Search results: 1467
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on different types of power semiconductor devices and its switching characteristics.
To study the operation, characteristics and performance parameters of controlled rectifiers.
To understand the operations of choppers and inverters.
To get acquainted with the applications of power electronics converters.
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J

- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
On completion of the course, student will be able to
|
CO1 |
Acquire familiarity towards Evolution of Management, principles of F.W.Taylor’s & Henry Fayol, Organizational structures and basics of management including concepts of MBO & MBE |
|
CO2 |
Gain knowledge on the types of business organization, designing a layout for a plant, and the safety measure to overcome industrial accidents. |
|
CO3 |
Recognize the importance of studying individual and group behavior at workplace and its effect on performance in organization |
|
CO4 |
Develop expertise knowledge on the impact of Leadership Communication and Group dynamics in industry |
|
CO5 |
Learn the basics of ethical behavior and corporate social responsibility practiced in industries |
|
CO6 |
Solve cases business, to do a role play based on the knowledge gained from the subject and also apply the gained knowledge in industries in real life situations |

- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S

- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: SAGARIKA S.R
COURSE OBJECTIVE
• To expose of the important legal aspects and legislations practice and profession. To make students to understand the important laws and act relevant to architecture.
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ARCHITECTURAL PROFESSION 8 Hrs. Importance of Architectural Profession - Role of Architects in Society - Career options open for Architects-Prerequisites for Private Practice - Types of practices (Partnership/ Proprietary Concern /Associate - Architect’s office and its management - Location, Infrastructure requirement - organizational structure, Basic accounts - Legal requirements, Registration of Firm, Tax Liabilities, Relationship with clients, contractors, Associate consultants and product Manufacturers.
UNIT 2 CODE OF CONDUCT AND ETHICS 8 Hrs. Role of Professional Body (The Indian Institute of Architects) History, Objectives, its relevance - Architects Act 1972 (Background, intent, objectives)- Council of Architecture (role and function with regard to Architectural practice) - Registration of Architects - Importance of Ethics - guidelines prescribed for professional code of conduct -punitive action for professional misconduct.
UNIT 3 STATUTORY PROVISIONS GOVERNING ARCHITECTURAL PROVISIONS 8 Hrs. Important Acts and Regulations governing the design of buildings- (Town & Country Planning Act, Consumer Protection Act, Copy Right Act, Persons with Disabilities Act, Coastal Regulation Zone Act, Heritage Act, Land Acquisition Act, Factories Act, Cinema Act)-Master Plan Provisions and Development regulations with reference to CMDA -Planning norms and Building Rules-Role of Planning Authority and local body - Building Approval process.
UNIT 4 EMERGING TRENDS 6 Hrs.
Meaning of GATS - Globalisation and its impact on architectural profession - Entry of Foreign Architects and their
impact in Indian Architectural practice - Information Technology and its impact -specialisation in the field of architecture
-Green Buildings and the governing laws.
. Max. 30 Hours

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To learn the fundamental programming concepts and methodologies which are essential to building good C/C++ program.
To demonstrate a thorough understanding of modular programming by designing programs which require the use of programmer-defined functions.
To impart the knowledge about pointers which is the backbone of effective memory handling.
To perform Inheritance, Overloading of operators, functions,constructors and File Handling
To demonstrate adeptness of object oriented programming in developing solutions to problems demonstrating usage of data abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance.
- Teacher: ANU BARATHI
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi K
To develop programs in C using basic constructs.
For develop applications in C using strings, pointers, functions, structures.
To develop applications in C using file processing.
To make the student learn a programming language.
To learn problem solving techniques.
To teach the student to write programs in C and to solve the problems
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To develop programs in C using basic constructs.
- To develop applications in C using strings, pointers, functions, structures.
- To develop applications in C using file processing.
- To make the student learn a programming language.
- To learn problem solving techniques.
- To teach the student to write programs in C and to solve the problems.
