Search results: 406
This course enable the students
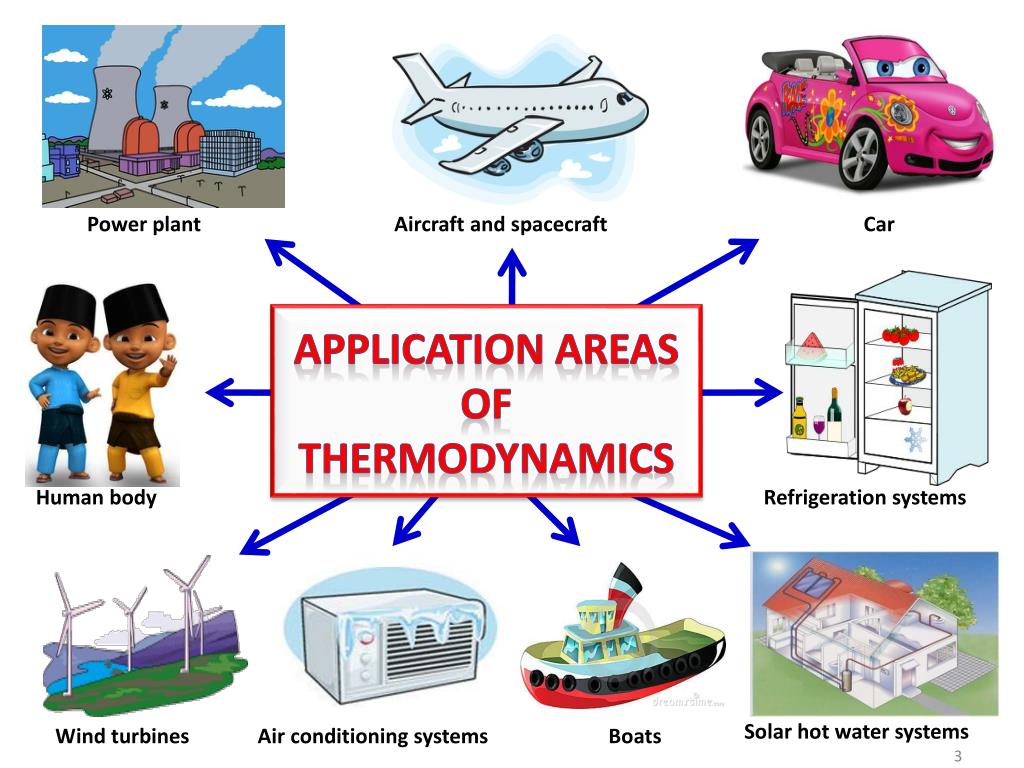
- To understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics
- To understand the air standard cycles and working principles of four stroke and two stroke engines
- To familiarize with the types of air compressors and their working principle
- To understand the working principles of refrigeration and air conditioning systems
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
In this course we would be recollecting basic concepts in number theory and their applications in solving real life problems. We would also learn about the prime numbers, factors of a number, sum of factors of a number and apply them to derive interesting characteristics of numbers.

- Teacher: FRANKLIN THAMIL SELVI M S
At the end of the course Students will be able to form and solve the nth degree algebraic equations. Using the concept relation between roots and coefficients of equations the student will be able to find the roots of the equation. Reciprocal equations can be solved using the newton’s method. The student will be able to find rank and inverse of a matrix by elementary transformation. Students get a clear idea on finding the characteristic equation and roots of the characteristic equation of a given matrices. Cayley Hamilton theorem gives him a clear idea to find the inverse and higher powers of the given matrix. Student can solve the system of equations using matrix methods

- Teacher: KAVITHA C
- Teacher: MARY METILDA M I
- Teacher: Subhashini N
The ability to identify, reflect upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject.
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
Statistics is a branch of Mathematics, that deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and the presentation of the numerical data.
Statistical inference is the process to draw conclusions about a process by using data analysis.

