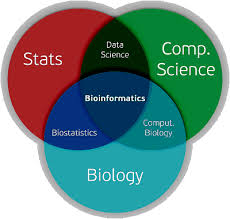
Search results: 1465
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
Goal
To diagnose, prevent and treat carious and non-carious tooth defects, pulpal and periapical pathologies, while restoring normal tooth form, function and esthetics, where indicated.
Objectives
Knowledge
§ The graduate should acquire the following knowledge during the period of training.
§ To diagnose carious and non-carious lesions and treat with simple restorative work.
§ To gain knowledge about aesthetic restorative material and to translate the same to patient’s needs.
§ To gain the knowledge about endodontic treatment on the basis of scientific foundation.
§ To carry out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To diagnose and manage traumatic injuries and to provide emergency endodontic treatment.
Skills
The student should attain following skills necessary for practice of dentistry
§ To use medium and high speed hand pieces to carry out restorative work.
§ Possess the skills to use and familiarize endodontic instruments and materials needed for carrying out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To achieve the skills to translate patients esthetic needs along with function.
Attitudes
§ Maintain a high standard of professional ethics and conduct and apply these in all aspects of professional life.
§ Willingness to participate in CDE program to update the knowledge and professional skill from time to time.
§ To help and participate in the implementation of the national oral health policy.
§ Should be able to motivate the patient for proper dental treatment and at the same time propermaintenance of oral hygiene should be emphasized which will help to maintain the restorative work and prevent future damage.
Competencies
At the completion of the undergraduate training program the graduates shall be competent in the following:
§ Competent to diagnose all carious lesions.
§ Competent to perform Class I and Class II cavities and their restoration with amalgam
§ Restore class V and Class III cavities with glass ionomer cement
§ Able to diagnose and appropriately treat pulpally involved teeth (pulp capping procedures)
§ Able to perform RCT for anterior teeth
§ Competent to carry out small composite restorations
§ Understand the principles of aesthetic dental procedures

- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Megavarnan R
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
History of profession of Pharmacy in India
Packaging materials
Pharmaceutical aids
Unit operations - Size reduction, Size separation, Mixing, Filtration, Drying, Extraction
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants
Novel Drug Delivery Systems

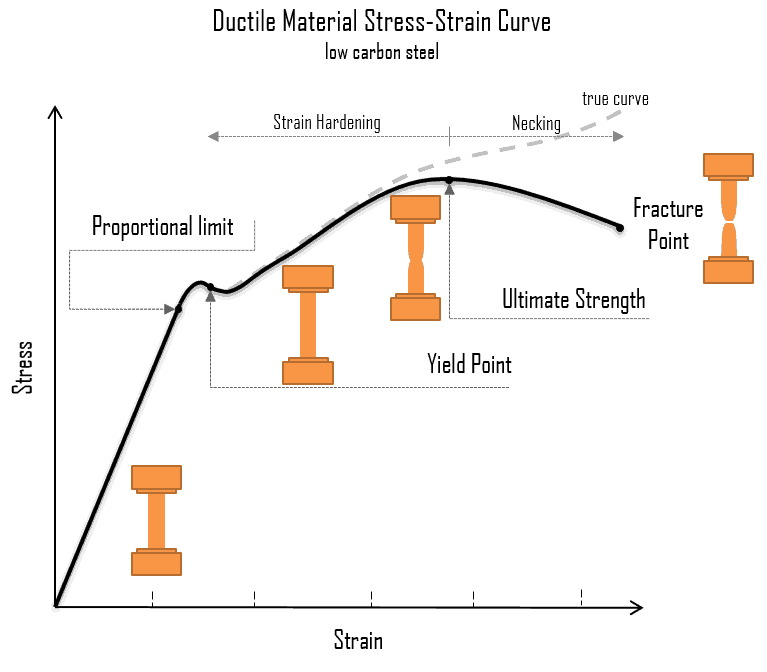
UNIT 1 CONCEPTOF SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS 9 Hrs. Concept of stress and strain, Hooke's law-Tension, Compression, and Shear, stress-strain diagram-Poisson's ratio, elastic constants and their relationship- Deformation of simple and compound bars. Principal plane, principal stress, maximum shearing stress - Uniaxial, biaxial state of stress-Mohr's circle for plane stresses.
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF BEAMS 9 Hrs. Types of beams and loads-shear force and bending moment diagrams for cantilevers, simply supported and overhanging beams. Theory of pure bending- assumptions in the simple bending theory, Flexure formula: its application to beams of rectangular, circular and channel, I&T Sections,: Combined direct and bending stresses in fore mentioned sections.
UNIT 3 DEFLECTION OF BEAMS 9 Hrs. Differential Equation of the Elastic Axis-Deflection and slope of beams-Double Integration, Area Moment and Macaulay’s methods for simply supported, Cantilever and overhanging beams.
UNIT 4 STRESSES IN SHAFTS, HELICAL SPRINGS AND THIN PRESSURE VESSELS 9 Hrs. Torsion of Circular Shafts–Shear Stresses and Twist in Solid and Hollow Shafts. Close and open Coil Helical springs. Stresses in Thin Walled Pressure Vessels.
UNIT 5 COLUMNS AND FAILURE THEORIES 9 Hrs. Columns- Member subjected to combined bending and axial loads, Euler's theory, Crippling load, Rankine's theory. Failure theories - Maximum Stress theory – Maximum Strain Theory – Maximum Shear Stress Theory – Distortion Theory – Maximum Strain energy theory. Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Analysis of different types of stresses and strains. CO2 - Analysis of different types of beams and loads acting on it. CO3 - Analysis of deflections in beams. CO4 - Analysis of stresses in shafts, helical springs and pressure vessels. CO5 - Analysis of Column structure and understanding of failure theories.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Malhotra,D.R.andGupta,H.C. ,“The Strength of Materials”, Satya PrakasanTech.India Publications, New Delhi, 2011.
2. Kazimi.S.M.A., “Solid Mechanics”, TataMcGrawHill,1976. Dym.C.L.and Shames I.H., Solid Mechanics”, McGraw hill,
Kogakusha, Tokyo, 2012.
3. Timoshenko.S.,Young,"Elements of Strength of Material", Vol. I & II, T.Van Nostrand CoInc, Princeton, N.J. 2012.
4. Ferdinand P.Beer, and Rusel l Johnston, E .,”Mechanics of Materials”, SI Metric Edition, McGrawHill, 2011.
5. Rajput. R.K.,”Strength of materials”, Fourth Edition,S.ChandLimited,2007



- Teacher: MALATHY BALARAMAN RAVINDRRAN
- Teacher: Dr.PRATHIBA GNANASEKARAN
Ø To understand the concepts of thermodynamics.
Ø To understand the concepts and applications of electrolytic conductance.
Ø To study the rate the order of reactions.
Ø To study the phase rule and its application to different system.

- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: ANU BARATHI
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi K
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
The aim of this course is to make the students understand the relationship between spaces and built form of given low rise, multi-room space program by generating solutions that are semantic with socio-cultural context, choice of material and the psychological requirements of the end-user.

- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To learn the fundamentals of Software-Defined Networks.
➢ To understand the separation of the data plane and the control plane.
➢ To study about SDN Programming.
➢ To study the various applications of SDN
➢ To learn the e- SDN Framework.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 9 Hrs.
How SDN Works – History and Evolution of Software Defined Networking (SDN)-Separation of Control Plane and Data Plane, IETF Forces, Active Networking.
UNIT 2 OPEN FLOW AND SDN CONTROLLERS 9 Hrs.
Open Flow Specification – Drawbacks of Open SDN, SDN via APIs, and SDN via Hypervisor-Based Overlays – SDN via Opening up the Device – SDN Controllers – General Concepts
UNIT 3 DATA CENTERS 9 Hrs.
Multitenant and Virtualized Multitenant Data Center – SDN Solutions for the Data Center Network – VLANs – EVPN – VxLAN – NVGRE. Network Virtualization: Concepts, Applications, Existing Network Virtualization Framework (VMWare and others), and Mininet based examples.
UNIT 4 SDN PROGRAMMING 9 Hrs.
Programming SDNs: Northbound Application Programming Interface, Current Languages and Tools, Composition of SDNs – Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and Software Defined Networks: Concepts, Implementation and Applications.
UNIT 5 SDN 9 Hrs. Juniper SDN Framework – IETF SDN Framework – Open Daylight Controller – Floodlight Controller – Bandwidth Calendaring – Data Centre Orchestration.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Analyse the evolution of software defined networks.
CO2 - Express the various components of SDN and their uses.
CO3 - Explain the use of SDN in the current networking scenario.
CO4 - Design and develop various applications of SDN.
CO5 - Understand and explain SDN Programming.
CO6 - An Ability to understand the SDN Frame work.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Paul Goransson and Chuck Black, ―Software Defined Networks: A Comprehensive Approach, 1 st Edition, Morgan Kaufmann, 2014.
2. Thomas D. Nadeau, Ken Gray, ―SDN: Software Defined Networks, O’Reilly Media, 2013.
3. Siamak Azodolmolky, ―Software Defined Networking with Open Flow, Packet Publishing, 2013.
4. Vivek Tiwari, ―SDN and Open Flow for Beginners, Amazon Digital Services, Inc., 2013.
5. Fei Hu, Editor, ―Network Innovation through Open Flow and SDN: Principles and Design, CRC Press, 2014.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 Questions of 2 marks each-No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 Questions from each unit with internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 M
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
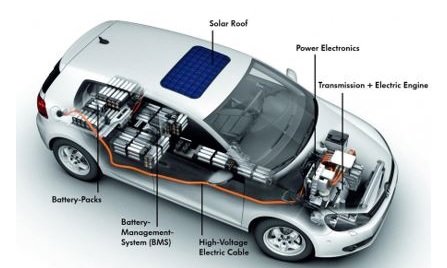
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Apply Vehicle concept to electric vehicle
CO2 - Analyze the power conversion technique of electric vehicle
CO3 - Examine the performance of different electric drive train
CO4 - Select the appropriate electric motor for electric propulsion system
CO5 - Select a suitable battery for electric vehicle
CO6 - Analyze the recent technique used in modern electric vehicle
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
Business Mathematics ,Logical Reasoning and Statistics integrated with Syllabus of CA Foundation.

The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in microbiology is to provide an understanding of the natural history of infectious diseases in order to deal with the etiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and control of infections in the community.
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). .Bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and algae are the major groups of microorganisms.
- Teacher: Prakash P
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
- The ability to identify reflects upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements.
- Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject
COURSE OUTCOME:
· CO1: Apply laws of mechanics to determine efficiency of simple machines with consideration of friction.
· CO2: Understand interference of sound waves and longitudinal standing waves
· CO3: Describe basic definition and conception of materials and physical properties of materials
· CO4: Understand the nature of thermodynamic properties of matter like internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, temperature, pressure and specific volume
· CO5: Understand the properties of light like reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction etc
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
Course objectives:
To introduce the basic concepts / theories of psychology relevant to architecture and the relationship between man and the environment.
To construct knowledge on the fundamentals of designing public areas, theories, solutions and policies related to urban design.
To familiarize the students with housing policies, need, demand and issues related to health and
environment.
- Differentiate between a descriptive and a prescriptive view on linguistic phenomena and between fundamental concepts and distinctions in linguistics
- discuss some basic concepts within diachronic variations in language with examples
- describe and illustrate basic concepts like Varieties of dialect, Register, within morphology, such as: defining word, illustrating word formation
- define and analyse linguistic material with regards to the basic Sentence Patterns: Intransitive Predicate Pattern, Transitive Predicate Pattern
- recall definitions of Transformational Generative Grammar. Supra- Sentential Grammar.
- Semantic roles account for basic concepts within semantics and pragmatics with a focus on lexical
- semantics (e.g synonymy, antonymy, hyponymy, homophony)