- COURSE OUTCOMES
- On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Develop C programs for simple applications making use of basic constructs, arrays and strings.
- CO2 - Develop C programs involving functions, recursion, pointers, and structures.
- CO3 - Design applications using sequential and random access file processing.
- CO4 - Read, understand and trace the execution of programs written in C language.
- CO5 - Implement Programs with pointers and arrays, perform pointer arithmetic, and use the pre-Processor.
- CO6 - Write programs that perform operations using derived data types

APPLIED PSYCHOLOGY
PLACEMENT: I SEMESTER
THEORY: 3 Credits (60 Hours)
DESCRIPTION: This course is designed to enable the students to develop understanding about basic concepts of
psychology and its application in personal and community life, health, illness and nursing. It further provides students
opportunity to recognize the significance and application of soft skills and self-empowerment in the practice of nursing.
COMPETENCIES: On completion of the course, the students will be able to
1. Identify the importance of psychology in individual and professional life.
2. Develop understanding of the biological and psychological basis of human behaviour.
3. Identify the role of nurse in promoting mental health and dealing with altered personality.
4. Perform the role of nurses applicable to the psychology of different age groups.
5. Identify the cognitive and affective needs of clients.
6. Integrate the principles of motivation and emotion in performing the role of nurse in caring for emotionally sick client.
7. Demonstrate basic understanding of psychological assessment and nurse‘s role.
8. Apply the knowledge of soft skills in workplace and society.
9. Apply the knowledge of self-empowerment in workplace, society and personal life.
| Unit | Time (Hrs) | Learning Outcomes | Content | Teaching/ Learning Activities | Assessment Methods | |
| I | 2 (T) | Describe scope, branches and significance of psychology in nursing | Introduction Meaning of Psychology Development of psychology – Scope, branches and methods of psychology Relationship with other subjects Significance of psychology in nursing Applied psychology to solve everyday issues | Lecture cum Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| II | 4 (T) | Describe biology of human behaviour | Biological basis of behavior –Introduction Body mind relationship Genetics and behaviour Inheritance of behaviour Brain and behaviour. Psychology and sensation – sensory process – normal and abnormal | Lecture Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| III | 5 (T) | Describe mentally healthy person and defense mechanisms | Mental health and mental