Search results: 1467
• Understand and implement the most popular learning algorithms.
• Perform feature selection and experimental set up on real tasks
• Analyze in detail about unsupervised learning, dimensionality concepts and neural networks.
• Evaluate multiple learning algorithms across several Robotic tasks

- Teacher: LUBNA KALAM
- Teacher: NIVETHA S
COURSE OUTCOMES :
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Model various parameters in communication channels.
CO2 - Analyze the suitability of IEEE standards for specific applications.
CO3 - Correlate ISO-OSI and TCP/IP reference models.
CO4 - Develop suitable error detection and error correction techniques for reliable communication.
CO5 - Analyze various transport layer protocols for Real Time Applications.
CO6 - Develop suitable routing and congestion control algorithms for Real World Problems.

- Teacher: GOMATHI T
- Teacher: SUDHA R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
Course Outcomes
On
completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1-Apply the mathematical concepts to compare
different types of optical fibers, modes and configuration.
CO2-Analyze
the transmission characteristics of optical fibers.
CO3-Examine
the optical sources and detectors for use in optical communication system.
CO4-Construct
launching and coupling of optical fibers.
CO5-Design
high speed optical communication networks.
CO6-Design wireless
communication system using Li-Fi.
- Teacher: JEGAN G
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand and gain complete knowledge about the fundamentals of MATLAB
programming.
- To develop and translate mathematical concepts to MATLAB code
- To provide data analytic skills by processing and visualization of data’s.
- To design and develop Simulink and MATLAB models for specific engineering
applications.
- Teacher: M Subramoniam .
- Teacher: MOHANA PRIYA G
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: AISHWARYA K
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Nandhitha N M
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: GEETHA P
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
· To study the fundamental concepts of robotics.
· To impart knowledge on various sensors & actuators.
· To acquire the concept of kinematics and inverse kinematics.
· To understand basics of deep learning and reinforcement learning
· To learn about applications of AI in robotics
COURSE OUTCOMES
After Completion of the course the students will be able to:
CO1: Classify robots based on their geometrical configurations
CO2: Analyse Robot Motion using forward and inverse kinematics
CO3: Apply Deep Learning techniques for robotic perception
CO4: Analyse the performance of DLNN in localization strategies of Robots
CO5: Apply Reinforcement Learning techniques for Robotics Motion Control
CO6: Formulate AI algorithms for given automation task.
- Teacher: RAJSHREE A
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSINI R
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
1. To reinforce the mathematical foundation with advanced topics.
2. To enable the student to appreciate the engineering aspect of mathematics.
3. To equip the student with tools to confront continual mathematical.
4. To understand probabilistic models and their applications.
5. To expose the students to different Transform techniques.
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To Understand the Architectural Overview of IoT
To Understand the IoT Reference Architecture and Real-World Design Constraints
To Understand the various IoT Protocols
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Choose appropriate hardware components for implementation of IoT applications.
CO2 - Analyze various IoT Application layer Protocols.
CO3 - Implement IoT-based systems for real-world problem
CO4 - Demonstrate state of the art methodologies in data representation and analysis.
CO5 - Apply appropriate IP based protocols and Authentication Protocols for IoT communication.
CO6 - Analyze security issues in IoT Communication
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Pandian R
To have a knowledge on basics of cloud
To provide students basic understanding and virtualization.
To discuss some scenarios of clouds in organizations
COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Articulate the main concepts, key technologies, strengths, and limitations of cloud computing CO2 - Analyze the core issues of cloud computing such as security, privacy, and interoperability.
CO3 - Develop applications based on public cloud and private cloud architectures.
CO4 - Demonstrate how storage and virtualization is carried out in the cloud platform.
CO5 - Create virtual machine based applications for real world problems.
CO6 - Apply the fundamental principles of multi-tier web applications and services in a cloud environment.

- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: MATHAN N
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Identify the main challenges associated with machine-to-machine communications with respect to the status quo in networking today.
- CO2 - Describe the standards, protocols and algorithms that are used to address the challenges in M2M communications.
- CO3 - Develop an understanding of edge and fog computing for data aggregation, filtering and detecting anomalies
- CO4 - Design and build a network based on the client server, as well as how to publish/subscribe to connect, collect data, monitor and manage assets.