- Teacher: Director Admin
- Teacher: Director Admin
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand importance of bioethics and biosafety. To understand legal social and economic impacts of biotechnology. To understand regulatory guidelines and their importance. To understand importance of patent.
Ø To understand procedure to apply for patent.
Ø To understand procedure of assessment of biosafety for biotech foods. To understand ethical implications of biotechnology.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSAFETY
Definition of ethics and Bioethics, Ethics in Biotechnology(positive and negative effects with classical examples – Rice with Vitamin A, No-till Agriculture, cotton without insecticide, reduced need for fertilizer, biological pest control , slow ripening fruits and controlled ripening, fast growing trees and fishes.
UNIT 2 GMO
Guidelines for research with transgenic organisms. Environmental impact of genetically modified organisms (beneficial and hazardous impact), Field trials with GMO, Containment levels. Biosafety protocol, Cartagena Biosafety protocol, Mechanism of implementation of biosafety guidelines. Biosafety and politics. Biosafety database.
UNIT 3 IMPLICATIONS OF BIOSAFETY
Awareness education on genetically engineered organism.-Transgene instability, gene flow, resistance/ tolerance of target organism, increase weedlessness, risks and uncertainty associated with Biotechnology. Containment levels and their impact on Environment- Containment- definition, types of containment, summary of recommended Biosafety levels for infectious agents, detail checklist–premises and lab equipment, Animal facilities, environment.
UNIT 4 GLP AND PATENTS
Gene technology laboratory. GLP and Bioethics- introduction, national Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), the GLP authority functions, Good Laboratory Practices- necessity, aspiration and responsibility. Procedure to apply patent, other intellectual properties viz copy rights, Rights, Plant breeder’s rights, trade secrets/ trade symbol etc. WTO, TRIPS, PCT and GATT. IPR problems and its hindrance.
UNIT 5 ETHICS.
Ethics in clinical trials and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) – Definition of clinical trials and GCP, general information about clinical trials, need to conduct clinical trials, faces ofclinical trials, institutional set ups for conducting clinical trials, ethics in clinical Biotechnology
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Safety Assessment by Thomas, J.A., Fuch, R.L. (2002), Academic Press.
2. Biological safety Principles and practices) by Fleming, D.A., Hunt, D.L., (2000). ASMPress.
3. Biotechnology - A comprehensive treatise. Legal economic and ethical dimensions VCH.Bioethics by Ben Mepham, Oxford University Press, 2005.
4. Bioethics & Biosafety by R Rallapalli & Geetha Bali, APH Publication, 2007
5. Bioethics & Biosaftey By Sateesh Mk (2008), Ik Publishers
6. Biosafety And Bioethics Rajmohan Joshi Publishers
- To provide the opportunity to gain knowledge on the formal and technical elements of literature
- To help the students to analyze and interpret the literary texts.
- To enhance the learners into the study of various literary forms.
- To make learners aware of the forms and content of language.
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Swarnamughi K
- Teacher: Director Admin
- Teacher: Prince Mary S
- Teacher: Padmapriya R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- This course introduces fundamental physical principles of both classical and modern optics as well as principles of optical design used in the engineering of optical systems.
- It also provides exposure to practical aspects of optical materials and devices.
- Its intention is to provide a foundation of basic principles, design methodology, and practical considerations needed to design nor use optical instruments in the biomedical engineering practice
- Teacher: Sabarivani A
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
- To familiarize students through an
effective blend of theory and practice in translation
- To focus the key concepts of the translation studies through various texts.
- To implement
the diverse approaches and strategies of translation.
- To compare a variety of issues in relation to translation.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
Objective of the Course: The ability to identify, reflect upon,
evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form
independent judgments. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on
quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject
- Teacher: Malliga P
AIRCRAFT COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
L T P Credits Total Marks
3 0 0 3 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To study the mechanics of composites in micro level and macro level.
To study the plate, shell and sandwich theories of composites for various applications.
To understand the fabrication methods and design of composite structures.
UNIT 1 MICROMECHANICS 9 Hrs.
Introduction - advantages and application of composite materials – types of reinforcements and matrices - micro mechanics
– mechanics of materials approach, elasticity approach- bounding techniques – fiber volume ratio – mass fraction – density
of composites. Effect of voids in composites
UNIT 2 MACROMECHANICS 9 Hrs.
Generalized Hooke’s Law - elastic constants for anisotropic, orthotropic and isotropic materials - macro mechanics stressstrain relations with respect to natural axis, arbitrary axis – determination of in plane strengths of a lamina - experimental
characterization of lamina. Failure theories of a lamina. Hygrothermal effects on lamina.
UNIT 3 LAMINATED PLATE THEORY 9 Hrs.
Governing differential equation for a laminate. Stress – strain relations for a laminate. Different types of laminates. in plane
and flexural constants of a laminate. Hygrothermal stresses and strains in a laminate. failure analysis of a laminate. Impact
resistance and interlaminar stresses. netting analysis.
UNIT 4 SANDWICH CONSTRUCTIONS 9 Hrs.
Basic design concepts of sandwich construction - materials used for sandwich construction - failure modes of sandwich
panels - bending stress and shear flow in composite beams.
UNIT 5 FABRICATION PROCESS AND REPAIR METHODS 9 Hrs.
Various open and closed mould processes, manufacture of fibers, importance of repair and different types of repair
techniques in composites – autoclave and non-autoclave methods.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Understand different constituent materials of composites and properties.
CO2 - Analyze the mechanical behaviour of laminated composites based on fiber direction.
CO3 - Understand the design and failure modes of sandwich composites.
CO4 - Analyse the Hygrothermal property and interlaminar shear strength of composite.
CO5 - Understand fabrication methods based on various applications .
CO6 - Understand different types of repair techniques in composites.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Dam Ishai., "Mechanics of Composite Materials", 2010.
2. Autar K Kaw, ‘Mechanics of Composite Materials’, CRC Press, 2012.
3. Madhuji Mukhapadhyay, Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structures, University Press, 2012.
4. Agarwal, B.D., and Broutman, L.J., "Analysis and Performance of Fibre Composites," John Wiley and sons. Inc., New
York, 95.
5. Lubin, G., "Handbook on Advanced Plastics and Fibre Glass", Von Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1989.
6. Calcote, L R. “The Analysis of laminated Composite Structures”, Von – Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York 1998.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 Question of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
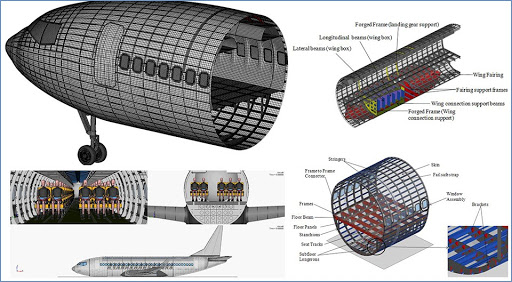
COURSE OBJECTIVES
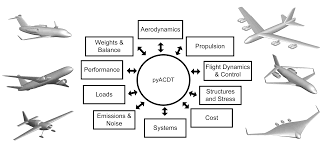
• To classify the types of Aircrafts and its data collection.
• To estimate the weight of an Aircraft pertaining to preliminary hand calculations
• To select the appropriate airfoil, wing tail, control surface and power plant for the preliminary design Aircraft.
• To analyze the performance of the preliminary design Aircraft.
• To perform the structural analysis of the preliminary design Aircraft.
• To design the landing gear opted for the newly designed Aircraft.
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Data collection.
2. Preliminary weight estimation.
3. Airfoil selection, Wing tail and control surfaces
5. Balance diagram.
6. Drag estimation.
7. Rate of climb calculations at various altitudes, Turn performance
8. Range and Endurance, Takeoff and landing distance calculation
10. V-n diagram
12. Shear force and bending moment diagrams of various aircraft structures.
13. Structural weight distribution.
14. Landing gear Design.
15. Detailed CAD drawings of wing, fuselage ,tail surfaces and control surfaces and their stress analysis using structural software
16. Detailed Design project report.
COURSE OUTCOMES
At the end of the course, student will be able to:
• CO1: Categorize the types of Aircraft and its specifications to perform the conceptual design of new Aircraft.
• CO2: Estimate the gross weight and payload weight of an Aircraft for the preliminary designed Aircraft.
• CO3: Deduct the appropriate selection of airfoil, wing-tail configuration for the preliminary Aircraft.
• CO4: Analyze the preliminary designed Aircraft’s performance and its control.
• CO5: Evaluate the structural analysis of airframe parts of the preliminary designed Aircraft.
• CO6: Design the appropriate landing gear that suits the preliminary designed Aircraft.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
List of experiment
1. V-n diagram
2. Wing and fuselage Design.
3. Shear force and bending moment diagrams of various aircraft structures.
4. Structural weight distribution.
5. Bending stress calculation.
6. Torque diagram
7. Shear flow calculations
8. Flexural shear flow
9. 3-view diagram based on the detailed design
10. Landing gear Design.
11. Detailed CAD drawings of wing, fuselage ,tail surfaces and control surfaces and their stress analysis using structural software
12. Detailed Design project report.
SAE4060 AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS AND MAIN

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concepts of applying Aero thermodynamics to air breathing propulsion. To familiarize the student's ability to analyze the concepts of compressor. To understand the basics of Axial Turbine. To understand the basics of Ramjet and Scramjet.
UNIT 1 THERMODYNAMICS OF AIR BREATHING PROPULSION 9 Hrs. History and classifications of Aero engines, Working of gas turbine engine – Thrust equation – Factors affecting thrust – Engine performance parameters – Efficiency, Specific fuel consumption, Methods of thrust augmentation – The propeller, turboprop, turbofan and turbojet engines characteristics.
UNIT 2 INLETS, COMBUSTION CHAMBER AND NOZZLES 9 Hrs. Introduction-Subsonic inlets-Supersonic inlets-Modes of Inlet operation- Gas turbine combustors-Types of combustion chamber-Fuel injector- Flame Tube cooling-Flame Stabilization-Flame holders- Theory of flow in isentropic nozzles – Losses in nozzles –Nozzle efficiency––nozzle choking –Over expanded and under expanded nozzles – Ejector and variable area nozzles.
UNIT 3 AIR COMPRESSOR 9 Hrs. Compressor and its classification- Centrifugal compressor - Work and compression ratio -Performance characteristicsCentrifugal compressor staging- Axial compressor-Work and compression ratio- Degree of reaction- Characteristic performance of a single stage axial compressor- Characteristic performance of a multistage axial compressor- Cascading of axial compressor-Compressor efficiency.
UNIT 4 AXIAL TURBINES 9 Hrs. Axial turbine stage -Velocity triangles and Power output - Elementary theory - Vortex theory- Limiting Factors of gas turbine design-Turbine performance- Turbine Blade cooling- Axial flow Turbine and compressor matching.
UNIT 5 RAMJET AND SCRAMJET 9 Hrs. Operating principle of RAMJET engine- RAMJET with afterburner- RAMJET performance- SCRAMJET working principleProblems faced in supersonic combustion.
Max 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOME On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Understand the working principles of gas turbine. CO2 - Comprehend the sound foundation in the design principles of inlets, combustion chambers, nozzles used in aircraft engines. CO3 - Learn the operation of compressors in aircraft engines. CO4 - Understand the concept of turbines in gas turbine propulsion systems. CO5 - Understand the principle and performance of ramjet and scramjet propulsion. CO6 - Applying the importance of Propulsion to Aircraft system.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Philip Hill and Carl Peterson, “Mechanics and thermodynamics of propulsion”, Pearson India, second edition 2010.
2. V.Ganesan., “Gas Turbines”, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, third edition, 2010.
3. Cohen.H, Rogers.G.F.C. and Saravanamuttoo.H.I.H, “Gas turbine theory”. Pearson education, fifth edition,2001.
4. Rathakrishnan E., “Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics”, Prentice-Hall India, 2012.
5. Saeed Farokhi, “Aircraft Propulsion”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc ., 2009.
6. Rolls Royce Jet Engine – 5thEdition – 1996.

