Search results: 1467
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To learn the various synchronization schemes.
To discuss about the spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To acquaint the students with the architecture, theory and operation of telecommunication systems, issues related to telecommunication systems and the services rendered by the system to the end users.
On completion of this course, the students will,
Acquire basic knowledge on telecommunication and various signaling related to it
Acquire knowledge on traffic in telecommunication systems
Acquire knowledge about QoS and various impairments

- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
COURSE OUTCOMES
|
CO1 |
Describe the overall cellular concepts |
|
CO2 |
Describe the step by step evolution of 1G to 5G networks |
|
CO3 |
Explain the 2G, 3G and B2G systems |
|
CO4 |
Describe the functional Architecture and Protocol of Bluetooth, ZigBee and RFID |
|
CO5 |
Explain the Functional architecture of GSM and GRPS |
|
CO6 |
Implement the testing of Cognitive Radios |

- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. Understand the microwave frequencies and derive the scattering parameter for the microwave network and to study and analyse the microwave system and components.
2. To study the characteristics of couplers and power dividers.
3. To study the microwave sources and solid state devices.
4. To measure the RF parameters and to study the functions of RF analyzers.
5. To study the system aspects of MIllimeter wave systems.
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Identify and formulate S matrix of microwave junctions.
CO2 - Explain couplers and power dividers.
CO3 - Classify the microwave tubes and explain their principle of operation.
CO4 – Perform microwave measurements and analyze the parameters.
CO5 - Analyze the basic radio receiver architecture.
CO6- Develop millimeterwave radio links for microwave transmission
SEC1406 Programming in HDL
After the completion of course student will be able to
|
CO1 |
Understand the requirements of VHDL design flow |
|
CO2 |
Interpret the Verilog language elements and its relevance to digital design |
|
CO3 |
Apply the Modelling Styles for Simulation, Synthesis and Test Bench Creation. |
|
CO4 |
Analyze the Performance Study of Combinational and Sequential logic design using Verilog |
|
CO5 |
Evaluate State Machine and Memory designs by Verilog |
|
CO6 |
Create and realize the system in FPGA using Verilog |