- CO5 - Develop device, gateway and server-side scripts and apps, enabling them to aggregate and analyze sensor data
- CO6 - Analyze and suggest suitable application-layer protocols and web services architectures for a seamless integration of various components within an IoT ecosystem.
- Teacher: MATHAN N
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To learn about the security issues in IoT and cloud computing.
Ø To learn about the cryptography solutions and issues in IoT.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF IoT ECOSYSTEM
IoT security issues, how to design an IoT system, Hardware, software and network security related to IoT systems. Basics of cryptographic solutions to IoT systems.
UNIT 2 OVERVIEW OF CLOUD COMPUTING AND ITS SERVICES
Cloud Computing Fundamental: Cloud computing definition, private, public and hybrid cloud.
Cloud types; IaaS, PaaS, SaaS.
UNIT 3 CHALLENGES IN CLOUD COMPUTING
Benefits and challenges of cloud computing, public vs. private clouds, Role of virtualization in enabling the cloud.
UNIT 4 SECURITY CONCEPTS IN CONTEXT TO IoT DEVICES
Security Concepts: Confidentiality, privacy, integrity, authentication, non-repudiation, Virtualization.
UNIT 5 IoT SECURITY THREATS AND COUNTER MEASURES
System-Specific Attacks: Guest hopping, attacks on the VM (delete the VM, attack on the control of the VM, code or file injection into the virtualized file structure), VM migration attack, hyper jacking.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. David Etter, “ IoT Security: Practical guide book “ Create Space, 1st Edition, 2016.
2. Drew Van Duren, Brian Russell, “Practical Internet of Things Security”, Packt, 1st Edition, 2016.
3. Sean Smith, “The Internet of Risky Things”, O'Reilly Media, 1st Edition, 2017.
4. Brian Russell, Drew Van Duren, “Practical Internet of Things Security: Design a security framework for an Internet connected ecosystem”, 2nd Edition, 2018.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
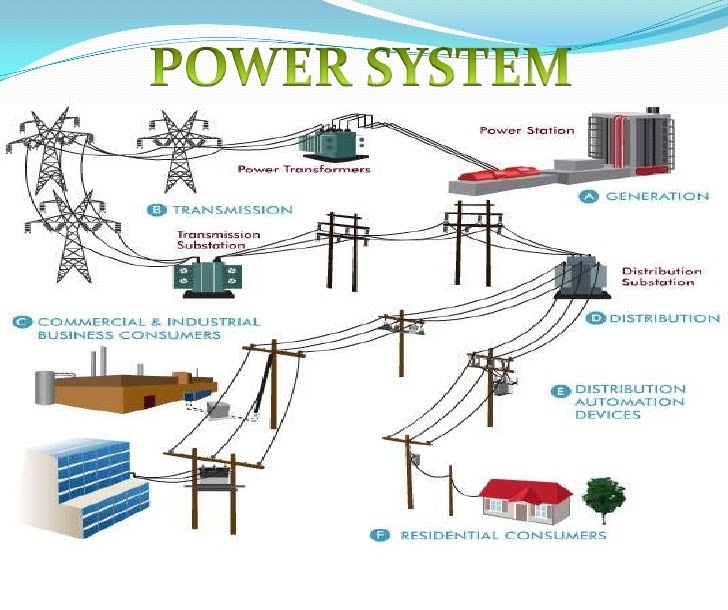
Power System Analysis is a blueprint of Power Systems. It discuss with per unit computations, Equivalent Circuit representations of all power system components, Impedance Diagram, Reactance Diagram, Symmetrical Components and Sequence Networks. It deals with the study of Power flow Analysis, Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical short Circuit Analysis, Stability Analysis.
Course Objectives
To impart knowledge in modelling of power system elements
To implement Numerical methods in power flow problem
To analyze the system in various faulted conditions.
To have a knowledge in stability and security of power systems
Course Outcomes
CO1: Model Impedance, Reactance networks and develop bus admittance matrix.
CO2: Examine load flow in a power grid using bus admittance matrix.
CO3: Examine fault currents and post fault voltages in symmetrical short circuit using bus impedance matrix.
CO4: Estimate fault currents and post fault voltages in unsymmetrical short circuit using symmetrical components.