- Teacher: MATHIYARASI M
COURSE OBJECTIVES To get clear cut idea about the stability of aircraft at various flight conditions.
UNIT 1 BASIC CONCEPTS 11 Hrs.
Aircraft Axis System, Coordinate Transformation, Aircraft Force Equations, Moment Equations, Basic Concept Of Stability And Control, Longitudinal And Lateral- Directional Equations, Kinematic Equation
UNIT 2 LONGITUDINAL DYNAMIC STABILITY AND CONTROL 12 Hrs.
Stick - fixed stability, control effectiveness, hinge moment, tabs, aerodynamic balancing, effects of freeing the stick. Control forces and force gradients. Critical conditions for stability and control.
UNIT 3 MANEUVERABILITY 11 Hrs.
Effect of maneuvers. Longitudinal dynamic stability, equations of motion of a disturbed aircraft, stability derivatives, characteristic equation for stick fixed case, modes and stability criterion, effect of freeing the stick.
UNIT 4 DYNAMIC STABILITY 11 Hrs.
Brief description of lateral and directional dynamic stability- spiral, divergence and Dutch roll. Response, automatic control, autorotation and spin. Determination Of Neutral Points And Maneuver Points In Flight Tests
UNIT5 MODERN CONTROL THEORY 15 Hrs.
Classical Vs modern control theory, introduction – state-space modeling, canonical transformation, controllability and observability, state-feedback design, application of modern control theory to aircraft autopilot design- stability augmentation, autopilot design, state observer, optimal control, problems . Introduction to aircraft autopilot design using classic control theory. Introduction to nonlinear problems in aircraft flight dynamics - Inertia coupling. - High angle of attack phenomena - Flexibility effects -Divergence.
Max.60 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Thomas R. Yechout, ‘An introduction to Aircraft Flight Mechanics’, AIAA educational Series; 2003.
2. Bernard Etkin, Lloyd Duff Reid, Dynamics of Flight, Stability & Control, 3rd ed, John Wiley & Sons, 1995
3. Malcom J Abzug, E E. Larrabee, Airplane Stability & Control , 2nd ed, Cambridge University Press,, 2002
4. Nelson. R.C., Flight Stability and Automatic Control, McGraw Hill, 1989.
5. Perkins, C, D.,and Hage, R,E., Airplane Performance, Stability and Control, Wiley Toppan, 1974.
(Computational problems can be given as assignments)

This course deals and integrates with the following concepts
- Differentiate baseband and passband transmissions & realize the needs for modulation.
- Explain the Functional blocks of a communication system & Classification of communications based on the type of modulation techniques and channels used.
- Analyze Amplitude modulation and their types (DSB-SC, SSB-SC and VSB) using mathematical equations, Frequency Spectrum, Band Width, and Power relations.
- Demonstrate the generation of AM at the transmitter side and de-modulation process using appropriate circuits.
- Compare FM with AM. Analyze single tone and multi-tone FM using mathematical equations, Frequency Spectrum, and Band Width. Differentiate WBFM from NBFM.
- Relate FM (as Indirect PM) and PM (as indirect FM) using mathematical proof with a functional block diagram set-up.
- Demonstrate the FM modulator (direct and indirect methods) at the transmitter side and demodulator process with suitable circuits.
- Various noise sources and types
- Analyze, AM, PM, PAM, PDM, PPM, and PCM using mathematical equations and demonstrate their modulation and demodulation /techniques.
- Understand the importance of the sampling process in pulse modulation systems and explain various multiplexing techniques with many message inputs.
- Demonstrate the working of AM and FM transmitters, Receivers, and Communication Systems.
- Performance evaluation and selection of appropriate modulation techniques for real-time applications.
- Working with Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.
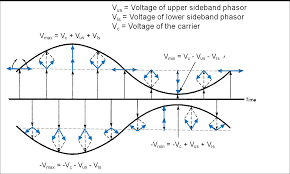
- Teacher: JEGAN G
Unit 1 explains the basic analytical principles, instrumentation behind the working of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Flame photometry.
Unit 2 discusses the working principle and analysis of compounds based on different separation techniques such as chromatography, HPLC and Electrophoresis
Unit 3 deals with different thermal methods of analysis such as TGA, DTA, DSC and their applications. The unit helps in understanding the basic concepts of the thermal methods.
Unit 4 helps to know the basic principles involved in electroanalytical techniques and estimation of elements by different methods.
Unit 5 deals with the study of concepts of various spectrometric analytical techniques such as spectrophotometry, turbidimetry and fluorimetry.

- Teacher: Supriya S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Introduce students to the concepts of dynamics.
The students are expected to develop working skills in the dynamic analysis of both particles and rigid bodies.
Master the basics of dynamics, including free body diagrams and kinematics.
Learn the mathematical formulations of dynamics problems

- Teacher: TWISHA SAIN

- Teacher: Vanitha S
- Teacher: Prakash P
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the basic principles and concepts of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science.
- To gain knowledge of various machine learning algorithms and their applications.
- To develop skills in data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model evaluation.
- To explore ethical considerations and challenges associated with AI and Data Science applications
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Analyze the software and hardware requirements to work with AI Algorithms.
CO2 - Simulate given problem scenario using appropriate AI libraries.
CO3 - Develop AI programming solutions for given problem scenario.
CO4 - Implement deep learning algorithms and solve real-world problems.
CO5 - Implement AI based edge computing solutions using GPUs.
CO6 - Analyze the performance of various ML algorithms for a specific application.

- Teacher: MOHANA PRIYA G
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
This course contains 5 units
Introduction to Astronomy , Different optical Techniques, Evolution-Formation And structure of Stars, Sun and Solar System and Space Astronomy

- Teacher: Helen Merina Albert
Audio Production theory : In this subject students can learn fundamental of Acoustics and Threshold of Hearing, Decibel,
Microphone and Loud Speakers. Theoretically understand The basics of Mic placement of Music Instruments. Also, They
Can learn Advanced Sound Recording Techniques. the importance of Audio Sampling and Cable & Connectors and
Recording and Reproduction Auro -3d Surround System.

COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the construction details of various types of automotive Frames and basic Chassis layouts
CO2 - Understand the basic function steering system and steering components
CO3 - Select the appropriate transmission system for various automobiles
CO4 - Comprehend the final drive system of a vehicle.
CO5 - Apply the knowledge for selection of suitable axles, wheels and tyres for a vehicle.
CO6 - Distinguish various types of suspension system, brake system.

The objectives of the course include to enable the students to understand the origin
and development of English drama thereby to critically appreciate the trends that influenced the theatre and drama.
The course provides them an insight into popular culture and its dramatic expressions.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.

- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
- Teacher: S B Reshma John
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: Vanitha S
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Attain in-depth knowledge and understanding of the big data technologies.
- CO2 - Understand the various search methods and visualization techniques for big data analytics.
- CO3 - Demonstrate the principles of bi data analytics using Big Data tools, Big Data Querying Tools, such as Pig, Hive and Impala.
- CO4 - Design and build big data applications and analyze issues in data storage, data privacy and security.
- CO5 - Demonstrate various techniques for mining data stream and applications using Map Reduce Concepts.
- CO6 - Use advanced analytical tools/ decision-making tools/ operation research techniques to analyze the complex problems.
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Provide the basics of organization of big data, architectural issues of big data tools.
- Study on Modern databases which currently exist in the field of computer science.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Attain in-depth knowledge and understanding of the big data technologies.
CO2 - Understand the various search methods and visualization techniques for big data analytics. CO3 - Demonstrate the principles of bi data analytics using Big Data tools, Big Data Querying Tools, such as Pig, Hive and Impala.
CO4 - Design and build big data applications and analyze issues in data storage, data privacy and security.
CO5 - Demonstrate various techniques for mining data stream and applications using Map Reduce Concepts.
CO6 - Use advanced analytical tools/ decision-making tools/ operation research techniques to analyze the complex
problems.

- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
- Gain knowledge of the context, concepts and process of entrepreneurship. Be better able to conceive and develop entrepreneurial opportunities. Be able to determine the feasibility of a new business concept.
Unit: I Project planning 12 Hrs
scope – problem statement – project goals – objectives – success criteria –
assumptions – risks – obstacles – approval process – projects and
strategic planning. Project implementation – project resource requirements –
types of resources – men –materials, finance. Case studies.
Unit: II Project monitoring 12 Hrs
Evaluation – control – project network technique –planning for monitoring and evaluation – project audits – project management information system – project scheduling – PERT & CPM –project communication – post project reviews and Case studies. Project team management – recruitment – organizing – human resources – team operating rules – project organization – various forms of project organizations. Closing the project – types of project termination – strategic implications – project in trouble – termination strategies – evaluation of termination possibilities.
Unit: III Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship 12 Hrs
Ideas to Reality, Proof of Concepts to Product realization, Strategic Management, Forms of Ownership and Franchising, Buying an existing Business, Business Models, Mobilization of Financial resources; Bank loans & Venture capitalism. Building a good Marketing Plan, Concepts in MSME. Accounting for planning, control, and motivation. Factors influencing capital acquisition and allocation. Financial decision making; Decision making under uncertainty; positive and normative models; Current issues in financial management. Case studies.
Unit: IV Industrial R&D and product development 12 Hrs
Product development and project management in Agri, Pharma, Health and other biotech industries. Overview of issues and techniques involved in conducting & outcome of research. The multidisciplinary nature of outcomes research: research design and methods, data collection measurement instruments and clinical endpoints, quality of life issues, behavior change, and cost-effectiveness. Analysis Transition from R&D to business units. Product development, market learning and transition from R&D. Management of radical innovation technologies vs. stage gate approach in product development. Case studies.
12 Hrs
Unit: V Rights and responsibilities of business
under the Indian Constitutional system.
Basic standards, rules, principles and issues relating to the law of
corporations; core issues affect the corporate governance of business;
relationship between management, boards and shareholders. Business laws
applied to Biotech industries. Regulatory issues in Biotech industries with
special reference to clinical trial of pharma products and field trials of
Agricultural products. Regulatory processes details. Intellectual property
in biotech. Business. Models around intellectual property, licensing issues.
Product development for commercial ventures. Bioethics and Current legal
issues. Ethics of new technology. Case studies.

- Teacher: Dayanandan Anandan
Biochemistry and biomolecules lab
- Teacher: Jancy Mary E
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
The major objective of Biochemistry is the complete understanding of all the chemical processes by the biomolecules associated with living cells at the molecular level. It also deals with the nutrition and their daily requirements, metabolism and the diseases associated with it. All the diseases or disorders have some biochemical involvement hence is useful in the diagnosis of any clinical condition and in its treatment by various by biochemical estimations.

- Teacher: Dr.Premjanu N
- Teacher: Srividya S
- Teacher: Jayashree S
To Understand the basic concepts in biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics and their significance.Use of plasma drug concentration-time data to calculate the pharmacokinetic parameters to describe the kinetics of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion. The concepts of bioavailability and bioequivalence of drug products and their significance will be explained clearly.

- Teacher: Ramya Selvam T
- Teacher: VIJAYA KUMAR VOLETI
COURSE OBJECTIVE
· Learn How to engineer a confident body language.
· The ability to interpret other people body language.
· To use body language online and improve online presence
- Teacher: HARITHA B
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to
- Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human body.
- Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
- Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of the human body.
- Perform the various experiments related to special senses and the nervous system.
- Appreciate coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system
- Teacher: Harini R R
- Teacher: SAI HARINI S
Know the history of profession of pharmacy
Understand the basics of different dosage forms, pharmaceutical incompatibilities and pharmaceutical calculations
Understand the professional way of handling the prescription
Preparation of various conventional dosage forms

- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
- Teacher: KAMALI S
Upon completion of the course the student shall be able to
1. Understand the behavioral needs for a Pharmacist to function effectively in the areas of pharmaceutical operation
2. Communicate effectively (Verbal and Non Verbal)
3. Effectively manage the team as a team player
4. Develop interview skills
5. Develop Leadership qualities and essentials

Upon completion of the course the student shall be able to
1. Understand the behavioral needs for a Pharmacist to function effectively in the areas of pharmaceutical operation
2. Communicate effectively (Verbal and Non Verbal)
3. Effectively manage the team as a team player
4. Develop interview skills
5. Develop Leadership qualities and essentials

- Teacher: Thulasibala V
Scope: The course deals with the various physical and physicochemical properties, and principles involved in dosage forms/formulations. Theory and practical components of the subject help the student to get a better insight into various areas of formulation research and development, and stability studies of pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Objectives: Upon the completion of the course student shall be able to
- Understand various physicochemical properties of drug molecules in designing the dosage forms
- Know the principles of chemical kinetics & to use them for stability testing and determination of expiry date of formulations
- Demonstrate the use of physicochemical properties in the formulation development and evaluation of dosage forms.

- Teacher: Harini R R
At the end of this course the students may be able understand the plant drugs and their uses

- Teacher: Elumalai A
- Teacher: Shanthini Nachiar
- Pharmaceutical jurisprudence it frames the law and different act to maintain the harmony in the society such as it plays an important role is sales, import, distribution, export of the pharmaceutical drugs.
- By keeping the above considerations following act like pharmacy act, Drug and cosmetic act, Drug magic remedies act, poisonous act, Narcotic and Psychotropics substances act etc... had been started with following committee members with the governing bodies like state and central government.
- Thereby the Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence / Forensic pharmacy may flourish all over India.

