Search results: 406
TEXTILE PROCESSING
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To enable the students to learn the preparatory steps of Textile wet processing
- To impart knowledge on various dyeing techniques.
- To provide the details printing and textile finishing.
UNIT I
Introduction - Wet processing- Areas and importance Production sequence of textile fabrics- flowchart. Process of removing impurities from fabrics – Singeing, Desizing, Scouring, Bleaching, Mercerizing.
UNIT II
Dyeing - Classification of dyes -Stages of dyeing - Different methods - Fiber dyeing - Stock Dyeing - Top Dyeing Yarn Dyeing - Methods – Skein Dyeing, Package dyeing, Warp beam Dyeing.Fabric Dyeing - Open Width Dyeing, Rope form Dyeing.Garment Dyeing - Methods – Exhaust Process, Continuous process.Colorfastness- Special dyeing effects cross dyeing- Union -Dyeing - tone on tone- Imperfections in dyeing.
Textile printing – Introduction - Method of printing - Block, Stencil, Hand -Screen, automatic Screen – Rotary- Screen, Roller, Ink -jet and Heat transfer Printing. Styles of printing - Direct Printing, Discharge Printing Resist Printing. Blotch Printing, Warp Printing - Burn- out Printing – Duplex Printing - Engineered print.
UNIT-IV
Fabric Printing - Fabric printing through vegetable blocks- Fabric resist-dyeing techniques. Silk painting using wax- urea and rock salt resists- Tie & Dye- Batik. Handmade Flock printing- Quilting by Hand, Imperfection in Printing. Fabric performance testing - Fabric test- Surface friction test- Appearance test- Functional test- Colorfastness.
UNIT V
Textile finishing - Classification of finishes- Aesthetic finishes and Functional finishes - Wrinkle-free finishes, Water repellent, Soil release finish, Special purpose finish, Anti-bacterial finish, Silicon finish, Denim finish. Fabric Care Labeling - Environmental Issues.

- Teacher: Savithiri S
SKILL ENHANCEMENT COURSE – I
TRADITIONAL SURFACE ORNAMENTATION
COURSE OBJECTIVES:- To impart basic skills in hand embroidering techniques, surface designing, and other ornamentation techniques.
- To introduce the students to various traditional embroidery techniques of India.
- To create awareness of the heritage of traditional embroideries of Indian culture.
LIST OF EXERCISES:
- Hand embroidery – Outline stitches, Filling Stitches, Decorative Stitches.
- Embroidery of North India – Chamba Rumal of Himachal Pradesh, Kashidha of Kashmir, Phulkari of Punjab.
- Embroidery of Southern India - Kasuti of Karnataka.
- Embroidery of Central India - Chikankari of Uttar Pradesh.
- Embroidery of Eastern India- Kantha of West Bengal, Sujani of Bihar, Pipli appliqué of Orissa.
- Embroidery of Western India- Kutch of Gujarat, Mirror work of Rajasthan.
- Embroidery of Tribal India – Toda Embroidery of Tamilnadu .

SKILL ENHANCEMENT COURSE – I
TRADITIONAL SURFACE ORNAMENTATIONEmbroidery is an art of decorating cloth with needlework using different types of thread to create fascinating designs. Embroidery can also be defined as an art of using stitches as an adorning feature by embellishing fabric or other material with designs, stitches in strands of threads on yarn using a needle. Embroidery may also include other materials like pearls, beads, sequins, etc. Embroidery is a craft of enhancing fabric with motifs, abstract design, patterns. Embroidery varies according to its underlying foundation fabric and whether the design is stitched on the top or through the base fabric.
Indian embroidery includes a wide variety of regional embroidery styles varying by different regions and materials used. Embroidery is India’s persistent eloquent tradition. Every state and region in India enjoys its own style. Needlework is not the only means of decorating the fabric but the fabrics are also embellished by stories of the community, with motifs emerging from natural surroundings, religious inscriptions, economic state, etc.
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To impart basic skills in hand embroider techniques, surface designing and other ornamentation techniques.
· To introduce the students to various traditional embroidery techniques of India.
· To create awareness on heritage of traditional embroideries of Indian culture.
LIST OF EXERCISES:
1. Hand embroidery – Outline stitches, Filling Stitches, Decorative Stitches.
2. Embroidery of North India – Chamba Rumal of Himachal Pradesh, Kashidha of Kashmir, Phulkari of Punjab.
3. Embroidery of Southern India - Kasuti of Karnataka.
4. Embroidery of Central India - Chikankari of Uttar Pradesh.
5. Embroidery of Eastern India- Kantha of West Bengal, Sujani of Bihar, Pipli appliqué of Orissa.
6. Embroidery of Western India- Kutch of Gujarat, Mirror work of Rajasthan.
7. Embroidery of Tribal India – Toda Embroidery of Tamilnadu .
COURSE OUTCOMES
Handmade items are recaptured as new personification and the manifestation of luxury. Many ancient embroidery styles are being reclaimed and popularized. These embroidery styles are not only gaining its acceptance among the Indian designers but are also very popular with the International labels. Mumbai is a trade hub for many luxury brands chasing Indian embroidery.
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Identification of regional embroideries developed by various communities
CO2: Understand the origin of technique and design with reference to colours, motifs, layouts of different
embroidered textiles.
CO3: Appreciate the finer nuances of embroideries.
CO4: learn about the evolution of embroidered textiles over a period of time

- Teacher: Krithika S
Traffic Characteristics and Forecasting
Traffic Surveys
Traffic Regulatory Measures
Traffic Safety and Environment
Traffic Management

- Teacher: Dr.V.Sampathkumar .
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the concept of transmission lines types, various line parameters, waveguide types and resonators.
To Characterize and analyze the transmission line parameters and Acquire knowledge about the waveguides and resonators.
To analyze transmission lines for various frequencies and also smith-charts.

- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
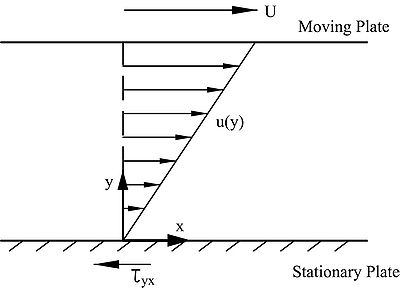
Momentum Transfer
Heat transfer
Mass transfer
Fluid flow processes
Analogy and flow measurement
- Teacher: Sathish S
