Search results: 406
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Learn the organization of a digital computer.
- Be exposed to the number systems.
- Learn to think logically and write pseudo code or draw flow charts for problems.
- Be exposed to the syntax of C.
- Be familiar with programming in C.
- Learn to use arrays, strings, functions, pointers, structures and unions in C.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Design C Programs for problems.
CO2 - Write and execute C programs for simple applications.
CO3 - Develop programs using the basic elements like control statements, Arrays and Strings.
CO4 - Solve the memory access problems by using pointers.
CO5 - Understand about the dynamic memory allocation using pointers which is essential for utilizing memory.
CO6 - Understand the uses of pre-processors and various header file directives.
APPLIED PSYCHOLOGY
PLACEMENT: I SEMESTER
THEORY: 3 Credits (60 Hours)
DESCRIPTION: This course is designed to enable the students to develop understanding about basic concepts of
psychology and its application in personal and community life, health, illness and nursing. It further provides students
opportunity to recognize the significance and application of soft skills and self-empowerment in the practice of nursing.
COMPETENCIES: On completion of the course, the students will be able to
1. Identify the importance of psychology in individual and professional life.
2. Develop understanding of the biological and psychological basis of human behaviour.
3. Identify the role of nurse in promoting mental health and dealing with altered personality.
4. Perform the role of nurses applicable to the psychology of different age groups.
5. Identify the cognitive and affective needs of clients.
6. Integrate the principles of motivation and emotion in performing the role of nurse in caring for emotionally sick client.
7. Demonstrate basic understanding of psychological assessment and nurse‘s role.
8. Apply the knowledge of soft skills in workplace and society.
9. Apply the knowledge of self-empowerment in workplace, society and personal life.
| Unit | Time (Hrs) | Learning Outcomes | Content | Teaching/ Learning Activities | Assessment Methods | |
| I | 2 (T) | Describe scope, branches and significance of psychology in nursing | Introduction Meaning of Psychology Development of psychology – Scope, branches and methods of psychology Relationship with other subjects Significance of psychology in nursing Applied psychology to solve everyday issues | Lecture cum Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| II | 4 (T) | Describe biology of human behaviour | Biological basis of behavior –Introduction Body