- Teacher: VINO T
COURSE OBJECTIVE
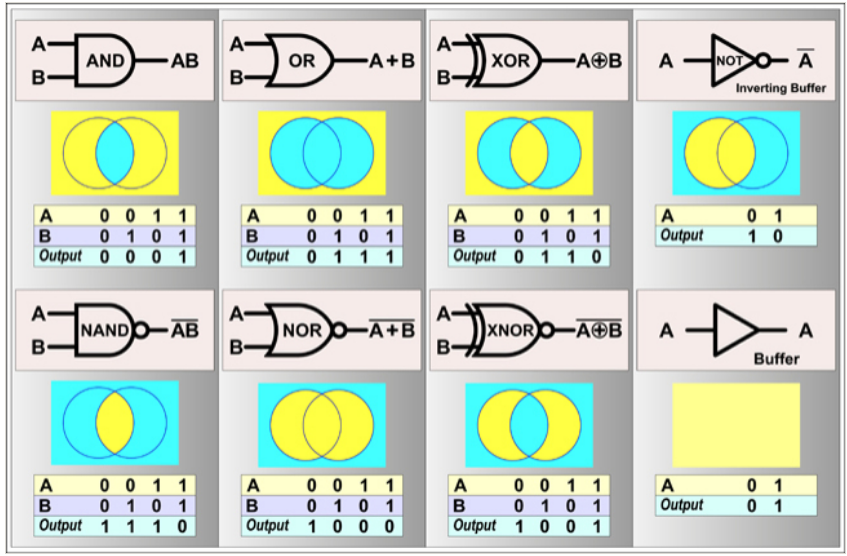
· To impart knowledge on various types of Binary logic
· To design a binary logic circuit for an arithmetic expressions
· To understand the usage of registers and counters used in various digital circuits
· To understand the design of memory devices used
· To get an exposure about the electronics behind design of Basic digital logical elements
- Teacher: Thaj Mary Delsy T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To acquaint the students with the construction, theory and operation of the basic electronic devices such as PN
junction diode, Bipolar and Field effect Transistors, Power control devices, LED, LCD and other Opto-electronic
devices, display devices and power semiconductors.
Ø To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semi-conductors and special semiconductor devices.
Ø To understand the method of biasing transistors.
Ø To familiarise the students with the analysis and design of Multistage Amplifier circuits.
Ø To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits of amplifiers and oscillators.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the method of biasing transistors.
To familiarize the students with the analysis and design of basic transistor Amplifier
circuits.
To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits.
To understand the frequency response of amplifiers.
To provide foundation and confidence to the students to troubleshoot and fault
analysis of power supplies and power amplifiers.
To develop current mirrors and differential operations.
UNIT 1 BIASING OF BJT AND FET 9 Hrs.
BJT– Need for biasing – Various biasing methods of BJT- Bias Circuit Design- DC Load Line –
DC analysis of Transistor circuits-AC Load Line- AC analysis of Transistor Circuits- Quiescent Point
–
Thermal stability - Stability factors - Biasing of JFET - Various biasing methods of JFET - JFET Bias
Circuit Design - MOSFET Biasing-Two port network.
UNIT 2 EQUIVALENT MODEL OF BJT AND FET AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Hybrid model- Analysis of CE, CC and CB amplifiers using Hybrid equivalent circuits to obtain
gain, input impedance and output impedance--Small Signal Amplifiers – Analysis of CE, CC and CB
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits to obtain gain, input impedance and output
impedance. Small Signal equivalent circuit of FET and MOSFET - Analysis of CS, CD and CG JFET
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits- Analysis of CS, CD and CG MOSFET amplifiers
using small signal equivalent circuits.
UNIT 3 MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIERS AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF BJT AND FET
AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Multistage Amplifiers- Methods of Coupling- RC Coupled- Transformer Coupled – Direct
Coupled Amplifiers- Amplifier frequency response – Miller effect- Frequency response of transistor
amplifiers with circuit capacitors – BJT frequency response – Low and High frequency analysis of
CE, CB, CC -Frequency response of FET - Low and High frequency analysis of CS, CG, CD JFET
& MOSFET.
UNIT 4 POWER SUPPLIES AND POWER AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Linear mode power supply - Rectifiers - Half-Wave Rectifier - Full-Wave Rectifier - Filters-L, C,
LC, CLC Filter- Regulators - Zener Diode regulator- Linear series, shunt voltage Regulators -
Switched mode power supply (SMPS) – Large Signal Amplifiers – Class A, Class B, Class C, Class
D- Distortion in power amplifiers.
UNIT 5 CURRENT MIRRORS AND DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS. 9 Hrs.
Current sources for biasing – Current steering circuits – Current mirror with improved performance
(Cascode mirror, Wilson, Widlar). Large and small signal operation of Differential pair circuit
Differential pair with active load - Frequency response of the Differential amplifier
Max. 45 Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquire knowledge of simple BJT circuits design and implement circuits with transistor
biasing design.
CO2 - Draw the equivalent circuits of BJT and FET.
CO3 - Understand the working principles, Frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET.
CO4 - Compare the frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET amplifiers.
CO5 - Design and troubleshoot simple power supplies and analyse the performance parameters of
power supplies. Understand and identify the performance level in power amplifiers and checking its
distortion levels.
CO6 – Design the differential amplifier and study the performance of current mirrors
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Millman J and Halkias C., “Integrated Electronics”, TMH, 2nd Edition, 2017.
2. S. Salivahanan, N. Suresh Kumar and A. Vallavaraj, “Electronic Devices and Circuits”, TMH,
2 nd Edition, 2017.
3. Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C.Smith, “Microelectronic Circuits”, Oxford University Press, Sixth
Edition, 2009.
4. Behzad Razavi, “Fundamentals of Microelectronics”, 1st edition, wiley publication, 2008.
5. Donald. A. Neamen, “Electronic Circuits Analysis and Design”, McGraw Hill Education (India)
Private Ltd., 3rd Edition, 2010.
6. Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nasheresky, ”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Pearson
Education, 11th Edition, 2013.
7. Floyd, “Electronic Devices”, Pearson Education, 9th Edition, 2012.
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To give a basic introduction to electronic components.
Ø To provide students knowledge about semiconductor diodes.
Ø To design the feedback amplifier circuits.
Ø To design the importance of digital circuits.
Ø To design the importance of PSPICE.
SECA1201-Digital Logic Circuits
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To impart knowledge on various types of Binary logics.
- To design a binary logic circuit for an arithmetic expressions.
- To understand the usage of registers and counters used in various digital circuits.
- To understand the design of memory devices used.
- To get an exposure about the electronics behind design of Basic digital logical elements.
- Teacher: VINO T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To discuss and understand fundamental concepts of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques.
Ø To understand the concepts of Frequency Modulation and De-Modulation techniques and compare with AM and PM.
Ø To understand the concepts of Analog Pulse modulation and De-Modulation techniques (PAM, PDM/PWM and PPM) & Multiplexing techniques and classifications.
Ø To apply different multiplexing techniques for AM, FM, PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
Ø To understand the various noises and their effect on Analog modulation systems.
Ø To discuss the working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Explain the Functional blocks of communication system, modulation techniques and Various noise sources and types.
CO2 - Analyse AM, FM, PM, PAM, PDM, PPM and PCM using mathematical equations and demonstrate their modulation and demodulation techniques.
CO3 - Illustrate sampling theorem and explain the importance of various multiplexing techniques.
CO4 - Demonstrate the working of AM and FM transmitters, Receivers and communication Systems.
CO5 - Performance evaluation and selection of appropriate modulation technique for real time applications.
CO6 - Working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
- To discuss and understand fundamental concepts of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques.
- To understand the concepts of Frequency Modulation and De-Modulation techniques and compare with AM and PM.
- To understand the concepts of Analog Pulse modulation and De-Modulation techniques (PAM, PDM/PWM and PPM) & Multiplexing techniques and classifications.
- To apply different multiplexing techniques for AM, FM, PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
- To understand the various noises and their effect on Analog modulation systems.
- To discuss the working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.

