Search results: 1467
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
To enable students opportunities to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts
To present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative
To improve their vocabulary in various aspects
To develop LSRW skills and to focus on creative writing

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
Introduce the students to basic principles, theories and practices in ELT.
Enable students to identify changes that took place over a period of time in the area.
Analyze the teaching approaches and methods. Recall basic approaches for teaching language with four skills.

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: MISHA T.P
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Esther Rajathi D J B
- Teacher: DEVA SHAILU P
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
- Teacher: Dr. D. Rajkumar
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To understand the basic principles of molecular spectroscopy in terms of the quantization of molecular energy and transitions between molecular energy levels when matter interacts with radiation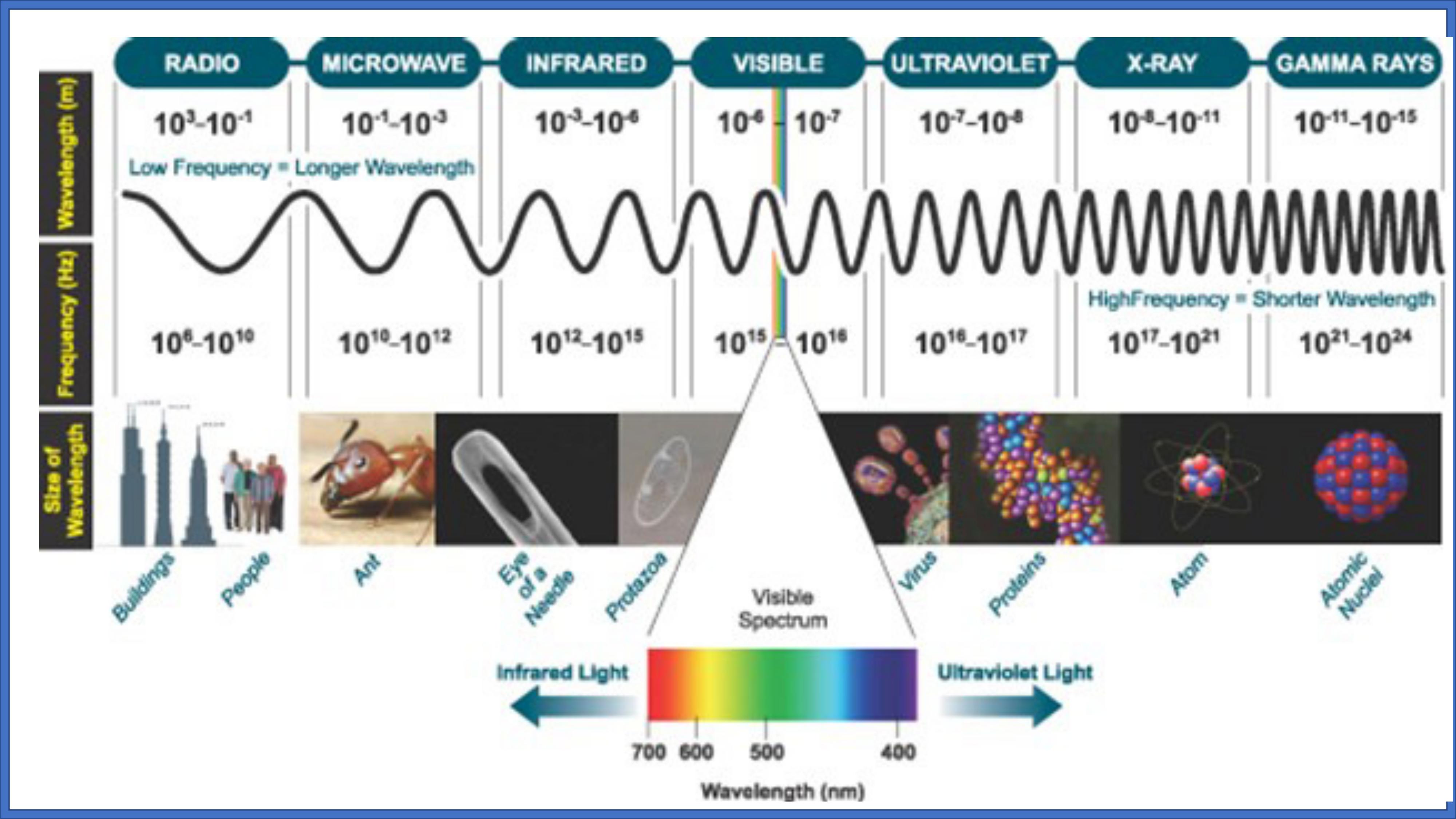
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
Unit 1: PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Unit 2: HEAT
Unit 3: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Unit 4: SOUND AND ACOUSTICS OF BUILDING
Unit 5: GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND PHYSICAL OPTICS
Course outcome:
CO1: Gain a basic knowledge of characterization of materials.
CO2: Explain statistical physics and thermodynamics as logical consequences of the postulates of statistical mechanics
CO3: Identify the Interaction of EM waves with matter in microscopic view given more values than previous.
CO4: Outline the importance of Acoustics and properties of sound in the modern society
CO5: Apply the principles and techniques of optics and defects in the selected problems.

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
Unit 1: Gravitation 10 Hrs
Keplers Laws- Newton’s law of gravitation, Determination of gravitational constant-Boy’s method, Poynting’s method-Gravitational field, Intensity of the field, Gravitational potential due to a spherical sphere, Escape velocity.

