Search results: 406
SCYA1102- ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY (CSE SPECIALIZATION,ECE, EEE, MECH, MECHATRONICS, AUTO, AERO, CIVIL)
This course is designed for the budding engineers to understand the significance of chemistry which forms the basic foundation of engineering. The course comprises of five units dealing with all the aspects of material science. Bonds to bands explains the fundamentals involved in the bond formation to the band theory of materials which finds significant applications in engineering. Molecular spectroscopy involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with materials in order to produce an absorption pattern from which structural or compositional information can be deduced. Functional materials deal with charge transport carriers such as soliton, polaron and bipolaron in conducting polymers that are utilized in engineering molecular devices. Carbon materials emphasize the structure, properties, production of fullerenes, graphene, CNT’s and their applications in the field of health, stealth and energy. Engineering materials covers the importance of Phase rule, Fuels and nanoparticles in the engineering and medicinal field.
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Supriya S
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Anand T
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Kavitha V
This course is designed for the budding engineers to understand the significance of chemistry which forms the basic foundation of engineering. The course comprises of five units dealing with all the aspects of material science. Bonds to bands explains the fundamentals involved in the bond formation to the band theory of materials which finds significant applications in engineering. Molecular spectroscopy involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with materials in order to produce an absorption pattern from which structural or compositional information can be deduced. Functional materials deal with charge transport carriers such as soliton, polaron and bipolaron in conducting polymers that are utilized in engineering molecular devices. Carbon materials emphasize the structure, properties, production of fullerenes, graphene, CNT’s and their applications in the field of health, stealth and energy. Engineering materials covers the importance of Phase rule, Fuels and nanoparticles in the engineering and medicinal field.
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Supriya S
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for under graduate students in chemistry to give an insight into the general aspects of organic reactions. The students will be able to understand the significance of functional groups, reactivity of the compounds and the types of reactions. On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1: Analyze the structure and reactivity of aromatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon
CO2: Apply the nucleophilic substitution and elimination mechanism of alkyl and aryl halides
CO3: Examine the structure and reactivity of alcohols and phenols
CO4: Examine the physical and chemical properties of ethers and epoxides
CO5: Apply the nucleophilic addition and electrophilic substitution mechanism to carbonyl compounds
CO6: Evaluate the basic concept of chemistry to real world applications
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for undergraduate students in chemistry with an insight into organic compounds preparations and synthesis. The course will provide a platform in understanding the molecular rearrangements which pave way in their industrial applications. At the end of the course, the participants will be able to
To understand the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds containing O, N, S.
To synthesize the carboxylic acids along with their reactivity nature.
To develop the practice of learning molecular rearrangements along with their mechanism.
To discuss the importance of active methylene groups in organic synthesis.

- Teacher: Subhenjit Hazra .
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Ramanjaneya Reddy G
- Teacher: Kavitha V
This course enables the students to elucidate the use of chemical kinetics in understanding reaction mechanisms and kinetics of fast reactions; to understand adsorption phenomena and enable the learners to understand the importance and significance of heterogeneous catalysis and to learn the kinetics of polymerization and experimental methods of determination of molar masses of polymers.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry consists of five units. The first unit deals with the study of stability of metal complexes based on EAN rule. Interpretation of structure and geometry of metal carbonyls through hybridization enhances the knowledge of synthesis of highly stable organometallic complexes by the selection of ligands for complexation. The second unit discusses the various chemical reactions involving metal carbonyls as reactants. The third unit deals with the various catalytic applications of metal carbonyls in different organic conversion reactions. The fourth unit discusses the involvement and role of transition metal ions in biological molecules and also includes their mechanism of action. The last unit give strong insight to different types of nuclear reactions and the applications of radioisotopes in different fields.