CO5: Evaluate the stability conditions in power grid for minor and major disturbances.
CO6: Develop the mathematical solution for achieving stability in power grid during transient state.
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
To understand the various applications of electronic devices for conversion and control of the electrical power.
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ÿ To analyze the electromechanical system.
ÿ To impart knowledge in construction details, principle operation and performance characteristics of DC machines and transformer.
ÿ To evaluate the different losses and performance of DC machines and transformer using different testing methods.
ÿ To analyze the performance characteristics of DC machines.
ÿ To impart knowledge in three phase transformer connection.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
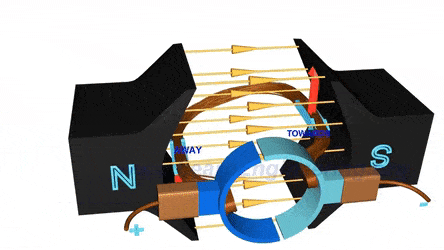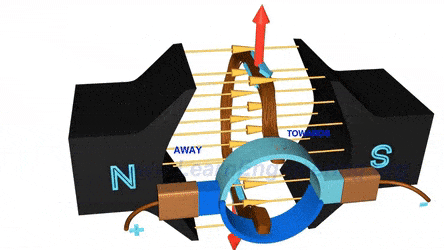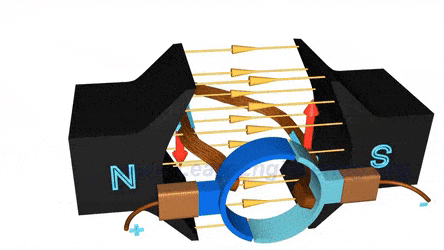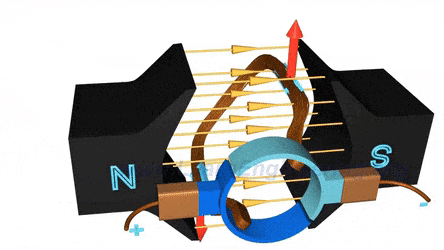
CO1 - Understand the concept of magnetic circuits.
CO2 - Explain the principle, types, effect of armature reaction and commutation of DC generator.
CO3 - Analyze the performance characteristics of DC motor using various testing methods.
CO4 - Understand the principle, equivalent circuit and performance of a single phase transformer.
CO5 - Compare the saving of copper of auto transformer with a two winding transformer.
CO6 - Analyze the various transformer connection for specific application.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge about the basic ideas and principles of Electrical Engineering.
To provide knowledge for the analysis of basic DC, AC and magnetic circuits.
