thereby to create and design user manual, identify technical words related to compound nouns to expand and to paraphrase, enact role plays to present the product, discuss facts and opinions of the product in pair and team work, read current topics to summarise in note form , listen to current issues to deduct meaning from the context, choose the right option, define technical words related to the reading materials.
CO 5: Summarise reading materials, use the ideas while writing essays, take, and differentiate meaning of homonyms and homophones
CO 6: Demonstrate the ability to work cooperatively in a small group environment, in activities developed for language learning in the classroom/ online for formative assessment purposes, use and develop rubrics for self reflection, apply elements of reasoning skills for critical reading, identify facts and opinions and make judgements independently, develop intellectual courage and perseverance in pair and group work.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah

Introduce the students to basic principles, theories and practices in ELT.
Enable students to identify changes that took place over a period of time in the area.
Analyze the teaching approaches and methods. Recall basic approaches for teaching language with four skills.

To create a strong base on the various sensors and transducers in mechanical system, interdisciplinary applications of Electronics, Electrical, Mechanical and Computer Systems for the Control of Mechanical and Electronic Systems
To design control system for computer application like CNC.

- Teacher: Sabarivani A
To help the student to see the need for developing a holistic perspective of life.
To sensitize the student about the scope of life – individual, family, society and nature/existence.
Strengthening self-reflection.
To develop more confidence and commitment to understand, learn and act accordingly.
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
- Teacher: NIVIN JOY
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
COURSE OBJECTIVE’S
- To understand the network architecture and protocols supported for connecting devices in a network.
- To gain the knowledge of framing in data link layer.
- To learn the functions of network layer and the routing strategies with their associated protocols.
- To introduce the protocols used for end to end packet delivery in transport layer.
- To understand the application layer protocols.

- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects or people called "things" that are embedded with software, electronics, network, and sensors that allows these objects to collect and exchange data. Students will learn various IoT concepts like IoT basics, IoT introduction, fundamentals of IoT, IoT with cloud and IoT with data analytics.

- Teacher: Anbuselvi G
- Teacher: Subapriya V
Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects or people called "things" that are embedded with software, electronics, network, and sensors that allows these objects to collect and exchange data. Students will learn various IoT concepts like IoT basics, IoT introduction, fundamentals of IoT, IoT with cloud and IoT with data analytics.

- Teacher: Sivasangari A
- Teacher: Nagarajan G
- Teacher: Lakshmanan L
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: BHANU SHREE T
- Teacher: Ulagamuthalvi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce Bit coin and other crypto currencies.
- To study the algorithms and techniques in block chain.
- To understand the practical aspects in the design of crypto currency.
- To understand the function of Block chains as a method of securing distributed ledgers.
- To design, code, deploy and execute a smart contract.