- Teacher: NITHYAKALYANI K
This course is designed to impart the fundamental knowledge on the regulatory
requirements for approval of new drugs, and drug products in regulated markets of
India & other countries like US, EU, Japan, Australia,UK etc. It prepares the students
to learn in detail on the regulatory requirements, documentation requirements, and
registration procedures for marketing the drug products.
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
- Teacher: Amudha S
This paper will provide an opportunity for the student to learn about development of
pharmacovigilance as a science, basic terminologies used in pharmacovigilance, the global scenario
of Pharmacovigilance, train students on establishing pharmacovigilance programme in an
organization, various methods that can be used to generate safety data and signal detection. This
paper also develops the skills of classifying drugs, diseases and adverse drug reactions.

- Teacher: Maria Shirley J
- Teacher: Nandhini M
Students will be able to:
• Identify and describe distinct literary characteristics of British literature from beginnings to the 18th century
• Identify the distinct literary genres of the tragedies, comedies, and histories present in Shakespeare's work • Demonstrate greater reading fluency of Elizabethan English
• Analyze Shakespeare's plays for their structure and meaning, using correct terminology
• Write analytically about Shakespeare's works, using MLA guidelines
• Effectively communicate ideas related to Shakespeare's plays during class and group activities.

To
make the learners aware of the social, a cultural and psychological implication
of the modern age liter

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
This course introduces students to the fundamentals of cancer, including its molecular basis, causes, progression, and treatment. It focuses on how normal cells transform into cancer cells and explores modern diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
- Teacher: Jemmy Christy H

To augment the knowledge imparted through lectures by discussion of practical cases to determine practice, critically
analyze application of knowledge in the professional context, experience simulated application procedure in a limited
context. Live case studies are to be undertaken and various aspects of the course to be taken up in the studios. Emphasis is
given to interaction with project technical staff and other stakeholders.

- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: JEYA JEEVAHAN J
- Teacher: Deepak J.R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the fundamentals of wind and solar energy and its conversion system
To study the various types of wind machines and to analyze its performance.
To study the radiation principles with respective solar energy estimation.
To discuss about solar thermal technologies and its applications.
To learn about PV technology principles and understand the various techniques of various solar cells.

- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the fundamentals of wind and solar energy and its conversion system
To study the various types of wind machines and to analyze its performance.
To study the radiation principles with respective solar energy estimation.
To discuss about solar thermal technologies and its applications.
To learn about PV technology principles and understand the various techniques of various solar cells.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
The Cell and Molecular Biology course is an in-depth exploration of the underlying chemistry and molecular biology in living cells. It is concerned with the physiological properties, metabolic processes, signaling pathways, life cycle, chemical composition and interactions of the cell with their environment.
Cell biology is the study of the structure and function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In this course the
students will learn different areas of cellular biology including the structure and functions of cell, its
organelles, synthesis and function of macromolecules such as carbohydrate, protein, lipid, DNA & RNA;
membrane structure and function; bioenergetics; cellular communication; and microscopic techniques to
understand the cell structure.
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: Jayashree S
This course will make the students to study the structure and bonding in polyhedral boranes and to understand the chemistry of Silicon, Sulphur and Phosphorus compounds. Consecutively, it will help the students to understand about the synthesis and reactivity of organometallic reagents and macrocycles. This course teaches the preparation and properties of various organyls and also to determine the properties and applications of lanthanides and actinide.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: Director Admin
- Teacher: Jayashree S
Clinical Biochemistry lab comprises of important biochemical test, which make the students to understand a broad range of experimental techniques in clinical Biochemistry and to enable them to demonstrate their ability to use the techniques in conducting scientific experiments and observations.

Clinical Biochemistry lab. Using this laboratory course students can learn how to estimate various Profile needed for patients with the diseased condition. In this Lab Diabetic profile, a Liver function test, a Cardiac profile, and a lipid profile will be discussed. Knowledge of clinical chemistry will be useful for their entrepreneurship as a biochemist in a reputed lab.
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah

- To
help the students acquire an understanding of the principles and methods of
communication and teaching.
- It helps to develop skill in communicating effectively, maintaining effective interpersonal relations, teaching individuals and groups in clinical, community health and educational settings.

- Teacher: Manjambigai M
- Teacher: Thivya N
- Teacher: S PRATHIBA
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To study the various types of communication techniques and their analysis based on Fourier transform
and to provide fundamental knowledge of pulse modulation techniques and their types.
Course Outcomes:
By the end of this course students will be able to
CO1: Design, operation, and troubleshoot of electronic systems
CO2: Solve electronic devices and systems using mathematical concepts.
CO3: Analyze electronics devices and circuits using computer simulations.
CO4: Analyze components associated with digital and analog electronic/communication systems.
CO5: Analyze basic wireless and communication circuits using computer simulations

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
This course will prepare the young pharmacy student to interact effectively with doctors,
nurses, dentists, physiotherapists and other health workers. At the end of this course the student
will get the soft skills set to work cohesively with the team as a team player and will add value to
the pharmaceutical business.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
This course will prepare the young pharmacy student to interact effectively with doctors,
nurses, dentists, physiotherapists and other health workers. At the end of this course the student
will get the soft skills set to work cohesively with the team as a team player and will add value to
the pharmaceutical business.

- Teacher: BHARATH KUMAR A.J.
COURSE OBJECTIVE
• The paper provides opportunities for students to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts that present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative.
• In this paper students will have an opportunity to improve their vocabulary related to immediate environment, practice speaking skills by discussing about issues based on reading texts, read texts that include everyday problems that provide opportunities to develop problem solving skills in cooperative learning situations, develop writing skills through writing essay, substance of a poem, letters and composition of dialogues.
• To Provide an opportunity for the students to participate in debate on the topics related to Environmental issues and
Discrimination in Society.

The paper provides opportunities for students to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts that present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative.
• In this paper students will have an opportunity to improve their vocabulary related to immediate environment, practice speaking skills by discussing about issues based on reading texts, read texts that include everyday problems that provide opportunities to develop problem solving skills in cooperative learning situations, develop writing skills through writing essay, substance of a poem, letters and composition of dialogues.
• To Provide an opportunity for the students to participate in debate on the topics related to Environmental issues and
Discrimination in Society.

- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
END SEMESTER MODEL
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Jemmy Christy H
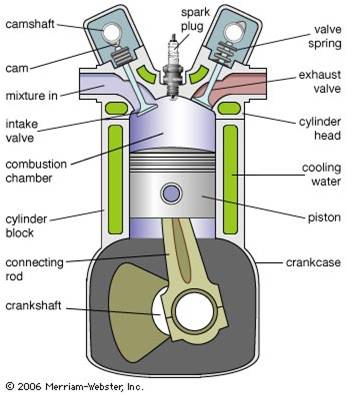
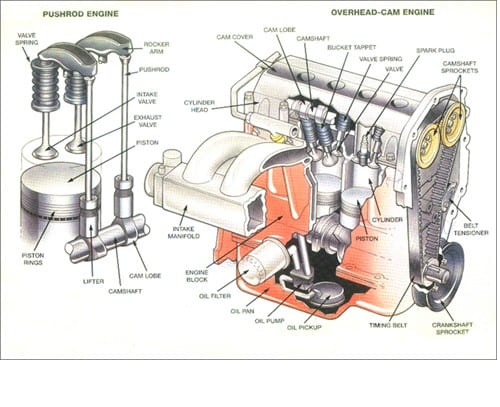
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINE DESIGN LAB
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Design and drawing of piston.
2. Piston pin and piston rings and drawing of these components.
3. Design of connecting rod small end and big end, shank design, design of big end cap, bolts and drawing
of the connecting rodassembly
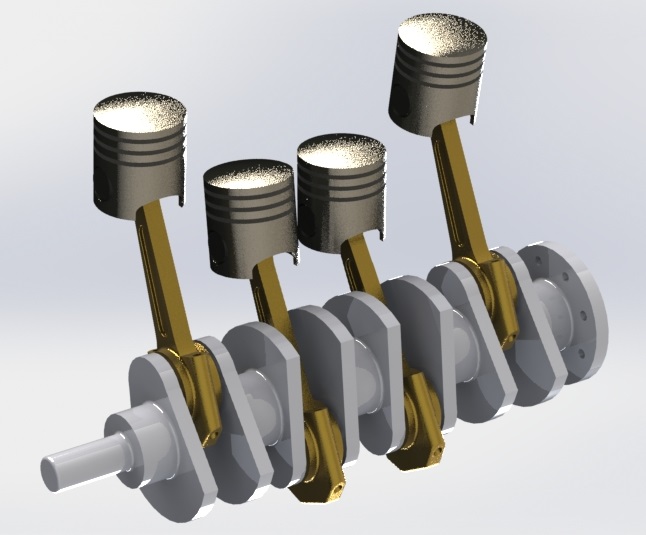
4. Design of crankshaft, balancing weight calculations.
5. Development of short and long crank arms, front end and rear end details, drawing of the crankshaft
assembly.
6. Design and drawing of flywheel.
7. Ring gear design, drawing of the flywheel including the development of ring gear teeth.
8. Design and drawing of the inlet and exhaust valves.
9. Design of cam and camshaft, cam profile generation, drawing of cam and camshaft.
10. Design of combustion chamber.
COMPUTER AIDED CHASSIS DESIGN LAB
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
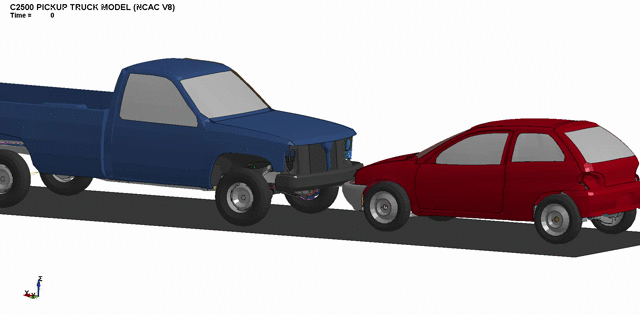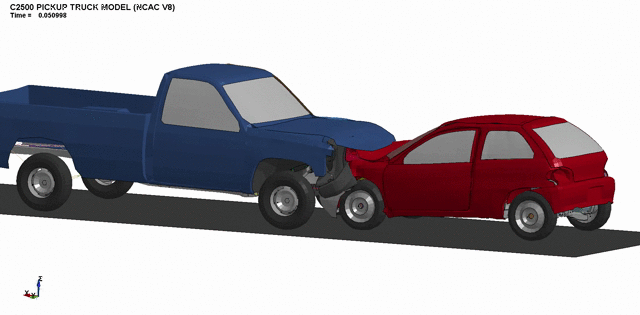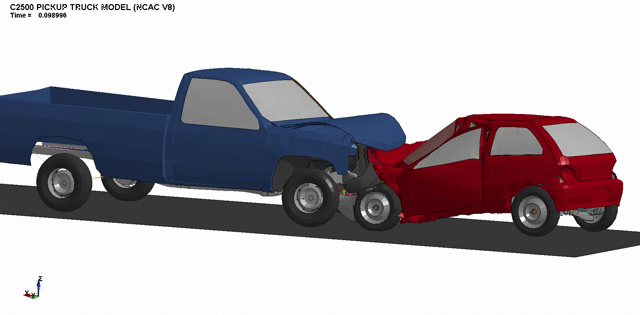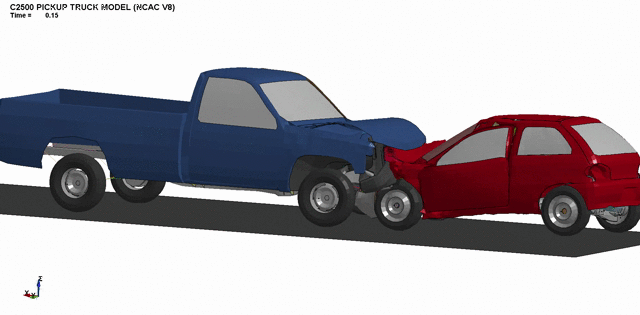
1. Design of heavy duty vehicle frame (Leyland, Tata etc.)
2. Design of light duty vehicle frame (Ambassador, Maruti van etc.)
3. Front bumper crashworthiness optimization.
4. Simulation of full-scale passenger car impacts.
5. Design of front axle and rear axle
6. Automotive styling: sketching, modeling, surfacing and visualization.
7. Design of differential
8. Design of steering systems along with any two types of steering gear box
9. Design of braking systems – hydraulic servo vacuum, compressed air power brakes.
10. Design of leaf spring, coil spring, torsion bar spring, hydraulic shock absorber
11. Design of clutch assembly of different types
12. Design of gear Box
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
Course Outcome:
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
· Become familiar with a range of CALL applications.
· Understand how particular technologies can be used to support learning in different situations.
· Increase knowledge and confidence in using technology in teaching/learning.
· Become aware of the social and cultural aspects of CALL.
· Evaluate technologies and implementations.