- Teacher: KALAIMATHI M
- Teacher: NIRMALA M
Dear Learners,
As we are aware that many real life problems could be modelled into a differential equation, this course helps you to explore various methods of solving the differential equations and the characteristic properties of such solutions. At the end of the course one would gain
Expertise in applying various methods to obtain non-trivial solutions to second order linear complete and reduced differential equations.
Learner would be able to understand nature, Qualitative properties and Essential characterization of the solution of reduced second order linear differential equation by direct analysis of its equation. Learn the procedure to obtaining power series solution to first and second order ordinary differential equation.
A learner would gain proficiency in solving Gauss Hyper geometric equation, homogeneous differential equation for large values of the independent variable. Familiarize some special functions of Mathematical Physics and their properties. Acquaintance to system to first order linear differential equation, solution to homogeneous linear system with constant coefficients, Isoperimetric problems and method of successive approximation.
- Teacher: VELANKANNI A
- Teacher: RAHIM K.H.
- Teacher: LEEMA NIVETHINI R
- Teacher: Cynthiya Margaret Indirani S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
• To understand how human behavior is influenced by social factors.
• To explore the psychological aspects of various social phenomena.
Unit I: Social Perception and Social Cognition (15 hours)
Nonverbal Communication- Facial Expressions of Emotion - The Covariation Model - The Fundamental Attribution Error - Self-Serving Attributions -The Bias Blind Spot- Confirmation bias. Social Cognition: Low-Effort Thinking - Types of Automatic Thinking- High-Effort Thinking - Errors in Social Cognition
Unit II: Social Influence (15 hours)
Conformity - Informational Social Influence - Normative Social Influence - Conformity and Social Approval - The Asch Line-Judgment Studies - Milgram’s Obedience Studies - Social Facilitation - Social Loafing - Group Polarization
Unit III: Attitudes (15 hours)
Attitude formation: How attitudes develop -Affective and Cognitive Bases of Attitudes - When and why do attitudes influence behavior - attitudes guide behavior - Change in attitudes toward the environment - The fine art of persuasion: Elements of persuasion - Resisting persuasion attempts - Cognitive dissonance - managing cognitive dissonance.
Unit IV: Prosocial Behavior (15 hours)
Positive Social Relations- Prosocial behavior: Basic Motives Underlying Prosocial Behavior: Personal Qualities and Prosocial Behavior Situational Determinants of Prosocial Behavior: – Helping influences – factors that increase and decrease Pro-social behaviour- Crowdfunding
Unit V: Stereotype, Prejudice and Discrimination (15 hours)
Stereotype: How members of different groups perceive inequality - The nature and origins of stereotyping - Prejudice and discrimination - Frustration and Aggression: The Scapegoat Theory - Social Identity Theory- The Self-Fulfilling Prophecy - Feelings and actions toward social groups - Why prejudice is not inevitable: Techniques for countering its effects.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will understand and apply theories and findings in social psychology.
2. Students will analyse the different methodologies in social psychology and their importance.
3. Students will evaluate and critique research in social psychology.
4. Students will create knowledge of social psychology with their own life experience.
5. Students will apply the knowledge of the psychological causes and consequences, towards the cure, for prejudice.
6. Students will remember the psychological aspects of various social phenomena.
References:
1. Baron, R. A., & Byrne, D. (2003). Social Psychology, 10th ed. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
2. Aronson, E., Wilson, T. D., & Akert, R. M. (2013). Social psychology.9th edition. Prentice Hall/Pearson Education.
3. Myers, D. G. (2002). Social Psychology, 7th ed. Int. Education: Mc Graw Hill.
4. Chaube, S. P., &Chaube, A. (2007). Ground Work for Social Psychology. New Delhi: Neelkamal.
5. Lindgren, Henry. C. (1973) An introduction to Social Psychology, John Wiley & Sons.
6. Kloos, B., Hill, j., Thomas, E., Wandersman, Elias, M. J., & Dalton, J.H. (2012). Community psychology: Linking individuals and communities. Wadsworth, Cengage.
7. Schneider, F.W., Gruman, A., Coults, L .M. (Eds.). (2012). Applied social psychology: Understanding and addressing social and practical problems. New Delhi: Sage publications.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable students to develop cognizance of the importance of human behavior.
To provide insight on individual and group behavior.
To familiarize with organizational culture, change and development processes.

