Search results: 406
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to
1. Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human body.
2. Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
3. Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of the human body.
4. Perform the various experiments related to special senses and the nervous system.
5. Appreciate the coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system
- Teacher: Dr.Aishwarya Srinivasan
|
SPYA4201 |
Core Practical 1 Experimental Psychology 1 |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
00 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES: 30 Hours
· To facilitate psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
Students are expected to administer, score and interpret ten of the following category.
1. Stress Coping Techniques
2. Meta Cognition Inventory
3.Self Concept Rating Scale
4.PGI Memory Scale
5.Human Maze Learning
6.Span of attention (Tachistoscope)
7.Study habits inventory
8.Comprehensive interest schedules (Female & Male)
9.Bells Adjustment Inventory
10. Muller lyer Illusion
11. Creativity test
References
1. Woodworth, R.S. and Scholesberg (1972) Experimental psychology. Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
2. Anastasi. & Susana Urbina (2004) 7th Edition.Psychological Testing, Pearson Education Inc., New Delhi.
3. Cronbach, L.J. (). Essentials of Psychological Testing.
4. Parameswaran & Ravichandra (2003) Experimental Psychology. Neel Kamal Publications.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will understand psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
2. Students will evaluate major concepts and empirical findings in tests and measurements.
3. Students will analyse real examples of psychological tests for usefulness, applicability, strengths and weaknesses, and validity.
4. Students will apply methods for evaluating the quality of psychological tests to real examples of psychological tests.
5. Students will remember knowledge of testing methods to measurement in real world situations.
6. Students will create material that compares and contrasts perspectives on some controversial issue (e.g., intelligence testing) within the field of psychological testing.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
SPYA4201 | Core Practical 1 Experimental Psychology 1 | L | T | P | Credits | Total Marks |
00 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES: 30 Hours
· To facilitate psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
Students are expected to administer, score and interpret ten of the following category.
1. Stress Coping Techniques
2. Meta Cognition Inventory
3.Self Concept Rating Scale
4.PGI Memory Scale
5.Human Maze Learning
6.Span of attention (Tachistoscope)
7.Study habits inventory
8.Comprehensive interest schedules (Female & Male)
9.Bells Adjustment Inventory
10. Muller lyer Illusion
11. Creativity test
References
1. Woodworth, R.S. and Scholesberg (1972) Experimental psychology. Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
2. Anastasi. & Susana Urbina (2004) 7th Edition.Psychological Testing, Pearson Education Inc., New Delhi.
3. Cronbach, L.J. (). Essentials of Psychological Testing.
4. Parameswaran & Ravichandra (2003) Experimental Psychology. Neel Kamal Publications.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will understand psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
2. Students will evaluate major concepts and empirical findings in tests and measurements.
3. Students will analyse real examples of psychological tests for usefulness, applicability, strengths and weaknesses, and validity.
4. Students will apply methods for evaluating the quality of psychological tests to real examples of psychological tests.
5. Students will remember knowledge of testing methods to measurement in real world situations.
6. Students will create material that compares and contrasts perspectives on some controversial issue (e.g., intelligence testing) within the field of psychological testing.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce students to aspects of fashion marketing and retailing
- To impart knowledge about various product standards and product specifications and the process of product development towards market need.
UNIT I (9Hrs)
Market - Meaning, Definition and Classification; Fashion Market - Activities of Fashion Marketing, Fashion Market Size and Structure, Marketing Environment - Micro and Macro Marketing Environment.
UNIT II (9Hrs)
New product development - Planning, design and development – Product Classification, Product life cycle – Concept of Marketing Mix, Market Segmentation, Targeting and positioning - Perpetual mapping- Product Mix and Range planning. Marketing research process. Pricing - objectives and methods of setting prices.
UNIT III (9Hrs)
Distribution Channels - Types, Levels, development. Promotion Mix – Analytical tools- BCG matrix, GE model. Consumer Behavior - influencing factors – Consumer Buying process. Types of Buyers. Brand development- Branding and its importance in Marketing. Retailing and wholesaling – promotion methods.
