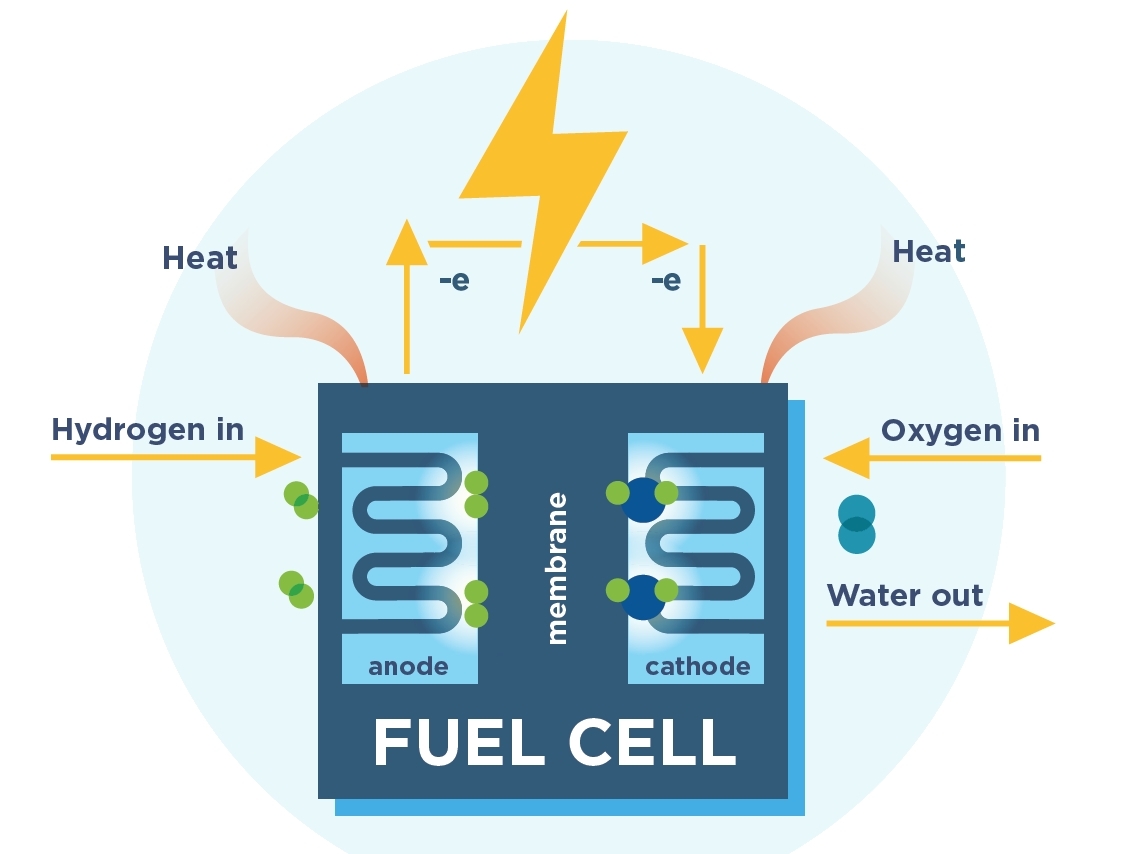
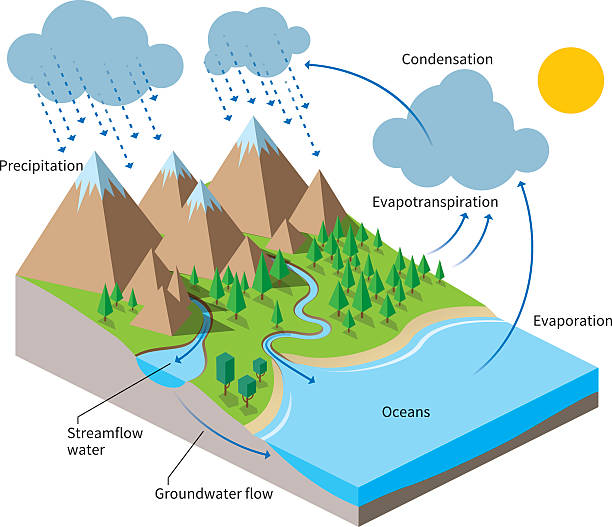
Search results: 360
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B

- Teacher: annieangelinepreethi .
- Teacher: Shamini G I
- Teacher: Indhu R
- Teacher: Surender R
- Teacher: Poonguzhali S
- Teacher: MERLIN MARY JENITHA
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B
- Teacher: Pandian R

- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Packialakshmi S
- Teacher: Director Admin
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
- Teacher: Prince Mary S
- Teacher: Padmapriya R

- Teacher: Aishwarya S

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
Animal biotechnology is the use of science and engineering to modify living organisms. The goal is to make products, to improve animals and to develop microorganisms for specific agricultural uses. Examples of animal biotechnology include creating transgenic animals (animals with one or more genes introduced by human intervention), using gene knock out technology to make animals with a specific inactivated gene and producing nearly identical animals by somatic cell nuclear transfer
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
- Teacher: THAMILSELVAN R
- This course is aimed give an understanding about the basics of biochemistry dealing carbohydrates, Amino acids, Lipids, nucleic acid and vitamins.

- Teacher: Jayashree S
- To ensure students to gain knowledge about the structure, properties and functions of biomolecules.
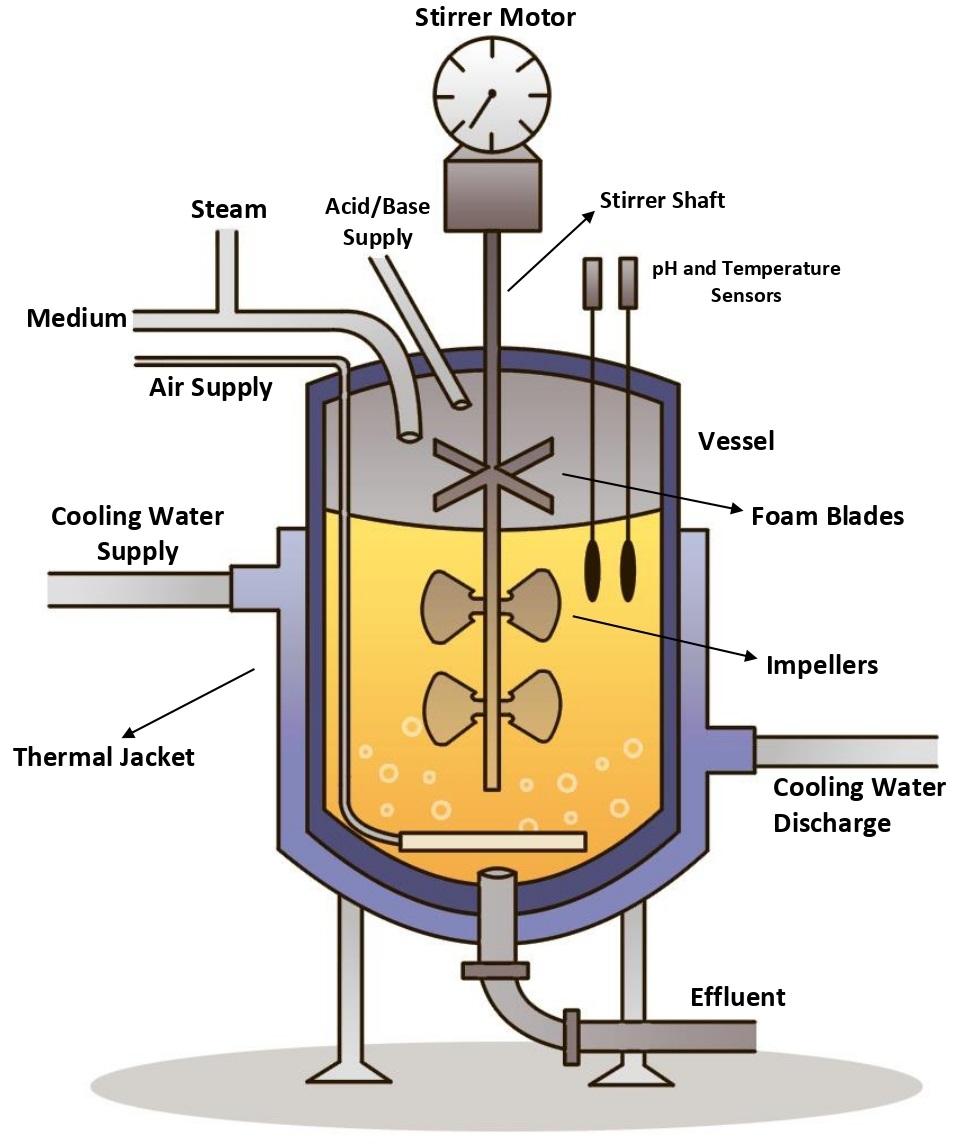
To develop the skills of the students in design operation, medium design, fermentation process, and metabolic stoichiometry.
To understand the modern industrial biotechnological process, sterilization, and growth kinetics of
microorganisms.
- Teacher: Prakash P
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: UMA MAGESHWARI L
- Teacher: Megavarnan R
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: RAVI T
- Teacher: Thaj Mary Delsy T
- Teacher: VINO T
- Teacher: Vijayakumar V

- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- Teacher: Bharathi M L
- Teacher: Sivagami P
- Teacher: Pandian R
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
- Teacher: Senthil Nayagam V
Course Objectives
To understand the method of biasing transistors.
To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits.
To understand the frequency response of amplifiers.
To provide foundation and confidence to the students to troubleshoot and fault analysis of power supplies and power amplifiers.
To develop current mirrors and differential operations.
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 – Design biasing circuits for BJT and FET.
CO2 – Analyze BJT and FET amplifiers using equivalent circuit models.
CO3 – Evaluate frequency response of BJT and FET amplifiers in different configurations.
CO4 – Design multistage amplifiers using BJT
CO5 – Analyze the performance of power supplies and power amplifiers.
CO6 – Design current mirrors and differential amplifiers
- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: SUBRAJA R
- Teacher: V.J.K.Kishor Sonti
- Teacher: Naresh Kumar Thapa
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
THIS COURSE SPEAKS ABOUT AND DEALS WITH THE VARIOUS TECHNOLOGICAL ASPECTS NEEDED IN HAND TO HANDLE AT EASE THE TECHY WORLD ALONGSIDE MASTERING ENGLISH.
- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
To understand and improve the knowledge of fermentation technology, growth kinetics, fermenter control
process, and various downstream process techniques.