- Teacher: Princy A.S
Course Objectives● To introduce the student to British poetry
● To immense drama from the age of Chaucer to Milton.
● To comprehend the development of trends in British drama and poetry. .
● To understand the theme, structure and style in British poetry, drama.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: MRITTIKA MAITRA
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: VISHALI S
- Teacher: MISHA T.P
Introduce the students to basic principles, theories and practices in ELT.
Enable students to identify changes that took place over a period of time in the area.
Analyze the teaching approaches and methods. Recall basic approaches for teaching language with four skills.

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: MISHA T.P
Statistics is a branch of Mathematics, that deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and the presentation of the numerical data.
Statistical inference is the process to draw conclusions about a process by using data analysis.

- Teacher: Andrew Michael A
- Teacher: KALAIMATHI M
- Teacher: NISHA R
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
Unit 1: PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Unit 2: HEAT
Unit 3: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Unit 4: SOUND AND ACOUSTICS OF BUILDING
Unit 5: GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND PHYSICAL OPTICS
Course outcome:
CO1: Gain a basic knowledge of characterization of materials.
CO2: Explain statistical physics and thermodynamics as logical consequences of the postulates of statistical mechanics
CO3: Identify the Interaction of EM waves with matter in microscopic view given more values than previous.
CO4: Outline the importance of Acoustics and properties of sound in the modern society
CO5: Apply the principles and techniques of optics and defects in the selected problems.

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
Course Name : Mechanics
Course Code: SPH1112
It consists five units.
Unit I : Dynamics
Unit II: statics and Hydrostatics
Unit III: Frame of Reference
Unit IV: Special Theory of Relativity
Unit V: Oscillations
- Teacher: Manjula M
The course is aimed
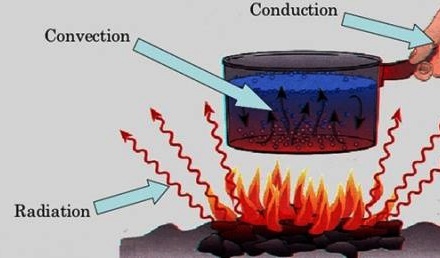
To acquire working knowledge of thermometry and calorimetry.
To acquire working knowledge of the zero-th, first and second law of thermodynamics.
To acquire basic understanding of liquid and solid cryogens working principle and their functionality
To understand conduction ,radiation and various law s such as Wien’s law, Planck’s law Rayleigh-Jean’s law
To link thermodynamics to the micro description used in Statistical Mechanics.
- Teacher: Helen Merina Albert
Course Outcomes
CO1: Understand the physical significance of Maxwell’s equations and hence estimate the speed of light.
CO2: Explain the basics and applications of LASER.
CO3: Explain the propagation mechanism of light through optical fiber.
CO4: Derive the relation between Numerical Aperture and Refractive indices.
CO5: Classify the types of optical fibers and attenuation mechanisms.
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
Course Objective:
➢ To enable students to understand the description of equations of motion of a system (using Lagrangian,
Hamiltonian mechanics and finally canonical transformation).
Course Outcomes:
Having successfully completed this course, students will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of
CO1: Derivation of Lagrange equation from D’Alembert principle
CO2: Apply the Lagrange equation to study the motion under central force problems
CO3: Apply the Lagrange equation to study the motion of rigid bodies.
CO4: Derivation of Hamilton equation of motion and apply the same for systems such as relativistic particles
and light rays.
CO5: Use of canonical transformation to find the constants of motion according to Hamilton-Jacobi theory

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To introduce the basic concepts of quantum mechanics.
➢ To realize the electronic structure of various materials via the band theory.
➢ To appreciate the role of quantum physics in the design and development of novel sensor devices.
➢ To understand the heat transfer mechanism in solids and fluids.

