Search results: 1467
Course Objectives
• To learn about wireless mobile communication standards and co-existence of 4G and 5G.
• To learn 5G network architecture, components, features and their benefits.
• To learn channel access methods, modulation and spectrum sensing techniques used in 5G wireless systems.
• To understand advanced wireless concepts such as Massive MIMO, Virtualized RAN and Network Slicing.
• To learn about mmWave communication systems and its use cases.
Course Outcomes:
On Completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 - Distinguish major mobile communication standards such as 3G, 4G and 5G
CO2 - Analyze various modulation and multiplexing techniques like OFDM, NOMA etc.
CO3 - Design system level architecture of 5G communication systems.
CO4 - Analyze spectrum sensing and sharing techniques in 5G systems.
CO5 - Assess the potential of mmWave spectrum for 5G applications.
CO6 - Apply the concepts of green communications in real life applications.

- Teacher: Dr. KRUTI DEEPA
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: MATHAN N
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
Course Objectives :
To explore the fundamental concepts of verilog
To understand systemVerilog data types and capabilities
To enumerate system Verilog RTL and abstraction
To analyze dynamic types and arrays for behavioral modeling
To evaluate System Verilog Assertions for design and verification
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1: Understand the digital system designs skills using VERILOG HDL based on IEEE-1364 standards and managed by Open Verilog International (OVI)
CO2: Model digital systems in Verilog HDL at different levels of abstraction
CO3: Know the simulation techniques and test bench creation.
CO4: Demonstrate the skill on writing test-benches for design of digital systems and connecting them with the design.
CO5 Verify and Analyze the complete systems through robust verification methods such as assertion based verification.
CO6 Design and verify the digital systems such as FIFOs, memories, ATM interfaces, etc. using the learnt methods and demonstrate the skills.

- Teacher: MATHAN N
UNIT I IoT FOR HEALTHCARE
Architecture of IoT for Healthcare , IoT based Health Monitoring System using Arduino, Healthcare monitoring Technique for Diabetes Patients, Remote Patient Monitoring- IoT Heart Rate Monitoring, remote monitoring of physiological parameters, ECG, EEG, and BP.
UNIT II IoT ENABLED SMART CITIES
Smart Energy meters, Smart home powered by IoT, Smart Lightining, Smart Traffic Control ,Smart Grid and Solar Energy Harvesting, Intelligent Parking System.
UNIT III IoT FOR SMART AGRICULTURE
Smart Agriculture, IoT Based Agriculture, Animal Intrusion detection in farms, soil moisture detection and Irrigation system, Livestock monitoring system, IoT based Greenhouse Environment Monitoring and controlling
UNIT IV IoT BASED INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION
IoT based gas leakage monitoring system, Temperature and liquid level monitoring in boilers, Wireless video surveillance robot, Automatic Solar Tracker, IoT in Logistics Sector
UNIT V IoT FOR SOCIETY
Medical Waste Management, Weather update system with IoT, Women security system,wearable glove to enable sign to speech conversation, IoT based air pollution meter, Improved productivity of staff and reduced human labor

- Teacher: M Subramoniam .
- Teacher: DIGANTA DAS
- Teacher: Dr. ANNA DEVI E
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: VINO T
Course Objectives
• To Recognize Different Key Paradigms For Machine Learning Concepts
• To Familiarize With Various Classifiers Used For Machine Learning
• To Understand And Differentiate Among Various Supervised Learning Concepts
• To Become Familiarize With Data Reduction And Feature Extraction Methods
• To Apply Suitable Machine Learning Algorithms For Simple Engineering Problems

- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
Course Objectives
• To explore the fundamental concepts of Image Processing
• To become conversant with various Image Enhancement and restoration techniques
• To study and understand various Morphological and segmentation concepts and techniques
• To analysis the pattern classifier techniques for image understanding
• To design Artificial Intelligence (AI) based image classification systems
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1- Apply Suitable Mathematical Concepts For The Measurement Of Quality In Digital Images.
CO2-Analyze the Performance of Image enhancement and image restoration techniques.
CO3-Analyze Various Morphological Image Processing and Segmentation Techniques.
CO4-Identify Suitable Pattern Classifier for Object Classification Problems.
CO5-Implement AI Based Image Classification Systems.
CO6-Solve Real World Problems Using AI
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand and gain complete knowledge about the fundamentals of MATLAB programming.
To develop and translate mathematical concepts to MATLAB code.
To provide data analytic skills by processing and visualization of data’s.
To design and develop Simulink and MATLAB models for specific engineering applications
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Recall and recollect the basic programming fundamentals
CO2 - Understand various array arithmetic procedures
CO3 - Analyze and develop different control structures using MATLAB
CO4 - Evaluate different interactive plotting methods
CO5 - Identify the need for GUI based operations for real time programming.
CO6 - Design and demonstrate applications based on communication systems, controllers etc.
- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: Poonguzhali S
Course Objectives:
- To Present the mathematical, statistical, and computational challenges of building neural networks
- To study the concepts of deep learning
- To introduce dimensionality reduction techniques
- To enable the students to know deep learning techniques to support real-time applications
- To examine the case studies of deep learning techniques
- Teacher: Ishwarya C
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Gomathi V
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
Course Outcomes
Co1 – Articulate Ehealth And Its Regulations
Co2 – Explore Medical Data Analytics And Records
Co3 – Appraise Digital Transformation In The Field Of Medicine
Co4 – Analyze Ai In Health Care Systems
Co5 – Design System Level Architecture For Health Information Systems
Co6 – Deploy Android Application On Devices

- Teacher: Naresh Kumar Thapa
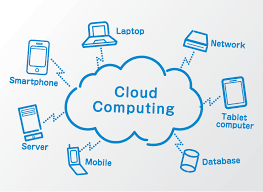
- The Internet of Things (IoT) involves the internet-connected devices we use to perform the processes and services that support our way of life.
- This Course provides an overview of Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud Computing concepts, infrastructures and capabilities.
- The course emphasises on the architecture, programming languages for IoT systems, different communication protocols and standards governing the system implementation and the migration of the data to the Cloud platforms for processing.
- Students will gain practical experience in the development of Cloud-based IoT systems and exposure to appropriate hardware and software platforms that underpin such development.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Design and interfacing of microcontroller-based embedded systems. High-level languages are used to interface the microcontrollers to various applications.

- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the components of embedded system and different communication protocols.
CO2 - Describe the differences between the general computing system and embedded system, also recognize the classification of embedded systems.
CO3 - Attain expertise with embedded system development and debugging tools.
CO4 - Apply the interrupt service mechanism in the design of embedded system.
CO5 - Design of real time embedded systems using the concepts of RTOS.
CO6 - Articulate the role of embedded systems in industry and provide feasible design solutions for given problem
statement.
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
To impart knowledge about the fundamental difference between general purpose and real time operating systems and thereby to learn the scheduling algorithms, porting and configuration of Real Time Operating System
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
This course cloud computing is specially framed for the students who are learning Embedded and IoT domain. On completion of the course, student will be able to articulate the main concepts, key technologies, strengths, and limitations of cloud computing. Identify the architecture and infrastructure of cloud computing, including SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, public cloud, private cloud, etc. They could able to demonstrate how storage and virtualization are used in the cloud platform and apply this in practice and also analyse the core issues of cloud computing such as security, privacy, and interoperability and evaluate various cloud computing solutions. They could able to suggest relevant cloud computing solutions according to the applications and also apply the fundamental principles of multi-tier web applications and services in a cloud environment.
This course covers Embedded-C programming of 8-bit & 32-bit microcontrollers and
IoT applications development using Python.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Real-Time Embedded Systems has to meet the severe time constraints imposed by critical applications. Real Time Operating Systems (RTOS) serve as a powerful and convenient software tool to develop time-critical embedded systems.
This Laboratory course provides a foundation for understanding the principles of RTOS and apply the concept of task scheduling, memory allocation and resource management in developing real-time systems.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Course Objectives
· To explore the fundamental
concepts of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
· To assess the applicability,
strengths, and weaknesses of the basic knowledge representation
· To impart machine learning
techniques
· To understand various CNNs
· To develop the solutions
for real-world problems using AI
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
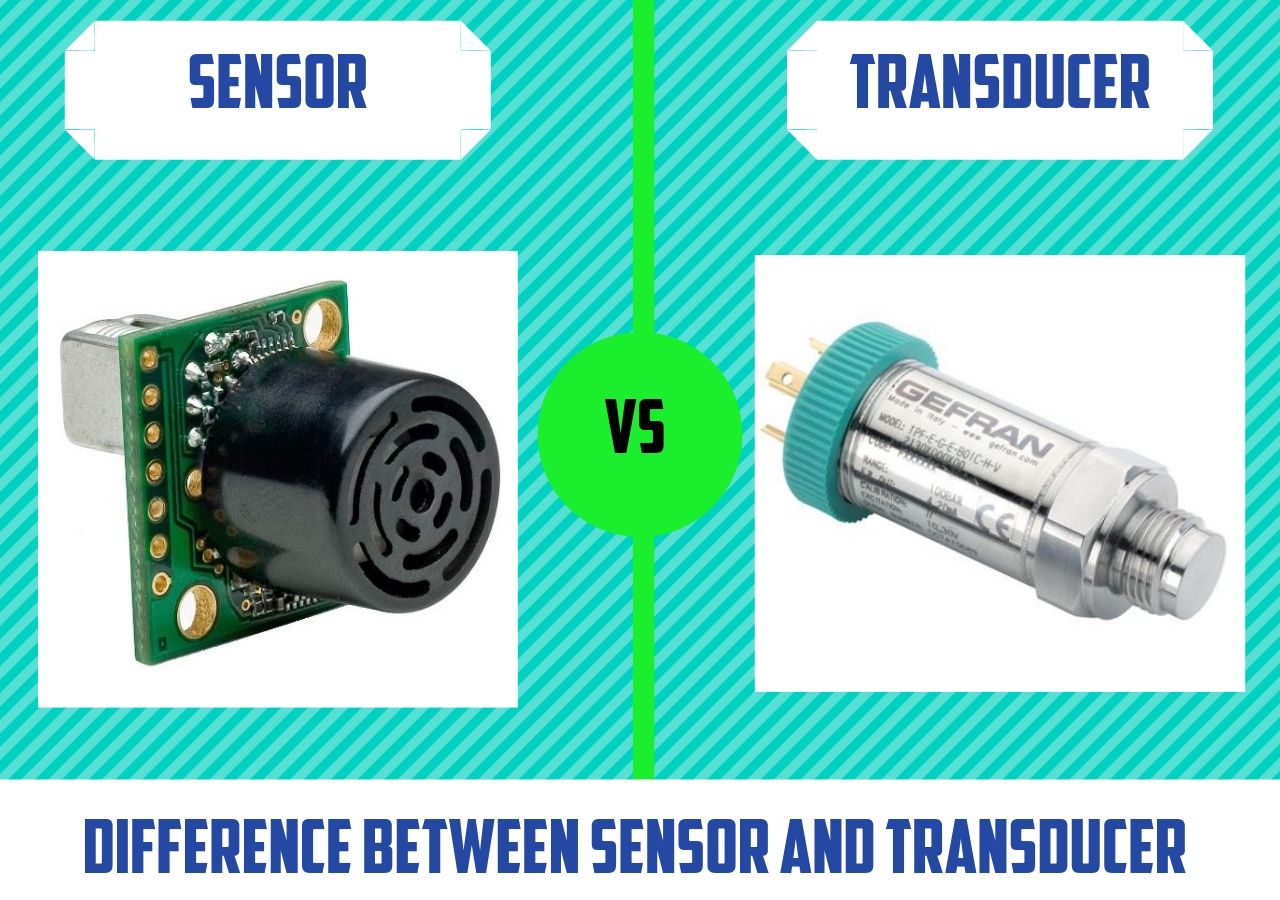
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To explain how digital circuit of large complexity can be built in a methodological way to acquire the knowledge about memory architectures.
- To illustrate how the concepts presented in the lectures are applied in practice, and how the need to accommodate different practically motivated trade-offs can lead to alternative implementations.
- To teach fundamental concepts of hardware description languages.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the steps for state table reduction and state assignment, ASM chart and ASM tables for the design of synchronous sequential design.
CO2 Determine the Real Time Challenges in the design of Asynchronous sequential circuits.
CO3 Elaborate the feasibility of sequential circuit design using PLA.
CO4 Evaluate the testing algorithms and perform the comparison study for digital circuits.
CO5 Design the Combinational logic circuits using VHDL.
CO6 Construct the low power sequential circuit using VHDL.

- Teacher: AISHWARYA K
- Teacher: EMIMAL M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: GEETHA P
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1- Minimize Boolean functions for computationally less complex implementations
CO2- Apply K map and tabulation method for minimization of Boolean functions
CO3 - Implement combinational logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO4 - Implement sequential logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO5 - Analyze the performance of various logic families
CO6 - Implement memory units with Programmable logic devices
- Teacher: JEGAN G