The studio will expose the students to various aspects of computer applications into Architectural Design and Construction. It will open up the horizons of technical advances and advantages of computational technologies through the use of computer modeling, rendering, and digital fabrication. Focus on the exploration of space and place-making through the use of computer modeling and design construction

Goal
To diagnose, prevent and treat carious and non-carious tooth defects, pulpal and periapical pathologies, while restoring normal tooth form, function and esthetics, where indicated.
Objectives
Knowledge
§ The graduate should acquire the following knowledge during the period of training.
§ To diagnose carious and non-carious lesions and treat with simple restorative work.
§ To gain knowledge about aesthetic restorative material and to translate the same to patient’s needs.
§ To gain the knowledge about endodontic treatment on the basis of scientific foundation.
§ To carry out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To diagnose and manage traumatic injuries and to provide emergency endodontic treatment.
Skills
The student should attain following skills necessary for practice of dentistry
§ To use medium and high speed hand pieces to carry out restorative work.
§ Possess the skills to use and familiarize endodontic instruments and materials needed for carrying out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To achieve the skills to translate patients esthetic needs along with function.
Attitudes
§ Maintain a high standard of professional ethics and conduct and apply these in all aspects of professional life.
§ Willingness to participate in CDE program to update the knowledge and professional skill from time to time.
§ To help and participate in the implementation of the national oral health policy.
§ Should be able to motivate the patient for proper dental treatment and at the same time propermaintenance of oral hygiene should be emphasized which will help to maintain the restorative work and prevent future damage.
Competencies
At the completion of the undergraduate training program the graduates shall be competent in the following:
§ Competent to diagnose all carious lesions.
§ Competent to perform Class I and Class II cavities and their restoration with amalgam
§ Restore class V and Class III cavities with glass ionomer cement
§ Able to diagnose and appropriately treat pulpally involved teeth (pulp capping procedures)
§ Able to perform RCT for anterior teeth
§ Competent to carry out small composite restorations
§ Understand the principles of aesthetic dental procedures

Goal
To diagnose, prevent and treat carious and non-carious tooth defects, pulpal and periapical pathologies, while restoring normal tooth form, function and esthetics, where indicated.
Objectives
Knowledge
§ The graduate should acquire the following knowledge during the period of training.
§ To diagnose carious and non-carious lesions and treat with simple restorative work.
§ To gain knowledge about aesthetic restorative material and to translate the same to patient’s needs.
§ To gain the knowledge about endodontic treatment on the basis of scientific foundation.
§ To carry out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To diagnose and manage traumatic injuries and to provide emergency endodontic treatment.
Skills
The student should attain following skills necessary for practice of dentistry
§ To use medium and high speed hand pieces to carry out restorative work.
§ Possess the skills to use and familiarize endodontic instruments and materials needed for carrying out simple endodontic treatment.
§ To achieve the skills to translate patients esthetic needs along with function.
Attitudes
§ Maintain a high standard of professional ethics and conduct and apply these in all aspects of professional life.
§ Willingness to participate in CDE program to update the knowledge and professional skill from time to time.
§ To help and participate in the implementation of the national oral health policy.
§ Should be able to motivate the patient for proper dental treatment and at the same time propermaintenance of oral hygiene should be emphasized which will help to maintain the restorative work and prevent future damage.
Competencies
At the completion of the undergraduate training program the graduates shall be competent in the following:
§ Competent to diagnose all carious lesions.
§ Competent to perform Class I and Class II cavities and their restoration with amalgam
§ Restore class V and Class III cavities with glass ionomer cement
§ Able to diagnose and appropriately treat pulpally involved teeth (pulp capping procedures)
§ Able to perform RCT for anterior teeth
§ Competent to carry out small composite restorations
§ Understand the principles of aesthetic dental procedures

- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: PRIYANKA L.S
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Megavarnan R
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
To introduce the principles, and techniques of construction management and its significance in construction management planning, scheduling and project costing. The study on management principles relating to Quality, Resource and Safety in construction of projects.

• To introduce the principles, and techniques of construction management and its significance in construction management planning, scheduling and project costing. The study on management principles relating to Quality, Resource and Safety in construction of projects.

- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
The objective of the course is to introduce and disseminate the knowledge about project management and their
application during the pre- construction and construction phase of a large construction project life cycle. And also to provide the basic understanding about the various project management methodologies used in various phases
like initiation, feasibility, design phase, bid and award phases, construction and closeout phases of a project.

- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
1.Display a working knowledge of the cultural and historical contexts of significant works prescribed for study
2. Identify and describe distinct literary characteristics of contemporary literature and demonstrate an understanding of how 21st century culture, trends, and historical events affect the literature produced today.
3. Analyze literary works from various genres for their structure and meaning, using correct terminology.
4. Write analytically about contemporary literature .
5. Effectively communicate ideas related to the literary works during class and group activities.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enrich the students in the field of Cryogenic Engineering and its Applications.
To learn the various Refrigeration processes, Equipment, Instruments, gas separation and Purification processes.
UNIT 1 CRYOGENIC FLUIDS AND MATERIAL PROPERTIES 9 Hrs.
Cryogenic Engineering – Properties of cryogenic fluids – Oxygen, Nitrogen, Argon, Neon, Flourine, Helium. Hydrogen, Properties of Solids – Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical-Super conductivity, Cryogenic applications.
UNIT 2 CRYOGENIC REFRIGERATION AND GAS LIQUEFACTION 9 Hrs.
Principle – Joule Thomson Expansion, Cascade processes, Ortho para hydrogen conversion, cold gas refrigerators, LindeHampson cycles, Claude and cascaded systems, magnetic cooling, Stirling Cycle, Pulse Tube refrigeration.
UNIT 3 CRYOGENIC EQUIPMENTS AND REQUIREMENTS 9 Hrs.
Cryogenics- Heat Exchangers, Compressors, Expanders, Effect of various parameters in performance and system optimization. Insulation and Storage equipment for cryogenic fluids, industrial storage and transfer of cryogenic fluids.
UNIT 4 GAS SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION 9 Hrs.
Ideal gas, Mixture characteristics – composition diagrams – gas separation – Principle of Rectification process– principle and working of air separation, principle and working of gas purification.
UNIT 5 CRYOGENIC INSTRUMENTATION 9 Hrs.
Grinding process; cylindrical grinding, surface grinding, center less grinding – honing, lapping, super finishing, polishing, buffing and hobbing. Metallic Coatings; electro plating, galvanizing, tin coating, anodizing. Organic Finishes; primers, oil paint, brushing, spraying and rubber base coatings.
Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Describe the basic concepts of various cryogenic fluids and materials.
CO2 - Understand the cryogenic refrigeration and gas liquefaction.
CO3 - Understanding the working principles of cryogenic equipment.
CO4 - Understanding the working of gas separation and purification.
CO5 - Understanding the instrumentation of cryogenic technology
CO6 - To design the cryogenic system based on the application.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Randal F. Barron, Cryogenic Systems, McGraw Hill, 2010.
2. Cryogenic Engineering, Van Nostrand Co. Inc. 2011.
3. Klaus D. Timmerhaus, Richard Palmer Reed, Cryogenic Engineering: 50 years of progress, Springer, 2011.
4. Hastlden, C., “Cryogenic Fundamentals”, Academic Press, 2001.
5. Walker, “Cryocoolers”, Plenum Press, 2000.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Design complex electronic systems interfacing multiple integrated circuits.
Design and conduct experiments, as well as analyze and interpret data.
Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs. .
Identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems. .
Use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice
COURSE OBEJCTIVES
To understand the technologies behind the embedded computing systems.
To acquire knowledge about microcontrollers embedded processors and their applications.
To analyze and develop software programs for embedded systems
To have knowledge about the working of a microcontroller system and its programming in assembly language.
To provide experience to integrate hardware and software for microcontroller applications systems.
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
➢ To introduce varies concepts related to the study of society and culture.
➢ To develop an understanding of art, craft and design in a variety of contexts with respect to space, function and climate.
➢ To expose the students to the principles of Vastushastra and Feng shui and its applications in interior design.

- Teacher: Shruthi Natarajan
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
- Teacher: Shamili V
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: KIRUBHASHANKAR C K
Data Communication is exchange of information through a transmission medium may be wired or wireless. Network is a set of devices connected by a communication link. Hence the course focuses on how communication is managed in a network and its basic protocols.
This course comprises of totally five chapters including the basics of data communication and networking concepts and various protocols in Physical, Data link and Transport Layers.

- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: V.J.K.Kishor Sonti
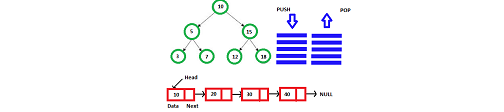
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To implement linear and non-linear data structures.
➢ To understand the different operations of search trees.
➢ To implement graph traversal algorithms and sorting algorithms.
➢ To get familiarized to binary tree traversal.
➢ To implement travelling salesman problem.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Program to find the largest and smallest number in an unsorted array.
2. Program to implement operations on a Singly linked list.
3. Program to implement operations on a doubly linked list.
4. Program to sort the elements using insertion sort.
5. Program to sort the elements using quick sort.
6. Program to sort the elements using merge sort.
7. Program to implement a Stack using an array and Linked list.
8. Program to implement Queue using an array and Linked list.
9. Program to implement Circular Queue.
10. Program to convert an infix expression to postfix expression.
11. Program to implement BFS and DFS
12. Program to implement N Queens problem.
13. Program to implement Binary Tree Traversal
14. Program to implement Travelling Salesman Problem
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Remembering the concept of data structures through ADT including List, Stack and Queues
CO2: Understand basic concepts about stacks, queues, lists, trees and graphs
CO3: Able to apply and implement various tree traversal algorithms and ensure their correctness
CO4: Ability to analyze algorithms and develop algorithms through step by step approach in solving problems with the help of fundamental data structures.
CO5: Compare and contrast BFS and DFS.
CO6: Design applications and justify use of specific linear and binary data structures for various applications
- Teacher: JESLIN SHANTHAMALAR JACOB SAMUEL
- Teacher: Roobini M S
- Teacher: Srinivasan N
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Sathya Bama R
- Teacher: Prince Mary S
- Teacher: NITHYA SEKAR
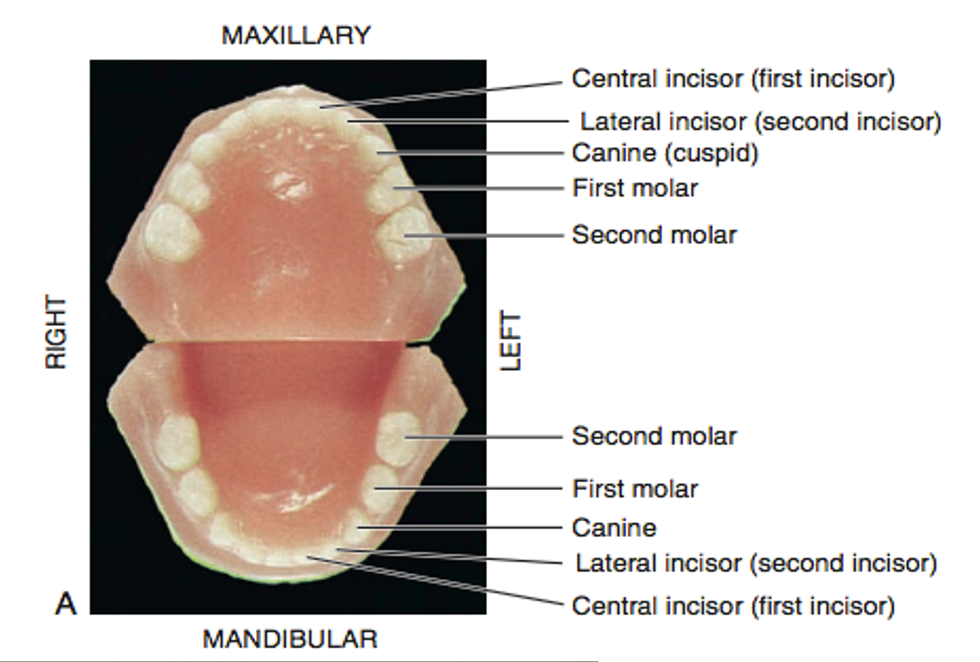
Dental Anatomy is defined as:
The study of dental anatomy, physiology, and occlusion provides one of the basic components of the skills needed to practice all phases of dentistry.
DESIGN-III (KID'S WEAR)
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the basic principles of research and learn various methods available for collecting and analysing data.
- To develop the ability to understand design strategies and plan design activities for women’s wear.
- To understand the application of various tools to fashion forecasting in Indian markets
- To comprehend fashion forecasting as a tool to understand consumer behavior in the Indian scenario.
Fashion Design Process for Kid’s Wear
- Inspiration Board - Collects different inspirational images, words, and objects (fabric, colour, textures, trims, paint chips, packaging, etc.) in the form of a paper poster, a bulletin board, a digital graphic, or a video.
- Research –- Exploring, Conceptualizing and visualizing information generated by observation and investigation. Record the all research information’s and creates a rich visual archive used to inspire designs from theme to final detail.
- Trend forecast for the desirable season.
- Market Research
- Mood Board - To create the theme for the range or collection with based on the trends of color, trims, fabrics, etc.
- Doodling - Sequential doodling, design concepts are developed through a process in which perceptually and conceptually proceeds by processing information.
- Form and Design development - Develop the concept and appearance of the fashion item Sketches & diagrams are develop Patterns & samples.
- Range development and design selection.
- Fashion illustration
- Flat drawing (Technical Drawing)
- Material exploration
- Photoshoot

