Search results: 1466
UNIT 1 DESIGN FUNDAMENTAL- The design process – Considerations of good design - Morphology of Design – Design Drawings , Computer Aided Engineering – Designing of codes and standards – Concurrent Engineering – Product life cycle – Technological Forecasting – Market Identification– Competition Bench marking – Systems Engineering – Life Cycle Engineering – Human Factors in Design – Industrial Design.
UNIT 2 DESIGN METHODS- Creativity and Problem Solving – Creativity methods – Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) - product Design Specifications– Conceptual design – Decision Theory – Decision Tree – Evaluation methods - Embodiment Design – Product Architecture Configuration Design - Parametric Design – Role of models in designs - Mathematical Modeling – Simulation – Geometric Modeling – Finite Element Modeling – Optimization – Search Methods – Geometric Programming – Structural and Shape Optimization.
UNIT 3 MATERIAL SELECTION PROCESSING AND DESIGN- Material Selection Process – Economics – Cost Vs Performance – Weighted property Index – Value Analysis – Role of Processing in Design – Classification of Manufacturing Process – Design for Manufacture – Design for Assembly – Designing for castings, Forging, Metal Forming, Machining and Welding – Residual Stresses – Fatigue, Fracture and Failure.
UNIT 4 PROBABILITY CONCEPTS IN DESIGN FOR RELIABILITY- Probability – Distributions – Test of Hypothesis – Design of Experiments – Reliability Theory – Design for Reliability – Reliability centered Maintenance – Robust Design Failure mode Effect Analysis.
UNIT 5 LEGAL AND ETHICAL ISSUES IN DESIGN AND QUALITY ENGINEERING- Introduction – The origin of laws – Contracts – Liability – Tort law – Product liability – Protecting intellectual
property – Legal and ethical domains – Codes of ethics – Solving ethical conflicts– case studies. Total Quality Concept –
Quality Assurance – Statistics Process Control – Taguchi Methods – Robust Design – Failure Model Effect Analysis.
Max: 45 Hrs.
|
SPYS 1601 |
Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms. Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
Effective Leadership
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80Marks
|
SPYA 1404 |
Open Elective 4 – Effective Leadership |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT-I
Meaning -Purpose - Leader in Government -Inner Core of leader - Social Response - Essential Behaviours of Good leaders
UNIT-II -
Characterstis of Leader -Types of Leader -Assessment of Leader - Pros and Cons
UNIT-III
Aspiration of Good Leader, Ethics of Leader, Value, Skills
UNIT-IV
Information and Commetments of leader, Communication and Commetments of Leaders
UNIT-V
Sustainabilty of Good Leader - 360 tools - Educating and Developing leader.
References:
1. Svendsen, A., & Laberge, M. (2007). “FOSTERing” collaborative stakeholder relationships. Notes for Practitioners Series: CoreRelation Consulting, Inc. Retrieved from http://masterfulfacilitation.com/ articles/fostering.pdf
2. Tardanico, S. (2013, January 15) 10 Traits of courageous leaders. Forbes: Leadership. Retrieved from https:// www.forbes.com/sites/susantardanico/2013/01/15/10-traits-of-courageous-leaders/#7b075cbb4fc0
3. Th omas, K., & Kilmann, R. (2002). Confl ict mode instrument. USA: Xicom Inc., subsidiary of CPP, Inc. TNS Employee Insights. (2014). 8 Tips to engage your employees. Retrieved from http://tns.tnsemployeeinsights.com/acton/media/2055/employee-engagement-tips-for-managers
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
|
SPSY 1501 |
Core Theory 8 - Psychopathology II |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To explore abnormality and understand the nature and course of development of various psychological disorders.
· To familiarize with research, theory, and methods of practice in abnormal psychology.
Unit I: (15 hours)
Schizophrenia- Clinical description; schizoohrenia subtypes; Causes of schzophrenia - Biological dimensions, psychological And Social contributions; Treatment
Unit II: (15 hours)
Mood Disorders- Clinical descriptions of mood disorders; Depressive Disorders; bipolar disorders: Causes of Mood disorders; Treatment
Unit III: (15 hours)
Substance related disorders: alcohol abuse and dependence; drug Abuse and dependence; causes of substance related disorders; Treatment
Unit IV: (15 hours)
Sexual Disorders: Sexual dysfunctions - causal factors & Treatment Sexual variants - Paraphilias, Incest & rape; causes and treatment
Unit V(15 hours)
Behaviour Disorders Of childhood and adolescence: Hyperactivity, Conduct disorders, delinquent behaviour, eating disorders, autistic Disorder, elimination disorder Visit to mental health/de addiction centers must be arranged
REFERENCE
1 Barlow David H & Durand, V.Mark (1995) Abnormal
Psycholgy, Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.