mind relationship Genetics and behaviour Inheritance of behaviour Brain and behaviour. Psychology and sensation – sensory process – normal and abnormal | Lecture Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| III | 5 (T) | Describe mentally healthy person and defense mechanisms | Mental health and mental hygiene Concept of mental health and mental hygiene Characteristic of mentally healthy person Warning signs of poor mental health Promotive and preventive mental health strategies and services Defense mechanism and its implication Frustration and conflict – types of conflicts and measurements to overcome Role of nurse in reducing frustration and conflict and enhancing coping Dealing with ego | Lecture Case discussion Role play | Essay Short answer Objective type | |
| IV | 7 (T) | Describe psychology of people in different age groups and role of nurse | Developmental psychology Physical, psychosocial and cognitive development across life span – Prenatal through early childhood, middle to late childhood through adolescence, early and mid-adulthood, late adulthood, death and dying Role of nurse in supporting normal growth and development across the life span Psychological needs of various groups in health and sickness – Infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and older adult Introduction to child psychology and role of nurse in meeting the psychological needs of
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay Short answer |
| V | 4 (T) | Explain personality and role of nurse in identification and improvement in altered personality | Personality Meaning, definition of personality Classification of personality Measurement and evaluation of personality – Introduction Alteration in personality Role of nurse in identification of individual personality and improvement in altered personality | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VI | 16 (T) | Explain cognitive process and their applications | Cognitive process Attention – definition, types, determinants, duration, degree and alteration in attention Perception – Meaning of Perception, principles, factor affecting perception, Intelligence – Meaning of intelligence – Effect of heredity and environment in intelligence, classification, Introduction to measurement of intelligence tests – Mental deficiencies Learning – Definition of learning, types of learning, Factors influencing learning – Learning process, Habit formation Memory-meaning and nature of memory, factors influencing memory, methods to improve memory, forgetting Thinking – types, level, reasoning and problem solving. Aptitude – concept, types, individual differences and variability Psychometric assessment of