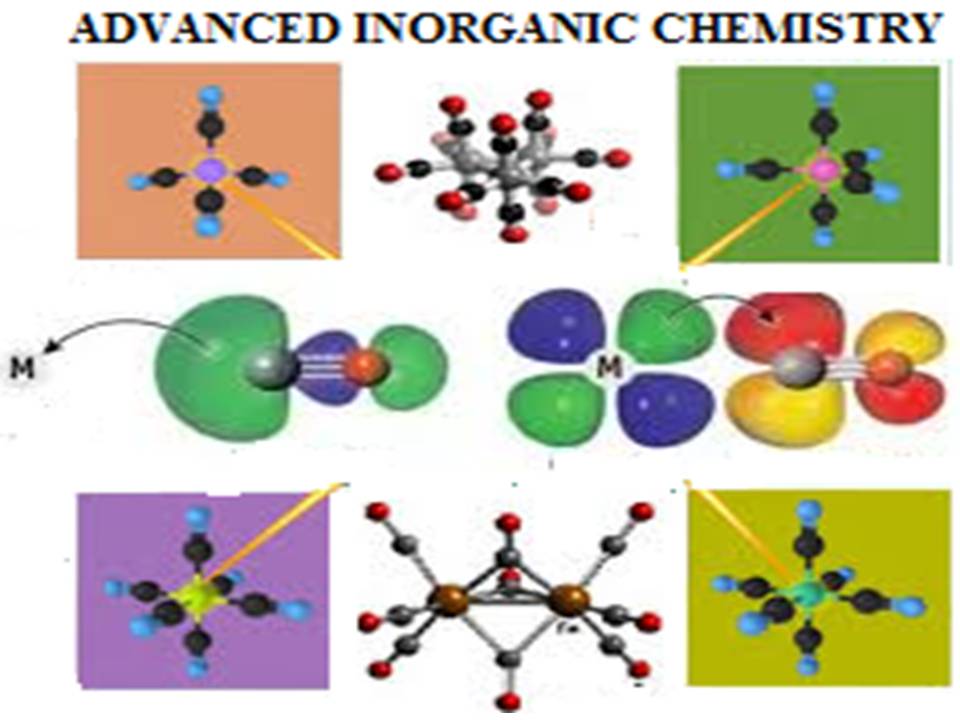
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Kavitha V
This course is aims to give a fundamentals of polymer characteristics and classification involved in a polymer reaction.This course is elaborated what are the types of polymerization reaction,mechanisms and properties. moulding process of polymers.
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the structure, isomerism, and bonding in coordination complexes.
CO2 - Deduce the crystal field splitting diagram for different geometries.
CO3 - Characterize the electronic spectra of metal complexes based on correlation diagrams.
CO4 - Evaluate the mechanistic pathway of metal complexes.
CO5 - Determine the stability of metal complexes using conventional methods. CO6 - Interpret the spectrum of different metal complexes with different geometries.
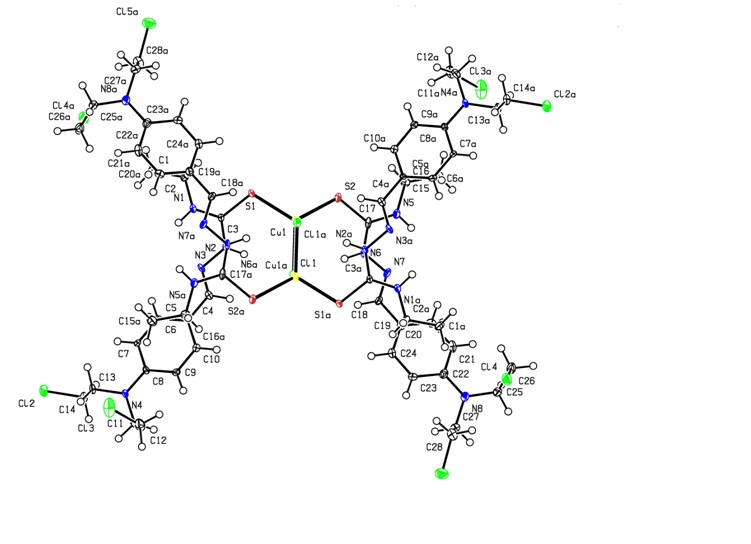
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
The course is designed for postgraduate students in chemistry to understand the organic reactions in natural systems and bio systems. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
- Analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions
- Elaborate on structural elucidation and chemical synthesis of alkaloids, terpenoids
- Understand the role of Supramolecules and their significance.
- Assess the importance of proteins and enzymes.
- Examine the action of drugs.
- Propose the structural activity for natural products.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To reinforce the concepts of 3D modelling.
- To enable them to experiment with forms, mapping, rendering and presentation techniques.
