Search results: 1466
|
SMEB1303 |
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Max.Marks 100 |
|
3 |
* |
0 |
3 |
OBJECTIVE:
- To study the aspects of Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
- To gain knowledge of different types of stresses, strain and deformation induced in the components due to external loads.
- To study the distribution of various stresses in the elements such as beams, shafts etc.
- To study the effect of component dimensions and shapes on the stresses and deformations.
UNIT 1: STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 9 Hrs
Rigid and Deformable bodies – Strength, Stiffness and Stability – Stresses; Tensile, Compressive and Shear –Deformation of simple and compound bars under axial load – Thermal stresses and strains. Elastic constants – Relation between Elastic constants - Strain energy and unit strain energy – Strain energy in uniaxial loads.
UNIT 2: ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN TWO DIMENSIONS 9 Hrs
Principal planes and stresses – Mohr’s circle for biaxial stresses – Maximum shear stress - simple problems- Stresses on inclined plane. Biaxial state of stresses – Thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Deformation in thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Efficiency of joint- Effect of Internal Pressure.
UNIT 3: BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES 9 Hrs
Types of beams - Supports and Loads – Shear force and Bending Moment in beams – Cantilever, Simply supported andOverhanging beams – SFD and BMD for inclined loads and couples.Stresses in beams – Theory of simple bending – Stress variation along the length and in the beam section – Effect of shape of beam section on stress induced.
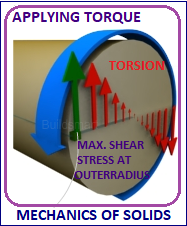
UNIT 4: TORSION 9 Hrs
Analysis of torsion of circular bars – Shear stress distribution – Bars of Solid and hollow circular section – Stepped shaft – Twist and torsion stiffness – Composite shafts Springs - Laminated springs, axial load and twisting moment acting simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs– Deflection of helical coil springs under axial loads – stresses in helical coil springs under torsion.
UNIT 5: BEAM DEFLECTION 9 Hrs
Columns – End conditions – Equivalent length of a column – Euler equation – Slenderness ratio – Rankine Gordon formula for columns.Elastic curve of Neutral axis of the beam under normal loads – Evaluation of beam deflection and slope: Double integration method, Macaulay Method, and Moment-area Method.
Max.45Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Understand the fundamentals of Stress and Elastic Constants.
CO2: Understand the concept of Principal stresses and thin shells.
CO3: Construct Shear force & Bending moment diagram and Bending stress.
CO4: Apply the Concept of Torsion for Circular Shafts and Understand the concept of Springs.
CO5: Understand the theory of Column and Beam deflection.
CO6: Analyze overall deflection aspects related to Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., “Strength of Materials”, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd.,Fifth Edition,2012
2. Punmia B.C. & Jain A.K., Mechanics of Materials, ,Laxmi Publications,2001
3. Ryder G.H, “Strength of Materials, Macmillan India Ltd”., Third Edition, 2002
4. Ray Hulse, Keith Sherwin & Jack Cain, “Solid Mechanics”, Palgrave ANE Books,2004.
5. Allan F. Bower, Applied Mechanics of Solids, CRC Press, 2009, 820 pages.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks : 100 Exam Duration : 3 Hrs.
PART A : 2 Questions from each unit, each carrying 2 marks 20 Marks
PART B : 2 Questions from each unit with internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
- Teacher: LAKSHMI SANKAR S
Drawings on types of bolted joints designed bolted joint - Types of the weld and welded joint - Steel in the foundation, beams, and columns with column base. - Types of tubular Trusses, connections of various members of tubular truss - tubular constructions.
- Teacher: Dr.Annamalai S

- Teacher: Eshanthini P
To emphasize the importance of sustainable design practices and strategies in urban planning and settlement
design.

TV production involves various elements that come together to create a successful TV show. So, if you are enamored by large houses and the over-the-top look of the show, then read on to know what all goes into making these sets into a reality on TV. At the end of the course, you will be a multi-skilled, industry-ready practitioner. Employability is a core feature of this course.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
The Television production process refers to the stages (phases) required to complete a media product, from the idea to the final master copy. This process can apply to any type of media production including film, video, television and audio recording.
The three main stages of production are:
- Pre-production: Planning, scripting & story boarding, etc.
- Production: The actual shooting/recording.
- Post-production: Everything between production and creating the final master copy.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
- Media law presents a wonderful opportunity to explore the many competing rights and interests in society as the rights to free expression, information, and a free media compete with other important rights including reputation, a fair trial, privacy, confidentiality, intellectual property and national security, along with the right to be free from discrimination in all its forms.
- It affords us a superb showcase of the role of the news media in the varied political systems internationally as governments select different points where free expression should be curtailed. You learn that free expression is a continuum, with fewer restrictions in some nations and alarming censorship in others.

- Teacher: NAZINI N
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To help students learn and analyze the various content in media so that they are aware of the content produced in media.
To understand how media constructs reality and to choose right tool to analyze content provided in print and electronic medium.
UNIT 1 MEDIA CONTENT
Media Content - Media text as arrangements of signs – Narrative, genre - discourse analysis –Text, intertextuality & context - institutions & ways of seeing discourse analysis – sources - technologies of the gallery & museum
UNIT 2 MARXISM & IDEOLOGY
Media as Manipulators: Marxism & Ideology – culture industry as mass deception – ideological meanings –arguments and criticisms – communication flows & consumer resistance, Media & public sphere - nation as imagined community - digital dilution of nation
UNIT 3 PSYCHOANALYSIS
Psychoanalysis: visual culture, visual pleasure & visual disruption – subjectivity, sexuality & conscious Audience studies : audience, fans, users , ethnographies of visual objects
UNIT 4 COMPOSITIONAL INTERPRETATION
Critical study of visual methodology –production –image – compositional interpretation: technology & image production – media ,gender & sexuality : construction of femininity , patriarchal romance & domesticity – empowering – media & masculinities.
UNIT 5 SEMIOLOGY
From quality to quantity: content analysis : introduction - four steps to content analysis – semiological study – selecting images for study - sign making meaning processes – social semiotics

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
The Visual Narrative Method course provides a comprehensive introduction to the theories and concepts that shape storytelling through visual media. Students will begin by exploring visual semiotics, which involves understanding how signs, symbols, and images create meaning. The course then delves into the basic elements of narrative structure, such as plot, character, and setting, and how these are expressed visually. Key topics include the principles of composition, the use of perspective, and the way time and motion are depicted in visual storytelling.In addition, the course examines how different cultures and societies interpret visual narratives, highlighting the impact of cultural context on audience perception. Ethical considerations are also addressed, particularly in terms of how people, cultures, and events are represented in visual media. By studying a variety of genres and engaging with real-world examples, students will learn how visual narratives can both reflect and influence societal values and ideologies.Throughout the course, students will engage in critical analysis of visual narratives, applying theoretical frameworks to deepen their understanding. The course culminates in a final project where students will choose a visual narrative to analyze in detail, allowing them to apply their knowledge and develop strong analytical skills. This course is designed to prepare students for advanced studies or careers in fields like media studies, film theory, and visual communication.
- Teacher: Prasanna Lakshmi S
- Teacher: RAJA N
To impart basic concepts meaning and models of development
To make students aware about problems and issues of the development.
To Inculcate knowledge of development communication and relations with media and society.
To Know the functioning of media in development coverage.
5. Understanding the rural India and its problems.

- Teacher: SENTHIL KUMARAN E