- Teacher: Jeyanthi P
- Teacher: Jeberson Retna Raj R
- Teacher: Srividhya S.R
- Teacher: Shamili P
This course aims at understanding important medically important virus its mode of infection, pathogenesis prophylaxis and treatment.
Topic: 1
- General Concepts: Virus history,
- Diversity,
- shapes,
- sizes
- components of genomes.
- Isolation and purification of viruses and components.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 2
- Consequences of virus infection to animals
Consequences of virus infection to human.
- Viral infection: affect on host
macromolecules.
- Viral infection: establishment of the antiviral state.
- Viruses counter attack mechanisms.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 3
- Classification of viruses and nomenclatures.
- Positive strand RNA viruses- Picornaviruses. Flaviviruses
- West Nile virus and Dengue virus.
- Coronaviruses- SARS pathogenesis
- Negative strand RNA viruses Paramyxoviruses. Orthomyxoviruses
- Influenza pathogenesis and Bird flu.
- Rhabdoviruses: Rabies pathogenesis.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 4
- dsRNA viruses-
- Reoviruses: structure, classification,
- Reoviruses: life cycle; reverse
transcription.
- Retroviruses: HIV, viral pathogenesis and AIDS.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 5
- Small DNA viruses: parvo,
- polyomaviruses.
- Large DNA viruses: Herpes,
- adeno-,
- poxviruses.
- Miscellaneous viruses.
- Assignment
- Quiz
- Dr.S.SUDHA: Bavani latha Muthiah
This course aims at understanding important medically important virus its mode of infection, pathogenesis prophylaxis and treatment.
Topic: 1
- General Concepts: Virus history,
- Diversity,
- shapes,
- sizes
- components of genomes.
- Isolation and purification of viruses and components.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 2
- Consequences of virus infection to animals
Consequences of virus infection to human.
- Viral infection: affect on host
macromolecules.
- Viral infection: establishment of the antiviral state.
- Viruses counter attack mechanisms.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 3
- Classification of viruses and nomenclatures.
- Positive strand RNA viruses- Picornaviruses. Flaviviruses
- West Nile virus and Dengue virus.
- Coronaviruses- SARS pathogenesis
- Negative strand RNA viruses Paramyxoviruses. Orthomyxoviruses
- Influenza pathogenesis and Bird flu.
- Rhabdoviruses: Rabies pathogenesis.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 4
- dsRNA viruses-
- Reoviruses: structure, classification,
- Reoviruses: life cycle; reverse
transcription.
- Retroviruses: HIV, viral pathogenesis and AIDS.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 5
- Small DNA viruses: parvo,
- polyomaviruses.
- Large DNA viruses: Herpes,
- adeno-,
- poxviruses.
- Miscellaneous viruses.
- Assignment
- Quiz
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
Unit: 1 – CELLS AND CELLULAR METABOLISM 12 Hrs
Introduction to human anatomy and physiology – Basic elements of life, characteristics and maintenance of life – levels of organisms, structure of matter, chemical constituent of cell – movement through cell membrane, life cycle of cells and control of cell reproduction, metabolic process, control of energy and metabolic reactions, metabolic pathway - nucleic acids and protein synthesis – change in genetic information.
Unit: 2 – TISSUES AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM 12 Hrs
Tissues – epithelial, muscular and nervous tissues – integumentary system, types of membranes, skin – accessory organs, disorders, regulations of body temperature – Bone structure, development, function and organization of skeleton – joints, classification, structures and movements – muscle, structure and types, actions and responses.
Unit: 3 – BODY SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS 12 Hrs
Blood, circulation and function – lymphatic system-Endocrine system, endocrine glands, structure and function – respiratory system, structure and function – cardiac system, structure and function.
Unit:4 – NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND SENSES 12 Hrs
Nervous tissue, cell membrane potential, classification of neurons and nerve fibres – meninges, spinal cord, brain – peripheral and autonomic nervous system – somatic and special senses, receptors and sensations (smell, taste, hearing, equilibrium and sight).
Unit: 5 – METABOLISM AND NUTRITION 12 Hrs
Digestive system, structure and function – urinary system, kidney and nephron, structure and function – reproductive system – metabolism and nutrition.
Max. 60 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology, 11th Edition, 2011, Martini, Nath, and Bartholomew.
2. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology, 12th Edition, 2017, Elaine N. Marieb and Suzanne M. Keller.
- Teacher: Beryl Vedha Y
This course provide the general introduction to different types of Immune cells, their function, cross talks and activation mechanism. Also gives over view about the primary and secondary immune organs, B-Cell, T-cell biology and their surface receptor. Immune responses, antigen nature, hypersensitivity, tumor immunology and autoimmune responses are covered in detail.
Thermal Engineering is the study of heating and cooling processes in open and closed environments. As an academic discipline, it involves the science of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To make the student understand the overall view of thermal engineering through topics such as Power cycles, IC Engines, Steam nozzles & turbine, air compressors and Refrigeration and Air conditioning.
- This subject enables the students to understand the principle of operation, construction and control of several thermal equipment's which find wide applications in a variety of fields like power generation, automobile industry, process industries, food preservation and human comfort.
- It provides the fundamentals for Power plant Engineering, Automobile Engineering, Turbo machinery and Refrigeration & Air conditioning (R&AC)