UNIT IV (9Hrs)
Fashion Retailing - Classification of Retailers – Onsite Retailing and Off-site Retailing; Types of Retail Store; Merchandising mix- Order Management- Out Sourcing – Vendor Management – Export Documents. Role of a fashion buyer, Fabric sourcing, Garment sourcing, Local sourcing, National sourcing & International sourcing. Range Planning.
UNIT V (9Hrs)
Fashion sales promotional programme for fashion marketing, communication in prop motion, Personal selling, and point of purchase. Fashion Advertising and preparation of advertising for apparel market, Advertising media used in apparel market, Apparel & Textile Trade s

Fashion Marketing and Retailing
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce students to aspects of fashion marketing and retailing
- To impart knowledge about various product standards and product specifications and the process of product development towards market need.
UNIT I (9Hrs)
Market - Meaning, Definition and Classification; Fashion Market - Activities of Fashion Marketing, Fashion Market Size and Structure, Marketing Environment - Micro and Macro Marketing Environment.
UNIT II (9Hrs)
New product development - Planning, design and development – Product Classification, Product life cycle – Concept of Marketing Mix, Market Segmentation, Targeting and positioning - Perpetual mapping- Product Mix and Range planning. Marketing research process. Pricing - objectives and methods of setting prices.
UNIT III (9Hrs)
Distribution Channels - Types, Levels, development. Promotion Mix – Analytical tools- BCG matrix, GE model. Consumer Behavior - influencing factors – Consumer Buying process. Types of Buyers. Brand development- Branding and its importance in Marketing. Retailing and wholesaling – promotion methods.
UNIT IV (9Hrs)
Fashion Retailing - Classification of Retailers – Onsite Retailing and Off-site Retailing; Types of Retail Store; Merchandising mix- Order Management- Out Sourcing – Vendor Management – Export Documents. Role of a fashion buyer, Fabric sourcing, Garment sourcing, Local sourcing, National sourcing & International sourcing. Range Planning.
UNIT V (9Hrs)
Fashion sales promotional programme for fashion marketing, communication in prop motion, Personal selling, and point of purchase. Fashion Advertising and preparation of advertising for apparel market, Advertising media used in apparel market, Apparel & Textile Trade shows and fairs. Advertising department and advertising agencies – structure and functions. Advertising Budget
TEXT /REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Fashion Marketing- Mike Easey, Black Well Science Ltd., United Kingdom. 1995.
2. Apparel Merchandising, An Integrated Approach, Krishnakumar.M, Abishek Publications 2010.
3. Apparel Merchandising, Robin Mathew, Book Enclave Publishers, Jaipur (2008).
4. Retail Management, Chetan Bajaj, RajnishTuli and Nidhi.V.Srivastava, Oxford University Press, New Delhi 2005.
5. Advertising, C N Sonatakki, Kalyani Publishers New Delhi 1989.
6. Marketing, RSN Pillai and Bhagavathi.S, Chand And Company Ltd, New Delhi 1987.
7. Fashion retailing: A multi-channel approach Diamond, ENew Jersey: Pearson/Prentice Hall. 2006.
8. Inside the fashion business.Jarnow, J., Guereira, M. & Judelle, B. (4thEd.). MacMillan: New York, 1987.
9.. Fashion marketing, Ed. Hines, T. and Bruce, M. Buttersworth Heinemann,Oxford. 2001

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To impart knowledge about fashion Industry.
- To Understand fashion Basics and terminologies.
- To know the various international fashion centers Brands.
UNIT I
Introduction to fashion - definition and origin. Fashion terminologies – Classic, FAD, Style, Trend, prêt-à-porter, Mass Fashion, Street Fashion, Fashion forecasting, Boutique, Haute couture, line, Collection, Avantgarde, Custom made. Factors influencing fashion – Political and legal, Geographic, Demographic, technological, economic, social and cultural, factors, Life style changes etc.
UNIT II
Levels of fashion industry- Couture, Ready to wear, Mass production. Fashion Focus –The designers Role, The Manufacturers Role, The Retailers Role. Scope of Fashion Business – Primary Level, Secondary Level, Retail level and the Auxiliary level.