- Teacher: Prakash P
- Teacher: SUFINA K

- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Esther Rajathi D J B
- Teacher: Shamili Devi G
- Teacher: Malavika J
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Swarnamughi K
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Kavipriya M
- Teacher: Mr. L. J. Binovin Lal, M. A., M. Phil., (Ph.D).
- Teacher: MRITTIKA MAITRA
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Dr. Safrine N
- Teacher: Aishwarya S
- Teacher: Anurekha S
- Teacher: Berlin Mary S
- Teacher: Nithyasri S
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
- Teacher: Thulasibala V
- Teacher: UMA MAGESHWARI L
- Teacher: SARASWATHI P.L
- Teacher: UMA MAGESHWARI L
- Teacher: SARASWATHI P.L
INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION -III B.SC PHYSICS-2019-2022
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
- Teacher: TWISHA SAIN
- Teacher: Dr. R PUGALENDHI -
- Teacher: Senthilkumar J
Course Objectives:
● To introduce the students to the body of literary writings that stands evergreen in the regions of Kenya, Africa,
Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Pakistan.
● To acquaint the students the various genres.
● To acquaint the students with different authors relating to different regions and literature.
● To make the students approach selected texts for their literary value and cultural importance.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Selvi M
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: RAJESH KANNA A
- Teacher: DR. ANU SUDHA PARAMASIVAM
- Teacher: PAVITHRA R
- Teacher: NACHIAPPAN SWAMINATHAN
- Teacher: PRAVDA CHIDAMBARANATHAN
- Teacher: Daflin Femi F
- Teacher: SAI CHARAN K.V
- Teacher: MELODY KHWAIRAKPAM
- Teacher: PRIYANKA M
- Teacher: Murali Balasubramaniam Arunachalakannan
- Teacher: Saranya Ramsridhar
- Teacher: Indu Bharkavi S K
- Teacher: Rajkumari Sriraman
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
Orthodontics is the branch of dentistry that corrects teeth and jaws that are positioned improperly. Crooked teeth and teeth that do not fit together correctly are harder to keep clean, are at risk of being lost early due to tooth decay and periodontal disease, and cause extra stress on the chewing muscles that can lead to headaches, TMJ syndrome and neck, shoulder and back pain.
- Teacher: Jyosthna A
- Teacher: VISWANATTH BALAJI
- Teacher: Hemamalini D
- Teacher: XAVIER DHAYANANTH
- Teacher: SHAHUL HAMEED FAIZEE
- Teacher: Ashwanthi K
- Teacher: MAYMA NATHASHA M
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA NANDHA
- Teacher: Santhosh Priya A K R
- Teacher: Vishnu Rekha Chamarthi
- Teacher: Dhanraj K
- Teacher: Sai Sarath Kumar K
- Teacher: SARASWATHI P.L
- Teacher: Sumaiyya S
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Yamini R
- Teacher: Dr. Sumathi H Rao
- Teacher: Dr Gayathri S
- Teacher: Shifa Fathima Shajahan
- Teacher: Geetha T
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Anu .
- Teacher: Pavani Bellamkonda
- Teacher: MANEESHWARI M
- Teacher: REESHMA RUCKSCHANDA
- Teacher: GOUSALYA V
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
Project - Digital Video Editing 2019 - 2022 Batch

- Teacher: RAJA N
- Teacher: Sankarakrishnan S
- Teacher: M V SRIKANTH
- Teacher: Pavani Bellamkonda
MICROWAVE NETWORKS AND COMPONENTS
POWER DIVIDERS AND COUPLERS
MICROWAVE SOURCES
MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS
MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETER WAVE SYSTEMS
- Teacher: JEGAN G
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To give the opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
- While upholding the standards of both national and international benchmarking in fashion design each student is required to design an individual collection reflecting originality creative flair with in-depth conceptualization and implementation of the design process combined with impeccable technical strength and quality.
- The focus is on global design with an Indian flavor that is an ideal blend of creativity with function and marketability.
- The Fashion Design Project will have to be carried out by each student in the eighth semester. The project will give ample opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
The guidelines for reference to develop design collection:
- The Fabric: Development and exploration of traditional resources (materials and techniques) towards contemporary expressions.
- The Image: Kaleidoscopic images encapsulated in time or space (History) to more globalized aspirations.
- The Attitude: From rejuvenation to revivalism- from transformation to transmutation- from the concrete to the sublime.
- The students may choose to specialize in any of the areas focusing on either women’s wear- menswear or children's clothing. Textiles may be combined with knits leather or any other suitable material while ensuring that the focus is on the extensive and prime usage of woven fabric.
The collection could fall in any one of the categories:
- . Sportswear
- Eveningwear
- Ethnic collection or Fusion
- Kids Wear
- Avant-Garde
- Theatre costume
- Institutional clothing or
- Any other category approved by the mentor

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
- Teacher: Anderson A
- Teacher: Vijayan M
Please upload your completed, verified, signed M. Tech Dissertation. Strictly adhere to the guidelines given for submission of the project report, No deviation is permitted.
End date: 05 May 2022
- Teacher: Premkumar J
UNIT 1 PREREQUSITES TO EVALUATE AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Properties of earth’s atmosphere and standard atmosphere, Forces and moments acting on a flight vehicle - Equation of motion of a rigid flight vehicle- Different types of drag – estimation of parasite drag co-efficient by proper area method- Drag polar of vehicles from low speed to high speeds.
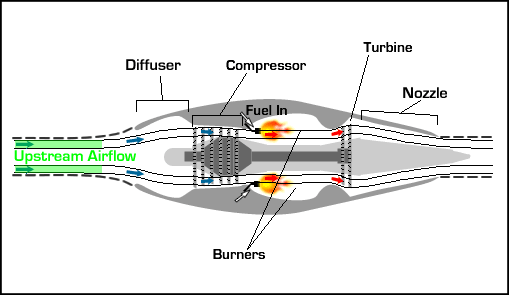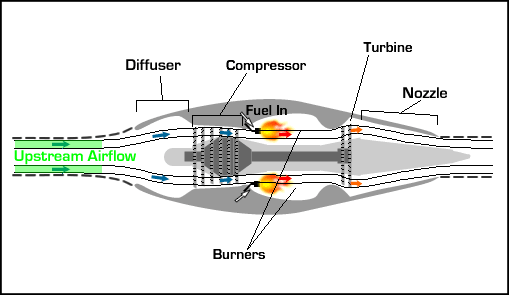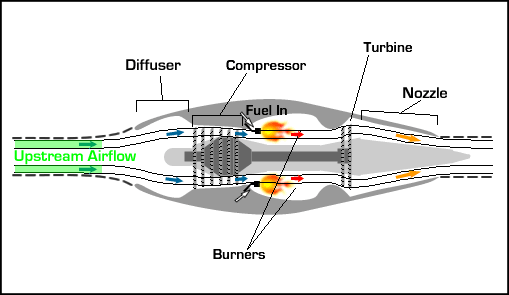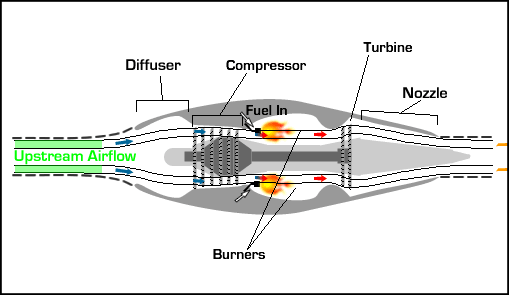
UNIT 2 ENGINE CHARACTERISTICS 9 Hrs. Variation of thrust, power with velocity and altitudes for air breathing engines – specific fuel consumption of piston engine and jet engine – ideal efficiency of engines- power plants for flight vehicles – limitations of power plants with Mach number and altitude.
UNIT 3 EVALUATION OF UN - ACCELERATED FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Airplane performance in steady level flight - Power available and power required curves. Maximum speed in level flight - Conditions for minimum drag and power required - steady climb descent and glide performance. Climb and Glide Hodograph, Range and Endurance. .
UNIT 4 ACCELERATED AND MANOEUVERING FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Accelerated level flight - Climbing and gliding flight, Maximum rate of climb and steepest angle of climb, minimum rate of sink and shallowest angle of glide –Take off – Landing-Turning performance. Bank angle and load factor – limitations on turn - V-n diagram.
UNIT 5 FLIGHT TESTING METHODS TO EVALUATE PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Flight - testing: Altitude definitions, Speed definitions, Air speed, altitude and temperature measurements. Errors and calibration. Measurement of engine power, charts and corrections. Flight determination of drag polar. Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the need for ISA.
CO2 - Analyze the flight performance with variations of pressure and density with altitude.
CO3 - Estimation of total drag and drag polar that influence the performance.
CO4 - Analyze the performance in un-accelerated flight conditions.
CO5 - Determination of speed limit, load limit, landing and takeoff distances of the aircraft.
CO6 - Know different testing methods to evaluate aircraft performanc