To determine the response of electrical circuits using various network theorems.
To gain knowledge about the working of various machines.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
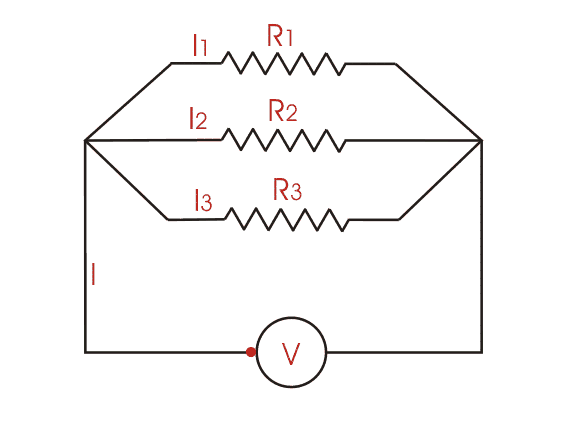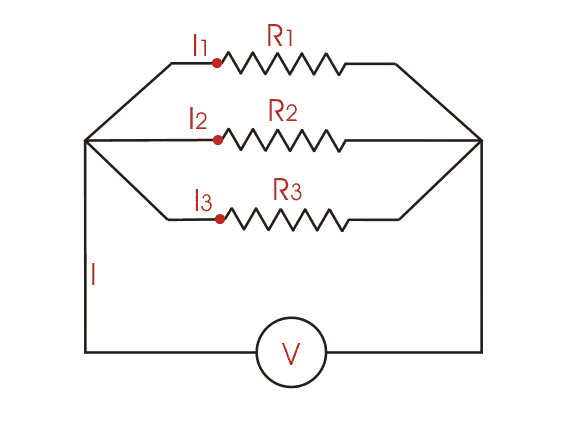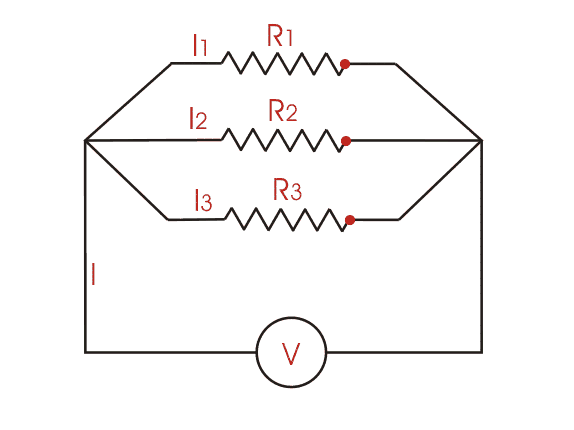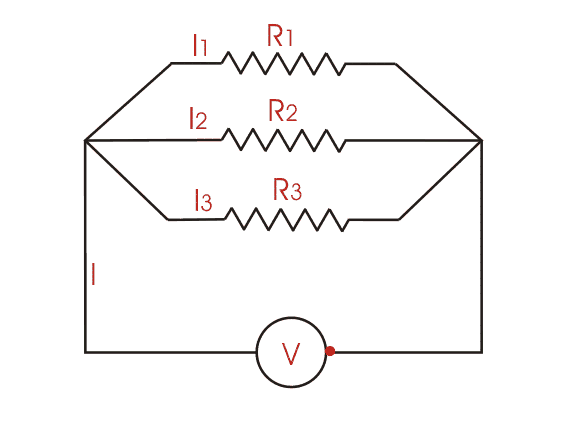
CO1 - Analyze electrical circuits using Kirchoff’s Laws and its application
CO2 - Compare the behavior of R, L and C and their combinations in AC circuits.
CO3 - Apply various network theorems for the analysis of electrical circuits
CO4 - Understand the basic concepts of magnetic circuits
CO5 - Describe the construction and working principle of DC and AC machines
CO6 - Demonstrate the various types of stepper motor.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on Construction and principle operation of Asynchronous and Synchronous machines.
To impart knowledge on not self-starting AC machines.
To convey knowledge on speed control of three-phase induction motors.
To analyze performance characteristics of Synchronous and Asynchronous machines.
To convey knowledge on synchronized operation of an Alternator with an Infinite bus bar.
UNIT
1 SYNCHRONOUSGENERATORS 10 Hrs.
Constructional features - EMF Equation - Armature Reaction - Synchronous Reactance - Voltage Regulation -Synchronous Impedance Method - MMF and Potier Methods - Synchronising & Parallel Operation - Two Reaction Theory - Determination of Xd and Xq (Slip test).
UNIT 2 SYNCHRONOUS MOTORS 9 Hrs.
Principle of Operation - Starting Methods - Effect of Increased Load with Constant Excitation - Effect of Changing Excitation on Constant Load - Different Torque - Power flow equation - Phasor diagram - V and inverted V curves - Hunting and suppression methods.