- Teacher: Anita Lett J
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Ø To acquire basic understanding of laboratory techniques.
Ø To educate the basics of instrumentation, data acquisition and interpretation of results.
Ø To educate and motivate the students in the field of science.
Ø To allow the students to have a deep knowledge of fundamentals of optics.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Determination of Young’s Modulus- Uniform bending Method.
2. Determination of Young’s Modulus- Non Uniform bending Method.
3. Determination of Rigidity Modulus of a wire – Torsional pendulum.
4. Determination of thermal conductivity of a bad conductor using Lee’s disc method.
5. Calibration of Voltmeter using potentiometer.
6. Calibration of Ammeter using potentiometer.
7. Determination of magnetic susceptibility using Quincke’s Method.
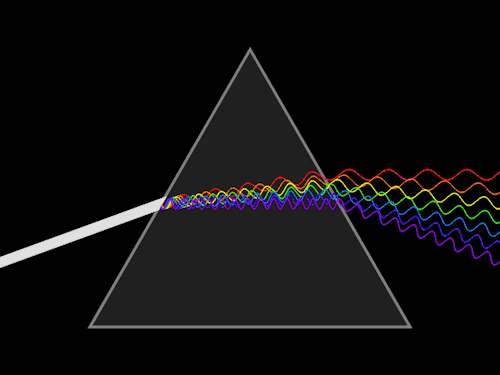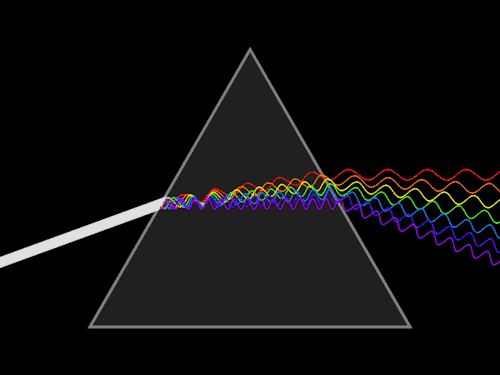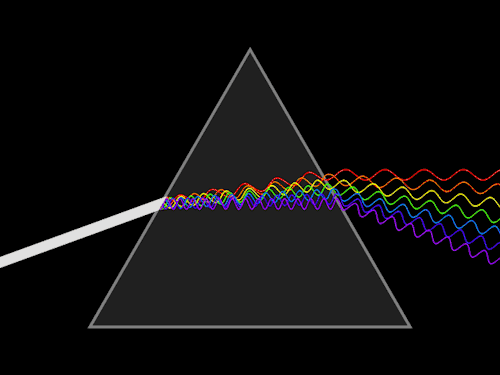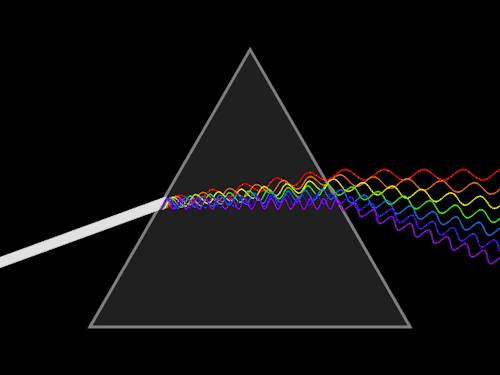
8. Determination of dispersive power of a prism using spectrometer.
9. Determination of Cauchy’s constant using spectrometer.
10. Determination of co-efficient of viscosity of a liquid by stokes method.
TEXT BOOKS
1. C.H. Bernard and C.D. Epp, John, Laboratory Experiments in College Physics
Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1995.
2. M.N. Srinivasan, A Textbook of Practical Physics, Sultan Chand & Sons, 1994.
REFERENCES
1. G. L. Squires, Practical Physics, 4th Edition, Cambridge University Press, 2001.
2. Geeta Sanon, B. Sc., Practical Physics, 1stEdition, S. Chand & Co, 2007.
3. Benenson, Walter, and Horst Stöcker, Handbook of Physics, Springer, 2002.
4. Chattopadhyay, Rakshit and Saha, An Advanced Course in Practical Physics, 8th
Edition, Books & Allied Ltd., 2007.
5. Indu Prakash and Ramakrishna, A Text Book of Practical Physics, 11th Edition, Kitab Mahal, 2011.
- S. MURUGESAN: Murugesan S
To study the thermal properties of materials by different methods.
To explain of the properties of macroscopic system.
Providing definitions of thermodynamic quantities and derivations of the laws of thermodynamics from the laws of quantum mechanics.

- Teacher: Murugesan S