- To prepare the student for mass production of furniture for various classes of people with the parameters of economy and culture
SYLLABUS:
UNIT 1 MATERIAL AND PROCESSES IN DESIGN
Material Deposition Processes Laser Deposition, Micro-Plasma Powder Deposition, Chemical vapour Deposition, Micro Welding, Powder Casting Metal 3D Printing, Powder Deposition 3D printing;
UNIT 2 SUBTRACTIVE MANUFACTURING
Subtractive Processes Electrochemical machining, Electro-Discharge machining, Ultrasonic Machining, Laser Beam Machining, Water jet machining, Abrasive Jet Machining, Plasma Arc machining; Cutting and Removal Water Jet Cutting, Plasma Cutting, Laser Cutting, Electro-Discharge Wire Cutting; Abrasive Jet Cutting
UNIT 3 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Additive Extrusion Processes Extruded Filament 3D printing, Clay 3D printing, Stereo lithography; Special Purpose Manufacturing processes- Rot molding, Layer Compression, Sheet contouring, Friction Welding
UNIT 4 SURFACE TREATMENT PROCESSES
Surface Treatment Processes Laser Etching, Acid/Base Etching, Electro Chemical Etching, Sand Blast Etching, Ultraviolet Etching, Photochemical Machining Electro Chemical Polishing
UNIT 5 CONSTRUCTIVE ASSIGNMENTS
Demonstrate comprehensive understanding through accompanying assignments, group discussions, and site visits.
COURSE OUTCOME:
- Understand the various subtractive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Compare the various new technologies being incorporated into manufacturing processes
- Comprehend the various subtractive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Discuss the various additive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Analyse the various surface treatment processes in the manufacturing of interior design elements.
- Develop systematic design approach and space planning through manufactured furniture as elements of design.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To develop methods for critical thinking and analysis.
- To help the students develop opinions on various design-related topics.
- To develop new platforms and formats for their writing.\
- To examine how space is conceived and conceptualised
- To evaluate texts
- To investigate “visual language”, symbolism, and some of the pictorial devices, materials, and techniques employed by designers to tell stories visually
COURSE OUTCOMES:
- CO1 Explore innovative ways of researching and writing about contemporary design and culture.
- CO2 Create valid arguments and to argue for and against ideas
- CO3 Analyse structure of oral and written arguments
- CO4 Critically evaluate design ideas.
- CO5 Understand and apply various spatial representations for their own designs.
- CO6 Produce a booklet of the ideas and themes discussed.
SYLLABUS:
UNIT 1 COMMUNICATION PRINCIPLES
Process of Communication. Transmission of ideas, facts & figures from one person to another. Kinds of Communication: Oral and Written, Verbal and Non-Verbal. Levels of Communication: Intrapersonal, Interpersonal, Group, Mass Communication.
UNIT 2 READING DESIGN
Reading skills: Model of reading to learning, reading tactics and strategies, reading purposes – associated apprehensions, reading for meaning, reading outcomes; Reading Space and its qualities; Presentations and writings of great design theorists
UNIT 3 DESIGN STORYTELLING AND NARRATIVES
Elements of a good story: facts, situation, characters, plot and resolution of a design project; Building context in the design process: Emotional, Environmental, Social context; Organising ideas- Personas, storyboards, and flowcharts; Documenting processes through writing
UNIT 4 REPRESENTATION OF SPACE
Innovation with orthographic drawings- beyond the plan, elevation, section; Perspectives and Montages; Maps and Models; Interior space and its occupation, experience and perception; Constructing and interpreting layers of meaning within interior spaces.
- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To get an insight into various products and accessories used in Interior Spaces.
- To understand relevant products designed according to user’s needs.
- To know about the role of accessories in interiors. Integration of accessories in interior design and stylistic development.
- To learn about the practical aspects of product design processes
COURSE OUTCOMES:
- CO1 Understand the role of product design and designers in our everyday environment.
- CO2 Analyse the various approaches to Product and accessories design for Interior Environments.
- CO3 Apply various human factors in the design of products and accessories.
- CO4 Develop approaches to design keeping practical aspects in mind.
- CO5 Approach towards Product Design in relation with various spaces
- CO6 Distinguish various design trends in the Indian and Global markets.
SYLLABUS
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
A brief introduction to Product Designing – Various elements – History of Product Design – Definition of Product Design, understanding of Product Design - Purpose of Product Design – Role of Product Designers. Design approaches in product and lifestyle accessories design with a focus on functionality, ergonomics, aesthetics, multiple usages etc.
UNIT 2 HUMAN FACTORS
Application of human factors data. Human activities, their nature and effects. Human response to climate. Visual, Auditory, Tactual, Olfactory human mechanisms, Physical space and arrangement. Evolving the strategy of design with integration of technical complexities and lifestyle influences. Development of the design of products and accessories to specific interiors and prevailing trends.
UNIT 3 DESIGN APPROACH
Design approach with limited constraints inherent in accessory products. Broad-based approach towards innovative design and application to multi products and multi-materials in manufacturing interior products and lifestyle accessories. Study of materials and processes adopted in accessories design. Stylistic development of interior products from the past to present with insight into technological advances and the influences of social, economic and political factors on their design. Form, Colour, Texture, Symbols, User-specific criteria, Material, Technology and recyclability, Packaging. Multiple Utility oriented approaches to Product Design.