- Teacher: KEVIN BENNETT S
- Teacher: Dr. ANAND T
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
Course Objectives:
• To be able to fix, process, embed tissues and make sections for micro section studies
• To be competent to make routine cytological preparation
UNITI Introduction to Histopathology and Cytopathology Techniques – Basic concepts and principles. Applications
UNITII Reception of specimens– Criteria, Requisites, Container, Identity, Labeling, Rejection
UNITIII Tissue processing- Micro techniques I
Basic steps, Fixing – Types of fixatives, Factors, Dehydration, Embedding
UNIT IV Micro techniques II
Microtomy, Staining, Mounting, Methods of decalcifications
UNIT V Equipment
Microscope, Microtome -Types, Uses, Parts, different types of microtome knives, care and maintenance, Automated tissue
processor- components, working and precautions during use, Tissue floating bath
UNIT VI Staining
Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, preparation of hematoxylin and eosin stains, Reticulin stain, PAP staining- components and
methods.
UNIT VII Cytology
Introduction to FNAC and Exfoliative cytology, Processing of fluids- Sputum, bronchial aspirates, bronchial washings, gastric
washings, Urine and other watery fluids, Cerebrospinal fluid
UNITVIII Museum techniques
The mounting of pathological specimens - Introduction., Preparation of specimen, Fixation of specimen- Kaiserling solution-1 and Kaiserlingsolution-2, Precaution taken for the Fixation of Specimens, Storage of Specimens, Mounting of Museum Specimens, Filling and Scaling
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Identify the basic structure of cells, tissues and organs and describe their contribution to normal function.
CO2 Interpret light- and electron-microscopic histologic images and identify the tissue source and structures.
CO3 Demonstrate common histology procedures such as embedding tissue in paraffin, tissue sectioning and
mounting, or routine staining of tissue sections
CO4 Describe common histology laboratory procedures used to prepare stained slides from tissue samples.
CO5 Outline the principles of histochemistry, and types of microscopies utilized in histology
CO6 Understand professional procedures in museum display, collections, care and preservation
Reference books
1. Bancroft's Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques by John D Bancraft /Edition 8 (2018)
2. Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Techniques: Including Museum Techniques / edition 3 (1974) by C. F. A. Culling
3. Hand book of Medical laboratory technology, 2nd edition by Robert H Carman, Christian Medical Association of India
(publishers)
4. Textbook of Medical Laboratory Technology/ edition 3 (2020) b
- Teacher: Premkumar J
- Teacher: Sudhakar T
• To introduce the concept of quality management
• To apply the significances of analyzers in automation
UNIT I Automation - Introduction, meaning, advantages, history
UNITII Continuous flow analyzers, Single channel continuous flow analyzers-advantages, disadvantages
UNIT III Multi channel flow analyzers, discrete auto analyzers - basic features, types, semi automated, fully automated Batch
analyzers
UNIT IV Random access analyzers (RAA), Component steps in fully automated analyzers, Auto analyzers based on
immunoassay techniques
UNIT V Micro particle enzyme immunoassay (MEIA), various random access analyzers - Hitachi- 704, BM/Hitachi -717
UNIT VI Centrifugal analyzers, ASCA, Dry chemistry analyzers, Dimension RxL clinical chemistry system, The
Heterogeneous Immunoassay module components, Beckman Array 360system, Mini Vidas analyzers
UNITVII Immulite automated immunoassay analyzers, Latest trends in Automation
UNIT VIII Biochips, Lab on a chip (LoC), Nano sensors - advantages and disadvantages, PCR & its applications.
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 Understand the principles of automation.
CO2 Identify role of automation in flow analyzers.
CO3 Recognise the types of analyzers and their significance.
CO4 Apply the theoretical understanding to practical usage.
CO5 Recognise the latest trends and quality practices.
CO6 Bridge the gap between clinical and industry in theory and practice of automation.
Reference Books
1. Laboratory management – Quality in Laboratory diagnosis – Candis A Kinkus, Demos medical publishers, 2011
2. Quality control in Laboratory – Gaffar Sarwar Zamman, Intech open publishers, 2011
3. Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods, Henry 23rd edition, 2016
- Teacher: James John
Course Objectives:
· To learn the basic histological and cytological procedures
· To understand the diagnostic applications of histological and cytological methods
List of Experiments
1. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining
2. PAP staining
3. Embedding
4. Microtome: Uses, care, and parts
5. PAS stain
6. Pearls stain
7. Reticulin stain
8. Giemsa stain
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 Demonstrate proficiency and expertise in the proper use of the light microscope in examining histological specimens on glass slides
CO2 Understand the basic concepts of tissue fixation, dehydration, embedding, sectioning, staining, and mounting of slides for histological examination, immunofluorescent staining, and electron microscopy
CO3 Differentiate the characteristics of tissues of the body (epithelium, connective, muscle, nerve) and their relationships in the various organ systems of the human body
CO4 Identify the histological features of selected tissues/organ systems resulting from disease processes
CO5 Examine how certain diseases can be diagnosed using histological and cytological methods
CO6 Demonstrate common histology procedures such as embedding tissue in paraffin, tissue sectioning, and mounting, or routine staining of tissue sections
- Teacher: James John
COURSE OBJECTIVES :
To learn the basic procedures
in coagulation studies
To apply techniques in the storage and handling of blood specimens
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
Course Objectives:
• To understand the basic quality laboratory processes
• To apply the quality control tools
1.
Demonstration of various
methods of quality control- Preparation of Quality control charts, a) Levy-
Jennings and b) Cusum charts
2. Demonstration of various methods of quality control- Westgard Rules to verify trends, biases, or errors in quality controls
3. Sources of error, variation, and their correction methods, CAPA - corrective action & preventive action, Intrinsic and extrinsic and random errors
4. Centrifugation techniques Basic principles, procedure, and working mechanism centrifugation techniques (zonal, differential, density gradient, and isopycnic centrifugation)
Lab-Separation of blood WBC using fycoll reagent
5. Chromatographic techniques- Principles and working procedures of various chromatographic techniques (Column, ion exchange, Gas –liquid, affinity, molecular- exclusion, thin layer, adsorption, and partition)
Lab Demonstration of Paper chromatography
6. Electrophoretic techniques- Principles and working procedures of various electrophoresis (Gel electrophoresis (vertical, horizontal)- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)-SDS and isoelectric focussing)
Lab- Demonstration of gel electrophoresis
7. Molecular techniques Isolation of DNA, RNA, Plasmids, and protoplast
Lab- Demonstration of DNA extraction and quality check.
8. Principle and QC procedure for lab instruments- parts, principle, maintenance, and care of microscope. microscope, incubator, Hot air oven, Autoclave, Centrifuge, Colorimeter, Spectrophotometer, Flame photometer, Refrigerator, pH meter
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 Understand the basics of Quality control.
CO2 Demonstrate the needs of Quality assurance and Quality management
CO3 Acquire the knowledge about costs and errors involved
CO4 Explore internal and external quality control
CO5 Analyze the current trends in laboratory accreditation
CO6 Apply the methods and tools of Quality control in laboratory
- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
In this course, we will be learning about various theories, philosophies and design processes characterizing the works of contemporary masters.
It allows an architect to consider a buildings or cities as more than a visual phenomenon and therefore the architect would have a more fundamental and culturally inclusive approach to architecture than an approach based purely on architect's own taste or style.

- Teacher: Arulmalar Ramaraj
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To develop an understanding of the advanced building services such as Air conditioning and fire safety and their application in the design of multi-storey buildings.
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
- Teacher: RAJESH KANNAN S
- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
- Teacher: Ramkumar R
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
- Teacher: Mohana Gopiraj N
- Teacher: Selvendiran S.G
- Teacher: Guruji V
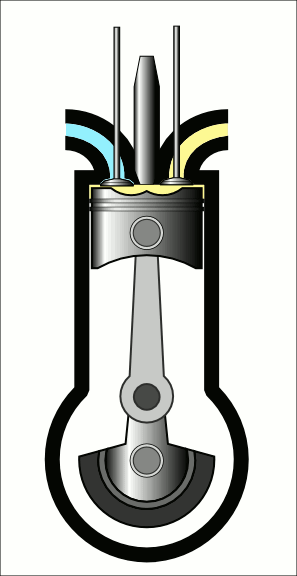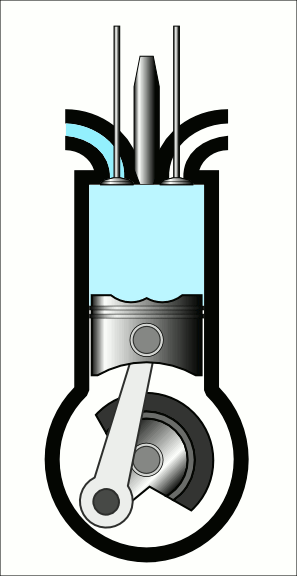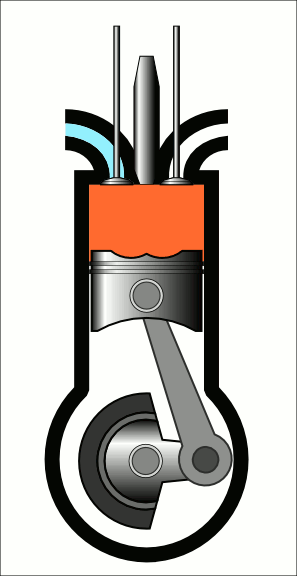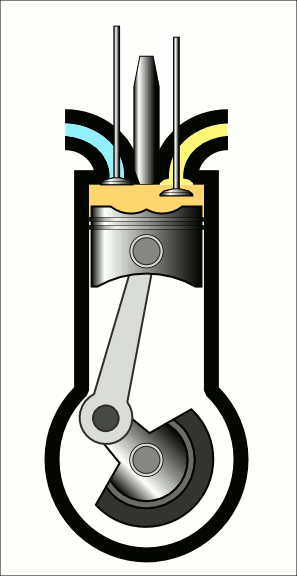
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Understand the diesel engine construction and its operation.
Understand the fuel injection system in CI Engine.
Gain knowledge on air motion & combustion phenomena in CI Engine.
Understand turbo charging and engine management system in IC Engines.
Understand CI engine performance.
Understand the principle of modern engine technology.
- Teacher: Dr. Ashwin Jacob
- Teacher: PURUSOTHAMAN M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Impart the knowledge of fundamentals of heat transfer
Deep understanding on the governing equations for convection heat transfer and the dimensionless parameters
Understand the temperature distribution and heat transfer rate in engine components
Familiarize with cooling system and measurement of heat transfer rate in IC engines

- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
- Teacher: JINO L
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
TO UNDERSTAND THE CONCEPTS OF RESEARCH
TO PROVIDE AN INSIGHT INTO THE TECHNIQUES OF RESEARCH
TO LEARN THE REQUISITES OF WRITING A RESEARCH REPORT

- Teacher: PALANI A
- Teacher: Rajeswari A
- Teacher: Bhavya B
- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: Dr JOHN PAUL M
- Teacher: LAVANYA M
- Teacher: Shahinabegum M
- Teacher: JOYCE S
- Teacher: Priyanka T
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR

- Teacher: Andrew George Dev .
- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: JAYASEELY M
- Teacher: UMAMAHESWARI S

- Teacher: Sailaja A
- Teacher: Nikkath Fathima G
- Teacher: Dr Sasirekha K
- Teacher: Kaavya K
- Teacher: Dr JOHN PAUL M
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
- Teacher: Geetha R
- Teacher: MD DANISH RAZA
- Teacher: JOYCE S
- Teacher: UMAMAHESWARI S
- Teacher: DHIVYA SATHISH
- Teacher: S SHANTHINI
- Teacher: Chinta Shriya
- Teacher: SANDHYA V

- Teacher: Dr. Moli Ghosh
- Teacher: Sairamya K
- Teacher: JOHN BRITTO M
- Teacher: REYYA PAWANI
- Teacher: SANDHYA V
- Teacher: Priyanka T
- Teacher: Nikkath Fathima G
- Teacher: DR. RANI J
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: P HAMEEM KHAN
- Teacher: Kalidasu K
- Teacher: Nivetha P
- Teacher: Dr Kishore Raaj S
- Teacher: PALANI A
- Teacher: Pujaa D
- Teacher: Yamuna D
- Teacher: Nivedhitha K.S
- Teacher: Nivetha P
- Teacher: Krishnakumari S
To gain knowledge about the fundamentals of management.
To understand the tools and techniques of the various aspects of management.
To apply management concepts in decision making.

- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
- Teacher: MD DANISH RAZA
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B
- Teacher: Kalidasu K
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi S
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Jesia Persis Preethi
- Teacher: Prabhakar Singh
- Teacher: Devi B
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
- Teacher: Haribabu R
- Teacher: Sankarakrishnan S
- Teacher: UMA MAGESHWARI L
- Teacher: MALATHY BALARAMAN RAVINDRRAN
- Teacher: Dr.PRATHIBA GNANASEKARAN
- Teacher: Revathy Rajendran
- Teacher: Priya Sathish
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To empower the students in the life sciences, who may have a pertinent scientific question that can be readily answered by computational techniques

- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Amit Kumar .
- Teacher: Manisha Koyimadatha
To introduce extensive knowledge in cell structure, functions, cell signaling pathways and transfer across membranes in cells.
To learn about the transmission, distribution, arrangement, and alteration of genetic information and how it
functions and is maintained in populations.
- Teacher: Krishnakumar S
Course Objectives:
1. To acquire knowledge about the various medical imaging techniques
2. To understand the fundamental principle and working of the medical imaging systems
involved in the diagnosis of health care
3. To apply different classical image processing techniques to different types of medical images
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to–
1. Demonstrate Knowledge and understand the basic image processing concepts such as relationship between pixels, basic transformation and color models
2. Implement image enhancement techniques in spatial and frequency domain for accomplishing image preprocessing task.
3. Evaluate and select image filtering techniques for image restoration process
4. Illustrate the steps involved in segmentation process and Morphological operations to solve a given medical image task.
5. Analyse the performance of image compression methods.
6. Recognize and assess how image processing techniques can be applied across all medical imaging modalities and applications.
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
- Teacher: Premkumar J
Big data is a phrase(like software development or testing) which describes about capturing, storing, querying, updating and analyzing of huge data sets that are so voluminous and complex that traditional data-processing application software are inadequate to deal with them.
Course Objectives:
- To understand the basics of Hadoop, MapReduce, Pig Latin
- Gain experience looking at analytics from a strategic perspective


- Teacher: Selvi M
- Teacher: VANATHI M
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
- Teacher: Ancy A
- Teacher: Subha Lakshmi K
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
To Understand the fundamentals of Object Oriented System Development
To understand the object oriented methodologies.
To use UML in requirements elicitation and designing.
To understand concepts of relationships and aggregations.
To test the software against its requirements specification

- Teacher: Ancy A
- Teacher: Aishwarya B
Data Communication -III Year B.SC- CS V Semester with 4 Credits and 45 Hours Duration . Max Mark-100

- Teacher: Subha Lakshmi K
- Teacher: Aishwarya B
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: Shamili V
- Teacher: Saranya P
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: Shamili V
SBSA3009- NETWORK SECURITY
This network security course covers advanced topics such as Public Key Encryption (with a focus on the RSA algorithm), authentication methods such as message encryption and MACs, intrusion detection techniques such as statistical anomaly and rule-based detection, password management strategies, and virus, worm, and other malware protection. Furthermore, it delves into firewall design ideas, characteristics, and configurations for optimal network security.

- Teacher: Ancy A
- Teacher: Saranya P
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: Ancy A


|
|
9-10 |
10-11 |
11.15-12.15 |
12.15-1.15 |
|
Monday |
|
|
ABT |
|
|
Tuesday |
|
|
|
|
|
Wednesday |
ABT |
|
ABT |
|
|
Thursday |
|
ABT |
|
|
|
Friday |
|
|
|
|
|
Saturday |
|
|
|
|
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To develop knowledge and technical’s skills on bioreactors and its various types.
To make understand the knowledge on growth parameters such as structure and unstructured models
- Teacher: Prakash P
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
- Teacher: Prakash P
- Teacher: Prabhakar Singh
This subject deals with the basic introduction of chemical industries and equipment used in them. This subject also explains the process involved in separating products from raw materials.

- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
The main focus of the course is on Bio-Chemical and environmental science. Students in this course will analyze various energy forms, including forces, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, kinetic energy, energy efficiency and renewable energy.

- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
Mass Transfer-II covers the fundamentals and basic concepts of separation and purification of mass through its transfer from one phase to the other.

- Teacher: Sathish S
Plant Design
Economics Introduction
Time value of money
Depreciation
Balance sheet and income statements

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
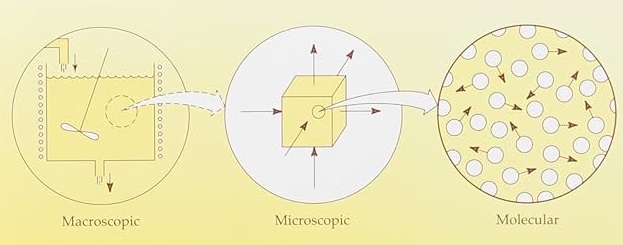
The subject deals with transport processes involved in fluid flow acquiring momentum, heat and mass flux. The subject also involves the Kinetics for microbial growth and measurement of the associated parameters through various kinetic models. Also the kinetic diffusion strategies is demonstrated using various equations and measurement techniques. Momentum, heat and mass transport share a very similar mathematical framework for fluid flow processes and the similarities between them are exploited to provide a deep understanding in microbial kinetic evaluations through different model equations.
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
Biochemical Engineering is a branch of chemical engineering that mainly deals with the design and construction of unit processes operations make use of microbial, animal and plant cells and components of cells such as enzymes to manufacture new products and destroy harmful wastes.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
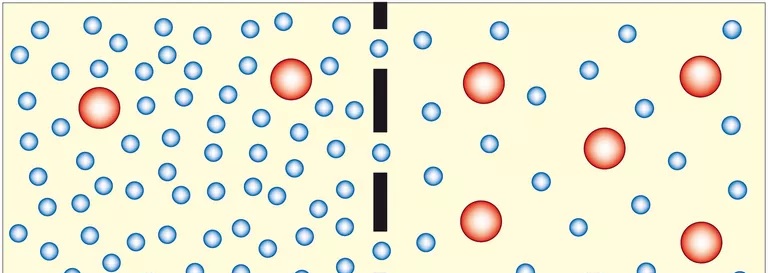
The study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems.
- Teacher: Sathish S
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai

- Teacher: Annam Renita A
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
Mechanism
Types
Prevention
Advancement
Case studies

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: MATHIYARASI M
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
Energy engineering or Energy Systems Engineering is a broad field of engineering dealing with energy efficiency, energy services, facility management, plant engineering, environmental compliance, sustainable energy and renewable energy technologies.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: GokulNath R
- Teacher: Dr.V.Sampathkumar .
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
- Teacher: Nirmala R
- Teacher: Packialakshmi S
- Teacher: Mohana Gopiraj N
- Teacher: Dr.Annamalai S
- Teacher: Priyanka T
Programming in c and c++ is a high level language.