2 Carson, Robert, Butcher, James V., Coleman,
James(1988): Abnormal Psychology and Modem Life, VIII edition, Scott.Frismand
& Co
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will apply the major concepts and theories of Abnormal Psychology
2. Students will create and explain the physiological, behavioural, and psychological correlates of abnormal behaviour.
3. Students will critically evaluate issues surrounding methods of assessing, diagnosing, and treating psychopathology.
4. Students will understand the historical foundations of current methods of assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of psychopathology.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
UNIT - I (15 hours)
Introduction of Human Resources Management: Definition, Importance of Human Resources, Objectives of Human Resources Management, Qualities of a good personnel manager – Need, type and scope – Advantage for a written policy - Human Resources policies and work Culture.
UNIT – II (15 hours)
Human Resource Planning: Human Resources Planning: Long and Short-term planning, Job. Recruitment and selection: Purposes, types and methods of recruitment and selection, Placement, Induction, Transfers, Promotions, Disciplinary actions, Termination of Services: Resignation, Dismissal, Retrenchment and Voluntary Retirement Schemes, Exit Interviews, Prevention of employee turnover.
UNIT - III (15 hours)
Performance Evaluation: Ranking, rating scales, critical incident method, Removing subjectivity from evaluation, MBO as a method of appraisal, Job evaluation, Criteria for Promotions and job enrichment.
UNIT - IV (15 hours)
Rewards Management: Wage and Salary Administration: Meanings, Calculation of Wage, Salary, Perquisites, Compensation Packages, Cost of Living Index and Calculation of Dearness Allowance, Rewards and Incentives: Financial and nonfinancial incentives, Productivity – linked Bonus, Compensation Criteria.
UNIT - V (15 hours)
HR Audit: Nature and Scope – Approaches to HR Audit Management of Differences: Grievance Handling – Discipline and Domestic Enquiry – Handling of Sexual Harassment in the Work Place – Introduction to Industrial Relations – Current Trends and Issues in HRM and Case Studies.
Reference Books:
1. Ashwathappa, K., Human Resource Management, 6th Edition, Tata McGrawHill Education Pvt. Ltd., 2010.
2. DeCenzo, D.A. and Robbins, S.P., Human Resource Management, 10th Edition, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd., 2011.
3. Dessler, G., Human Resource Management, 12th Edition, Pearson, 2011.
4. Ivanecevich, J.M., Human Resource Management, 10th Edition, Tata McGrawHill Education Pvt. Ltd., 2010. 5. Mamoria, C.B. and Gaonkar, S.V., Personnel Management, Himalaya Publishing House, 2011.
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80Marks
|
SPYA 1602 |
Professional Core 10 – Rehabilitation Science |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT :I (15Hours)
Rehabilitation psychology: overview and concepts- Nature and scope of rehabilitation psychology- Concepts of ability and disability – Recovery - symptom control and rehabilitation - Establishment of division 22 of APA.
UNIT :II (15 Hours)
Importance and applications - Rehabilitation of addictions - drug and alcohol - Rehabilitation after abuse and violence - Palliative care and pain management - role of psychologists.
UNIT: III (15 Hours)
Rehabilitation of persons with physical disabilities – physical - psycho- social and vocational rehabilitation.
UNIT :IV (15 Hours)
Biopsychosocial and social model –Psychodynamic - behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counseling - Cognitive- behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counselling.
UNIT: V (15 Hours )
Parental care and support systems for persons with disabilities - Assessment of persons with disabilities - Legal issues in rehabilitation for persons with disabilities - overview of PWD act - RCI act - national trust act - United Nations convention on the rights of persons with disabilities.
