Search results: 1467
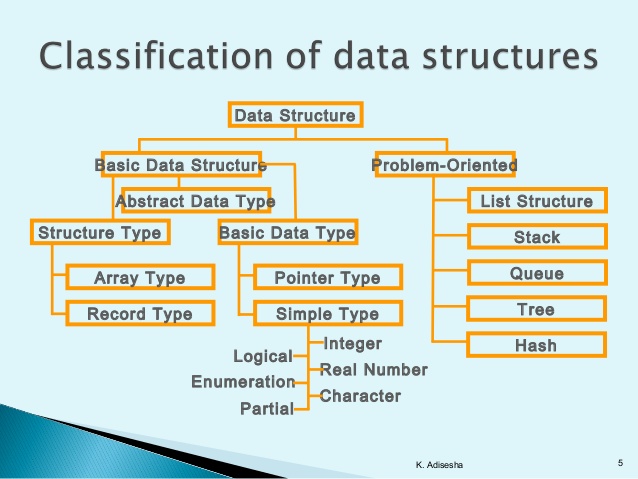
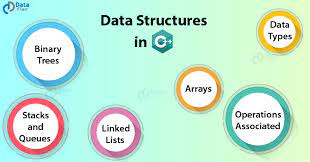
Data Structures in C are used to store data in an organised and efficient manner. The C Programming language has many data structures like an array, stack, queue, linked list, tree, etc. A programmer selects an appropriate data structure and uses it according to their convenience.
Data Structure in C Programming Language is a specialized format for organizing and storing data. In General data structure types include the file, array, record, table, tree.. etc.
- Array: Array is collection of similar data type, you can insert and deleted element form array without follow any order.
- Stack: Stack work on the basis of Last-In-First-Out (LIFO). Last entered element removed first.
- Queue: Queue work on the basis of First-In-First-Out (FIFO). First entered element removed first.
- Linked List: Linked list is the collection of node, Here you can insert and delete data in any order.
- Tree: Stores data in a non linear form with one root node and sub nodes.
- Teacher: Nirmalrani V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Software process models and compare their applicability.
- Identify the key activities in managing a software project.
- Concepts of requirements engineering and Analysis Modelling.
- Apply systematic procedure for software design and deployment.
- Compare and contrast the various testing and maintenance.
- Teacher: Pravin A
- Teacher: Ronald Tony A
- Teacher: Yovan Felix A
- Teacher: hemalatha c
- Teacher: Deepa D
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: Albert Mayan J
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Kamalesh Murari Devakannan
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: Aroul Canessane R
- Teacher: Shalini R
- Teacher: Vignesh R
COURSE OBEJCTIVES
• To understand the technologies behind the embedded computing systems
• To acquire knowledge about microcontrollers embedded processors and their applications
• To analyze and develop software programs for embedded systems
• To have knowledge about the working of a microcontroller system and its programming in assembly language
• To provide experience to integrate hardware and software for microcontroller application systems