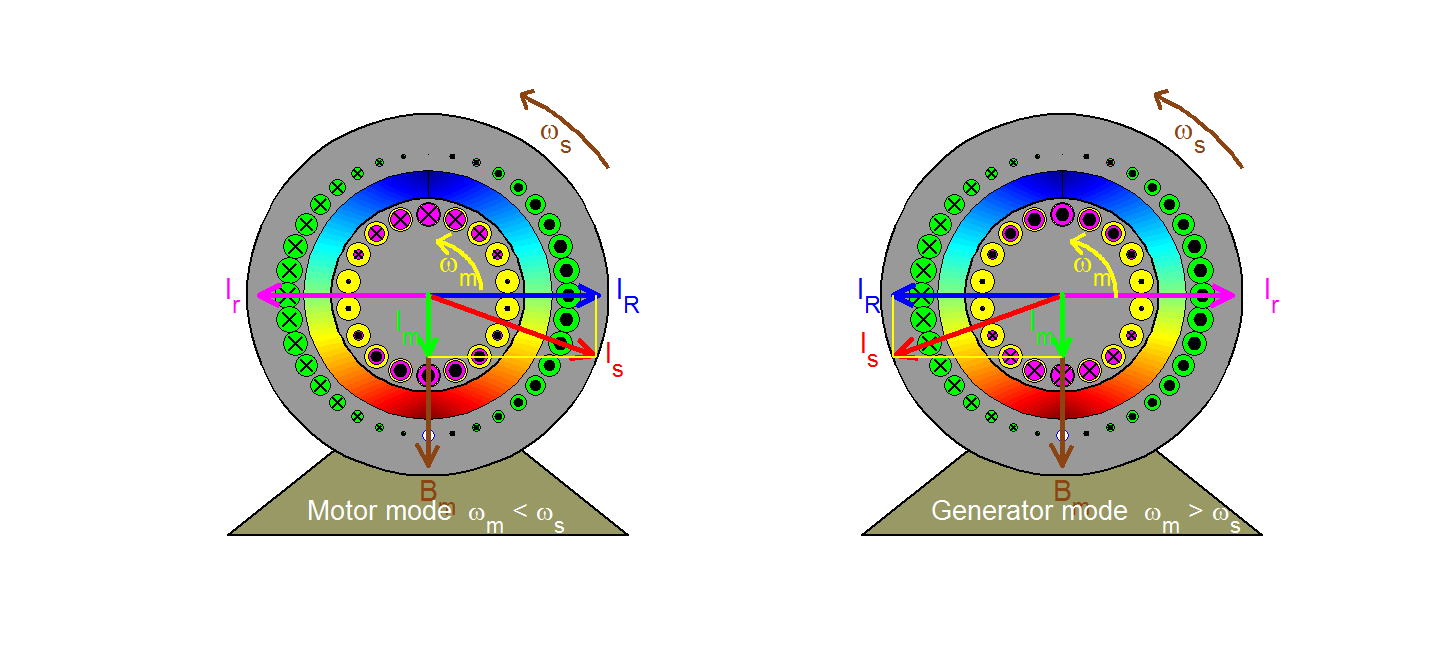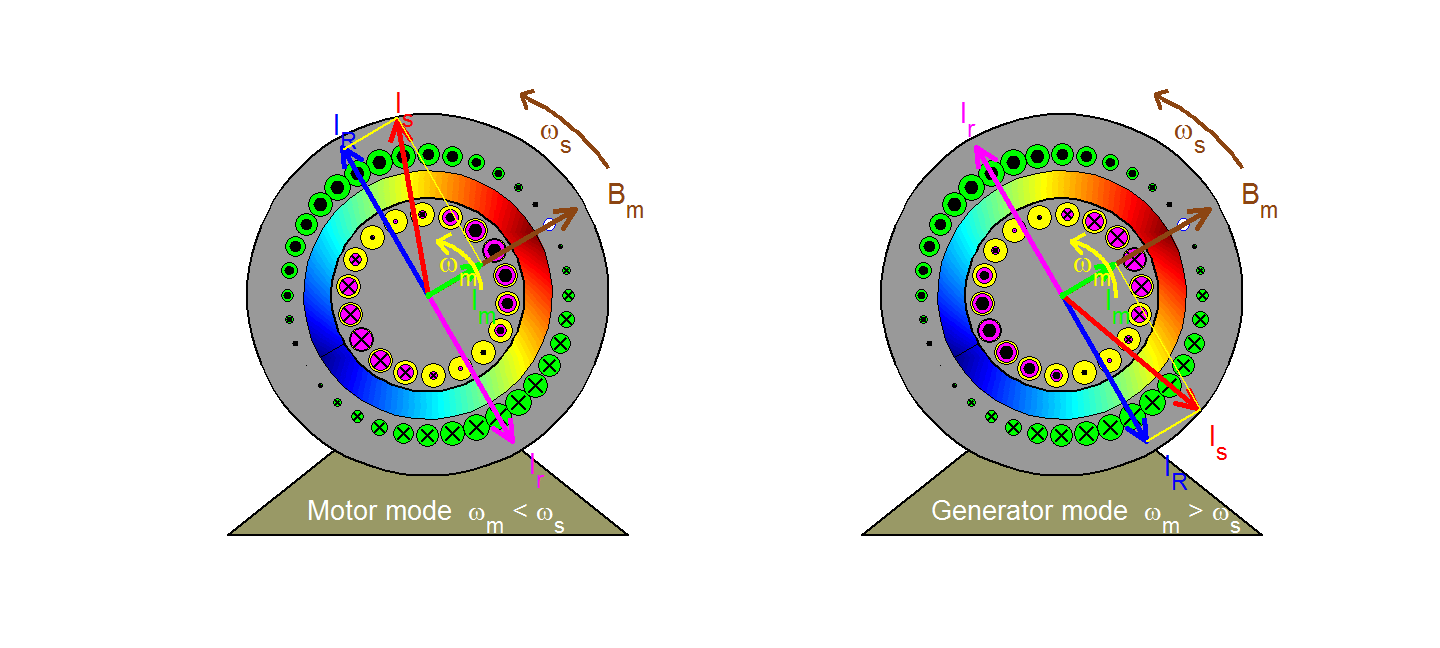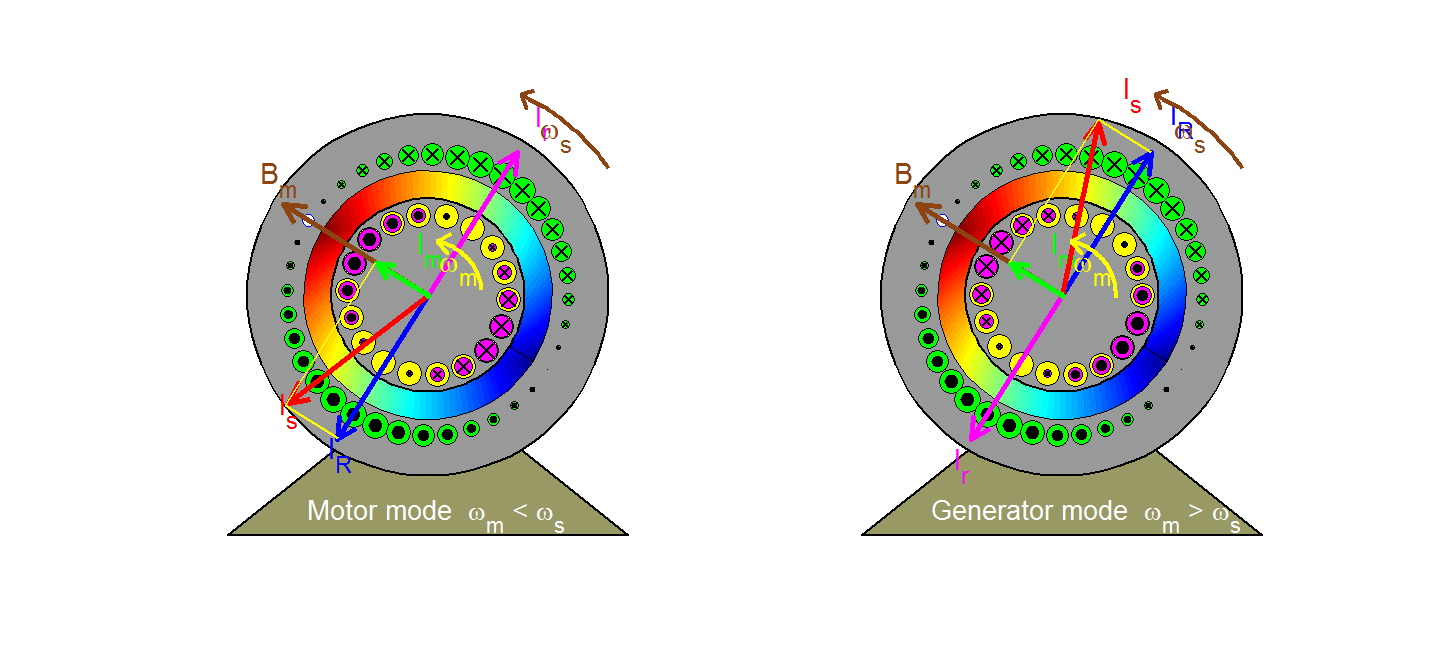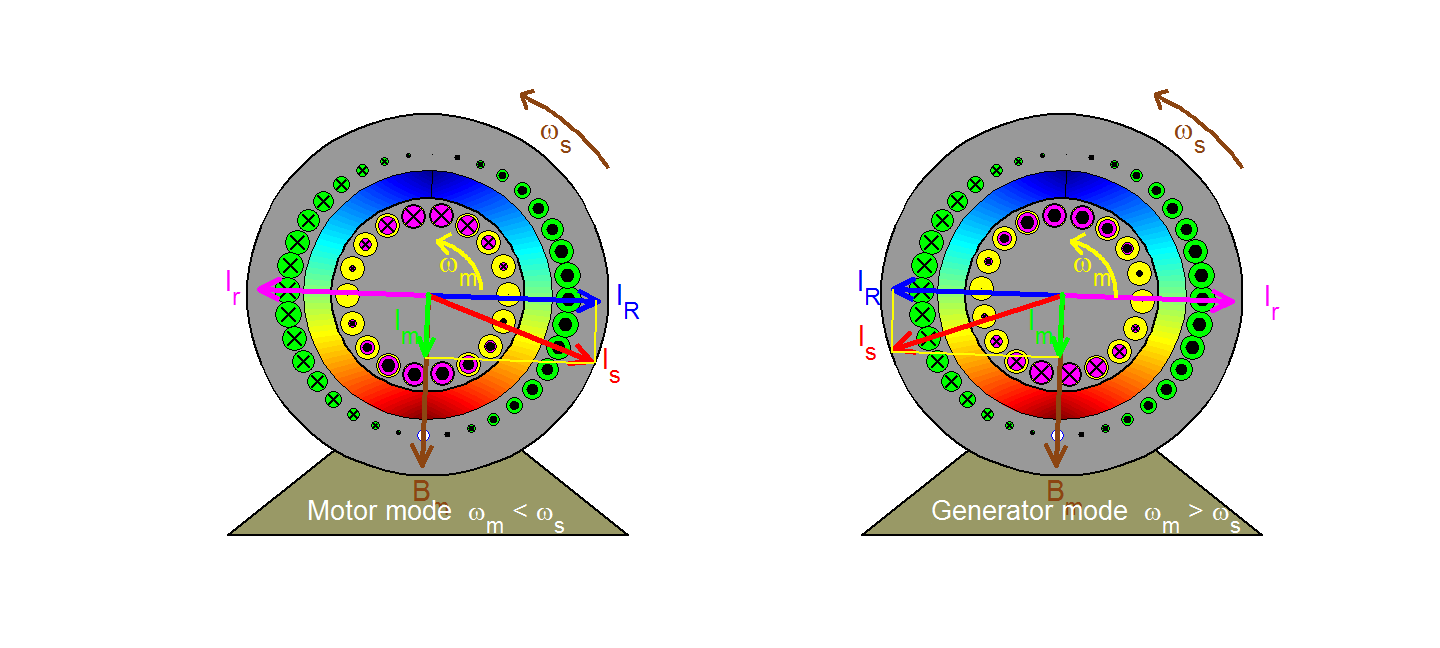
UNIT 3 THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTORS 9 Hrs.
Construction - Types of 3- Phase Induction Motors - Rotating Magnetic Fields - Torque Equation – Condition for Maximum Torque - Slip, Torque Slip Characteristics - Power Stages in Induction Motors - Losses and Efficiency - Plugging - Cogging and Crawling - Concept of Induction Generator.
UNIT 4 CIRCLE DIAGRAM AND CONTROL METHODS OF 3- PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 9 Hrs.
No load and Blocked rotor tests - Equivalent circuit - Construction of Circle diagram - Starting methods - Speed control - Double cage Induction motor.
UNIT 5 SINGLE PHASE AC MOTORS 8 Hrs.
Double Field Revolving Theory - Types of Single Phase Induction Motor - Equivalent Circuit (Qualitative) -Repulsion Motor - Series Motor - Universal motor, AC Servomotor, Linear Induction Motor, Hysteresis motor. Max. 45 Hrs.