Books for study
1. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company
2. Falvo, D.R. (2013). Medical and psychosocial aspects of Chronic Illness and disability (5th ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning
3. Frank, G.R., Rosenthal, M., Caplan, B. (2010). Handbook of Rehabilitation Psychology. American Psychological Association.
7. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
Books for reference
1. Federici, S. Scherer M.J. (2012). Assistive Technology Assessment Handbook (Eds.). Boca Raton, FL :Taylor and Francis Group.
2. Riggar, T.F. & Maki, D.R. (2004). Handbook of Rehabilitation Counselling (Eds). New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
3. Stuss, D.T., Winokur, G. & Robertson, I.H. (2008).Cognitive neurorehabilitation. UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
SPYS 1601 | Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy | L | T | P | Credits | Total Marks |
4 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with the nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms.Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Remember professional standards of therapeutic counselling practice.
2. Understand the theory and practice of a relational approach to counselling.
3. Evaluate and integrate a range of theoretical approaches into a coherent model of practice.
4. Apply the knowledge, skills and understanding of the reflective practitioner.
5. Create an environment to work competently with diversity and with an anti-oppressive practice.
6. Analyse participation in and potential contribution to the changing (local and global) social, professional and organisational context for therapy.
References:
1.Hersen, M. & Sledge, W. (2002). Encyclopedia of psychotherapy.Academic Press.
2.Yalom, I. (2009). The Gift of Therapy. Harper Perennial: New York.
3.Gobbard, G. Beck, J. Holmes, J. (2007). Oxford Textbook of Psychotherapy. OUP: London.
4.Gerring, R.J. & Zimbardo, P.G. (2006). Psychology and Life. Pearson.
- Teacher: KINJARI K
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: SHYAM SRINIVASAN K
|
SPYB1101 |
General Psychology I |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To generate interest in Psychology.
- To introduce the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behavior.
- To understand the various theories in Psychology.
- To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 12 Hrs
Psychology as a science – The History of Psychology – Schools - Modern Perspectives – Psychology in India- Methods: Introspection – Observation – Survey – Experiment – Case Study – Correlation Research - Scope of psychology. Fundamentals of Indian Psychology.
UNIT 2 SENSATION, PERCEPTION 12 Hrs
Sensation: Meaning –
Psychophysics -Thresholds – Weber’s Law – Adaptation – Basic sensation:
Vision – Hearing – Touch and other Skin senses – Olfaction- Gustation - Proprioception:
Kinesthetic sense – Vestibular sense Perceptual processing – Perception: Role
of attention in perception - Perceptual organization - Perceptual sets -
Perceptual constancies - Depth perception - Illusions - Extra Sensory
Perception. - Factors that influence perception – Depth perception.
UNIT 3 LEARNING 12 Hrs Definition – Nature- Principles of learning - Classical conditioning - Operant Conditioning - Principles of reinforcement – Punishment- Schedules of Reinforcement – Shaping – Learned Helplessness - Cognitive Learning - Latent Learning – Insight Learning – Observational Learning.
UNIT 4 MEMORY 12 Hrs
Memory: Definition - Processes of memory: Encoding – Storage – Retrieval – The information processing model - Stages of memory: Sensory memory – Short term memory – Long term memory – Forgetting: Meaning – Forgetting Curve-Theories of forgetting - Causes – Memory and Brain – Improving memory.
UNIT 5 THINKING AND LANGUAGE 12 Hrs
Thinking and language - Thinking process - Concepts - Problem-solving - Creative thinking - Reasoning – Inductive and Deductive reasoning, Language: Nature - Main Components of Language.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1: To understand the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behaviour.
CO2: To evaluate the various theories in Psychology.
CO3: To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
CO4: To remember the dynamics of the important cognitive processes.
CO5: To create and evaluate interventions and strategies and enhance the basic as well as higher-order cognitive functions.
CO6: Students will be able to identify the major fields of study and theoretical perspectives within psychology and analyse their similarities and differences.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Cicarelli, S. K. & White, J. N. (2021). Psychology 6th edition. Pearson India Education Services Pvt Ltd.
2. Kalat, J. W. (2021). Introduction to Psychology 12th edition. Cengage Learning.
3. Feldman, R. S. (2020). Understanding Psychology. 15th Edition. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
4. Morgan,C.T., King,R.A., Weisz, J.R., & Schopler,J. (2004). Introduction to Psychology. 7th Edition.NewDelhi:TataMcGraw-Hill.