- Teacher: Malliga P
Course Name : Mechanics
Course Code: SPH1112
It consists five units.
Unit I : Dynamics
Unit II: statics and Hydrostatics
Unit III: Frame of Reference
Unit IV: Special Theory of Relativity
Unit V: Oscillations
- Teacher: Manjula M
The course is aimed
To acquire working knowledge of thermometry and calorimetry.
To acquire working knowledge of the zero-th, first and second law of thermodynamics.
To acquire basic understanding of liquid and solid cryogens working principle and their functionality
To understand conduction ,radiation and various law s such as Wien’s law, Planck’s law Rayleigh-Jean’s law
To link thermodynamics to the micro description used in Statistical Mechanics.
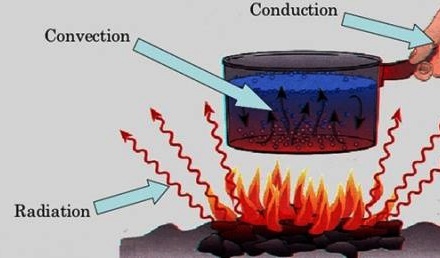
- Teacher: Helen Merina Albert
Course Outcomes
CO1: Understand the physical significance of Maxwell’s equations and hence estimate the speed of light.
CO2: Explain the basics and applications of LASER.
CO3: Explain the propagation mechanism of light through optical fiber.
CO4: Derive the relation between Numerical Aperture and Refractive indices.
CO5: Classify the types of optical fibers and attenuation mechanisms.
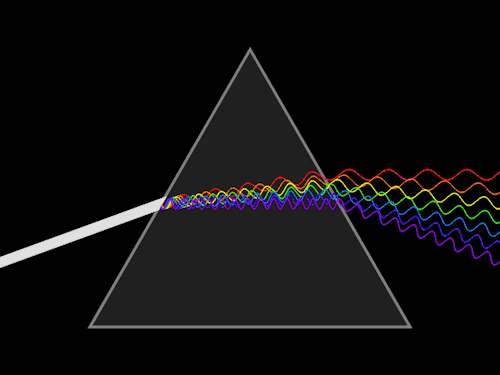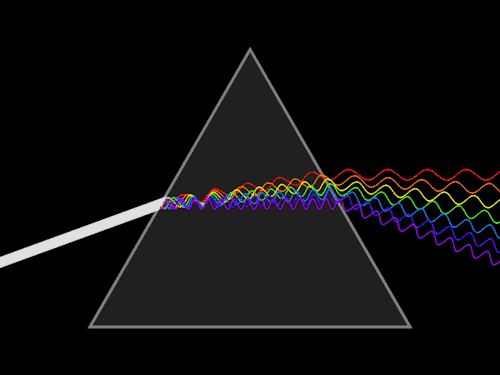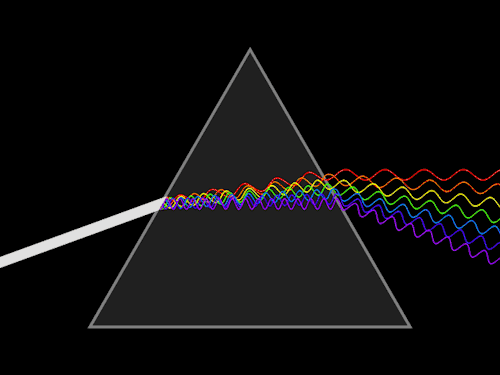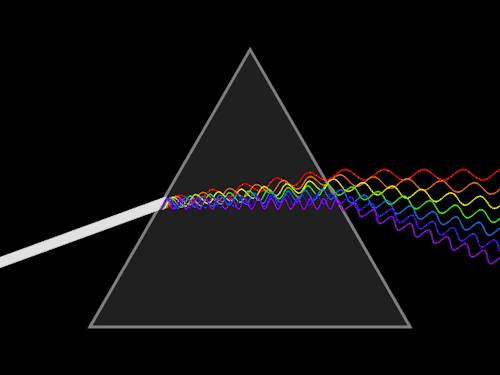
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
· It introduces to the fundamentals of diode theory, P.N junctions and bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
· It covers the basics and design of field effect transistors (FET) and transistors amplifiers.
· It explains the various feedback transistor and operational amplifiers.
· It deals with various number systems and Boolean algebra.
· It mainly focuses on the analysis and design of combinational logic systems.
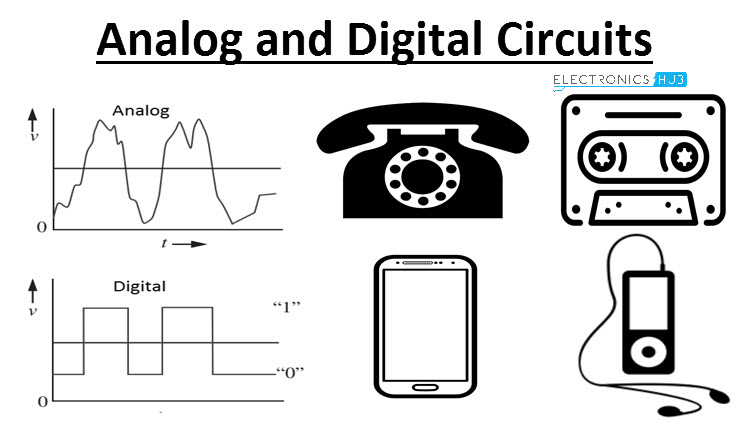
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
COURSE OBJECTIVE
· To understand the basic architecture of 16 bit and 32-bit microprocessors.
· To understand interfacing of 16 bit microprocessor with memory and peripheral chips involving system design.
· To learn simple programs with 8085microprocessor.
· To learn the design aspects of I/O and Memory Interfacing circuits.
· To understand the concept of 8051 microcontroller
To provide the knowledge of different measurement techniques for different parameters to be measured in industries.
Choose the appropriate instrument based on the ranges of parameters to be measured.
Differentiate between different types of measuring technique for a parameter.

- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K




