Search results: 1467
This course aimed to understand microbiology of marine environment with special emphasis on microbiological ecology, taxonomy, nutrient cycle, food microbiology and microbial biodegradation.

- Teacher: Jesia Persis Preethi
This course aims at understanding important medically important virus its mode of infection, pathogenesis prophylaxis and treatment.
Topic: 1
- General Concepts: Virus history,
- Diversity,
- shapes,
- sizes
- components of genomes.
- Isolation and purification of viruses and components.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 2
- Consequences of virus infection to animals
Consequences of virus infection to human.
- Viral infection: affect on host
macromolecules.
- Viral infection: establishment of the antiviral state.
- Viruses counter attack mechanisms.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 3
- Classification of viruses and nomenclatures.
- Positive strand RNA viruses- Picornaviruses. Flaviviruses
- West Nile virus and Dengue virus.
- Coronaviruses- SARS pathogenesis
- Negative strand RNA viruses Paramyxoviruses. Orthomyxoviruses
- Influenza pathogenesis and Bird flu.
- Rhabdoviruses: Rabies pathogenesis.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 4
- dsRNA viruses-
- Reoviruses: structure, classification,
- Reoviruses: life cycle; reverse
transcription.
- Retroviruses: HIV, viral pathogenesis and AIDS.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 5
- Small DNA viruses: parvo,
- polyomaviruses.
- Large DNA viruses: Herpes,
- adeno-,
- poxviruses.
- Miscellaneous viruses.
- Assignment
- Quiz
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø This course aims on studying interaction of microorganisms and food in relation to food-borne diseases, food spoilage and bioprocessing of food and dairy products.
Ø To make students learn about technologies to render foods and dairy products safe and analytical techniques for monitoring of food biological safety.

- Teacher: Usha Nandhini S
- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: Prakash P
Clinical Microbiology course will give us a comprehensive knowledge about the microbes.
With this we will get to know the classification, structure and function of the microbes.
Moreover, we will have a thorough idea about their role on human health.
Also we will come to know about different life threatening diseases caused by the microbes.
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
- Teacher: Jancy Mary E
Unit: 1 – CELLS AND CELLULAR METABOLISM 12 Hrs
Introduction to human anatomy and physiology – Basic elements of life, characteristics and maintenance of life – levels of organisms, structure of matter, chemical constituent of cell – movement through cell membrane, life cycle of cells and control of cell reproduction, metabolic process, control of energy and metabolic reactions, metabolic pathway - nucleic acids and protein synthesis – change in genetic information.
Unit: 2 – TISSUES AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM 12 Hrs
Tissues – epithelial, muscular and nervous tissues – integumentary system, types of membranes, skin – accessory organs, disorders, regulations of body temperature – Bone structure, development, function and organization of skeleton – joints, classification, structures and movements – muscle, structure and types, actions and responses.
Unit: 3 – BODY SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS 12 Hrs
Blood, circulation and function – lymphatic system-Endocrine system, endocrine glands, structure and function – respiratory system, structure and function – cardiac system, structure and function.
Unit:4 – NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND SENSES 12 Hrs
Nervous tissue, cell membrane potential, classification of neurons and nerve fibres – meninges, spinal cord, brain – peripheral and autonomic nervous system – somatic and special senses, receptors and sensations (smell, taste, hearing, equilibrium and sight).
Unit: 5 – METABOLISM AND NUTRITION 12 Hrs
Digestive system, structure and function – urinary system, kidney and nephron, structure and function – reproductive system – metabolism and nutrition.
Max. 60 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology, 11th Edition, 2011, Martini, Nath, and Bartholomew.
2. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology, 12th Edition, 2017, Elaine N. Marieb and Suzanne M. Keller.
- Teacher: Beryl Vedha Y
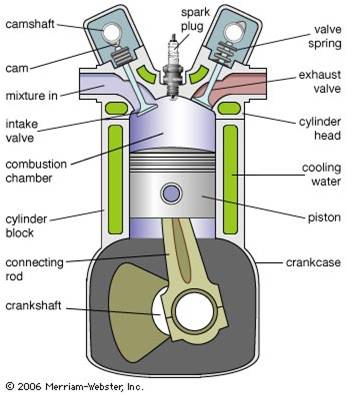
Thermal Engineering is the study of heating and cooling processes in open and closed environments. As an academic discipline, it involves the science of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To make the student understand the overall view of thermal engineering through topics such as Power cycles, IC Engines, Steam nozzles & turbine, air compressors and Refrigeration and Air conditioning.
- This subject enables the students to understand the principle of operation, construction and control of several thermal equipment's which find wide applications in a variety of fields like power generation, automobile industry, process industries, food preservation and human comfort.