5. Baron, R. A. (2010) Psychology (5th ed.). New Delhi, India: Pearson India Education Services Pvt Ltd.
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
Unit I: Motivation (15 hours)
Motivation – Meaning - Approaches-Instinct - Drive reduction - Arousal – Incentive -, Cognitive - Humanistic- Maslow’s Need hierarchy – Types-Physiological Motivation [Hunger, Thirst, Sex, Maternal drive] - Psychological motivation [Achievement, Affiliation, Power, Parenting.
Unit II: Intelligence and Assessments(15 Hours)
Concepts and nature of Individual differences – Intelligence - Theories of intelligence- factor and cognitive theories - Characteristics of Intelligence tests - Types of Intelligence tests - Determinants of Intelligence.
Unit III: Emotion (15 Hours)
Emotion - Meaning - Physiological basis of emotions – Theories-James Lange Theory - Cannon Bard Theory - Cognitive Theory.
Unit IV : Personality (15 Hours)
Definition - Approaches – Psychodynamic – Humanistic - Social – Cognitive approach - Assessment of Personality – Questionnaire - Rating Scales and Projective tests – Characteristics - Advantages and disadvantages.
Unit V: Altered States of Consciousness (15 Hours)
Consciousness – Nature – Waking - Sleep and Daydreaming - Biological Rhythms – Circadian - Stages - Dreams-Content, Links between dreams and waking .
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. To understand the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behaviour.
2. To evaluate the various theories in Psychology.
3. To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
4. To remember the dynamics of the important cognitive processes.
5. To create and evaluate interventions and strategies and enhance the basic as well as higher-order cognitive functions.
6. Students will be able to identify the major fields of study and theoretical perspectives within psychology and analyse their similarities and differences.
References:
1.Morgan,C.T, King,R.A., Weisz,J.R., and Schopler,J. (2004). Introduction to Psychology, 7th
edition,24th reprint.NewDelhi:TataMcGraw-Hill.
2. Baron, R.A. (1996). Psychology. 3ed. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
3. Lahey, B. B. (1998). Psychology: An Introduction. New Delhi: Tata Mc Graw Hill.
4. Feldman, R. S. (2002). Understanding Psychology. New Delhi: Tata Mc Graw Hill.
5. Bootzin, R. R., Bower, G. H., Crocker, J., & Hall, E. (1991). Psychology Today. London: Mc Graw Hill.

- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
SPYA1302 - Life Span Development
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To explore the various influences on child and adolescent development processes.
· To explore the psychology of exceptional children.
· To explore the various influences on development processes concerning adulthood and aging, taking into consideration the individual, familial and societal contexts.
Unit I : INTRODUCTION (15 hours)
Developmental Psychology - Conception, Pregnancy,And Birth - Stages of Pregnancy –Conception –Implantation -The first trimester -The second trimester - The third trimester - Prenatal Care - Drug use during pregnancy - -Stages of Childbirth - The postpartum stage of childbirth
Unit II : INFANCY AND EARLY CHILDHOOD(15 hours)
Physical and cognitive development- Reflexes and motor skills -Sensation and perception- Psychosocial development – Family Relationships -Attachment – Parenting -Sexuality in Infancy and Toddlerhood - Gender Development - Gender identity -Psychological and social influences on gender identity - Gender roles early childhood: physical and Cognitive development –psychosocial development.
Unit III : MIDDLE CHILDHOOD and ADOLESCENCE(15 hours)
Physical And Congnitive Development –Physical Development in Middle Childhood and Adolescence- Physical changes - Brain and nervous system development - Motor skills – Health - Cognitive Development in Middle Childhood and Adolescence - Self-Concept - Social Cognition - Family Relationships - Peer Pressure - Sexuality in Middle Childhood
Unit IV : Early Adulthood and Middle Adulthood(15 hours)
Physical And Cognitive Development - Physical Development In Early Adulthood And Middle Adulthood – Health in Adulthood - Intellectual Development in Adulthood - Independence In Early Adulthood - Establishing A Career - Psychosocial Development - Crisis -Relationships In Middle Adulthood
Unit V :LATE ADULTHOOD (15 hours)
Physical Development in Late Adulthood - Health in Late Adulthood - Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease - Intelligence and Memory - Relationships - Late adulthood and sexuality - Relationships with adult children - Elderly abuse - Relationships with grandchildren .