- Teacher: SAHAYA ANSELIN NISHA A
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
Electronic Devices and Circuits, deals with the design and applications of electronic devices and circuits such as passive components, diodes, triodes and transistors, rectification and power supplies,amplifying circuits, electronic instruments, and oscillators.

- Teacher: Nirmal Raj S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand operational principles and characteristics of semiconductor electronic devices.
➢ To learn about analog electronic circuits such as rectifiers, regulators and amplifiers.
➢ To learn about Boolean algebra and basic building blocks of digital systems.
➢ To learn about optimized implementation of combinational and sequential digital circuits and systems.
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
- Teacher: VINO T
On completion of the course, student will be able to
Design and analyze the Feedback amplifiers.
Design and analyze the Oscillators.
Analyze the performance of Tuned Amplifiers.
Analyze the types of Multivibrators.
Develop the application using Time Based Generator.
Develop the application using Blocking Oscillator.
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
** To understand the concepts of Feedback amplifiers.
** To identify the design and analysis of Oscillators.
**To familiarize with the performance of Tuned Amplifiers.
**To learn the types of Multi-vibrators.
** To focus on Time Based Generator and Blocking Oscillator.
- Teacher: annieangelinepreethi .
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: Lalithakumari S
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
- Teacher: Magthelin Therase
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Discuss the fundamental concepts of wave propagation in Transmission Lines and Wave Guides.
CO2 - Analyze the line parameters and various losses in transmission lines.
CO3 - Apply smith chart for line parameter and impedance calculations.
CO4 - Evaluate the characteristics of parallel plane and rectangular wave guides.
CO5 - Evaluate the characteristics of Circular waveguides.
CO6 - Evaluate the characteristics of resonators.

- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V