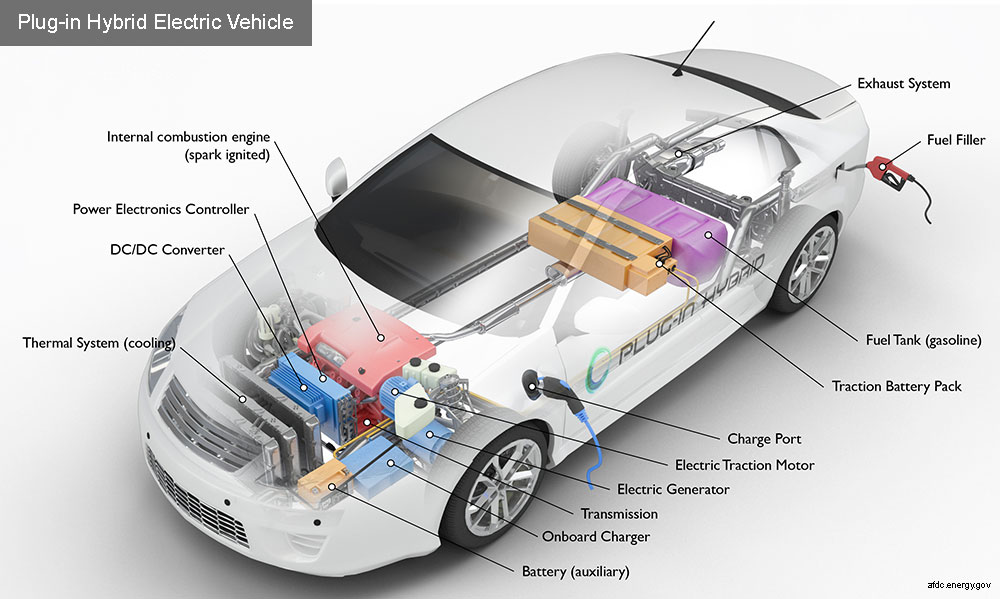
Search results: 406
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To introduce the skills and knowledge relevant to the practice of professional journalism.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
Introduction to journalism, Subfields within Journalism, Key concepts and objectives of Journalism - Introduction to architectural journalism, skills needed, reporting, writing, editing, photography, columnists, public relationships, criticism.
UNIT 2 TECHNOLOGIES IN JOURNALISM
Environment, Social Change, Persuasion Interviewing techniques, Argument and debate as a technique in the investigation of social problems; evidence, proof, refutation, persuasion; training in argumentative speaking, theories of journalism, Introduction to architectural software needed in journalism and photography, Video coverage, walkthrough of buildings, production of contemporary architectural journalism. Understanding the individual demands in the context of newspapers, radio, film, and television.
UNIT 3 PRESENTATION TECHNIQUES
Text preparations, Mode of presentation, Standards and Guidelines for documentation, Code of ethics, Basic knowledge on Press laws, Press Council of India, Public Debate, Navigating Information Networks for Mass Media with relevance to searches on Architectural topics, User generated contents for analysis of various issues on Architecture, creating an online forum and platform for exchange of ideas and information, to critically contrast outputs of selected individual pieces of journalism.
UNIT 4 IMPLICATIONS FOR ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
Regional, National and International discussion forums, Changes in contemporary and historical design practices, Discussions on topics needed in an architectural journal and current issues- types of journals, works of key architectural journalists, Public Discourse on the Internet, Mass Media and Public Opinion critically appraise selected individual pieces of journalism.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala

- Teacher: Arhannaraju .
- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
In this course, we will be learning about various theories, philosophies and design processes characterizing the works of contemporary masters.
It allows an architect to consider a buildings or cities as more than a visual phenomenon and therefore the architect would have a more fundamental and culturally inclusive approach to architecture than an approach based purely on architect's own taste or style.

- Teacher: Kaviya .
- Teacher: Arulmalar Ramaraj
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To develop a comprehensive knowledge about Conservation and its importance in today’s context.
To enhance the skills of the graduate to understand various principles and practices in the field of
architectural conservation.
To familiarize the students with an overview of best practices in conservation charters, various
conservation processes, techniques and skills through case studies.
- Teacher: Guruji V
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Ability to understand and analyze the influence of historical, social, cultural and economic aspects on Architectural manifestations. CO2 Research and understand the role of scale and proportion in defining the character of a built form
CO3 Critique and decode the fineness in construction techniques and judicious use of materials.
CO4 Assess the architectural character and detailing in both historical and contemporary buildings
- Teacher: Selvendiran S.G
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To understand the various aspects of natural and mechanized ventilation.
- To give a comprehensive introduction and the principles of natural and artificial lighting.
- To explore the fundamentals of integrating services in buildings.

- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
Exposing to issues, challenges in the design of industrial buildings and large built forms involving alternative construction materials and technology. Orienting the students on the need for creating sustainable environment through sound Green building principles.

- Teacher: Brindha K
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
Course Objectives:
The students should be able to
1. Acquire the knowledge of Electrical and Electronics engineering concepts.
2. Understand the construction and applications of Electrical and electronics components in various automotive electrical circuits.
3. Understand the construction and working of various automotive electrical systems and components.
4. Identify, demonstrate and compare the various components and systems of Auto
electrical systems.
Course Outcomes
CO1 : Enumerate the construction, characteristics and maintenance of battery, lighting system and different accessories in a typical automobile after careful inspection.
CO2 : Explain the construction, characteristics and maintenance of starting and ignition system and diagnose the ignition system fault of any vehicle.
CO3 : List out the principles and characteristics of charging system components and demonstrate their working with suitable tools.
CO4: Describe the principles and architecture of electronics systems and its components present in an automobile related to instrumentation, control, security and warning systems.
CO5: Enumerate the principles, application, construction and
specification of different sensors and actuators usable in typical
automobile by suitable testing.

- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
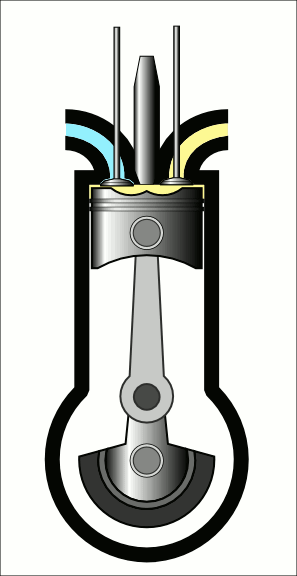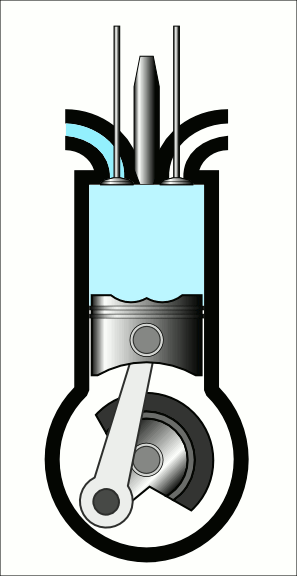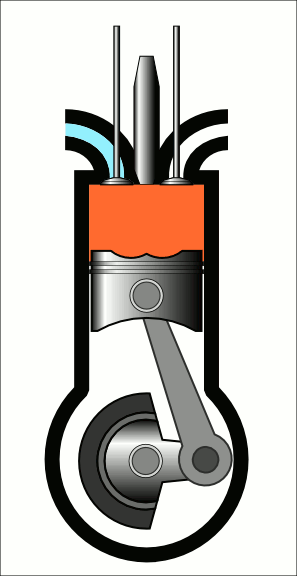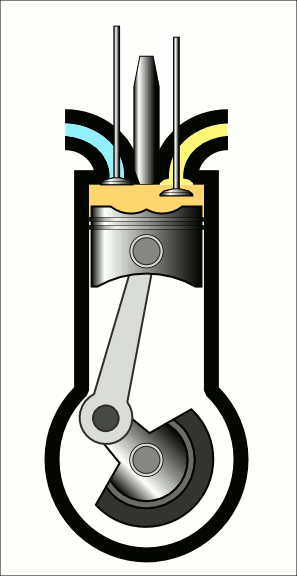
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Understand the diesel engine construction and its operation.
Understand the fuel injection system in CI Engine.
Gain knowledge on air motion & combustion phenomena in CI Engine.
Understand turbo charging and engine management system in IC Engines.
Understand CI engine performance.
Understand the principle of modern engine technology.
- Teacher: Dr. Ashwin Jacob
- Teacher: PURUSOTHAMAN M
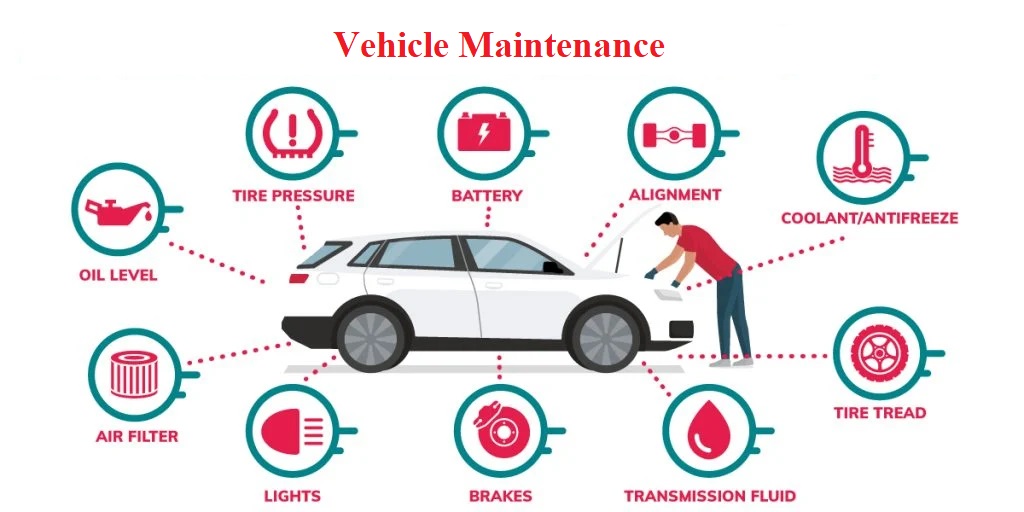
SAUA1702 VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know about the various methods of maintaining vehicles and their subsystems.
To impart knowledge on engine maintenance – repair and overhauling.
To understand step by step procedure for maintain the various automotive sub systems.
UNIT 1 MAINTENANCE, WORKSHOP PRACTICES, SAFETY AND TOOLS 9 Hrs.
Maintenance – need, importance, primary and secondary functions, policies - classification of maintenance work - vehicle
insurance - basic problem diagnosis, automotive service procedures – workshop operations – workshop manual .safety –
personnel, machines and equipment, vehicles, fire safety - first aid, basic tools – special service tools – measuring
instruments – condition checking of seals, gaskets and sealants, scheduled maintenance unscheduled maintenance
services – service intervals - towing and recovering, reports, log sheets, trip sheets and other forms.
UNIT 2 ENGINE AND ENGINE SUBSYSTEM MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