UNIT 4 PRACTICAL ASPECTS
Consumer Motivations Identification of user needs and Driving Factors; Emotional Design, Sensibility, Social Ethics and Concerns; Market Gaps, Market-Oriented Innovation; Business Evolution Product Planning for the future, Disruptive Innovation; Basic understanding of construction principles, modelling, rapid prototyping, with broad orientation to the socio-cultural and historical context of the sector. Orientation to Indian as well as global context of interiors, trends and market.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To acquaint students with the basic elements/principles of design and visual art.
- Understanding the basic characteristics of different techniques, mediums and its practical applications.
- To develop a perspective of artistic and creative expression through experimentation with different tools, techniques and medium in two and three-dimensional visual art forms
UNIT 1 CONCEPT AND MEANING OF VISUAL ARTS
Definition and meaning of Visual Art; Categorization of Visual Art- Fine art, Contemporary arts, Decorative arts and crafts, Applied arts
UNIT 2 ELEMENTS AND PRINCIPLES OF VISUAL ARTS
Elements of Visual Art: color, form, line, shape, space, texture, and value; Principles of Composition of Visual Art: balance, emphasis, harmony, movement, pattern, proportion, repetition, rhythm, unity, and hierarchy.
UNIT 3 2 DIMENSIONAL ARTS AND FORMS
2D Methods & techniques; Drawing and Painting, Still life, Life drawing, Composition, Collage, Print making, Photography, Wall painting, Posters, Folk art forms, etc.
UNIT 4 3 DIMENSIONAL ARTS AND FORMS
3D Methods & techniques; Sculpture, Clay modelling, Terracotta, Carving and relief work, Paper Mache, Mask making, Construction (using waste materials), Pottery, Installations, Folk art forms, etc.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course the student will be able to:
CO1: Understand the categorizations of visual art.
CO2: Apply elements (line, shape, form, texture, color, value, and space) and principles (repetition, variety, rhythm, proportion, movement, balance, emphasis, and unity) in work that effectively communicates their ideas.
CO3: Identify and discriminate between types of shape (geometric and organic), colors (primary, secondary, complementary, intermediates, neutrals, tints, tones, shades, and values), lines (characteristics, quality), textures (tactile and visual), and space (background, middle ground, foreground, placement, perspective, overlap, negative, converging lines positive, size, color), and balance (symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial)
CO4: Interpret and analyse the use of proportion, rhythm, variety, repetition, and movement in their work and the works of others.
CO5: Comprehend the various three dimensional art forms.
CO6: Develop and apply skills using a variety of two dimensional and three dimensional media, tools, and processes to create works that communicate personal meaning.

- Teacher: Ramkumar R

- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
This course covers the characteristics of the Indian accounting environment and its financial reporting requirements for companies, and expands on advanced aspects of corporate activities, such as the Issue of Shares and debentures, redemptions, company final accounts, valuation of shares and goodwill and internal reconstruction, and provides comprehensive coverage of consolidation issues and equity investments.

- Teacher: Yamuna D
Course Objectives
- To Introduce the principle of light propagation through optical fiber
- To understand signal distortion mechanisms in the fiber
- To Introduce optical transmitters and receiver for the fiber and the fiber optic couplers, connector involved
- To Introduce optical network concepts and components involved and its applications

- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. Understand the microwave frequencies and derive the scattering parameter for the microwave network and to study and analyse the microwave system and components.
2. To study the characteristics of couplers and power dividers.
3. To study the microwave sources and solid state devices.
4. To measure the RF parameters and to study the functions of RF analyzers.
5. To study the system aspects of MIllimeter wave systems.
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Identify and formulate S matrix of microwave junctions.
CO2 - Explain couplers and power dividers.
CO3 - Classify the microwave tubes and explain their principle of operation.
CO4 – Perform microwave measurements and analyze the parameters.
CO5 - Analyze the basic radio receiver architecture.
CO6- Develop millimeterwave radio links for microwave transmission
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To acquaint the students with the construction, theory and operation of the basic electronic devices such as PN
junction diode, Bipolar and Field effect Transistors, Power control devices, LED, LCD and other Opto-electronic
devices, display devices and power semiconductors.
Ø To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semi-conductors and special semiconductor devices.
Ø To understand the method of biasing transistors.
Ø To familiarise the students with the analysis and design of Multistage Amplifier circuits.
Ø To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits of amplifiers and oscillators.
