Search results: 1467
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To familiarize the student with the design and analysis of Rectifiers and power supplies.
Ø To understand different Transistor biasing circuits.
Ø To understand Small signal analysis of FET and MOSFET amplifiers.
Ø To understand working of feedback amplifiers, oscillators, tuned amplifiers and multivibrators
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand basic construction, equivalent circuits and characteristics of basic electronics devices.
CO2 - Understand basic linear electronics circuits and their working principle.
CO3 - Design and analyze DC Power supplies.
CO4 - Design and analyze multistage amplifiers.
CO5 - Design negative feedback amplifier circuits and oscillators.
CO6 - Analyze and design solid state power amplifier circuits.
- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To widen capability for analyzing the needs of analogue and digital communication systems
Ø To comprehend various analogue and digital modulation techniques for generation and detection.
Ø To acquire theoretical knowledge of each block in AM, FM transmitters and receivers
Ø To be familiar with sampling and quantization principles
Ø To understand the various band pass signaling schemes
Ø To know the fundamentals of spread spectrum modeling and speech coding.

- Teacher: Sharanya C
- Teacher: RAJESWARI D
- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Surender R
- Teacher: Dr.I.Rexiline Sheeba
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
|
Course Outcomes On completion of the course, the student will be able to CO1 - Analyze LTI Discrete Time Systems using DFT and FFT CO2 - Design of digital filters like FIR and IIR Filter CO3 - Evaluate the effect of finite word length while designing a digital filter CO4 - Employ signal processing strategies in multirate signal processing CO5 - Apply the signal processing technique in speech signal and image processing CO6 - Build filter design algorithm in DSP processor |
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To study the basics of Embedded System.
- To explain the various development tools in embedded System.
- To get a knowledge in embedded programming and acquire a knowledge in embedded system application

- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
COURSE OUTCOMES :
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Analyze the architecture and functional operations of 8051 microcontroller.
CO2 – Apply the 8051 microcontroller for addressing the Engineering problems.
CO3 - Analyze the architecture, functionalities of PIC 16F877A Microcontroller and apply for addressing the Engineering problems.
CO4 - Analyze the suitability of various interfacing bus devices for applications.
CO5 -.Analyze the operation of the real time operating system (RTOS) for embedded applications.
CO6 - Evaluate the concept of RTOS in real time embedded system.

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: V SIVAPRAKASH
- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
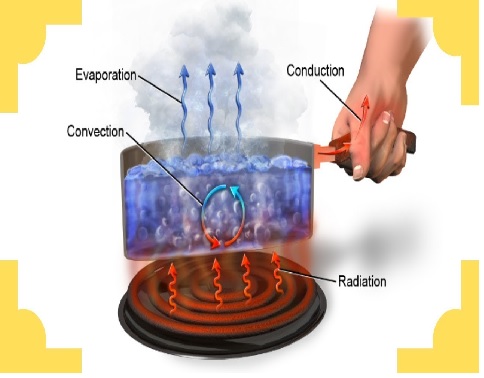
Heat Transfer course demonstrates the three modes of heat transfer through conduction, convection and radiation. Along conduction the heat flow through steady state and unsteady state systems were elaborated in detail through the access of one, two and three dimensional systems. Convection highlights the fluid flow under the influence of various flows accustomed with the applications of various flow equations. The radiation mechanisms were described through the application of various electromagnetic laws. Design of Heat transfer equipment such as heat ex-changers and evaporation units were also well discussed using the fundamental and derived equations governing heat transfer process.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Compare the amino acid sequence and structure of proteins relating this information to the function of proteinsCO2 - Analyze several techniques used for isolation and characterisation of proteins
CO3 - Appraise protein databases as a storehouse for the latest information in protein research
CO4 - Analyse the protein sequence for their structural properties
CO5 - Apply appropriate tools to predict the structure of proteins
CO6 - Appraise enzymes and different protein design strategies used to design completely new proteins tailored to specific tasks
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Compare the amino acid sequence and structure of proteins relating this information to the function of proteinsCO2 - Analyze several techniques used for isolation and characterisation of proteins
CO3 - Appraise protein databases as a storehouse for the latest information in protein research
CO4 - Analyse the protein sequence for their structural properties
CO5 - Apply appropriate tools to predict the structure of proteins
CO6 - Appraise enzymes and different protein design strategies used to design completely new proteins tailored to specific tasks
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Gracelydiaphoebe M
- Teacher: Muthulakshmi A
S614BLH38 - CYBER FORENSICS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To learn about the Cyber Crime and to Understand the concepts of open source tools
To learn about Cyber Forensics and to identify and report the forensic on disk level
To learn about Cyber Investigation and to Implement forensic concepts in network level
To learn about Evidence Management and to Analyze Virtual machine forensic
To learn about Cyber Laws and Authorities and Analyze various cloud forensic

- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: Jemmy Christy H
- Teacher: Theboral J
To give students a broad and challenging experience that will formulate their thought process by in-depth investigation, analysis and critical review of relevant materials.
To enable their understanding, cognitive and communicative skills, critic the existing practices in Sustainable Architecture based on the current practices, new trends and technologies.
To provide students an opportunity to cultivate specialization in the areas of their own interest and undertake academic research or develop specific sustainable design independently
Dissertation work includes processes such as: Research area identification; hypothesis of research topic; literature sourcing and search; aim and objective definition; formulation of methodology; field study planning; survey data collection, analysis and result presentation; literature study; conceptual an empirical :compilation and inference drawing; research study validation through case studies, field application and simulation models; discussion of research findings; study conclusion and recommendation formulations.

- Teacher: Catherine S
To identify an area of research and design interest related to sustainable architecture and develop a thesis synopsis
To facilitate the independent research skills of students
To acquire a fresh approach in formulating an effective methodology that will help in the flow of the research
The intent of pre thesis is to initiate the selection of thesis topic in the beginning of the third semester itself. The students shall work three alternative topics by studying and analyzing the published research papers of their interest area and give justification for the selection of the topics which will be assigned to him / her to proceed to the next phase.
The subject for special study shall be conceptual or practical but pertaining to sustainable building and environment design practices.

- Teacher: Catherine S
- Teacher: Kavitha S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To channelize the knowledge constructed on ‘sustainable principles in architecture’ and successful integration in the identified typology
The project provides students an opportunity for academic research to cultivate specialization in the areas of their own interest under the overall guidance of the faculty.
The objective of the seminar work is to train the students to prepare state of art report by assimilation of concepts / ideas on a chosen topic in the area of Sustainable Architecture.

- Teacher: Kavitha S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To undergo professional training in a firm to get experience of handling various environmental design practice, Sustainable developments and learn latest software trending in the market.
To utilize the forum to discuss key issues in the projects, keep track of the different sustainable approaches, communicate with the stakeholders and get an overall view of the contract administration.
The final project report will comprise of an in-depth research and analysis of activities in the form of drawings & relevant details, schematic charts & reports, photographs, documentation of the project, comments, suggestions, etc to appraise the efficiency in progress of work.