cognitive processes – Introduction Alteration in cognitive processes | Lecture Discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VII | 6 (T) | Describe motivation, emotion, attitude and role of nurse in emotionally sick client | Motivation and emotional processes Motivation – meaning, concept, types, theories of motivation, motivation cycle, biological and special motives Emotions – Meaning of emotions, development of emotions, alteration of emotion, emotions in sickness – handling emotions in self and other Stress and adaptation – stress, stressor, cycle, effect, adaptation and coping
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type |
| VIII | 4 (T) | Explain psychological assessment and tests and role of nurse | Psychological assessment and tests – introduction Types, development, characteristics, principles, uses, interpretation Role of nurse in psychological assessment | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Short answer Assessment of practice |
| IX | 10 (T) | Explain concept of soft skill and its application in work place and society | Application of soft skill Concept of soft skill Types of soft skill – visual, aural and communication skill The way of communication Building relationship with client and society Interpersonal Relationships (IPR): Definition, Types, and Purposes, Interpersonal skills, Barriers, Strategies to overcome barriers Survival strategies – managing time, coping stress, resilience, work – life balance Applying soft skill to workplace and society – Presentation skills, social etiquette, telephone etiquette, motivational skills, teamwork etc. Use of soft skill in nursing | Lecture Group discussion Role play Refer/Complete Soft skills module | Essay and short answer |
| X | 2 (T) | Explain self empowerment | Self-empowerment Dimensions of self-empowerment Self-empowerment development Importance of women‘s empowerment in society Professional etiquette and personal grooming Role of nurse in empowering others | Lecture Discussion | Short answer Objective type |
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable the student to understand the modern mechatronics components.
To present the underlying principles and alternatives for mechatronics systems design.
To provide the student with the opportunity for hands-on experience with the related components of the technology for diverse domains of application.
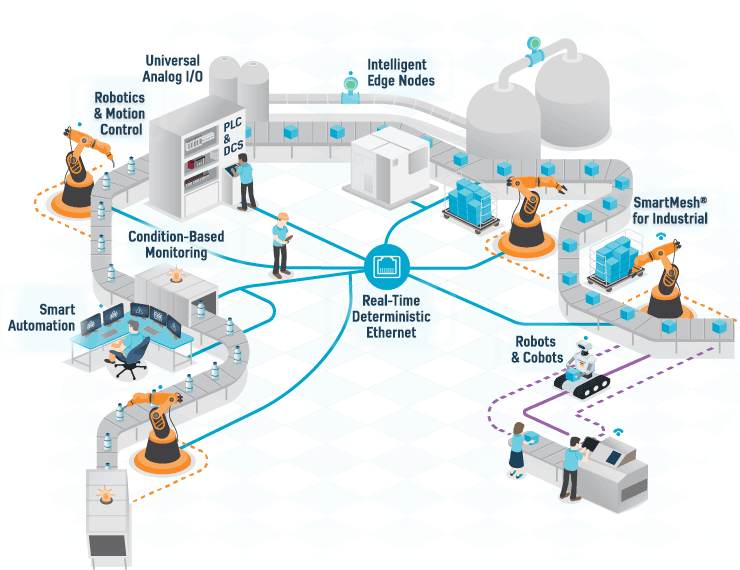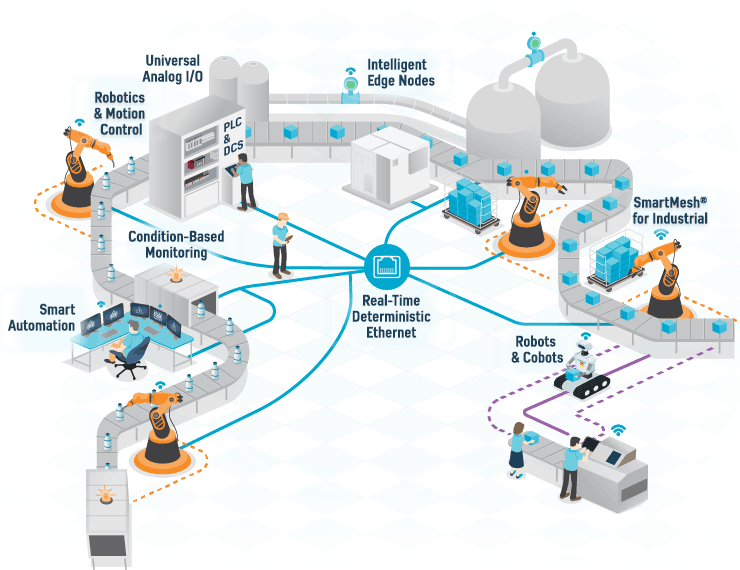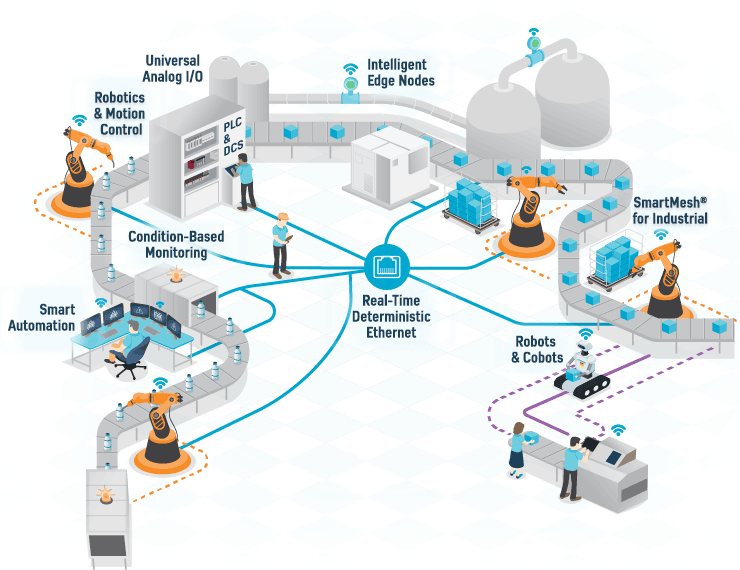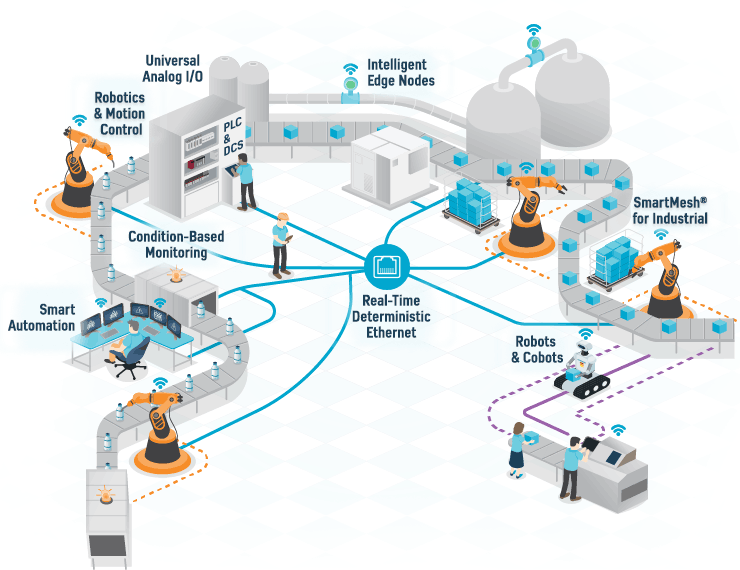
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquaint students with core knowledge in visual information processing and learning.