hygiene Concept of mental health and mental hygiene Characteristic of mentally healthy person Warning signs of poor mental health Promotive and preventive mental health strategies and services Defense mechanism and its implication Frustration and conflict – types of conflicts and measurements to overcome Role of nurse in reducing frustration and conflict and enhancing coping Dealing with ego | Lecture Case discussion Role play | Essay Short answer Objective type | |
| IV | 7 (T) | Describe psychology of people in different age groups and role of nurse | Developmental psychology Physical, psychosocial and cognitive development across life span – Prenatal through early childhood, middle to late childhood through adolescence, early and mid-adulthood, late adulthood, death and dying Role of nurse in supporting normal growth and development across the life span Psychological needs of various groups in health and sickness – Infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and older adult Introduction to child psychology and role of nurse in meeting the psychological needs of
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay Short answer |
| V | 4 (T) | Explain personality and role of nurse in identification and improvement in altered personality | Personality Meaning, definition of personality Classification of personality Measurement and evaluation of personality – Introduction Alteration in personality Role of nurse in identification of individual personality and improvement in altered personality | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VI | 16 (T) | Explain cognitive process and their applications | Cognitive process Attention – definition, types, determinants, duration, degree and alteration in attention Perception – Meaning of Perception, principles, factor affecting perception, Intelligence – Meaning of intelligence – Effect of heredity and environment in intelligence, classification, Introduction to measurement of intelligence tests – Mental deficiencies Learning – Definition of learning, types of learning, Factors influencing learning – Learning process, Habit formation Memory-meaning and nature of memory, factors influencing memory, methods to improve memory, forgetting Thinking – types, level, reasoning and problem solving. Aptitude – concept, types, individual differences and variability Psychometric assessment of cognitive processes – Introduction Alteration in cognitive processes | Lecture Discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VII | 6 (T) | Describe motivation, emotion, attitude and role of nurse in emotionally sick client | Motivation and emotional processes Motivation – meaning, concept, types, theories of motivation, motivation cycle, biological and special motives Emotions – Meaning of emotions, development of emotions, alteration of emotion, emotions in sickness – handling emotions in self and other Stress and adaptation – stress, stressor, cycle, effect, adaptation and coping