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide a clear understanding on the basic concepts, Building Blocks of Embedded Systems.
- To teach the fundamentals of Embedded processor Modeling, Bus Communication in processors, Input/output interfacing.
- To introduce processor-scheduling algorithms, Basics of Real time operating systems.
- To discuss on aspects required in developing a new embedded processor, different Phases& Modeling of embedded system.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the components of embedded system and different communication protocols.
CO2 - Describe the differences between the general computing system and embedded system, also recognize the
classification of embedded systems.
CO3 - Attain expertise with embedded system development and debugging tools.
CO4 - Apply the interrupt service mechanism in the design of embedded system.
CO5 - Design of real time embedded systems using the concepts of RTOS.
CO6 - Articulate the role of embedded systems in industry and provide feasible design solutions for given problem
statement.
To enable the students, understand the principles of composition and its importance in Architecture and to understand role of transformation of form in Architecture
To know the importance of spatial qualities and to experiment and understand the art of space arrangement
To enable Conceptualization in architecture through creative thinking and to analyse the functional relationship between
space, user and built environment
- Teacher: VIJENDRANATH R
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: SHOBANA SUBRAMANIAN
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Assess the site and surroundings and its relationship with the activity, space for the given architectural program.
CO2 Analyze and evaluate a design of given space by dissecting the case studies and evolve inferences.
CO3 Application of anthropology and spatial data for arriving at requirements of the given space.
CO4 Apply the knowledge on climate responsive building design and implement appropriate design strategies.
CO5 Build a Process for Design evolution and communicate through drawings – plan, elevation and sections and final presentation with renderings.
CO6 Evaluation of the design through creation of miniature models and experimentation of space design and 3D through the explored models.
- Teacher: Selvendiran S.G
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
⮚ The studio aims at widening the avenues of creativity and allows inquiring more on lateral thinking.
⮚ The emphasis is on understanding the process of design as a proactive and analytical tool towards generating alternatives which forms the foundation for future design
⮚ To introduce students to various ideas and techniques of creative thinking and communication; To provide students
with a foundation in design through the comprehension of elements and principles of composition;
- Teacher: Arulmalar Ramaraj
With an intention meet the aforementioned objectives, ‘ANEW Residence’ is introduced as the design problem with five stages in the third semester. The thrust area of the Design Studio is on the ‘Materials and Construction Studio I (SARA2202) that has been offered in semester II and the theory courses offered in the current semester ‘Climatology (SARA1303) and ‘Principles of site planning (SARA1304)’. The design problem framed in the current semester will focus on incorporating the knowledge already gained as part of the Materials and Construction Studio I as well as the information that will be comprehended through the courses ‘Climatology’ and ‘Principles of site planning’ in the current semester.

- Teacher: Selvendiran S.G
- Teacher: EVELYN JENY V
Fashion Design II will focus on generating garment details to enable better
understanding of comfort and function and garment detail as design feature
culminating in Men’s wear garment. It aims to train students to see proportion
and shape in relation to human form while developing basic skills and
knowledge in fashion material and processes and technical areas of garment
manufacturing In Design - design process with a focus on detailing- functional & commercial
aspects of Design. Subject will start with a simple detailing concept and explore
it to the maximum and create workable ideas to generate a range of Men’s wear
garments – presentation through sketches- paper- models- photography- notes
of reference

Design-II (Men's Wear)
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the basic principles of research and learn various methods available for collecting and analyzing data.
- To develop the ability to understand design strategies and plan design activities for women’s wear.
- To understand the application of various tools to fashion forecasting in Indian markets
- To comprehend fashion forecasting as a tool to understand consumer behavior in the Indian scenario.
Fashion Design Process for Women’s Wear
- Inspiration Board - Collects different inspirational images, words, and objects (fabric, colour, textures, trims, paint chips, packaging, etc.) in the form of a paper poster, a bulletin board, a digital graphic, or a video.
- Research –- Exploring, Conceptualizing and visualizing information generated by observation and investigation. Record the all research information’s and creates a rich visual archive used to inspire designs from theme to final detail.
- Trend forecast for the desirable season.
- Market Research
- Mood Board - To create the theme for the range or collection with based on the trends of color, trims, fabrics, etc.
- Doodling - Sequential doodling, design concepts are developed through a process in which perceptually and conceptually proceeds by processing information.
- Form and Design development - Develop the concept and appearance of the fashion item Sketches & diagrams are develop Patterns & samples.
- Range development and design selection.
- Fashion illustration
- Flat drawing (Technical Drawing)
- Material exploration
- Photoshoot

- Teacher: gayathri N
COURSE OBJECTIVES
This course is meant to give them a broad exposure to the understanding of various concepts of Linux Kernel and Device Driver Programming.
The course will provide the students with
(i) The core concepts of operating systems
(ii) the knowledge of Linux Kernel architecture and device driver framework,
(iii) the methodology to write Programs for chosen embedded devices, and
(iv) the skill to use basic techniques for debugging in Linux device drivers and
(v) basic understanding of Linux based embedded system design.
Experiments will run in synchronism with the lectures to support the methods and techniques taught in the lectures. Through the experiments, the students will
(i) learn how to setup environment for developing and debugging device drivers,
(ii) gain confidence to write/customise Linux device drivers, debug and test them using a target platform.
Learning Outcome of students are
(i) Understanding of complex Linux Kernel framework and extending this knowledge to understand any type of operating system
(ii) Writing device drivers for simple embedded devices
(iii) Basic scripting to building the Linux Kernel and Device Drivers
(iv) Demonstrate end-end data flow from device to application
(v) Demonstrate various debugging techniques when the system crashes due to a malfunctioning Kernel or Device Driver
(vi) Plan and execute simple device driver development projects.

- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Shanthi Thangam M
After the completion of this course, Students will be able...
To know the principles of formatting (sampling , quantization and encoding)
To analyze the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To analyze various digital modulation techniques and compare with analog modulation techniques
To under stand the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To review the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: JEGAN G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Design PCM systems.
CO2 - Apply the knowledge of signals and system and evaluate the performance of digital communication system in the presence of noise.
CO3 - Design and implement band pass signaling schemes and analyze the spectral characteristics of band pass signaling schemes.
CO4 - Design encoder and decoder for the error control codes like block code, cyclic code. CO5 - Analyze the digital communication system with spread spectrum modulation.
CO6 - Examine the theoretical concepts through laboratory experiments, analyze and interpret the results to provide valid
conclusions.
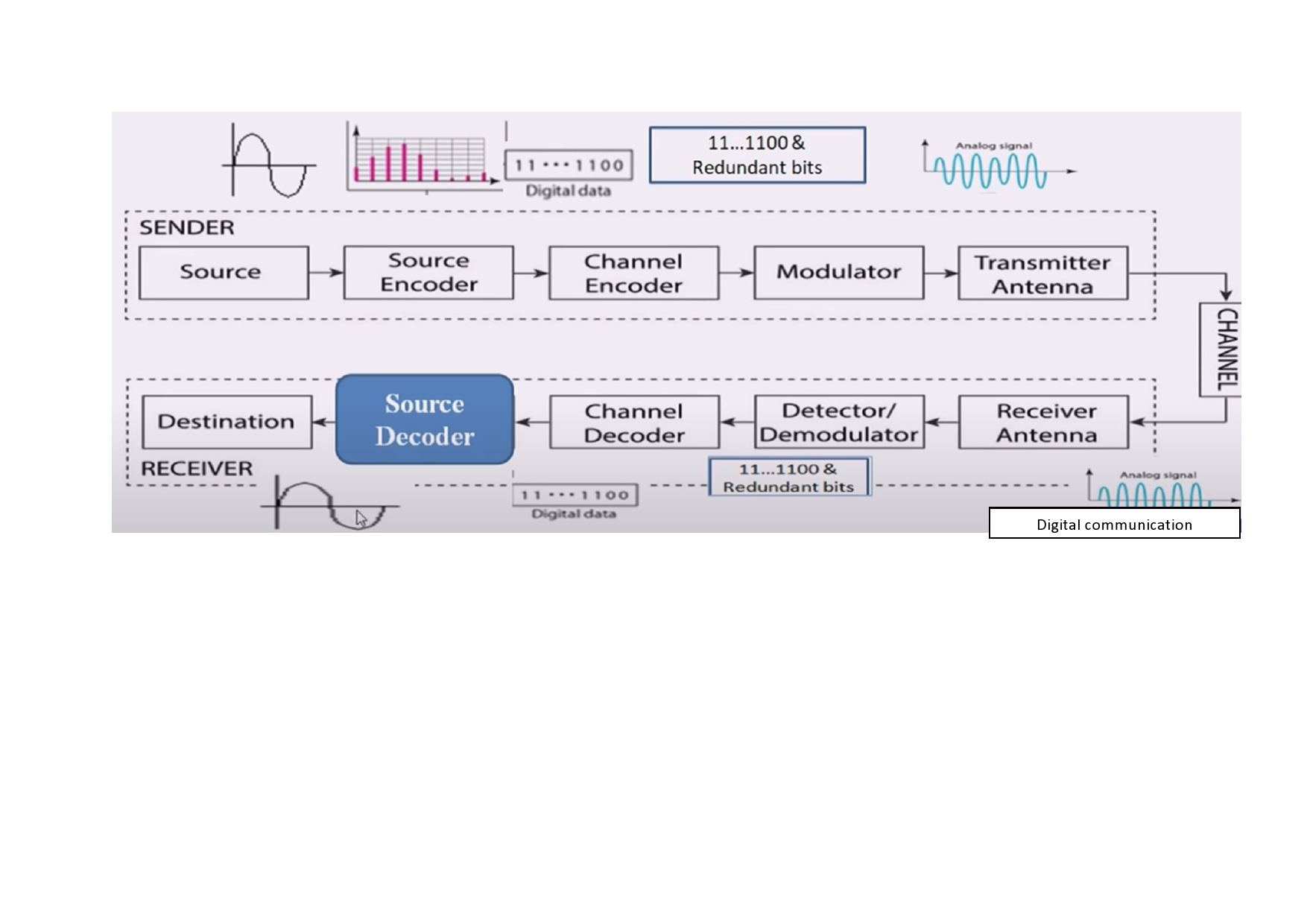
- Teacher: JEGAN G
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
Define
truth table; Construct truth table of the compound statements, list equivalent Propositions, Evaluate problems on implication and Equivalence laws, Distinguish PCNF and PDNF, Solve
problems on Inference theory for Propositional Calculus and Predicate Calculus. Identify semigroup and Monoid, Analyze properties of semigroups and monoids. Understand Equivalence Relation and partially ordered relation, List basic properties of Lattices and Boolean algebra. Analyze Lattices as Algebraic
system. Develop
supremum and infimum in Boolean function.

- Teacher: Srividhya S
The Main Objective of this Course is to improve the Analytical, logical thinking of the Students which in turn improves their ability of giving conclusions based on quantitative information , model the engineering problems and obtain its solutions mathematically. On completion of this course, students will be able to understand science, engineering and computer science problems analytically and logically
This topic deals with Logic-Set theory-Graph theory -Group theory- Numerical methods to solve the equations and Numerical interpolation ,differentiation and integration.

- Teacher: PRIYA SHIRLEY MULLER
Drug Store and Business Management is a study maintenance of Drug store as per norms, Sales Promotions, Recruitment and Training of Pharmacist and accountancy(Trial Balance and Balance sheet).