- It provides the fundamentals for Power plant Engineering, Automobile Engineering, Turbo machinery and Refrigeration & Air conditioning (R&AC)

COURSE OBJECTIVES
· To understand the layout and working of conventional and non-conventional power plants
· To understand the working power plant equipment’s and instruments
· To understand the economics of power plants and environmental aspects
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Nagpal G.R., Power Plant Engineering - Khanna Publishers, 1996.
2. Domkundwar, Power Plant Engineering - Dhanpat Rai & Sons, Delhi, 1988.
3. Vopal and Stortzki,” Power Plant Engineering”, PHI, 2007.
4. El Wakil M.N., “Power Plant Technology”, McGraw Hill, 1985.
5. Joel Weisomon and Roy Eckart, “Modern Power Plant Engineering”, PHI, 1985.
6. Rai G.D., "Non conventional sources of Energy”, Khanna Publishers Delhi, 1994.
Time table: ODD SEM (2020-2021)| Time/Day order | 8.30- 9.30 | 9.30-10.30 | 10.30-11.00 | 11.00-12.00 | 12.00-1.00 |
| Monday | |||||
| Tuesday | SME1304 | ||||
| Wednesday | SME1304 | ||||
| Thursday | SME1304 | ||||
| Firday | SME1304 | ||||
| Saturday |

- Teacher: R Siva
Finite element analysis (FEA) is a computerized method for predicting how a product reacts to real-world forces, vibration, heat, fluid flow, and other physical effects. Finite element analysis shows whether a product will break, wear out, or work the way it was designed.
FEA enables you to predict potential design issues and therefore minimize risk to your product, profits, and your business. With FEA you can test the impact of varying conditions (stress, vibration, buckling, fatigue, creep, heat, etc.) on your design.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Understand the capabilities of FEM and its importance in Engineering.
To introduce the concepts of Mathematical Modeling of Engineering Problems.
COURSE OUTCOMES
|
CO1:Understand the Fundamental Theory of Finite Element Method. |
|
CO2: Select and interpret Finite Element analysis results for design and evaluation purposes. |
|
CO3:Solve plain elasticity problem using energy approach |
|
CO4:Solve one dimensional heat transfer problems and two dimensional scalar variable problem using ANSYS. |
|
CO5:Develop a basic understanding of the limitations of the Finite Element method and understand the possible error sources in its use. |
|
CO6:Examine the longitudinal vibration, transverse vibration of beams, Mesh Generation and Errors in the finite element method. |
UNIT 1 1D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 9 Hrs.
Historical Background -Basic concept of FEM- steps involved in FEA - Variational Formulation of Boundary value problem - Rayleigh Ritz Method - Weighted Residual methods-Finite Element Modeling - Element Equations - Shape functions -Bar, Beam Elements - stepped bar, tapered bar-simple problems
UNIT 2 2D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 10 Hrs.
Basic Boundary Value Problems in 2 Dimensions - Triangular, quadrilateral, higher order elements - Poisson and Laplace Equations - Weak Formulation - Elements Matrices and Vectors -.Natural Co-ordinate System - Lagrangian Interpolation Polynomials - Iso-parametric Elements - Formulation -Numerical Integration -2D Triangular elements - rectangular elements - Illustrative Examples.
UNIT 3 SOLUTION TO PLANE ELASTICITY PROBLEMS 8 Hrs.
Introduction to Theory of Elasticity - Plane Stress - Plane Strain and Axisymmetric Formulation - Principle of virtual work - Element matrices using energy approach.
UNIT 4 APPLICATIONS IN HEAT TRANSFER & FLUID MECHANICS 9 Hrs.
One dimensional heat transfer element - application to one-dimensional heat transfer problems- scalar variable problems in 2-Dimensions - Applications to heat transfer in 2- Dimension - Application to problems in fluid mechanics in 2-D.
UNIT 5 SPECIAL TOPICS 9 Hrs.
Vibrational problems - equations of motion based on weak form -longitudinal vibration of bars - transverse vibration of beams Mesh Generation-Errors in the finite element method - various measures of errors- accuracy of the solution- Eigen value Problems - h & p elements- Applications of FEM software to solve simple problems, types of solver - a brief.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. J.N Reddy. “An Introduction to the Finite Element Method” , Mc Graw Hill, International Edition, 1993.
2. Seshu, P, “Text Book of Finite Element Analysis”, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi,2007.
3. Segerlind L.J,“Applied Finite Element Analysis”, John Wiley, 1984.
4. Rao. S.S, “Finite Element Method in Engineering” , Pergamon Press, 1989.
5. Chandrupatla & Belagundu , “Finite Elements in Engineering”, Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd., 1997.