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Understand theory and research in physical, cognitive, communication, emotional, and social development of the Child , Adolescence and adult.
2. Understand the physical, cognitive, communication, emotional, and social development of the infant and child..
3. Apply knowledge of infant and child development to facilitate and understanding of developmental outcomes.
References:
1.Papilla, Diane E, Olds, Sally Wendoks(1992): Human Development, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co
2.Shaffer, David R. (1996): Developmental Psychology, IV Edition, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company.
3.Hurlock, E.: Developmental Psychology (1980), Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co.
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
Unit I: Introduction to Statistics (15 hours)
Introduction to Statistics: the meaning of statistics - Need and importance of statistics in psychology - Prerequisites for studying statistics- Descriptive and inferential statistics - Frequency Distribution and Graphic representation of data: Histogram - Bar diagram - Pie Chart - Scatter Plot.
Unit II: Measures of Central Tendency and Variability (15 hours)
Computation of Mean, Median and Mode and their uses. Measures of variability: Computation of quartile and standard deviations - Cumulative distribution - Percentiles standard scores and their uses. Normal distribution curve: Characteristics and application - Kurtosis and Skewness.
Unit III: Parametric tests (15 hours)
Correlations: Meaning and methods – Characteristics - Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation - Point-Biserial Correlation and Phi - Biserial and Tetrachoric Correlation - Tests of Significance: t- test - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA): One way and Two way Analysis of Variance,
Unit IV: Non-parametric tests (15 hours)
Spearman’s Rank Correlation –Regression: Simple linear regression – Multiple Regression - Chi Square Test - Wilcoxon signed rank test - Mann- Whitney U test - Kruskal-Wallis (KW) test - Friedman's test
Unit V: Test construction and standardization (15 hours)
Characteristics of a good test - Steps in test construction: Item-analysis - determination of item difficulty - item discrimination - problems of item analysis - Introduction to SPSS: Meaning- Uses of SPSS in Statistics and Research.

- Teacher: KRISHNAPRIYA B
|
SPYB4001 |
Personality Development |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To enable the students to
· Understand the meaning and nature of personality
· Analyze their attitudes for personal enrichment
· Understand the concept of motivation and achievement motivation
· Maintain healthy relationships with others in turn developing personalities
UNIT – I: Meaning and Nature of Personality 15 Hours
Personality: Definitions, Meanings, Elements of personality, Types of Personality, Determinants of personality, Personality SWOT Analysis.
UNIT – II: Personality Enrichment 15 Hours
Self esteem, Self concept, Advantages of high self esteem, Characteristics of people with high and low self esteem, Steps to building positive self esteem, Attitude, Factors that determine our attitude., Benefits of a positive attitude and consequences of a negative attitude, Steps to building a positive attitude.
UNIT – III: Motivation 15 Hours
Motivation: Meaning and nature, The difference between inspiration and motivation, Motivation redefined, External motivation vs. Internal motivation, Achievement motivation
UNIT – IV: Success 15 Hours
Defining success-Real or imagined obstacles to success, Qualities that make a person successful, Reasons for failure – Interpersonal skills, Dealing with seniors, colleagues, juniors, customers, suppliers at the workplace.
UNIT – V: Positive Relationships & Personality 15 Hours
Positive Relationships – Factors that prevent building and maintaining positive relationships, the difference between ego and pride, the difference between selfishness and self interest, Steps for building a positive personality, Body language: understanding body language, Projecting positive body language.
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. To understand different elements of personality
2. They can able to know different types of Personality
3. Students can understand determinants of personality
4. To understand advantages of high self esteem
5. Students will be able to acquire the skills to manage time and relationship
6. Students can identify the factors that prevent building and maintaining positive relationships
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
- Nathan Dorman (2004) Personality Development Abishek Publication, New Delhi.
- Jafar Mahmud (2004) Introduction to Psychology APH Publishing Corporation, New Delhi.
- Zig Ziglar (2000) See You at the Top Magna Publishing Co. Ltd., Mumbai.
- Shiv Khera (1998) You can win MacMillan India Ltd., New Delhi.
