Search results: 360
- Teacher: Sankarakrishnan S
- Teacher: M V SRIKANTH
- Teacher: Pavani Bellamkonda
MICROWAVE NETWORKS AND COMPONENTS
POWER DIVIDERS AND COUPLERS
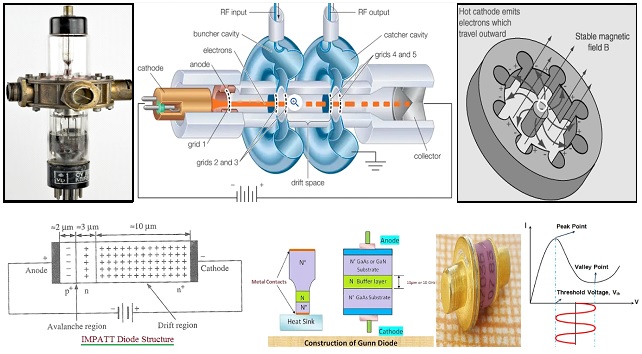
MICROWAVE SOURCES
MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS
MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETER WAVE SYSTEMS
- Teacher: JEGAN G
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To give the opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
- While upholding the standards of both national and international benchmarking in fashion design each student is required to design an individual collection reflecting originality creative flair with in-depth conceptualization and implementation of the design process combined with impeccable technical strength and quality.
- The focus is on global design with an Indian flavor that is an ideal blend of creativity with function and marketability.
- The Fashion Design Project will have to be carried out by each student in the eighth semester. The project will give ample opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
The guidelines for reference to develop design collection:
- The Fabric: Development and exploration of traditional resources (materials and techniques) towards contemporary expressions.
- The Image: Kaleidoscopic images encapsulated in time or space (History) to more globalized aspirations.
- The Attitude: From rejuvenation to revivalism- from transformation to transmutation- from the concrete to the sublime.
- The students may choose to specialize in any of the areas focusing on either women’s wear- menswear or children's clothing. Textiles may be combined with knits leather or any other suitable material while ensuring that the focus is on the extensive and prime usage of woven fabric.
The collection could fall in any one of the categories:
- . Sportswear
- Eveningwear
- Ethnic collection or Fusion
- Kids Wear
- Avant-Garde
- Theatre costume
- Institutional clothing or
- Any other category approved by the mentor

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
- Teacher: Anderson A
- Teacher: Vijayan M
Please upload your completed, verified, signed M. Tech Dissertation. Strictly adhere to the guidelines given for submission of the project report, No deviation is permitted.
End date: 05 May 2022
- Teacher: Premkumar J
UNIT 1 PREREQUSITES TO EVALUATE AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Properties of earth’s atmosphere and standard atmosphere, Forces and moments acting on a flight vehicle - Equation of motion of a rigid flight vehicle- Different types of drag – estimation of parasite drag co-efficient by proper area method- Drag polar of vehicles from low speed to high speeds.
UNIT 2 ENGINE CHARACTERISTICS 9 Hrs. Variation of thrust, power with velocity and altitudes for air breathing engines – specific fuel consumption of piston engine and jet engine – ideal efficiency of engines- power plants for flight vehicles – limitations of power plants with Mach number and altitude.
UNIT 3 EVALUATION OF UN - ACCELERATED FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Airplane performance in steady level flight - Power available and power required curves. Maximum speed in level flight - Conditions for minimum drag and power required - steady climb descent and glide performance. Climb and Glide Hodograph, Range and Endurance. .
UNIT 4 ACCELERATED AND MANOEUVERING FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Accelerated level flight - Climbing and gliding flight, Maximum rate of climb and steepest angle of climb, minimum rate of sink and shallowest angle of glide –Take off – Landing-Turning performance. Bank angle and load factor – limitations on turn - V-n diagram.
UNIT 5 FLIGHT TESTING METHODS TO EVALUATE PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Flight - testing: Altitude definitions, Speed definitions, Air speed, altitude and temperature measurements. Errors and calibration. Measurement of engine power, charts and corrections. Flight determination of drag polar. Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the need for ISA.
CO2 - Analyze the flight performance with variations of pressure and density with altitude.
CO3 - Estimation of total drag and drag polar that influence the performance.
CO4 - Analyze the performance in un-accelerated flight conditions.
CO5 - Determination of speed limit, load limit, landing and takeoff distances of the aircraft.
CO6 - Know different testing methods to evaluate aircraft performanc

- Teacher: KEVIN BENNETT S
- Teacher: Dr. ANAND T
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
Course Objectives:
• To be able to fix, process, embed tissues and make sections for micro section studies
• To be competent to make routine cytological preparation
UNITI Introduction to Histopathology and Cytopathology Techniques – Basic concepts and principles. Applications
UNITII Reception of specimens– Criteria, Requisites, Container, Identity, Labeling, Rejection
UNITIII Tissue processing- Micro techniques I
Basic steps, Fixing – Types of fixatives, Factors, Dehydration, Embedding
UNIT IV Micro techniques II
Microtomy, Staining, Mounting, Methods of decalcifications
UNIT V Equipment
Microscope, Microtome -Types, Uses, Parts, different types of microtome knives, care and maintenance, Automated tissue
processor- components, working and precautions during use, Tissue floating bath
UNIT VI Staining
Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, preparation of hematoxylin and eosin stains, Reticulin stain, PAP staining- components and
methods.
UNIT VII Cytology
Introduction to FNAC and Exfoliative cytology, Processing of fluids- Sputum, bronchial aspirates, bronchial washings, gastric
washings, Urine and other watery fluids, Cerebrospinal fluid
UNITVIII Museum techniques
The mounting of pathological specimens - Introduction., Preparation of specimen, Fixation of specimen- Kaiserling solution-1 and Kaiserlingsolution-2, Precaution taken for the Fixation of Specimens, Storage of Specimens, Mounting of Museum Specimens, Filling and Scaling
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Identify the basic structure of cells, tissues and organs and describe their contribution to normal function.
CO2 Interpret light- and electron-microscopic histologic images and identify the tissue source and structures.
CO3 Demonstrate common histology procedures such as embedding tissue in paraffin, tissue sectioning and
mounting, or routine staining of tissue sections
CO4 Describe common histology laboratory procedures used to prepare stained slides from tissue samples.
CO5 Outline the principles of histochemistry, and types of microscopies utilized in histology
CO6 Understand professional procedures in museum display, collections, care and preservation
Reference books
1. Bancroft's Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques by John D Bancraft /Edition 8 (2018)
2. Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Techniques: Including Museum Techniques / edition 3 (1974) by C. F. A. Culling
3. Hand book of Medical laboratory technology, 2nd edition by Robert H Carman, Christian Medical Association of India
(publishers)
4. Textbook of Medical Laboratory Technology/ edition 3 (2020) b
- Teacher: Premkumar J