UNIT III
Types of designers – High fashion Designer, Stylist, and Freelance Designer. Sources of design inspiration. Biography of various Indian Fashion designers - Manish Malhotra, Ritu kumar, Ritu berri, Tarun Tahilani, Wendell Rodricks, Abu Jani and Sandeep Khosla, JJ Valaya, Manish Arora, and Rohit Bal. Study of international Designers - Coco Chanel, CK, Donatella Versace, Gucci, Giorgio Armani.
UNIT IV
Study of International Fashion centers – France, Italy, England, Germany, Canada, New York. Study of Fashion Brands –National Brand - International Brand - Designer Brand, Luxury fashion brand.
UNIT V
Theories of Fashion - Trickle up, Trickle-down and Trickle across. Fashion Cycle - Classic, FAD, Trend, Style. Fashion Seasons – International market and Indian market. The concepts of formal wear, casual wear, party wear, sportswear, jeanswear, swimwear, beachwear, and its functional aspects.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Gain knowledge on fashion terminologies.
CO2: Understand the levels of fashion Industry.
CO3: Obtain knowledge about the success of various fashion designers.
CO4: Gain knowledge on Fashion Capitals and Fashion Brands.
CO5 Understand the theories of fashion.

- Teacher: gayathri N
A more advanced technique of dental prosthesis which involves preparation of supporting teeth and elaborate/laborious laboratory procedures in fabricating a fixed denture with extensive knowledge in materials used, such as casting alloys, casting procedures, and investments, dental ceramics. This course deals with the biological, mechanical, and aesthetic details in fabricating a fixed partial denture for adults.

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To create a strong base on the various sensors and transducers in mechanical system, interdisciplinary
applications of Electronics, Electrical, Mechanical and Computer Systems for the Control of Mechanical and
Electronic Systems
To design control system for computer application like CNC.
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
To suggest synthetic route for simple organic
compounds with stereochemistry
To make the students understand and appreciate the concept
of stereochemistry and reaction mechanism
To know the nature of addition in pericyclic
reactions
To learn the alpha cleavage and gamma hydrogen
transfer reactions
To understand the photochemical organic reactions
and rearrangement reactions
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
SMEA1602 GAS DYNAMICS AND JET PROPULSION
(Use of approved gas tables is permitted)
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To discuss the concepts of compressible and Incompressible fluids.
To understand Mach number variation on area ratio.
To impart in depth knowledge on the flow characteristics through constant area duct.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPRESSIBLE FLUID FLOW 9 Hrs.
Concept of compressible flow, Energy and momentum equations, various regions of flow, fluid velocity, stagnation state, velocity of sound, critical states, Mach number, critical mach number, Crocco number, types of waves, mach cone, mach angle, effect of mach number on compressibility.
UNIT 2 FLOW THROUGH VARIABLE AREA DUCTS 9 Hrs.
Isentropic flow through variable area duct, T-S and h-s diagrams for nozzle and diffuser flows, area ratio as a function of Mach number, Mass flow rate through nozzles and diffusers, effect of friction in flow through nozzles.
UNIT 3 FANNO FLOW AND RAYLEIGH FLOW 9 Hrs.
Flow in constant area duct with friction - Fanno curves, and Fanno Flow equations, variation of flow properties, variation of Mach number with duct length. Flow in constant area duct with heat transfer, Rayleigh line and Rayleigh flow equations, variation of flow properties, maximum heat transfer.
UNIT 4 NORMAL SHOCK AND OBLIQUE SHOCKS 9 Hrs.
Governing equations, variation of flow parameters, static pressure, static temperature, density, stagnation pressure, entropy across normal shock and oblique shocks. Normal shocks - stationary and moving, applications. Prandtl Meyer equation, impossibility of shock in sub-sonic flows, flow in convergent and divergent nozzles with shock, Flows with oblique shock.
UNIT 5 JET AND SPACE PROPULSION 9 Hrs.
Aircraft propulsion, types and working of jet engines - energy transfer in jet engines, thrust, thrust power, propulsive and overall efficiencies, thrust augmentations in turbo jet engines, ram jet and pulse jet engines. Rocket propulsion, types of rocket engines, Liquid and solid fuel rocket engines, Introduction to Electrical and Nuclear rockets-Space Flights, Orbital and escape velocity.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Recall the fundamental concepts of compressible fluid flow.