CO2 - Implement Digital Image Processing Mechanisms.
CO3 - Analyze and design Digital Image Generation Mechanisms.
CO4 - Representation of geometry and subdivision methods.
CO5 - Describe the Learning Methods in Vision.
CO6 - Comprehend the concepts related three dimensional object representations.
- Teacher: CHITRA P
This course provide introduction to the basic principles and techniques used in the field of chemical engineering, providing a solid understanding of the fundamentals of the application.

- Teacher: Annam Renita A
To acquire basic understanding of concepts and laws of thermodynamics, volumetric properties of fluids and thermodynamic properties of fluids
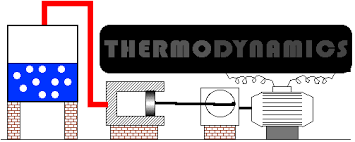
- Teacher: Annam Renita A
The Real-Time Embedded Systems specialization is a course taking you from a beginning practitioner, to a more advanced real-time system analyst and designer. Knowledge and experience gained on hard to master topics such as predictable response services, when to allocate requirements to hardware or software, as well as mission critical design will enhance your engineering talent. You will gain experience building a simple, but real, system project with real-time challenges, that will boost your confidence.

- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
|
SPYA1303 |
Research Methodology – I |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To understand the basic principles that governs psychological research.
· To understand the variables, sample, and various methods in research
· To be familiar in writing research report
Unit I: Introduction (15 hours)
Meaning of research - Objectives of research- Various steps in research - Types of research - Significance of research - Research methods versus methodology - Review of literature - Problems encountered by researchers in India - Ethical consideration in psychological research.
Unit II: Measurement and Scaling Techniques (15 hours)
Measurement in research - Measurement scales - Source of errors in measurement – Scaling -meaning of scaling - Scale construction techniques - Test development and standardization - Reliability - Validity.
Unit III: Variables and Methods of data collection (15 hours)
Meaning of variable – Various types of variables - Observation methods - Survey method - Questionnaire methods - Interview method –types of interview – Checklist - Rating scales.
Unit IV: Sampling fundamentals and Methods of Psychological Research (15 hours)
Sample - Sample size and its determination – types of sampling - Estimation and estimating population proportion - Testing of hypothesis - Experimental - Quasi-experimental - Case studies.
Unit V: Interpretation and Report Writing (15 hours)
Meaning of interpretation - Precaution in interpretation - Mechanics for writing a research report steps involved in writing research report - Precaution in writing research reports.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Understand the fundamentals of research including research problem, literature review, and hypothesis and so on.
2. Understand the different types of research design used in psychological research and be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of different designs.
3. Apply knowledge of statistics and methodology to undertake various key steps (e.g., design, data collection, screening, preparation, analysis of data, and write-up of research results) to create research of a high quality in an area of psychology.
4. Apply knowledge of research methodology in further study and professional practice.
References:
1. Michael Smithson, (2000), Statistics with Confidence: An Introduction for Psychologists, sage publications.
2. David C. Howell (2012), Statistical Methods for Psychology Cengage Learning.
3. Guilford, J.P. (1973), Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and Education,.McGraw Hill Kogakusha.
4. Ferguson, George, A. (1976), Statistical Analysis in Psychology & Education, McGraw Hill, Kogakusha.
5. Mangal, S. K. (2004), Statistics in Psychology and Education. 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, Delhi
6.Kothari, C. R. (2007). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques. 2nd ed. New Age International Publishers.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
- COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Understand control structures, functions and Arrays in C.
- Construct modules for real time applications using Functions in C.
- Comprehend pointers and file handling mechanisms
CO2 - Build simple solution for any given problem statement using various components of problem solving techniques and measure its efficiency in terms of time and space.
CO3 - Infer and examine the roots and foundation of C programming‘s key concepts like data types, operators.
CO4 - Devise and correlate the use of different core concepts such as arrays and functions in C language.