- Teacher: Sundar Rajan G T
- Teacher: Sivagami P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Software process models and compare their applicability.
- Identify the key activities in managing a software project.
- Concepts of requirements engineering and Analysis Modelling.
- Apply systematic procedure for software design and deployment.
- Compare and contrast the various testing and maintenance.
- Teacher: Pravin A
- Teacher: Ronald Tony A
- Teacher: Yovan Felix A
- Teacher: hemalatha c
- Teacher: Deepa D
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: Albert Mayan J
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Kamalesh Murari Devakannan
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: Aroul Canessane R
- Teacher: Shalini R
- Teacher: Vignesh R
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the micro level dataflow in various units of computer.
CO2 - Demonstrating the impact of control memory operations and multi-process or characteristics.
CO3 - Examining the different types of memory and experimenting the mapping techniques.
CO4 - Select the suitable process scheduling technique for optimized function of operating systems.
CO5 - Critically upraising the deadlock in CPU and other memory management techniques.
CO6 - Design and Developing optimized architecture for stand-alone applications.
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
- Teacher: Deepa A
- Teacher: Viji Amutha Mary A
- Teacher: Shamreen Ahamed B
- Teacher: LAVANYA G
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
- Teacher: MERLIN MARY JENITHA
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Anandh Sree R
- Teacher: Asha R
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
- Teacher: LAKSHMI PRIYA S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To have an overview of different types of operating systems.➢ To learn and implement the concept of process management.
➢ To observe the concept of storage management.
➢ To understand the concept of I/O and file systems.
➢ To learn the basics of Linux Programming.
- Teacher: Mary Posonia A
- Teacher: Ruby Angel
- Teacher: Ankayarkanni B
- Teacher: Saravanan D
- Teacher: Ashok Kumar K
- Teacher: Mary Gladence L
- Teacher: Dr.Sridevi N
- Teacher: Maya Gopal P S
- Teacher: Ramya R
- Teacher: Subhashini R
- Teacher: POTHUMANI S
- Teacher: Prince Mary S
SCSA1503 - COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce two and three dimensional graphical structure.
- To design 2D and 3D methods and Models.
- To explore the visible surface detection with illumination and color models.
- To understand the concepts involved in multimedia and basis tools.
- To gain knowledge on Multimedia compression and animations.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1 : Identify the various line and circle drawing algorithm.
CO2 : Study the various transformations in 2D and 3D objects.
CO3 : Understand the concepts of curves and surface.
CO4 : Apply transformation and clipping algorithm in 2D and 3D objects.
CO5 : Design Illumination and color models.
CO6 : Implement 2D and 3D Transformation concepts in Real world Applications
SYLLABUS
UNIT 1 BASICS OF COMPUTER GRAPHICS 9 Hrs.
Output primitives- Survey of Computer Graphics- Overview of Graphics System- Line drawing Algorithm (DDA Line Drawing Algorithm, Bresenhams Line Drawing Algorithm)-Circle drawing Algorithm- Curve Drawing Algorithm- Attributes of output Primitives- Antialiasing.
UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 8 Hrs.
2D Transformation and other transformation – 2D and 3D Viewing- Line Clipping(Cohen Sutherland)– Polygon Clipping (Sutherland Hodgeman) – Logical Classification Input Function.
UNIT 3 3D CONCEPTS AND CURVES 10 Hrs.
3D Object: Representation Method- B-Rep- Sweep Representation- 3D Transformation – curve generation – Splines – Beziers – Blending of curves other interpolation techniques- Display Durves and Surface – Shape Description Requirements – Parametric function – 3D Concept Introduction – Fractals and Self Similarity – Successive refinement of Curves – Koch Curves and Paeno Curves
UNIT 4 METHODS AND MODELS 8 Hrs.
Visual Surface detection methods – Illumination models – Halftone Patterns – Dithering Techniques – Polygon Rendering Methods – Ray Tracing Methods – Color methods – Color Applications.
UNIT 5 MULTIMEDIA BASICS AND TOOLS 10 Hrs.
Multimedia Basics and Tools – Introduction to Multimedia – Compression and Decompression – Data and File Format Standards – Digital voice and audio video image animation- Introduction to photoshop- workshop tools- Navigating window – Importing and Exporting Images – Operations on Images – resize, Crop, rotate. Introduction to Flash – Elements of Flash Documents – Flash Environment- Drawing Tools – Flash Animation Importing and Exporting – Adding Sounds – Publishing Flash Movies.
Max. 45 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics C Version, 2 nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006.
2. Fabio Ganovelli, Massimiliano Corsini, Sumanta Pattanaik, Marco Di Benedetto “Introduction to Computer Graphics: A Practical Learning Approach” Taylor and Frainces Group. 2015.
3. Tay Vaughan ,”Multimedia”, 5th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2001.
4. Ze-Nian Li, Mark S. Drew ,”Fundamentals of Multimedia”, Prentice Hall of India, 2004.
5. D.P. Mukherjee , “Fundamentals Of Computer Graphics And Multimedia ” Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, 2006.
6. D. McClelland, L.U.Fuller, ”Photoshop CS2 Bible”, Wiley Publishing, 2005
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: SundaraVelarani K
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: DEVIPRIYA M
- Teacher: SANTHIYA P
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: AMSHAVALLI R S
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: sageengrana s
- Teacher: NITHYA SEKAR
- Teacher: Anandhi T
- Teacher: SUBATHRA G
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
CO1 : Comprehend machine learning solutions to classification, regression and clustering problems
CO2 : Understand the strengths and weaknesses of many popular machine learning approaches.
CO3 : Interpret the results of the algorithms.
CO4 : Select suitable model parameters for different machine learning techniques.
CO5 : Design algorithms for real world problems using machine learning algorithm.
CO6 : Gain experience of doing independent study and research.

- Teacher: Dr. Santha Sheela A C
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Mary Gladence L
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: Mercy Paul Selvan Paul selvan
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI PRIYA S
- Teacher: Revathy S
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: MERLIN MARY JENITHA
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: srividhya .
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: SUDHA D
- Teacher: Kamatchi KS
- Teacher: Asha R
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
- Teacher: Gowri S
- Teacher: POTHUMANI S
- Teacher: Sundar R
SCSA3015-DEEP LEARNING
- Teacher: Ruby Angel
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: VINOTHINI E
- Teacher: VANATHI M
- Teacher: SUDHA R
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
- Teacher: AMSHAVALLI R S
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: NITHYA SEKAR
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
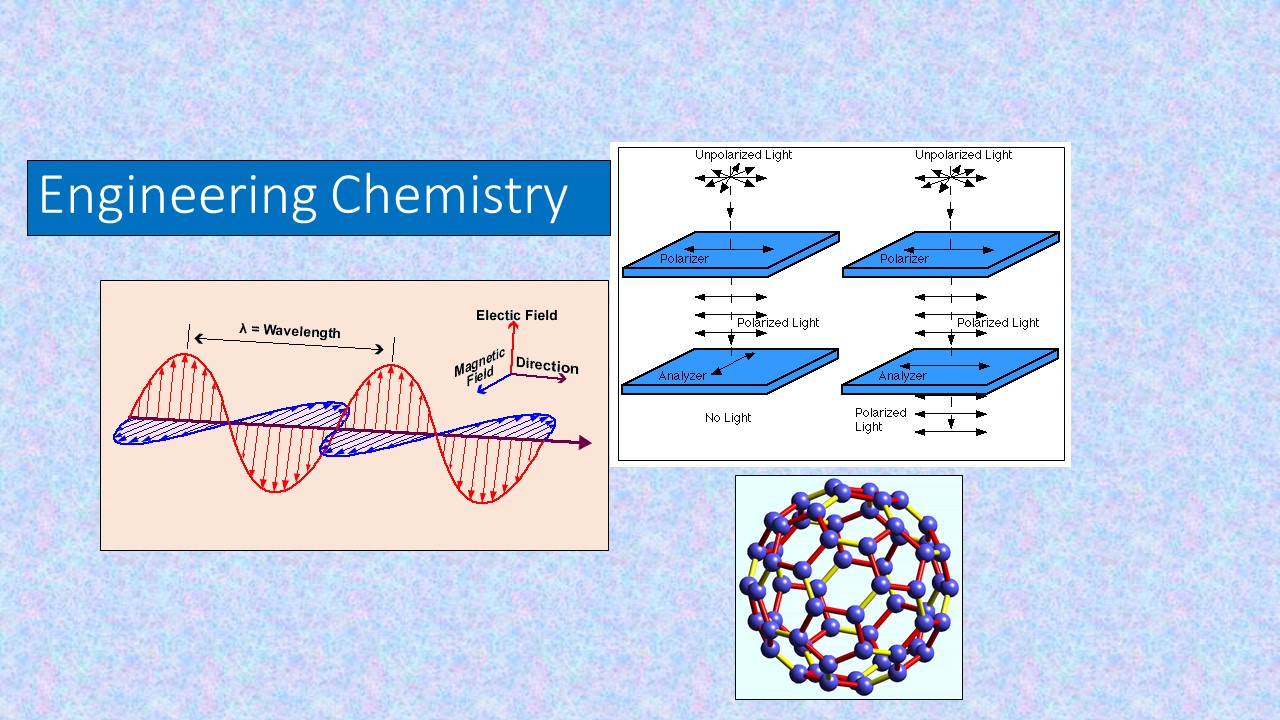
This course is designed for the budding engineers to understand the significance of chemistry which forms the basic foundation of engineering. The course comprises of five units dealing with all the aspects of material science. Bonds to bands explains the fundamentals involved in the bond formation to the band theory of materials which finds significant applications in engineering. Molecular spectroscopy involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with materials in order to produce an absorption pattern from which structural or compositional information can be deduced. Functional materials deal with charge transport carriers such as soliton, polaron and bipolaron in conducting polymers that are utilized in engineering molecular devices. Carbon materials emphasize the structure, properties, production of fullerenes, graphene, CNT’s and their applications in the field of health, stealth and energy. Engineering materials covers the importance of Phase rule, Fuels and nanoparticles in the engineering and medicinal field.
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
- Teacher: Vengatesh P
- Teacher: Sunitha S
The course is intended for undergraduate students in chemistry with an insight into organic compounds preparations and synthesis. The course will provide a platform in understanding the molecular rearrangements which pave way in their industrial applications. At the end of the course, the participants will be able to
To understand the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds containing O, N, S.
To synthesize the carboxylic acids along with their reactivity nature.
To develop the practice of learning molecular rearrangements along with their mechanism.
To discuss the importance of active methylene groups in organic synthesis.