CO2 - Demonstrate the significance of mach number on compressibility.
CO3 - Differentiate isothermal flow and isentropic flow.
CO4 - Apply the concept of normal shocks to different turbo machines.
CO5 - Estimate the heat transfer in flow through constant area ducts.
CO6 - Calculate the propulsive power in jet engines.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Yahya S.M., ”Fundamental of Compressible flow”, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2003.
2. Cohen H., Rogers R.E.C. and Sravanamutoo, “Gas Turbine Theory”, Addison Wesley Ltd., 2001.
3. Hill D. and Peterson C., “Mechanics & Thermodynamics of Propulsion “, Addison Wesley, 1992.
4. Ganesan V., “Gas Turbines”, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company, New Delhi, 1999.
5. Sutton G.P., “Rocket Propulsion Elements”, John Wiley, New York, 1975.
6. J.D. Anderson, "Modern compressible flow", McGraw Hill Education, 3rd Edition, 2002.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos). More specifically, it is devoted to the study of the structural, biochemical, and functional changes in cells, tissues, and organs that underlie disease. By the use of molecular, microbiologic, immunologic, and morphologic techniques, pathology attempts to explain the whys and wherefores of the signs and symptoms manifested by patients while providing a rational basis for clinical care and therapy. It thus serves as the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine, and is the scientific foundation for all of medicine
For II BDS
|
SPYA1401 |
Professional Core 5– Gerontology |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
Unit I INTRODUCTION (15 Hours)
Gerontology- Definition, concept, History, importance and scope, Old Age- Definition, meaning and concept, Demographics of Aging, Characteristics of old age. Myths and stereotypes about aging.
Unit II PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS OF ELDERLY (15 hours)
Changes and Developmental tasks of Old age- Cognitive, physical, psychological and social. Symptoms of mental illness in old age-Stress- Different forms of stressors in old age, Depression, Alzheimer’s and dementia, confusions due to multiple medications, loneliness, panic disorder, fear of death, anxiety. Reduced mental and cognitive ability, Insomnia, substance abuse, suicidal tendency, Falls.
Unit III POLICIES AND PROGRAMMES FOR AGED (15 hours)
Help Age International- Evolution, objectives, programmes, health and Nutrition, protection of elderly consumers, Housing and environment, Family, Social Welfare, income security and employment, education, recommendations for implementation. International Federation on Aging, WHO and old age.
Unit IV OLD AGE CARE (15 hours)