General engine service- dismantling of engine components- engine repair- working on the underside, front, top, ancillariesservice
of basic engine parts, cooling and lubricating system, fuel system, intake and exhaust system, electrical system -
electronic fuel injection and engine management service - fault diagnosis- servicing emission controls.
UNIT 3 TRANSMISSION AND DRIVELINE MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Clutch- general checks, adjustment and service- dismantling, identifying, checking and reassembling transmission,
transaxle- road testing- removing and replacing propeller shaft, servicing of cross and yoke joint and constant velocity jointsrear
axle service points removing axle shaft and bearings- servicing differential assemblies- fault diagnosis.
UNIT 4 STEERING, BRAKE, SUSPENSION, WHEEL MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Inspection, maintenance and service of hydraulic brake, drum brake, disc brake, parking brake, bleeding of brakes.
inspection, maintenance and service of mc person strut, coil spring, leaf spring, shock absorbers, dismantling and assembly
procedures, wheel alignment and balance, removing and fitting of tyres, tyre wear and tyre rotation, inspection, maintenance
and service of steering linkage, steering column, rack and pinion steering, recirculating ball steering service-worm type
steering, power steering system.
UNIT 5 AUTO ELECTRICAL AND AIR CONDITIONING MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Maintenance of batteries, starting system, charging system and body electrical -fault diagnosis using scan tools,
maintenance of air conditioning parts like compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator - replacement of hoses- leak
detection- AC charging- fault diagnosis, vehicle body repair like panel beating, tinkering, soldering, polishing, painting.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Gain knowledge about vehicle operation and maintenance, service schedules etc.
CO2 - Apply the concepts of scheduling.
CO3 - Understand Maintenance of engine sub system and Repair
CO4 - Understand maintenance procedures like repairing, overhauling
CO5 - Describe the basic concepts of steering, brake, suspension and wheel maintenance.
CO6 - Analyze the testing methods for checking battery, starter motor, charging systems, ignitions system.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Ed May, “Automotive Mechanics”, Volume 1 and 2, 8th edition, McGraw Hill Publications, 2009.
2. Vehicle Service Manuals of reputed manufacturers.
3. Bosch Automotive Handbook, Tenth Edition, 2017.
4. Automotive Mechanics W.H. crouse.2010.
5. James D Halderman, “Advanced Engine Performance Diagnosis” 6 edition, Pearson, 2015
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 questions of 2 marks each - No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
- Teacher: RAM PRAKASH S
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
Automotive safety is the study and practice of design, construction, equipment and regulation to minimize the occurrence and consequences of traffic collisions involving motor vehicles. The course gives an introduction to safety and vehicle structural crashworthiness and crash testing, types of impacts, and impact with rebound, driver assistance systems in automobiles, concept of crumble zone,characteristics of vehicle structure, role of safety systems in automobiles, importance of ergonomics in automotive safety.

- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable students to develop cognizance of the importance of human behavior.
To provide insight on individual and group behavior.
To familiarize with organizational culture, change and development processes.

- Teacher: DR. RANI J
- Teacher: JOHN BRITTO M
- Teacher: Shahinabegum M
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
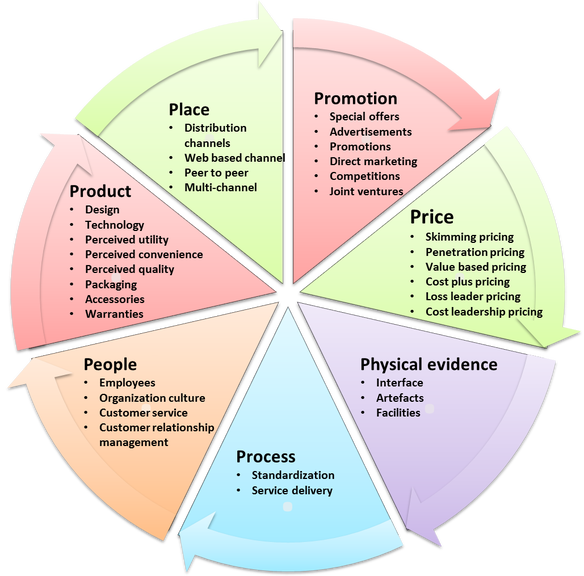
This is course will help to identify the key factors in successful marketing of business. This will highlight the emerging trends in marketing channels, process, segments, tools etc. This will mainly used to identify the customer's need and satisfaction for customer relationship management.

- Teacher: Raja M
- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
Cell Biology- Structure and Function and Mechanism of cell has to elucidated
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
SBBA 1203 INTRODUCTION OT BIOCHEMISTRY L T P Credits Total Marks 5 0 0 3 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
This course is aimed give an understanding of the basics of biochemistry dealing carbohydrates, Amino acids, Lipids, nucleic acid and vitamins.
UNIT 1: CARBOHYDRATES 12 Hrs. Carbohydrate – Definition, Classification, biological significance, structure of glucose, digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
UNIT 2: PROTEINS 12 Hrs. Amino acids – structure, classification (Essential and non-essential, protein and non-protein amino acids). Proteins – definition, classification and structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary).
UNIT 3: LIPIDS 12 Hrs. Lipids – definition, classification and biological significance. Structure, properties and functions of fatty acids.
UNIT 4 NUCLEIC ACIDS 12 Hrs. Nucleic acids – Structure of DNA and its functions. Different forms of DNA. Different types of RNA and its functions.
UNIT 5 VITAMINS 12 Hrs. Vitamins – Source, biological function, daily requirement and deficiency symptoms of fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K) and water soluble vitamins (Ascorbic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, niacin, pantothenic acid, lipoic acid, biotin, folic acid and vitamin B12).
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry-David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox, Macmillan Worth Publishers.
2. Harper―s Biochemistry-Rober K. Murray, Daryl K. Grammer, McGraw Hill, Lange Medical Books. 25th edition.
3. Fundamentals of Biochemistry-J.L. Jain, Sunjay Jain, Nitin Jain, S. Chand & Company.
4. Biochemistry-Dr. Amit Krishna De, S. Chand & Co., Ltd. END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION
PAPER PATTERN Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 questions of 2 marks each - No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks

|
Course objectives This course is aimed give an understanding about the basics of microbiology dealing types of microbes, classification & characterization |
- Dr.S.Usha Nandhini: Usha Nandhini S
|
Course objectives This course is aimed give an understanding about the basics of microbiology dealing types of microbes, classification & characterization |
- Teacher: Jayashree S