- Teacher: ARUN SUNDAR M
- Teacher: Shanmugapandiyan P
- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ÿ To Give a Introduction to Electrical machines.
ÿ To explain how electrical power is converted in to mechanical Power.
ÿ To explain how Mechanical power is converted in to Electrical Power.
ÿ To explain the importance of load test on the electrical machines.
- Teacher: Bharathi M L
- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To construct the amplifier circuits.
To design the oscillator circuits.
To design the feedback amplifier circuits.
To design the importance of digital circuits. ÿ To design the importance of PSPICE.

- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
To understand the concepts of combinational and sequential circuits and to design combinational logic circuits using digital IC’s.Course Outcomes:
By the end of this course students will be able to
CO1: Design the amplifier circuit for given specification and analyze them discuss oscillator principles, oscillator types and frequency stability as it relates to its operation.
CO2: Analyze and Design the different types of Oscillators. Discuss ideal and practical operational amplifier (op amp)their electrical parameters, need for op amp.
CO3: Explain and design different application circuits using op amp.
CO4: Construct the basic block of communication system. State the principles of modulation and explain the different modulation techniques.
CO5: Describe the theory and operation of radio systems and super-heterodyne receivers. Solve simple examples.

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
ELEMENTS OF TEXTILES
Course Code -SFD1103
ObjectiveElements of Textiles is to understand the important characteristic of different fabrics used Commercially. Students will learn to identify various fabrics textile by their look, appearance and feel. The knowledge gained through this subject will enable to select the right fabric for a particular end-use. They will be introduced to Basic surface ornamentation like Embroidery .
UNIT I
Introduction to Fibers - Classification of Textile fibers - Natural and Manmade fibers. Primary and secondary characteristics
of textile fibers. Swatch file collection with different types of fibers - Cotton, Linen, Wool, Synthetic.
UNIT II
Manufacturing process, properties and uses of natural fibers and Manmade fibers. Natural Fibers – cotton, linen, jute, silk,
wool, and hair fibers. Manmade fibers – Rayon and its types, nylon, polyester and acrylic.
UNIT III
Spinning - Introduction, Spinning methods - Chemical Spinning and Mechanical Spinning. Chemical spinning – Wet, Melt &
Dry spinning of filament yarns. Mechanical Spinning – cotton system - sequence of process, objectives of blow room,
carding, drawing, combing, roving and ring spinning.
UNIT IV
Yarn – definition. Properties of Yarn - Yarn numbering systems – Direct and indirect system of yarn count. Yarn twist.
Classification of yarns – Simple yarn, Single yarn, Ply yarn, Novelty Yarns.
UNIT V
Basic fabric formation methods – Woven, Knitted and Nonwoven fabrics. Manmade Weaving process - Basic weaves used
in commercial fabric - End use of fabrics - different type of weaves. Introduction to knitting, Types of Knitting, Applications of
knitwear. Fabric Sourcing and market awareness - Fabric Analysis - Swatch file collection with various types of weaves and
fabrics.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Classify the various sources of fibers and
CO2: Elaborate the manufacturing process of fibers
CO3: Understand the process of spinning sequences.
CO4: Classify yarns and analyze its attributes.
CO5: Understand the different types of fabric formation methods
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Textiles, Sara J. Kadolph, Pearson publication, 2009.
2. Fabric Science -5th edition, Joseph J Pizzuto, Fairchild Publications, Newyork ,1980.
3. Handbook of Nonwovens- Edited by R J Russell, Woodhead Publishing Ltd, England, 2007.
4. Knitting Technology- B.Ajgoankar, Universal Publishing Corporation, Mumbai, 1998.
5. Fibre to Fabric, Bernard P Corbman, (6th edition), Tata McGraw - Hill Education, 2003

This course would help to understand the underlying principles of embedded operating systems and
develop device drivers for various I/O modules.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- In this course, students learn about hardware and software aspects of embedded systems.
- The course focus on 8-bit and 32 bit microcontrollers, introducing advanced topics including communication interfaces, advanced IO devices and other peripherals.
- The course will provide a hands-on experience in designing and programming an embedded system using a microcontroller-based development platform.

COURSE OBJECTIVES ÿ
To understand the programming of ARM processor.
ÿ To teach to interface ARM processor with other peripherals and system design using ARM processor.
ÿ To apply the programming concepts related to TMS320C24X processor.
ÿ To teach interfacing of DSP processor with other peripherals.
ÿ To design DSP controller for speed control of DC motor.
EMBEDDED LAB USING ARM CONTROLLER
1. Arithmetic operations manipulation and logical operations
2. Interfacing of Switch
3. Interfacing of LED
4. Interfacing of LCD
5. Interfacing of DC Motor.
DSP LAB EXPERIMENTS USING 2407 & ASSOCIATED PERIPHERALS
1. Perform 16 bit Addition, subtraction & multiplication.
2. Study on PWM generation using Timer 1,2,3.
3. Study of two PWM generation using full compare unit.
4. Study of six pulse PWM generation using full compare unit with dead band timer.
5. Perform Analog to Digital conversion for an Analog input.
6. Perform variable speed of DC Motor using TMS 320C2407
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To study the basics of Embedded System.
- To explain the various development tools in embedded System.
- To get a knowledge in embedded programming and acquire a knowledge in embedded system application

- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
- Teacher: Pandian R
COURSE OUTCOMES: At the end of the course,
the students will be able to
· Get knowledge on Technology and Digital Literacy
· Apply online tools and strategies and enjoy working in an online environment
· Write, create and complete the assignments online
· Create accounts in various social networks and to handle the common platform carefully.
· Create PPT, Blogs, HTML pages and upload in the website.

- Teacher: Vigneshwari S
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
|
SPYA1202 |
Professional Elective II Environmental Psychology |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT I(15 hours)
Environmental Psychology: History – Scope - Research Methods: Questionnaire studies - Laboratory experiments - Computer simulation studies - Field studies -Case studies- Overconsumption: Our Ecological Footprint – Energy – Water – Food -Material Goods.
UNIT II(15 hours)
Climate Change as a Unique Environmental Problem: Public Understanding of Climate Change - Assessing the Risk of Climate Change - Environmental Stress: Conceptualizations of Stress - Effects of Environmental Stress
UNIT III (15 hours)
Measuring Environmental Behaviour Values and Pro - Environmental Behaviour -Theory of Planned Behaviour - Protection Motivation Theory - The Norm Activation Model - The Value‐Belief‐Norm Theory of Environmentalism - Goal‐Framing Theory
UNIT IV (15 hours)
Social Norms and Pro - Environmental Behaviour, Emotions and Pro - Environmental Behaviour, Symbolic Aspects of Environmental Behaviour-Restorative Environments Research: Stress Recovery Theory - Attention Restoration Theory
UNIT V (15 hours)
Informational Strategies to Promote Pro- Environmental Behaviour: Changing Knowledge, Awareness, and Attitudes - Encouraging Pro Environmental Behaviour with Rewards and Penalties - Persuasive Technology to Promote Pro - Environmental Behaviour
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
This course introduces you to the study of human-environment interactions from a geographic perspective, with a special emphasis on agriculture. ... These themes include: human population growth, consumption, biodiversity, climate change, and environmental health.

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
- Teacher: Krithika S
To make Students learn structural and functional relationships in proteins and altering their structure in order
to function ‘better’. To provide basic knowledge of enzyme technology and use of enzymes as tools in industry, agriculture and
medicine
- Teacher: oviya R.P
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to
1. Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human body.
2. Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
3. Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of the human body.
4. Perform the various experiments related to special senses and the nervous system.
5. Appreciate the coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system
- Teacher: Dr.Aishwarya Srinivasan
This course is designed to impart basic knowledge on public health, epidemiology, preventive
care and other social health related concepts. Also, to emphasize the roles of pharmacists in the
public health programs.
- Teacher: Magaline Breezy M.K
|
SPYA4201 |
Core Practical 1 Experimental Psychology 1 |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
00 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES: 30 Hours
· To facilitate psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
Students are expected to administer, score and interpret ten of the following category.
1. Stress Coping Techniques
2. Meta Cognition Inventory
3.Self Concept Rating Scale
4.PGI Memory Scale
5.Human Maze Learning
6.Span of attention (Tachistoscope)
7.Study habits inventory
8.Comprehensive interest schedules (Female & Male)
9.Bells Adjustment Inventory
10. Muller lyer Illusion
11. Creativity test
References
1. Woodworth, R.S. and Scholesberg (1972) Experimental psychology. Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
2. Anastasi. & Susana Urbina (2004) 7th Edition.Psychological Testing, Pearson Education Inc., New Delhi.
3. Cronbach, L.J. (). Essentials of Psychological Testing.
4. Parameswaran & Ravichandra (2003) Experimental Psychology. Neel Kamal Publications.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will understand psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
2. Students will evaluate major concepts and empirical findings in tests and measurements.
3. Students will analyse real examples of psychological tests for usefulness, applicability, strengths and weaknesses, and validity.
4. Students will apply methods for evaluating the quality of psychological tests to real examples of psychological tests.
5. Students will remember knowledge of testing methods to measurement in real world situations.
6. Students will create material that compares and contrasts perspectives on some controversial issue (e.g., intelligence testing) within the field of psychological testing.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
|
SPSY4501 |
Core Practical 4 Experimental Psychology 4 |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
0 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES: 30 Hours
· To facilitate psychological testing and measurement, in view of an in-depth understanding of psychological processes.
Students are expected to administer, score and interpret ten of the following category
1 Emotional Intelligence
2. Experiments on Social conformity
3. Psychological Hardiness
4. Peer Pressure Scale
5. General Wellbeing
6. Mental Health Chick list
7. Achievement Motivation
8. Mirror drawing
9. Job Involvement Scale
10. Job satisfaction
11. Organizational Climate
12. Stress Scale
References
1.Woodworth, R.S. and Scholesberg (1972) Experimental psychology. Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
1. Anastasi. & Susana Urbina (2004) 7th Edition. Psychological Testing, Pearson Education Inc., New Delhi.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will apply methods for evaluating the quality of psychological tests to real examples of psychological tests.
2. Students will remember knowledge of testing methods to measurement in real world situations.
3. Students will create material that compares and contrasts perspectives on some controversial issue (e.g., intelligence testing) within the field of psychological testing.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
FABRIC MANIPULATION TECHNIQUES
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To develop skills in fabric manipulation techniques through subtraction and construction techniques.
- To enhance the student’s skills in fabric manipulation and improve the style to putting their own stamp on their project.
- To create a decoration to enhance its attraction to the individual.
LIST OF EXERCISES:
- Embroidery and fabric manipulation - Gathering, Shirring, Pleating, Tucking, Smocking, And Quilting.
- Embellishment through addition - Appliqué/ Applied Works, Piping Couching, Stitching/ Hand Stitching,
Beads and beading
- Embellishment through subtraction - Decoupe/ Reverse Technique, Cutwork, Drawn Thread, Pulled Work
- Beads and beading - Tambour Work, Hand Beading, French Beading
- Construction techniques - Patchwork, Applied Patchwork, Long Cabin Patchwork, Trimming (Fringe Trim, Sewing Trim)

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Yuva Poornima A
- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
Fashion Illustration is the art of communicating fashion ideas in a visual form that originates with illustration, drawing and painting and also known as Fashion sketching, Fashion sketching plays a major role in designing to preview and visualize designs before sewing actual clothing.