Crisis Intervention-medical (skilled care) versus non-medical (social care), Promoting independence in old age and improving mobility. Assessing and planning health care surgery, communicable diseases.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
Green technology is the application of the environmental science and technology for the development and application of products, equipment and systems to conserve the natural resources and environment, as well as to minimize or mitigate the negative impacts on the environment from human activities

- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
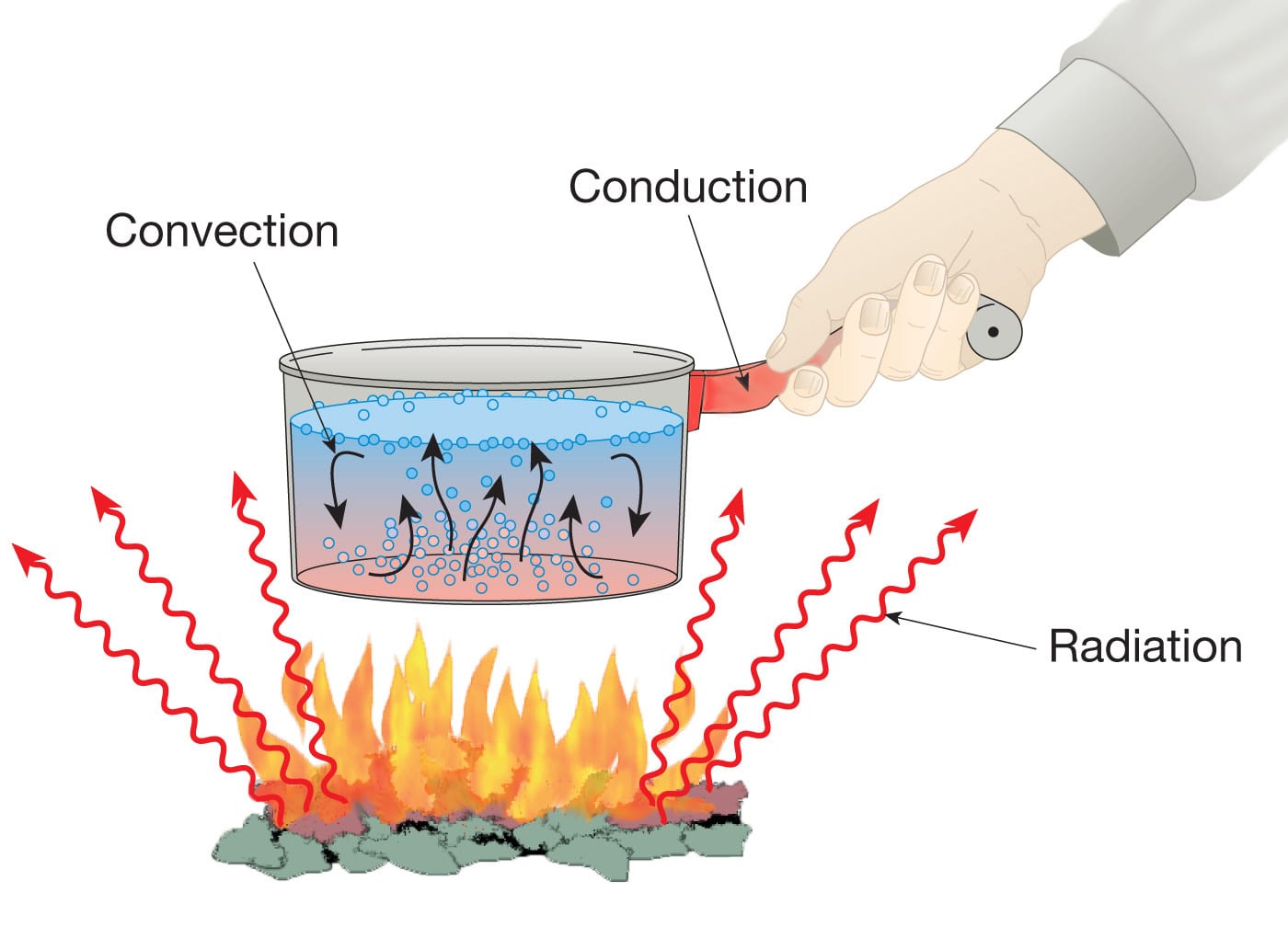
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH COMPOSITE WALL
2. MEASUREMENT OF SURFACE EMMISSIVITY
3. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH LAGGED PIPE
4. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH NATURAL CONVECTION
5. COUNTER FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER
6. PARALLEL FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER
7. THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF METAL ROD

To develop an insight into the architecture of prehistoric era and early civilizations
To impart perception about the social, religious and political character of various indigenous civilizations and how it influenced the built form and settlement
To emphasize the combined influence of geography, climate, religions, beliefs and culture in shaping the built environment
This course aims at introducing the students to the History of English during Literature and Great Writers in English.
It conveys the depth of thought, richness of emotion, and insight into the character. It leads intellectually and emotionally, and deepens our understanding of our history, society, and each of our lives.

- Teacher: Amutha Monica
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To explore the diverse factors that shaped the built forms during Neolithic, bronze and Iron Age.
- To understand the planning principles and the construction techniques adopted in the Early Iron Age.
- To understand the space development and structural quality in roman architecture.
COURSE OUTCOME:
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Outline the role of tangible and intangible factors that influenced the architecture during the Neolithic and bronze age.
CO2 Appraise the salient characteristics of Greek architecture.
CO3 Comprehend the other factors influencing architecture in India.
CO4 Analyze the contributing factors for the design development of different styles.
CO5 Compare and Contrast various styles on the basis of the contributing factors responsible for their development.
CO6 Discuss the influence of factors in determining the architectural character and features from Neolithic to late iron age.

- Teacher: Swetha N.M
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
- Teacher: Dr.Aishwarya Srinivasan