6. Cook, Robert Davis et al, “Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis” , Wiley, John & Sons,1999.
7. George R Buchanan, “Schaum’s Outline of Finite Element Analysis”, McGraw Hill Company, 1994.
8. Taylor.C and Hughes.J.B. “Finite Element Programming of the Navier Stoke equation” Pineridge Press Limited, UK 1981
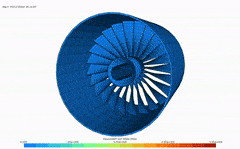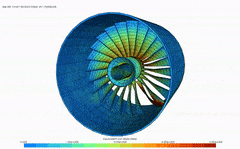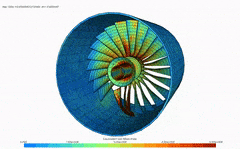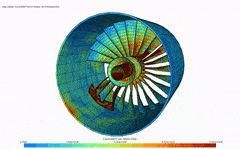
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
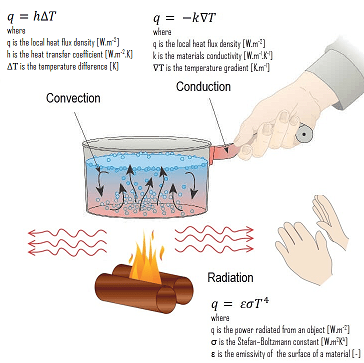
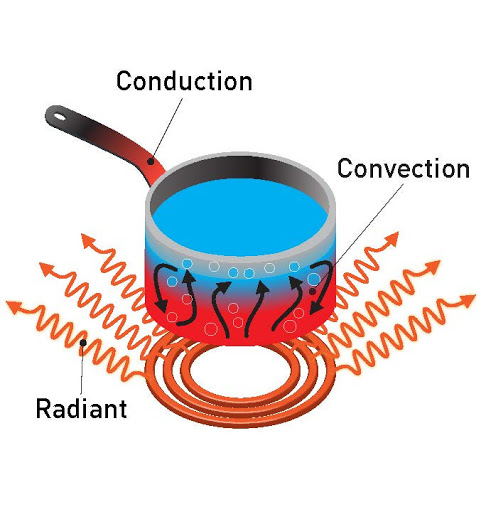
CO1 - Understand the basic modes of heat transfer and Compute temperature distribution in steady-state
and unsteady-state heat conduction.
CO2 - Understand and analyze heat transfer through extended surfaces.
CO3 - Interpret and analyse forced and free convection heat transfer.
CO4 - Explore the real time applications of radiation mode of heat transfer.
CO5 - Design heat exchangers using LMTD and NTU methods.
CO6 - Relate the mass transfer concepts for various industrial applications
- Teacher: Anderson A
- Product Design as a design field involves designing or creating products that will be used by consumers. Thus, while designing anything, a product designer needs to ensure that the product being designed is easy and safe to use.
- Product Design is related to all the work that is done between an idea coming to mind and finally seeing the product in the hands of the customer
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF MATERIALS- Crystallography: Basics, Atomic radius and Atomic packing factor of BCC, FCC & HCP, Miller’s indices, Allotropy, Solid solutions and intermetallic compounds. Atomic Diffusion: Laws of diffusion, Factors affecting diffusion. Phase diagrams: Solidification of metals, Phase rules, Construction of phase diagram, Isomorphous diagram, Eutectic diagram showing partial solid solubility, Peritectic system.
UNIT 2 FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS ALLOYS- Ferrous alloys: Cooling curve of pure iron, Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagram, Critical points in Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagrams, Classification of ferrous alloys, Influence of alloying elements, Designation systems, Types of steels and cast iron, Typical compositions, properties and applications of ferrous alloys. Non-ferrous alloys: Typical compositions, properties and applications of Aluminium and its alloys, Copper & its alloys, Ti & its alloys, and Nickel & its alloys.
UNIT 3 STRENGTHENING PROCESSES- Heat treatment of steel: TTT diagram and CCT diagram. Heat treatment processes: Annealing, Normalizing, Tempering and Quenching, Jominy quency test for hardenability. Case hardening: Carburizing, Nitriding, Cyaniding, Carbonitriding, Flame hardening and Induction hardening. Others: Dispersion strengthening & Precipitation hardening
UNIT 4 FAILURE OF MATERIALS AND TESTING- Tensile testing: Significance, Universal testing machine, Stress–strain curve for ductile & brittle material, Results. Hardness Testing: Significance, Rockwell harness test, Brinell’s hardness test and Vicker’s hardness test, Results. Impact testing – Significance, Charpy impact test and Izod impact test, Results. Failure of materials: Defects in materials, Deformation mechanisms, Failure mechanisms and influencing factors of ductile and brittle failures, fatigue failure, creep failure and impact failure.
UNIT 5 MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION AND SELECTION - X-ray diffraction (XRD): Bragg’s law of diffraction, Powder, rotating crystal and Laue methods to determine the crystal
structure. Optical microscopy: Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and Applications of optical
microscopes. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and
Applications of SEM. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample
preparation and Applications of TEM. Materials selection: Engineering materials and their properties, Materials selection
charts, Material selection strategy, Factors affecting materials selection, Case studies.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
- Teacher: JINO L