- Teacher: Sathya K B
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
· To understand the concepts of Internet of Things
· To identify the various elements of an IoT System.
· To understand the various means of communication from Node / Gateway to Cloud Platforms.
· To transfer data from IoT devices to various cloud providers.
· To make students aware of various domain specific applications and challenges while implementing IoT solutions.
- Teacher: Menaka D
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand the fundamentals of Object Oriented System Development.
➢ To understand the object oriented methodologies.
➢ To use UML in requirements elicitation and designing.
➢ To understand concepts of relationships and aggregations.
➢ To test the software against its requirements specification.
- Teacher: Pravin A
- Teacher: SATHIYARAJ A
- Teacher: Yovan Felix A
- Teacher: Ruby Angel
- Teacher: Deepa D
- Teacher: NANCY KIRUPANITHI D
- Teacher: SUBATHRA G
- Teacher: Albert Mayan J
- Teacher: Refonaa J
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: Lakshmanan L
- Teacher: DHARANI M.K.
- Teacher: Kamalesh Murari Devakannan
- Teacher: USHA N S
- Teacher: Abirami R
- Teacher: Aroul Canessane R
- Teacher: Vignesh R
- Teacher: Gomathi R M
- Teacher: Gayathri S
- Teacher: Gowri S
- Teacher: HEMALATHA S
- Teacher: Srinivasulu Senduru
- Teacher: Anandhi T
SCSA1503 - COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce two and three dimensional graphical structure.
- To design 2D and 3D methods and Models.
- To explore the visible surface detection with illumination and color models.
- To understand the concepts involved in multimedia and basis tools.
- To gain knowledge on Multimedia compression and animations.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1 : Identify the various line and circle drawing algorithm.
CO2 : Study the various transformations in 2D and 3D objects.
CO3 : Understand the concepts of curves and surface.
CO4 : Apply transformation and clipping algorithm in 2D and 3D objects.
CO5 : Design Illumination and color models.
CO6 : Implement 2D and 3D Transformation concepts in Real world Applications
SYLLABUS
UNIT 1 BASICS OF COMPUTER GRAPHICS 9 Hrs.
Output primitives- Survey of Computer Graphics- Overview of Graphics System- Line drawing Algorithm (DDA Line Drawing Algorithm, Bresenhams Line Drawing Algorithm)-Circle drawing Algorithm- Curve Drawing Algorithm- Attributes of output Primitives- Antialiasing.
UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 8 Hrs.
2D Transformation and other transformation – 2D and 3D Viewing- Line Clipping(Cohen Sutherland)– Polygon Clipping (Sutherland Hodgeman) – Logical Classification Input Function.
UNIT 3 3D CONCEPTS AND CURVES 10 Hrs.
3D Object: Representation Method- B-Rep- Sweep Representation- 3D Transformation – curve generation – Splines – Beziers – Blending of curves other interpolation techniques- Display Durves and Surface – Shape Description Requirements – Parametric function – 3D Concept Introduction – Fractals and Self Similarity – Successive refinement of Curves – Koch Curves and Paeno Curves
UNIT 4 METHODS AND MODELS 8 Hrs.
Visual Surface detection methods – Illumination models – Halftone Patterns – Dithering Techniques – Polygon Rendering Methods – Ray Tracing Methods – Color methods – Color Applications.
UNIT 5 MULTIMEDIA BASICS AND TOOLS 10 Hrs.
Multimedia Basics and Tools – Introduction to Multimedia – Compression and Decompression – Data and File Format Standards – Digital voice and audio video image animation- Introduction to photoshop- workshop tools- Navigating window – Importing and Exporting Images – Operations on Images – resize, Crop, rotate. Introduction to Flash – Elements of Flash Documents – Flash Environment- Drawing Tools – Flash Animation Importing and Exporting – Adding Sounds – Publishing Flash Movies.
Max. 45 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics C Version, 2 nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006.
2. Fabio Ganovelli, Massimiliano Corsini, Sumanta Pattanaik, Marco Di Benedetto “Introduction to Computer Graphics: A Practical Learning Approach” Taylor and Frainces Group. 2015.
3. Tay Vaughan ,”Multimedia”, 5th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2001.
4. Ze-Nian Li, Mark S. Drew ,”Fundamentals of Multimedia”, Prentice Hall of India, 2004.
5. D.P. Mukherjee , “Fundamentals Of Computer Graphics And Multimedia ” Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, 2006.
6. D. McClelland, L.U.Fuller, ”Photoshop CS2 Bible”, Wiley Publishing, 2005
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: SundaraVelarani K
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: DEVIPRIYA M
- Teacher: SANTHIYA P
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: AMSHAVALLI R S
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: sageengrana s
- Teacher: NITHYA SEKAR
- Teacher: Anandhi T
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Describe and discuss constraints unique to wearable and ubiquitous computing platforms and applications
Design, develop and evaluate a wearable computing application, Apply state-of-the-art hardware and software development tools to computer system design
Communicate both orally and in writing with other members of a team.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 :Understand advanced and emerging technologies
CO2 :Extend the knowledge achieved and apply it to solve real world problems
CO3 :Understanding of different methodologies for research on wearable technology
CO4 : Ability to analyse ethical issues related to the Wearable devices
CO5 : To contribute innovative thinking and innovation processes
CO6 : Ability to integrate several domain through wearable technology
- Teacher: Viji Amutha Mary A
CO1:Address the challenges in Conventional System and to deal with missing and incomplete data.
CO2: Understand the various phases of Data Analytic Lifecycle and its influence over Business Models.
CO3: Analyse distinct techniques for Classification and Clustering.
CO4: Apply the principles of Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic towards advanced data analytics.
CO5: Synthesize knowledge to address Streaming Data Models and Computing.
CO6: Design and Build Real Time Applications with Streaming Data Model

- Teacher: Sethuraman .
- Teacher: GEETHANJALI D
- Teacher: Saravanan M
CO1 : Comprehend machine learning solutions to classification, regression and clustering problems
CO2 : Understand the strengths and weaknesses of many popular machine learning approaches.
CO3 : Interpret the results of the algorithms.
CO4 : Select suitable model parameters for different machine learning techniques.
CO5 : Design algorithms for real world problems using machine learning algorithm.
CO6 : Gain experience of doing independent study and research.

- Teacher: Dr. Santha Sheela A C
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Mary Gladence L
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: Mercy Paul Selvan Paul selvan
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI PRIYA S
- Teacher: Revathy S
- The Objectives of this course is to explore the principles, algorithms, and data structures involved in the design and construction of compilers. Compiler Design will teach students the fundamental concepts and techniques used for building a simple compiler.
- The course will introduce the theory and tools that can be employed in order to perform syntax-directed translation of a high-level programming language into an executable code.
- This course includes context-free grammars, lexical analysis, parsing techniques, symbol tables, error recovery, code generation, and code optimization.
- At the end of the course, students will understand different considerations and phases of compilation, the impact of language attributes upon the compilation process, the effect of hardware feature on the generated code and the practical fundamentals of compiler implementation.

- Teacher: Mary Posonia A
- Teacher: Ankayarkanni B
- Teacher: Usha Nandini D
- Teacher: Gopika G S
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Selvi M
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Yogitha R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ Identify the problem.
➢ To analyse the various steps in program development.
➢ Evaluate and select the best algorithm to solve the problem.
➢ Deploy suitable methods to get the desired output.
➢ Create the solutions for various Real-World Problems

- Teacher: Geetha C
- Teacher: NAFEES MUNEERA M
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Vaishnnave M P
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: Anandhi T
- Teacher: GOWRI MANOHARI V
- Teacher: Nirmalrani V
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: Jabez J
- Teacher: Vaishnnave M P
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the concepts of Procedure Oriented Programming.
To handle conditional and Looping Statements in different scenarios.
To learn and employ concepts of ADTs.
To apply Linear Data Structures – lists, stacks, and queues in real time applications.
To apply concepts of Non Linear Data structures namely Trees and Graphs.
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: SAROJINI PREMALATHA J
- Teacher: Dr.Sridevi N

- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: VANATHI M