Finite element analysis (FEA) is a computerized method for predicting how a product reacts to real-world forces, vibration, heat, fluid flow, and other physical effects. Finite element analysis shows whether a product will break, wear out, or work the way it was designed.
FEA enables you to predict potential design issues and therefore minimize risk to your product, profits, and your business. With FEA you can test the impact of varying conditions (stress, vibration, buckling, fatigue, creep, heat, etc.) on your design.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Understand the capabilities of FEM and its importance in Engineering.
To introduce the concepts of Mathematical Modeling of Engineering Problems.
COURSE OUTCOMES
|
CO1:Understand the Fundamental Theory of Finite Element Method. |
|
CO2: Select and interpret Finite Element analysis results for design and evaluation purposes. |
|
CO3:Solve plain elasticity problem using energy approach |
|
CO4:Solve one dimensional heat transfer problems and two dimensional scalar variable problem using ANSYS. |
|
CO5:Develop a basic understanding of the limitations of the Finite Element method and understand the possible error sources in its use. |
|
CO6:Examine the longitudinal vibration, transverse vibration of beams, Mesh Generation and Errors in the finite element method. |
UNIT 1 1D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 9 Hrs.
Historical Background -Basic concept of FEM- steps involved in FEA - Variational Formulation of Boundary value problem - Rayleigh Ritz Method - Weighted Residual methods-Finite Element Modeling - Element Equations - Shape functions -Bar, Beam Elements - stepped bar, tapered bar-simple problems
UNIT 2 2D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 10 Hrs.
Basic Boundary Value Problems in 2 Dimensions - Triangular, quadrilateral, higher order elements - Poisson and Laplace Equations - Weak Formulation - Elements Matrices and Vectors -.Natural Co-ordinate System - Lagrangian Interpolation Polynomials - Iso-parametric Elements - Formulation -Numerical Integration -2D Triangular elements - rectangular elements - Illustrative Examples.
UNIT 3 SOLUTION TO PLANE ELASTICITY PROBLEMS 8 Hrs.
Introduction to Theory of Elasticity - Plane Stress - Plane Strain and Axisymmetric Formulation - Principle of virtual work - Element matrices using energy approach.
UNIT 4 APPLICATIONS IN HEAT TRANSFER & FLUID MECHANICS 9 Hrs.
One dimensional heat transfer element - application to one-dimensional heat transfer problems- scalar variable problems in 2-Dimensions - Applications to heat transfer in 2- Dimension - Application to problems in fluid mechanics in 2-D.
UNIT 5 SPECIAL TOPICS 9 Hrs.
Vibrational problems - equations of motion based on weak form -longitudinal vibration of bars - transverse vibration of beams Mesh Generation-Errors in the finite element method - various measures of errors- accuracy of the solution- Eigen value Problems - h & p elements- Applications of FEM software to solve simple problems, types of solver - a brief.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. J.N Reddy. “An Introduction to the Finite Element Method” , Mc Graw Hill, International Edition, 1993.
2. Seshu, P, “Text Book of Finite Element Analysis”, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi,2007.
3. Segerlind L.J,“Applied Finite Element Analysis”, John Wiley, 1984.
4. Rao. S.S, “Finite Element Method in Engineering” , Pergamon Press, 1989.
5. Chandrupatla & Belagundu , “Finite Elements in Engineering”, Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd., 1997.
6. Cook, Robert Davis et al, “Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis” , Wiley, John & Sons,1999.
7. George R Buchanan, “Schaum’s Outline of Finite Element Analysis”, McGraw Hill Company, 1994.
8. Taylor.C and Hughes.J.B. “Finite Element Programming of the Navier Stoke equation” Pineridge Press Limited, UK 1981
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
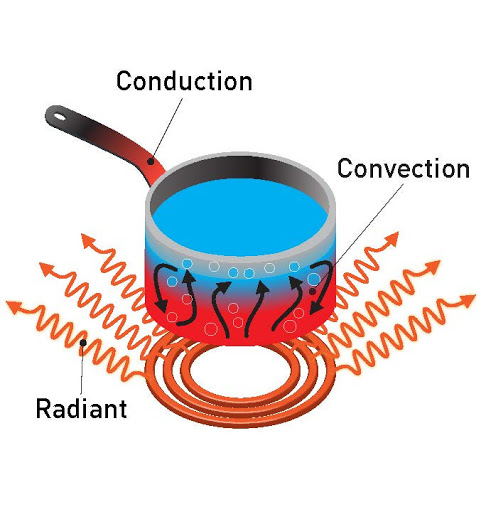
CO1 - Understand the basic modes of heat transfer and Compute temperature distribution in steady-state
and unsteady-state heat conduction.
CO2 - Understand and analyze heat transfer through extended surfaces.
CO3 - Interpret and analyse forced and free convection heat transfer.
CO4 - Explore the real time applications of radiation mode of heat transfer.
CO5 - Design heat exchangers using LMTD and NTU methods.
CO6 - Relate the mass transfer concepts for various industrial applications
- Teacher: Anderson A
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF MATERIALS- Crystallography: Basics, Atomic radius and Atomic packing factor of BCC, FCC & HCP, Miller’s indices, Allotropy, Solid solutions and intermetallic compounds. Atomic Diffusion: Laws of diffusion, Factors affecting diffusion. Phase diagrams: Solidification of metals, Phase rules, Construction of phase diagram, Isomorphous diagram, Eutectic diagram showing partial solid solubility, Peritectic system.
UNIT 2 FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS ALLOYS- Ferrous alloys: Cooling curve of pure iron, Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagram, Critical points in Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagrams, Classification of ferrous alloys, Influence of alloying elements, Designation systems, Types of steels and cast iron, Typical compositions, properties and applications of ferrous alloys. Non-ferrous alloys: Typical compositions, properties and applications of Aluminium and its alloys, Copper & its alloys, Ti & its alloys, and Nickel & its alloys.
UNIT 3 STRENGTHENING PROCESSES- Heat treatment of steel: TTT diagram and CCT diagram. Heat treatment processes: Annealing, Normalizing, Tempering and Quenching, Jominy quency test for hardenability. Case hardening: Carburizing, Nitriding, Cyaniding, Carbonitriding, Flame hardening and Induction hardening. Others: Dispersion strengthening & Precipitation hardening
UNIT 4 FAILURE OF MATERIALS AND TESTING- Tensile testing: Significance, Universal testing machine, Stress–strain curve for ductile & brittle material, Results. Hardness Testing: Significance, Rockwell harness test, Brinell’s hardness test and Vicker’s hardness test, Results. Impact testing – Significance, Charpy impact test and Izod impact test, Results. Failure of materials: Defects in materials, Deformation mechanisms, Failure mechanisms and influencing factors of ductile and brittle failures, fatigue failure, creep failure and impact failure.
UNIT 5 MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION AND SELECTION - X-ray diffraction (XRD): Bragg’s law of diffraction, Powder, rotating crystal and Laue methods to determine the crystal
structure. Optical microscopy: Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and Applications of optical
microscopes. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and
Applications of SEM. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample
preparation and Applications of TEM. Materials selection: Engineering materials and their properties, Materials selection
charts, Material selection strategy, Factors affecting materials selection, Case studies.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
- Teacher: JINO L