- Teacher: Subhenjit Hazra .
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is framed for undergraduate chemistry students to bridge the conceptual ideas in analytical chemistry with practical experiment for better understanding. The course will create a platform for the students to undergo hands-on training in preparing the solutions with safe handling of chemicals and glasswares. The course promotes analytical skills among the students in quantitative and qualitative analysis. At the end of the course, the students will be able to
Acquire analytical skills in handling equipments , glassware and chemicals.
Compile, Analyze and interpret the volumetric data for calculation with greater accuracy and precision.
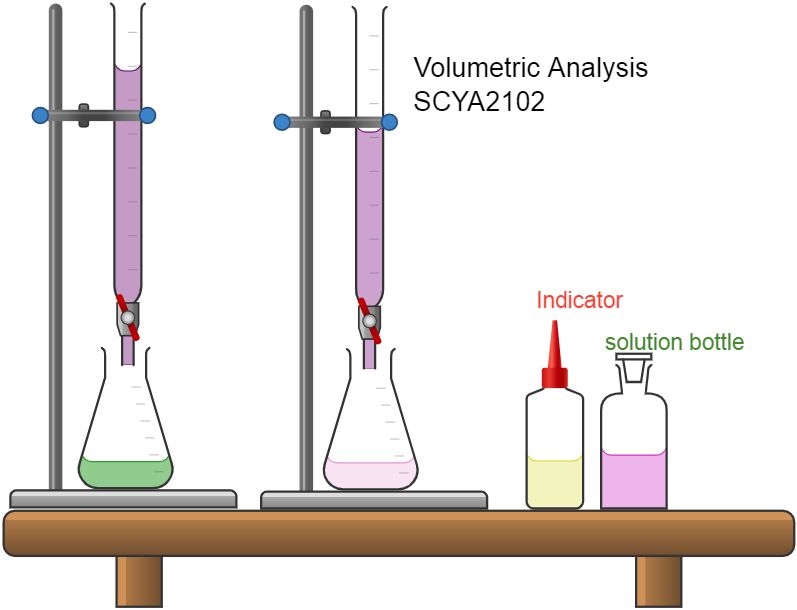
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Ramanjaneya Reddy G
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course will give an insight in understanding the strategies involved in designing a chemical reaction. and highlights the importance of oxidizing and reducing agents in functional group conversion reactions. It provides an platform in understanding the name reactions and molecular rearrangement in organic chemistry. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1) Construct a single step retrosynthetic pathway for organic reaction.
2) Interpret and design the products in organic chemical reactions.
3) Formulate and predict the products based on Metal-mediated organic chemical reactions.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
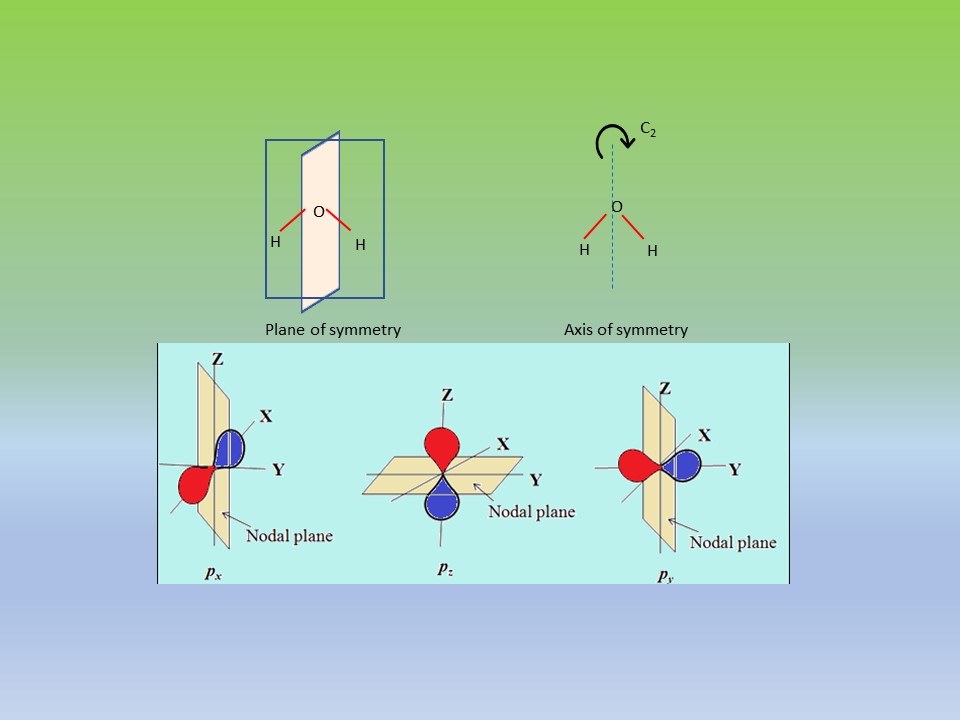
This course deals with the fundamentals of quantum chemistry in sub-atomic level such as wave properties, Uncertainty principle, de-Broglie hypothesis, Schrodinger equation, operators and eigen functions. Applications of quantum chemistry to one-dimensional harmonic oscillator, three-dimensional hydrogen atom, angular momentum and spin angular momentum, quantum numbers, shapes of atomic orbitals are discussed. Approximation methods- Perturbation and variation methods and its application to helium atom is dealt in a simplified manner. The latter part of the course covers the mathematical treatment of symmetry elements and point groups of molecules in predicting the chirality, chemical bonding, polarisability, molecular orbitals and spectroscopic transitions.
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Krithiga T
This practical course enables the students to understand the construction binary and ternary phase diagrams; to gain practical knowledge in the synthesis of nanomaterials; to know about the practical applications of uv-visible spectrophotometer; and to learn the use of Ostwald’s viscometer for molecular mass determination.
- Teacher: Krithiga T
On completion of the course the student will be able to
Elaborate on structural elucidation and chemical synthesis of alkaloids.
Discuss on structural determination and stereochemistry of terpenoids and carotenoids.
Explain on classification and properties of proteins and lipids.
Design the synthesis of proteins.
Analyze and compare the synthesis and properties of five, six and fused ring heterocyclic compounds.
Predict the structural activity of antibiotics and vitamins
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: Juvilasri Vignesh
- Teacher: Ramkumar R
- Teacher: RAJESH KANNAN S

- Teacher: Arhannaraju .
- Teacher: Sindhumeenaatchi .
- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
SEC1406 Programming in HDL
After the completion of course student will be able to
|
CO1 |
Understand the requirements of VHDL design flow |
|
CO2 |
Interpret the Verilog language elements and its relevance to digital design |
|
CO3 |
Apply the Modelling Styles for Simulation, Synthesis and Test Bench Creation. |
|
CO4 |
Analyze the Performance Study of Combinational and Sequential logic design using Verilog |
|
CO5 |
Evaluate State Machine and Memory designs by Verilog |
|
CO6 |
Create and realize the system in FPGA using Verilog |

- Teacher: VINO T
- Teacher: Shamini G I
- Teacher: Dr. SUMATHI M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: MATHAN N
- Teacher: RAVI T

- Teacher: Kanchana D
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: Dr.I.Rexiline Sheeba
- Teacher: Magthelin Therase

- Teacher: Bhuvana B P
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: PARUTHI ILAM VAZHUTHI P
- Teacher: PURUSHOTHAMAN S
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø Understand the architecture of Microprocessors and Microcontrollers viz. 8085,8086 and 8051
Ø Familiarize the students in writing assembly programming and interfacing with peripherals.
Ø Provide foundation and confidence to the students to solve real world problem using Microprocessors and
Microcontrollers
- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
To study the basics of Embedded System and the various development tools in Embedded System and to gain knowledge in Embedded programming and acquire knowledge in Embedded system applications
- Teacher: Kanchana D
- Teacher: Pandian R
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
- Teacher: JOANY R M
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
Course Objectives
• To learn about wireless mobile communication standards and co-existence of 4G and 5G.
• To learn 5G network architecture, components, features and their benefits.
• To learn channel access methods, modulation and spectrum sensing techniques used in 5G wireless systems.
• To understand advanced wireless concepts such as Massive MIMO, Virtualized RAN and Network Slicing.
• To learn about mmWave communication systems and its use cases.
Course Outcomes:
On Completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 - Distinguish major mobile communication standards such as 3G, 4G and 5G
CO2 - Analyze various modulation and multiplexing techniques like OFDM, NOMA etc.
CO3 - Design system level architecture of 5G communication systems.
CO4 - Analyze spectrum sensing and sharing techniques in 5G systems.
CO5 - Assess the potential of mmWave spectrum for 5G applications.
CO6 - Apply the concepts of green communications in real life applications.

- Teacher: Dr. KRUTI DEEPA
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: MATHAN N
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: Somasekar M
- Teacher: YOKESH V
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To gain knowledge in the designing of state space analysis.
- To obtain the state transition matrices and the solution of state equations.
- To design a state observer using the concept of controllability and observability.
- To have a clear understanding in Digital Data Systems.
- To have an exposure in different stability analysis of Nonlinear Systems

- Teacher: Meenakshi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To analyze the electromechanical system.
To impart knowledge in construction details, principle operation and performance characteristics of DC machines and transformer.
To evaluate the different losses and performance of DC machines and transformer using different testing methods.
To analyze the performance characteristics of DC machines.
To impart knowledge in three phase transformer connection.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the concept of magnetic circuits.
CO2 - Explain the principle, types, effect of armature reaction and commutation of DC generator.
CO3 - Analyze the performance characteristics of DC motor using various testing methods.
CO4 - Understand the principle, equivalent circuit and performance of a single phase transformer.
CO5 - Compare the saving of copper of auto transformer with a two winding transformer.
CO6 - Analyze the various transformer connection for specific application.
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
COURSE OBJECTIVES
· Pattern making concentrate on developing basic pattern of Children.
· Students will learn about Various drafting methods for Children’s garments