CO5 - Formulate real time solutions through programs using structure and union in C language.
CO6 - Design and develop various application oriented program for solving real time societal problems.
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
➢ To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semi-conductors.
➢ To familiarize on the principle of operation, capabilities and limitation of various advanced semiconductor devices and its practical application.
➢ To design practical circuits with alternate electronic devices.
➢ To study Nano devices.

- Teacher: annieangelinepreethi .
- Teacher: Rajasekar B
- Teacher: Dr. SUMATHI M
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: Indhu R
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
* To acquaint the students with the construction, theory, and operation of the basic electronic devices such as PN junction diode, Bipolar and Field-effect Transistors, Power control devices, LED, LCD, and other Optoelectronic devices.
*To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semiconductors.
* To familiarize on the principle of operation, capabilities, and limitations of various advanced semiconductor devices and its practical application.
* To design practical circuits with alternate electronic devices.
* To study about the display devices and power semiconductors.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Apply the knowledge of basic semiconductor materials and understand fabrication processes.
CO2 - Analyse the characteristics of various electronic devices like diode, transistor etc.
CO3 - Classify and analyse the various circuit configurations of Transistor and MOSFETs.
CO4 - Illustrate the qualitative knowledge of Power electronic Devices.
CO5 - Become Aware of the latest technological changes in Display Devices.
CO6 - Apply the knowledge of basic semiconductor materials and understand fabrication processes.
- Teacher: Bhuvana B P
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: YOKESH V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To familiarize the student with the design and analysis of Rectifiers and power supplies.
Ø To understand different Transistor biasing circuits.
Ø To understand Small signal analysis of FET and MOSFET amplifiers.
Ø To understand working of feedback amplifiers, oscillators, tuned amplifiers and multivibrators
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand basic construction, equivalent circuits and characteristics of basic electronics devices.
CO2 - Understand basic linear electronics circuits and their working principle.
CO3 - Design and analyze DC Power supplies.
CO4 - Design and analyze multistage amplifiers.
CO5 - Design negative feedback amplifier circuits and oscillators.
CO6 - Analyze and design solid state power amplifier circuits.
- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: V SIVAPRAKASH
- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
This course enable the students
- To understand the fluid properties, flow characteristics and hydrostatic force on surfaces.
- To study the equation of motions such as mass, momentum and energy equation and their practical applications.
- To understand the working principle of of hydraulic machines such as pumps and turbines
- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
A knowledge of fluid mechanics is essential for the chemical engineer because the majority of chemical-processing operations are conducted either partly or totally in the fluid phase.
- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
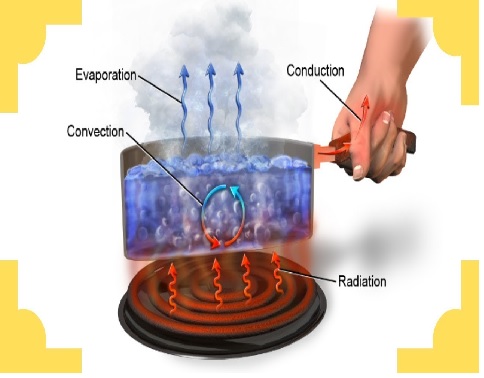
Heat Transfer course demonstrates the three modes of heat transfer through conduction, convection and radiation. Along conduction the heat flow through steady state and unsteady state systems were elaborated in detail through the access of one, two and three dimensional systems. Convection highlights the fluid flow under the influence of various flows accustomed with the applications of various flow equations. The radiation mechanisms were described through the application of various electromagnetic laws. Design of Heat transfer equipment such as heat ex-changers and evaporation units were also well discussed using the fundamental and derived equations governing heat transfer process.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To know the fundamentals of innate and acquired immunity. To understand how immune system fights and
combats the infection and diseases. To get an insight about the principle mechanism of immunity
- Teacher: Usha Nandhini S