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type |
| VIII | 4 (T) | Explain psychological assessment and tests and role of nurse | Psychological assessment and tests – introduction Types, development, characteristics, principles, uses, interpretation Role of nurse in psychological assessment | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Short answer Assessment of practice |
| IX | 10 (T) | Explain concept of soft skill and its application in work place and society | Application of soft skill Concept of soft skill Types of soft skill – visual, aural and communication skill The way of communication Building relationship with client and society Interpersonal Relationships (IPR): Definition, Types, and Purposes, Interpersonal skills, Barriers, Strategies to overcome barriers Survival strategies – managing time, coping stress, resilience, work – life balance Applying soft skill to workplace and society – Presentation skills, social etiquette, telephone etiquette, motivational skills, teamwork etc. Use of soft skill in nursing | Lecture Group discussion Role play Refer/Complete Soft skills module | Essay and short answer |
| X | 2 (T) | Explain self empowerment | Self-empowerment Dimensions of self-empowerment Self-empowerment development Importance of women‘s empowerment in society Professional etiquette and personal grooming Role of nurse in empowering others | Lecture Discussion | Short answer Objective type |
- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Jayaprakash Venugopal
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable the student to understand the modern mechatronics components.
To present the underlying principles and alternatives for mechatronics systems design.
To provide the student with the opportunity for hands-on experience with the related components of the technology for diverse domains of application.
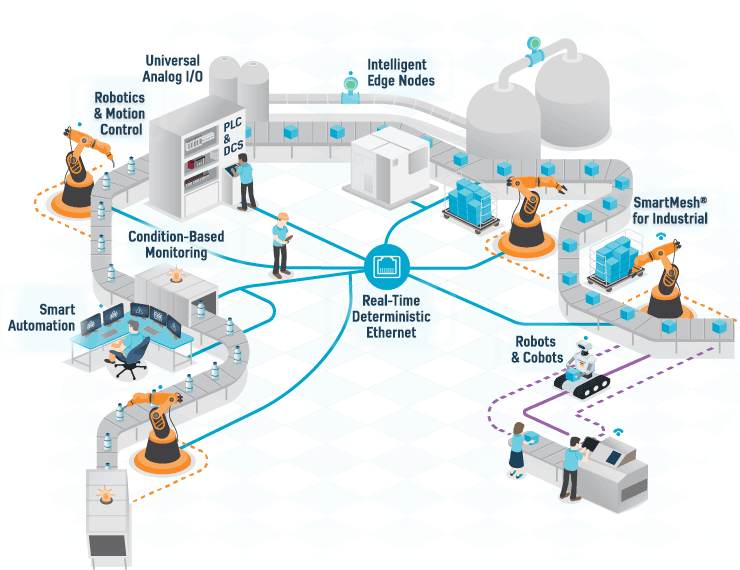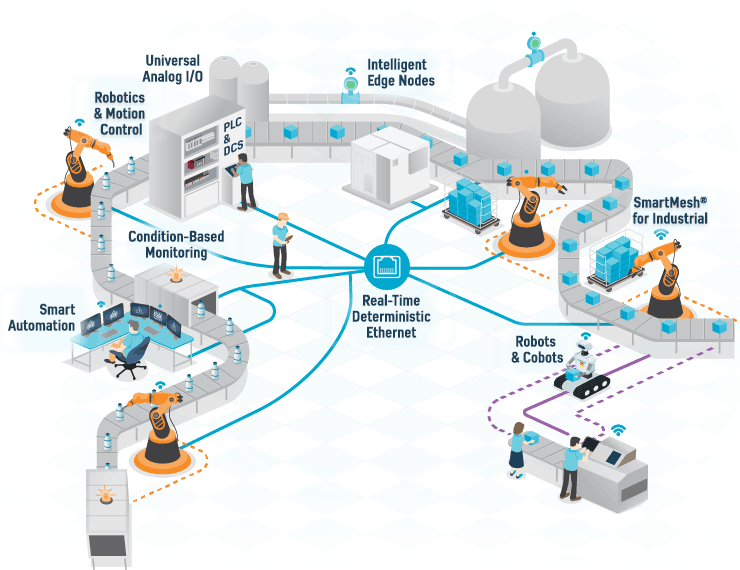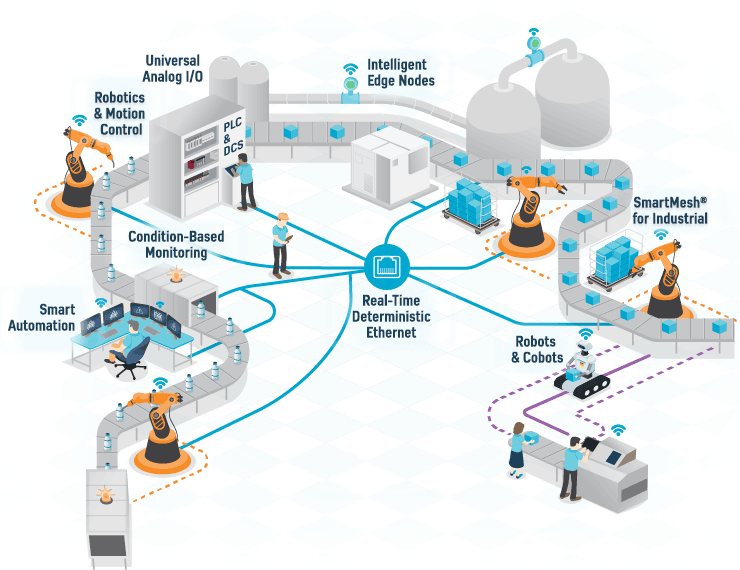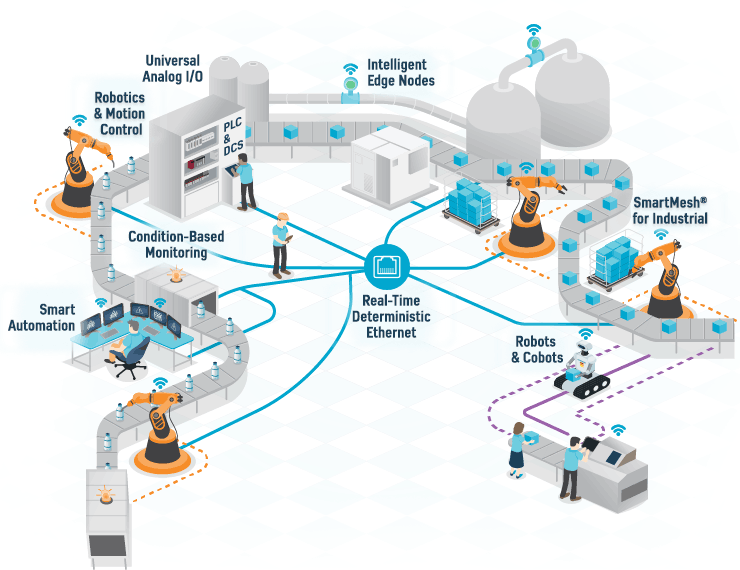
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquaint students with core knowledge in visual information processing and learning.
CO2 - Implement Digital Image Processing Mechanisms.
CO3 - Analyze and design Digital Image Generation Mechanisms.
CO4 - Representation of geometry and subdivision methods.
CO5 - Describe the Learning Methods in Vision.
CO6 - Comprehend the concepts related three dimensional object representations.
- Teacher: CHITRA P