- Teacher: Savithiri S
FASHION PSYCHOLOGY AND GROOMING
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To enable students to understand the trends in Clothing behavior
- Gain an insight into the planning process involved in Wardrobe Clothing selection.
UNIT I
Fashion flow chart - Fashion terminology - Cycle influences - Elements of fashion design - History of fashion. Introduction to Clothing, Understanding, and Purpose of clothing - Protection, Modesty, attraction. Social & Psychological aspects of fashion.
UNIT II
Clothing Values, Clothing Culture, Men and Women clothing and Ornamentation, Groups, Role & status of clothing. Clothing according to climatic conditions.
UNIT III
Selection of clothes, - Clothes for children, middle age, adults, types of clothes, according to human figure - Different material for different clothes - Color suitable for different garments.
UNIT IV
Modern Clothing-Youth style and fashion, Teddy boy, skins modes, hippies, punks, taste of youth and their life style. Ancient to modern clothing, minis maxis, unisex, fit women, glamorous woman. Casual and formal clothing. Fashion for all, ready to wear fashion, mass marketing of fashion.
UNIT V
Planning for clothing needs, Clothes for school, Clothes for parties, Clothes for sports, Clothes for resting Wardrobe Planning
COURSE OUTCOMES
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Understand terms involved in Fashion and Clothing .
CO2: Understand the selection of clothes for various age Groups .
CO3: Gain knowledge on Wardrobe Planning.
CO4: Planning for various clothing needs for different climatic conditions.
CO5: Know the Modern Clothing
TEXT/ REFERENCE BOOKS:
- ‘ A History of Fashion’ , Black A.J. (1985) , USA Orbits Publishing Ltd. Rouse E. (1989),
- ‘Understanding Fashion’,UK, Blackwell Science
- ‘The Dictionary of Costume’,Wilcox T. UK,- Bats ford Ltd.
- Fashion & color Mary Garthe, Rockport Publishers - Encyclopedia of fashion detail by Patric John, Ireland Batsford

- Teacher: SARANYA N
- Teacher: Savithiri S
- Teacher: SARANYA N
- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
- Teacher: Savithiri S
- Teacher: Krithika S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- The design portfolio is the expression of the graduating student’s creativity design technical expertise and illustration and presentation skills. It is a body of work that is the culmination of all previous semesters’ learning and a visual expression of integrative learning.
- The students document all their presentable work done through all semesters and those that portray the student’s areas of interest.
- The portfolio can be an effective means of communicating the capacities and capabilities of the students to anyone who seeks their skills and talents
COMPONENTS OF PORTFOLIO:
1. Individual design philosophy that manifests itself in all design projects
2. Design Projects: Industry–oriented: The projects should exhibit a thorough understanding of industry segmentation e.g. buying a house- export house- corporate house- in the house design team of brands/boutiques- designer unit both couture and RTW- Self – generated briefs as an expression of the student’s individual design aesthetics. Each project must be specifically geared and suitably edited and presented to best demonstrate both the creative and commercial orientation of the student.
The ability to integrate multi-pronged learning of the previous semesters with special aptitude research- historical referencing of fashion/ costume- assessment of fabric suitability to justify sourcing/development of surface design techniques- extended/edited range plan- illustrations both hand – done and on computers along with flat working drawings and specification sheets would be essential attributes.
3. Demonstrated awareness and competence in the latest design-oriented computer software as required intensively by the industry
4. Suitable presentation techniques and graphics
5. Marketing and Visual Merchandising of designs through logo design- packaging etc.
6. Catalogues and advertisements for line promotion may also be made

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
• The paper provides opportunities for students to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts
that present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative.
• To provide an opportunity to the students to improve their vocabulary
• To develop skills relating to creative writing.


- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Swarnamughi K
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Berlin Mary S
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John

- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
- Teacher: MRITTIKA MAITRA
At the end of the course, the students will be able to
• get knowledge on Communication and its types
• enjoy working in an online environment knowing the listening strategies
• learn how to face various audience
• learn how to impress the audience by communicating Eff
- Teacher: Malavika J
Course Objectives:
To make the learners aware of the social, cultural and psychological implications of the Neo-classical.
To familiarize the students with the evolution of the genre of fiction in Britain.
To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
To provide knowledge on the Romantic age of British Literature.
- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
Course Objectives:
• To make the learners aware of the social, a cultural and psychological implication of the modern age
• To familiarize the students with the evolution of the different genre in Britain.
• To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
• To provide knowledge on the Romantic age and Victorian Age of British Literature.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce students to the works of significant critics.
To encourage students to undertake further reading in critical movements and critical theory.
To enable the students to apply principles of criticism to literary texts.
To make them aware of theories from Romantics to the present era.

- Teacher: Thulasibala V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To develop static websites and dynamic web applications.
➢ To learn new emerging web technologies.
➢ To gain knowledge and skills required for web development careers.
➢ To develop skills in the use and application of specific methods in user experience design.
- Teacher: Tina Victoria A
- Teacher: Geetha C
- Teacher: hemalatha c
- Teacher: P RAJASEKAR
- Teacher: Dhamodaran S
Mobile application development is the process of creating software applications that run on a mobile device, and a typical mobile application utilizes a network connection to work with remote computing resources.

- Teacher: Tina Victoria A
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: sageengrana s
This course deals with the various social network media and their effectiveness. It also make analysis of various networks and their effectiveness in communication.
- Teacher: Anu Disney D
- Teacher: Urmela S
- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
Mechanical engineering plays a dominant role in enhancing safety, economic vitality, enjoyment and overall quality of life throughout the world. Mechanical engineers are concerned with the principles of force, energy and motion. Mechanical engineering is a diverse subject that derives its breadth from the need to design and manufacture everything from small individual parts and devices (e.g. microscale sensors and inkjet printer nozzles) to large systems (e.g. spacecraft and machine tools).
The role of a mechanical engineer is to take a product from an idea to the marketplace. In order to accomplish this, a broad range of skills are needed. Since these skills are required for virtually everything that is made, mechanical engineering is perhaps the broadest and most diverse of engineering disciplines.

- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
To understand the concept and basic mechanics of metal cutting, working of standard machine tools such as
lathe, shaping and allied machines, milling, drilling and allied machines, grinding and allied machines and
broaching.
To understand the basic concepts of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) of machine tools and CNC
Programming.
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To discuss the concepts of compressible and Incompressible fluids.
To understand Mach number variation on area ratio.
To impart in depth knowledge on the flow characteristics through constant area duct.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPRESSIBLE FLUID FLOW 9 Hrs.
Concept of compressible flow, Energy and momentum equations, various regions of flow, fluid velocity, stagnation state, velocity of sound, critical states, Mach number, critical mach number, Crocco number, types of waves, mach cone, mach angle, effect of mach number on compressibility.
UNIT 2 FLOW THROUGH VARIABLE AREA DUCTS 9 Hrs.
Isentropic flow through variable area duct, T-S and h-s diagrams for nozzle and diffuser flows, area ratio as a function of Mach number, Mass flow rate through nozzles and diffusers, effect of friction in flow through nozzles.
UNIT 3 FANNO FLOW AND RAYLEIGH FLOW 9 Hrs.
Flow in constant area duct with friction - Fanno curves, and Fanno Flow equations, variation of flow properties, variation of Mach number with duct length. Flow in constant area duct with heat transfer, Rayleigh line and Rayleigh flow equations, variation of flow properties, maximum heat transfer.
UNIT 4 NORMAL SHOCK AND OBLIQUE SHOCKS 9 Hrs.
Governing equations, variation of flow parameters, static pressure, static temperature, density, stagnation pressure, entropy across normal shock and oblique shocks. Normal shocks - stationary and moving, applications. Prandtl Meyer equation, impossibility of shock in sub-sonic flows, flow in convergent and divergent nozzles with shock, Flows with oblique shock.
UNIT 5 JET AND SPACE PROPULSION 9 Hrs.
Aircraft propulsion, types and working of jet engines - energy transfer in jet engines, thrust, thrust power, propulsive and overall efficiencies, thrust augmentations in turbo jet engines, ram jet and pulse jet engines. Rocket propulsion, types of rocket engines, Liquid and solid fuel rocket engines, Introduction to Electrical and Nuclear rockets-Space Flights, Orbital and escape velocity.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Recall the fundamental concepts of compressible fluid flow.
CO2 - Demonstrate the significance of mach number on compressibility.
CO3 - Differentiate isothermal flow and isentropic flow.
CO4 - Apply the concept of normal shocks to different turbo machines.
CO5 - Estimate the heat transfer in flow through constant area ducts.
CO6 - Calculate the propulsive power in jet engines.

- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
- Teacher: LAKSHMI SANKAR S
- Teacher: Bupesh Raja V.K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the underlying principles of operation of different IC engines and components.To provide knowledge on emission formation, control, alternate fuel etc.
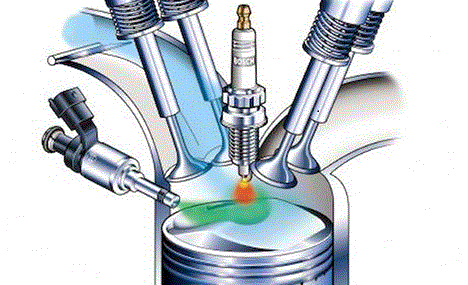
- Teacher: Senthilkumar J
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the underlying principles of operation of different IC engines and components.To provide knowledge on emission formation, control, alternate fuel etc.
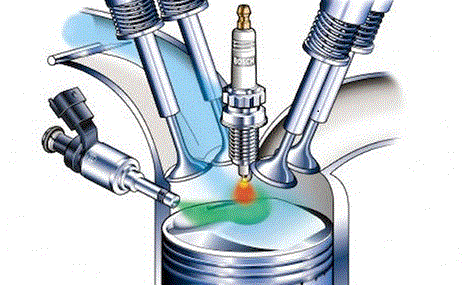
- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
- Teacher: Vijayan M
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: JEYA JEEVAHAN J
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
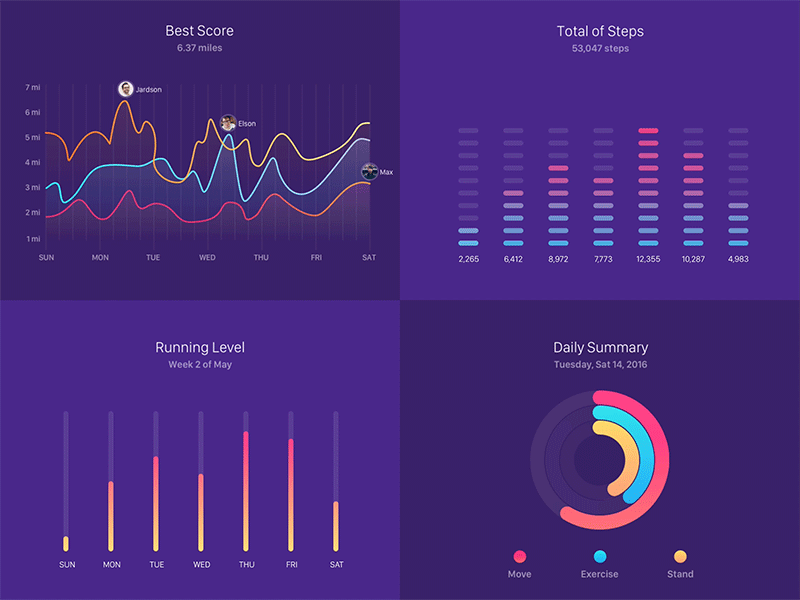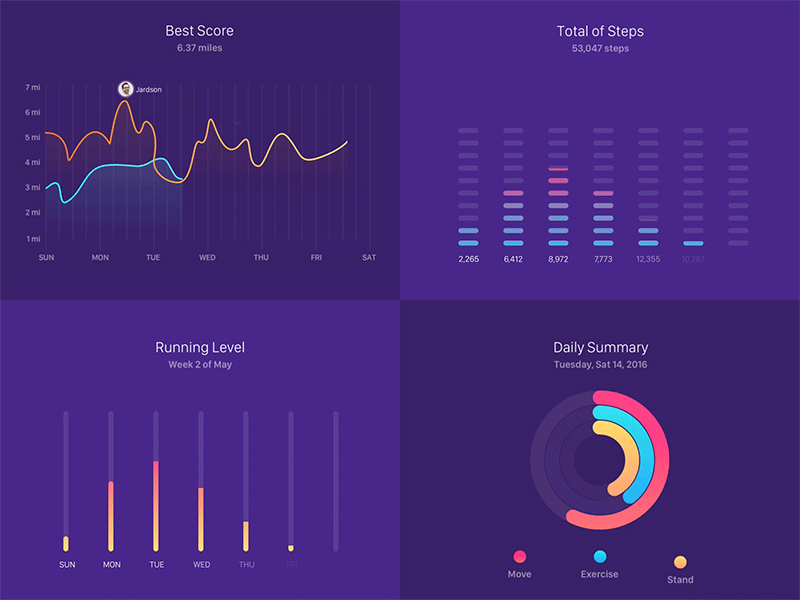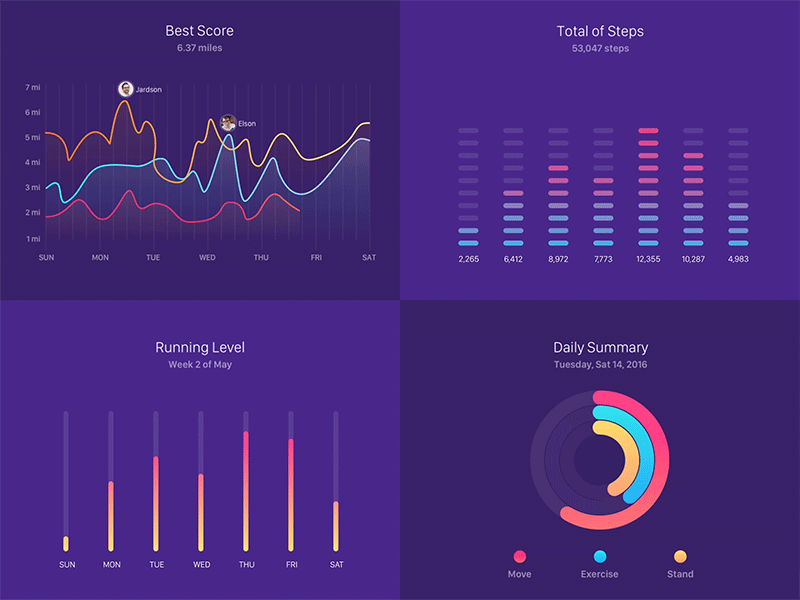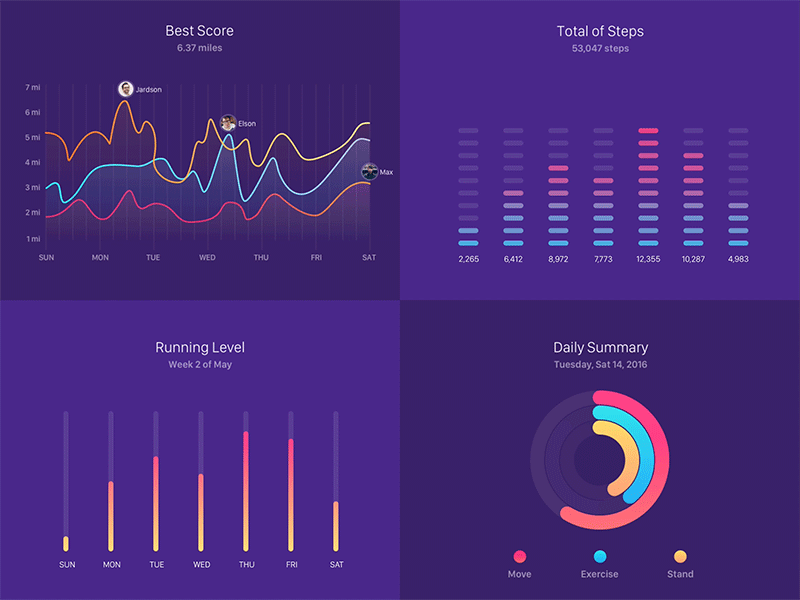
- Teacher: ANGEL D
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M

- Teacher: PARAMESWARI R
- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
- Teacher: Malliga P
- Teacher: Sridharan Sundharam
|
SPYS 1601 |
Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms. Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
- Teacher: KINJARI K
- Teacher: SNEHALATA U SHENOY
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80Marks
|
SPYA 1602 |
Professional Core 10 – Rehabilitation Science |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT :I (15Hours)
Rehabilitation psychology: overview and concepts- Nature and scope of rehabilitation psychology- Concepts of ability and disability – Recovery - symptom control and rehabilitation - Establishment of division 22 of APA.
UNIT :II (15 Hours)
Importance and applications - Rehabilitation of addictions - drug and alcohol - Rehabilitation after abuse and violence - Palliative care and pain management - role of psychologists.
UNIT: III (15 Hours)
Rehabilitation of persons with physical disabilities – physical - psycho- social and vocational rehabilitation.
UNIT :IV (15 Hours)
Biopsychosocial and social model –Psychodynamic - behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counseling - Cognitive- behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counselling.
UNIT: V (15 Hours )
Parental care and support systems for persons with disabilities - Assessment of persons with disabilities - Legal issues in rehabilitation for persons with disabilities - overview of PWD act - RCI act - national trust act - United Nations convention on the rights of persons with disabilities.
Books for study
1. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company
2. Falvo, D.R. (2013). Medical and psychosocial aspects of Chronic Illness and disability (5th ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning
3. Frank, G.R., Rosenthal, M., Caplan, B. (2010). Handbook of Rehabilitation Psychology. American Psychological Association.
7. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
Books for reference
1. Federici, S. Scherer M.J. (2012). Assistive Technology Assessment Handbook (Eds.). Boca Raton, FL :Taylor and Francis Group.
2. Riggar, T.F. & Maki, D.R. (2004). Handbook of Rehabilitation Counselling (Eds). New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
3. Stuss, D.T., Winokur, G. & Robertson, I.H. (2008).Cognitive neurorehabilitation. UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
SPYS 1601 | Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy | L | T | P | Credits | Total Marks |
4 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with the nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms.Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Remember professional standards of therapeutic counselling practice.
2. Understand the theory and practice of a relational approach to counselling.
3. Evaluate and integrate a range of theoretical approaches into a coherent model of practice.
4. Apply the knowledge, skills and understanding of the reflective practitioner.
5. Create an environment to work competently with diversity and with an anti-oppressive practice.
6. Analyse participation in and potential contribution to the changing (local and global) social, professional and organisational context for therapy.
References:
1.Hersen, M. & Sledge, W. (2002). Encyclopedia of psychotherapy.Academic Press.
2.Yalom, I. (2009). The Gift of Therapy. Harper Perennial: New York.
3.Gobbard, G. Beck, J. Holmes, J. (2007). Oxford Textbook of Psychotherapy. OUP: London.
4.Gerring, R.J. & Zimbardo, P.G. (2006). Psychology and Life. Pearson.
- Teacher: KINJARI K
This is for M.Com First year students (2022-24 batch)

- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
- Teacher: Monisha Kumari S
To
make students aware of the various forms of research and teach them how to go
about in writing a thesis.

- Teacher: SENTHIL KUMARAN E
- Teacher: SENTHIL KUMARAN E
The Television production process refers to the stages (phases) required to complete a media product, from the idea to the final master copy. This process can apply to any type of media production including film, video, television and audio recording.
The three main stages of production are:
- Pre-production: Planning, scripting & story boarding, etc.
- Production: The actual shooting/recording.
- Post-production: Everything between production and creating the final master copy.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
SVCB1303 INTRODUCTION TO SOCIAL MEDIA, BATCH 2023 - 2026

- Teacher: RAJA N
Transfer students 2018 Batch - CAE exams April 2022
- Teacher: Deepak J.R