- Walter Doyle Staples (2000) Think Like a Winner Magna Publishing co. Ltd., Mumbai\
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3Hrs.
PART - A: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PART - B: 2 Questions from each UNIT of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80 Marks
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
|
SPYA1604 |
Professional Elective II – Stress Management
|
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
100 |
Objectives
1. To understand how the stressors will change the Life events or life change events.
2. To know the different Theories of Stress.
3. To highlight the different types of relaxation technique to reduce stress.
Unit-I (15 hours)
Introduction: The science and sources of stress – Stress and health – Types of stress –concept of stress – Causes of stress –Theories of stress - Response-based concept of stress - Event-based concept of stress
Unit –II (15 hours)
Stressors -Life events or life change events -Chronic stressors -Effects of stress on the body -Enhancing awareness about managing stress - The health belief model and its application to stress management: an in -depth investigation.
Unit – III (15 hours)
Relaxation: Meaning – Sleep – Sleep related disorders - Relaxation techniques: yoga and meditation –Biofeedback -Progressive muscle relaxation - Autogenic training -Visual imagery - Self-hypnosis - Humor, stress, and relaxation - Mindfulness meditation.
Unit IV (15 hours)
Coping mechanisms: Method Based on Rational Emotive Therapy-Method Based on Simplified Kundalini Yoga -Method Based on Gestalt Therapy - Systematic Desensitization - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy -Regular physical activity and exercise.
Unit –V (15 hours)
Implementing a Stress Reduction Plan: Importance of implementing a plan - Stages of change - Determining goals, objectives, and targets: goal setting: Establishing objectives - Deciding targets -Social support.
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
Unit I : Introduction (15 hours)
Positive psychology: Definition; goals and assumptions; Relationship with health psychology, developmental psychology, clinical psychology. Activities: Personal mini experiments; Collection of life stories from magazines, websites, films etc and discussion in the class.
Unit II: Positive emotions, Well-being and Happiness (15 hours)
Positive emotions: Broaden and build theory; Cultivating positive emotions; Happiness- hedonic and Euaimonic; Well- being: negative vs positive functions; Subjective well –being: Emotional, social and psychological well-being; Model of complete mental life. Test: The positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS-X); The satisfaction with life scale (Diener et al, 1985); Practice ‘Be happy’ attitude
Unit III :Self-control, Regulation and Personal goal setting (15 hours)
The value of self-control; Personal goals and self-regulation; Personal goal and well-being; goals that create self-regulation; everyday explanations for self-control failure problems. Activity: SWOT analysis
Unit IV: Positive Cognitive States and Processes (15 hours)
Resilience: Developmental and clinical perspectives; Sources of resilience in children; Sources of resilience in adulthood and later life; Hope. Optimism- How optimism works; variation of optimism and pessimism; Resilience. Spirituality: the search for meaning(Frankl); Spirituality and well-being; Forgiveness and gratitude. Test: Mental well-being assessment scale; Test: Signature strength
Unit V :Applications of Positive Psychology (15 hours)
Positive schooling: Components; Positive coping strategies; Gainful employment Mental health: Moving toward balanced conceptualization; Lack of a developmental perspectives. Activity: An action plan for coping. Test: Brief COPE assessment scale
References:
1.Snyder, C.R. & Lopez, S.J. (2002). Handbook of positive psychology.(eds.). New York:Oxford University Press.
2.Baumgardner, S.R & Crothers, M.K.(2009). Positive Psychology.U.P: Dorling KindersleyPvt Ltd.
3.Carr, A. (2004). Positive psychology, The science of happiness and human strengths.NewYork: Routledge.
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
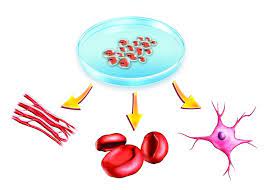
This course is to familiarize students with fundamental process of human embryology and developmental biology, which provide solid foundation on stem cell biology, regulation of stem cells and human diseases connected to stem cell biology.
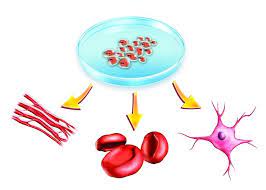
This course is to familiarize students with fundamental process of human embryology and developmental biology. This course will provide the solid foundation on stem cell biology, regulation of stem cells and human diseases connected to stem cell biology.