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce students to aspects of fashion marketing and retailing
- To impart knowledge about various product standards and product specifications and the process of product development towards market need.
UNIT I (9Hrs)
Market - Meaning, Definition and Classification; Fashion Market - Activities of Fashion Marketing, Fashion Market Size and Structure, Marketing Environment - Micro and Macro Marketing Environment.
UNIT II (9Hrs)
New product development - Planning, design and development – Product Classification, Product life cycle – Concept of Marketing Mix, Market Segmentation, Targeting and positioning - Perpetual mapping- Product Mix and Range planning. Marketing research process. Pricing - objectives and methods of setting prices.
UNIT III (9Hrs)
Distribution Channels - Types, Levels, development. Promotion Mix – Analytical tools- BCG matrix, GE model. Consumer Behavior - influencing factors – Consumer Buying process. Types of Buyers. Brand development- Branding and its importance in Marketing. Retailing and wholesaling – promotion methods.
UNIT IV (9Hrs)
Fashion Retailing - Classification of Retailers – Onsite Retailing and Off-site Retailing; Types of Retail Store; Merchandising mix- Order Management- Out Sourcing – Vendor Management – Export Documents. Role of a fashion buyer, Fabric sourcing, Garment sourcing, Local sourcing, National sourcing & International sourcing. Range Planning.
UNIT V (9Hrs)
Fashion sales promotional programme for fashion marketing, communication in prop motion, Personal selling, and point of purchase. Fashion Advertising and preparation of advertising for apparel market, Advertising media used in apparel market, Apparel & Textile Trade s

Fashion Marketing and Retailing
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce students to aspects of fashion marketing and retailing
- To impart knowledge about various product standards and product specifications and the process of product development towards market need.
UNIT I (9Hrs)
Market - Meaning, Definition and Classification; Fashion Market - Activities of Fashion Marketing, Fashion Market Size and Structure, Marketing Environment - Micro and Macro Marketing Environment.
UNIT II (9Hrs)
New product development - Planning, design and development – Product Classification, Product life cycle – Concept of Marketing Mix, Market Segmentation, Targeting and positioning - Perpetual mapping- Product Mix and Range planning. Marketing research process. Pricing - objectives and methods of setting prices.
UNIT III (9Hrs)
Distribution Channels - Types, Levels, development. Promotion Mix – Analytical tools- BCG matrix, GE model. Consumer Behavior - influencing factors – Consumer Buying process. Types of Buyers. Brand development- Branding and its importance in Marketing. Retailing and wholesaling – promotion methods.
UNIT IV (9Hrs)
Fashion Retailing - Classification of Retailers – Onsite Retailing and Off-site Retailing; Types of Retail Store; Merchandising mix- Order Management- Out Sourcing – Vendor Management – Export Documents. Role of a fashion buyer, Fabric sourcing, Garment sourcing, Local sourcing, National sourcing & International sourcing. Range Planning.
UNIT V (9Hrs)
Fashion sales promotional programme for fashion marketing, communication in prop motion, Personal selling, and point of purchase. Fashion Advertising and preparation of advertising for apparel market, Advertising media used in apparel market, Apparel & Textile Trade shows and fairs. Advertising department and advertising agencies – structure and functions. Advertising Budget
TEXT /REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Fashion Marketing- Mike Easey, Black Well Science Ltd., United Kingdom. 1995.
2. Apparel Merchandising, An Integrated Approach, Krishnakumar.M, Abishek Publications 2010.
3. Apparel Merchandising, Robin Mathew, Book Enclave Publishers, Jaipur (2008).
4. Retail Management, Chetan Bajaj, RajnishTuli and Nidhi.V.Srivastava, Oxford University Press, New Delhi 2005.
5. Advertising, C N Sonatakki, Kalyani Publishers New Delhi 1989.
6. Marketing, RSN Pillai and Bhagavathi.S, Chand And Company Ltd, New Delhi 1987.
7. Fashion retailing: A multi-channel approach Diamond, ENew Jersey: Pearson/Prentice Hall. 2006.
8. Inside the fashion business.Jarnow, J., Guereira, M. & Judelle, B. (4thEd.). MacMillan: New York, 1987.
9.. Fashion marketing, Ed. Hines, T. and Bruce, M. Buttersworth Heinemann,Oxford. 2001

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To impart knowledge about fashion Industry.
- To Understand fashion Basics and terminologies.
- To know the various international fashion centers Brands.
UNIT I
Introduction to fashion - definition and origin. Fashion terminologies – Classic, FAD, Style, Trend, prêt-à-porter, Mass Fashion, Street Fashion, Fashion forecasting, Boutique, Haute couture, line, Collection, Avantgarde, Custom made. Factors influencing fashion – Political and legal, Geographic, Demographic, technological, economic, social and cultural, factors, Life style changes etc.
UNIT II
Levels of fashion industry- Couture, Ready to wear, Mass production. Fashion Focus –The designers Role, The Manufacturers Role, The Retailers Role. Scope of Fashion Business – Primary Level, Secondary Level, Retail level and the Auxiliary level.
UNIT III
Types of designers – High fashion Designer, Stylist, and Freelance Designer. Sources of design inspiration. Biography of various Indian Fashion designers - Manish Malhotra, Ritu kumar, Ritu berri, Tarun Tahilani, Wendell Rodricks, Abu Jani and Sandeep Khosla, JJ Valaya, Manish Arora, and Rohit Bal. Study of international Designers - Coco Chanel, CK, Donatella Versace, Gucci, Giorgio Armani.
UNIT IV
Study of International Fashion centers – France, Italy, England, Germany, Canada, New York. Study of Fashion Brands –National Brand - International Brand - Designer Brand, Luxury fashion brand.
UNIT V
Theories of Fashion - Trickle up, Trickle-down and Trickle across. Fashion Cycle - Classic, FAD, Trend, Style. Fashion Seasons – International market and Indian market. The concepts of formal wear, casual wear, party wear, sportswear, jeanswear, swimwear, beachwear, and its functional aspects.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Gain knowledge on fashion terminologies.
CO2: Understand the levels of fashion Industry.
CO3: Obtain knowledge about the success of various fashion designers.
CO4: Gain knowledge on Fashion Capitals and Fashion Brands.
CO5 Understand the theories of fashion.

- Teacher: gayathri N

Course Objectives:
· To familiarize students through an effective blend of theory and practice in translation
· To focus the key concepts of the translation studies through various texts.
· To implement the diverse approaches and strategies of translation.
· To compare a variety of issues in relation to translation.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
Course objectives:
To understand literary texts and their authors in cultural and historical context.
To enhance reading literary fiction to develop empathy, theory of mind, and critical thinking.
To identify and cogently discuss the literary style of a text.
To interpret the literary images and symbols to infer their relationship to the main themes.

Filmmaking (or, in any context, film production) is the process by which a film is made. It's a non-linear methodology that evolved from the practical experiences in its beginnings, which was framed by what technology would allow; initially cameras holding only 10 minutes of negative raw stock at a time yet easily mobile. The methodology allowed for shots to be repeated as often as necessary for best performance and scenes shot out of order for the advantage of convenience and economics. The process is used today in the making of theatrical films, films made for cable, terrestrial television, streaming platforms, and is a process familiar to making documentaries, music videos, and student films. Filmmaking involves a number of complex and discrete stages including an initial story, idea, or commission, through screenwriting, casting, shooting, sound recording and pre-production, editing, and screening the finished product before an audience that may result in a film release and an exhibition. Filmmaking takes place in many places around the world in a range of economic, social, and political contexts, and using a variety of technologies and cinematic techniques.A film that was produced with the intent of fitting into a specific genre (such as science fiction, romantic comedy, horror, or film noir) with an existing audience.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
- Teacher: Director Admin
A more advanced technique of dental prosthesis which involves preparation of supporting teeth and elaborate/laborious laboratory procedures in fabricating a fixed denture with extensive knowledge in materials used, such as casting alloys, casting procedures, and investments, dental ceramics. This course deals with the biological, mechanical, and aesthetic details in fabricating a fixed partial denture for adults.


- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
To impart knowledge on the classification of food groups, composition and nutritive value of different food ingredients. To understand the role of each food group in cookery.

- Teacher: Priya S
To understand the refining process of petroleum.
To develop understanding about various types of fuels, lubricants and their properties
To understand the importance of Alternate fuels available.

- Teacher: Dr. Ashwin Jacob
- The lab course is designed to train the students in basic techniques of Biochemistry.

To suggest synthetic route for simple organic
compounds with stereochemistry
To make the students understand and appreciate the concept
of stereochemistry and reaction mechanism
To know the nature of addition in pericyclic
reactions
To learn the alpha cleavage and gamma hydrogen
transfer reactions
To understand the photochemical organic reactions
and rearrangement reactions
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
SMEA1602 GAS DYNAMICS AND JET PROPULSION
(Use of approved gas tables is permitted)
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To discuss the concepts of compressible and Incompressible fluids.
To understand Mach number variation on area ratio.
To impart in depth knowledge on the flow characteristics through constant area duct.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPRESSIBLE FLUID FLOW 9 Hrs.
Concept of compressible flow, Energy and momentum equations, various regions of flow, fluid velocity, stagnation state, velocity of sound, critical states, Mach number, critical mach number, Crocco number, types of waves, mach cone, mach angle, effect of mach number on compressibility.
UNIT 2 FLOW THROUGH VARIABLE AREA DUCTS 9 Hrs.
Isentropic flow through variable area duct, T-S and h-s diagrams for nozzle and diffuser flows, area ratio as a function of Mach number, Mass flow rate through nozzles and diffusers, effect of friction in flow through nozzles.
UNIT 3 FANNO FLOW AND RAYLEIGH FLOW 9 Hrs.
Flow in constant area duct with friction - Fanno curves, and Fanno Flow equations, variation of flow properties, variation of Mach number with duct length. Flow in constant area duct with heat transfer, Rayleigh line and Rayleigh flow equations, variation of flow properties, maximum heat transfer.
UNIT 4 NORMAL SHOCK AND OBLIQUE SHOCKS 9 Hrs.
Governing equations, variation of flow parameters, static pressure, static temperature, density, stagnation pressure, entropy across normal shock and oblique shocks. Normal shocks - stationary and moving, applications. Prandtl Meyer equation, impossibility of shock in sub-sonic flows, flow in convergent and divergent nozzles with shock, Flows with oblique shock.
UNIT 5 JET AND SPACE PROPULSION 9 Hrs.
Aircraft propulsion, types and working of jet engines - energy transfer in jet engines, thrust, thrust power, propulsive and overall efficiencies, thrust augmentations in turbo jet engines, ram jet and pulse jet engines. Rocket propulsion, types of rocket engines, Liquid and solid fuel rocket engines, Introduction to Electrical and Nuclear rockets-Space Flights, Orbital and escape velocity.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Recall the fundamental concepts of compressible fluid flow.
CO2 - Demonstrate the significance of mach number on compressibility.
CO3 - Differentiate isothermal flow and isentropic flow.
CO4 - Apply the concept of normal shocks to different turbo machines.
CO5 - Estimate the heat transfer in flow through constant area ducts.
CO6 - Calculate the propulsive power in jet engines.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Yahya S.M., ”Fundamental of Compressible flow”, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2003.
2. Cohen H., Rogers R.E.C. and Sravanamutoo, “Gas Turbine Theory”, Addison Wesley Ltd., 2001.
3. Hill D. and Peterson C., “Mechanics & Thermodynamics of Propulsion “, Addison Wesley, 1992.
4. Ganesan V., “Gas Turbines”, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company, New Delhi, 1999.
5. Sutton G.P., “Rocket Propulsion Elements”, John Wiley, New York, 1975.
6. J.D. Anderson, "Modern compressible flow", McGraw Hill Education, 3rd Edition, 2002.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
The course provides opportunities for students to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts that present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative. The thrust is on preparing students to effectively communicate by applying reflective thinking practices. Students will have an opportunity to improve their vocabulary related to immediate environment, practice speaking skills by discussing about issues based on reading texts, read texts that include everyday problems that provide opportunities to develop problem solving skills in cooperative learning situations, develop writing skills through writing paragraphs and letters based on prompts, by summarizing poems, writing email/ letters and composition of dialogues/paragraphs.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
• To develop the four basic skills of listening, reading, speaking, and writing, through an integrated approach.
• To improve comprehension and critical thinking skills.

- Teacher: Prasanna Lakshmi S
- Teacher: Jayashree S
Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos). More specifically, it is devoted to the study of the structural, biochemical, and functional changes in cells, tissues, and organs that underlie disease. By the use of molecular, microbiologic, immunologic, and morphologic techniques, pathology attempts to explain the whys and wherefores of the signs and symptoms manifested by patients while providing a rational basis for clinical care and therapy. It thus serves as the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine, and is the scientific foundation for all of medicine
For II BDS
- Teacher: oviya R.P
|
SPYA1401 |
Professional Core 5– Gerontology |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
Unit I INTRODUCTION (15 Hours)
Gerontology- Definition, concept, History, importance and scope, Old Age- Definition, meaning and concept, Demographics of Aging, Characteristics of old age. Myths and stereotypes about aging.
Unit II PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS OF ELDERLY (15 hours)
Changes and Developmental tasks of Old age- Cognitive, physical, psychological and social. Symptoms of mental illness in old age-Stress- Different forms of stressors in old age, Depression, Alzheimer’s and dementia, confusions due to multiple medications, loneliness, panic disorder, fear of death, anxiety. Reduced mental and cognitive ability, Insomnia, substance abuse, suicidal tendency, Falls.
Unit III POLICIES AND PROGRAMMES FOR AGED (15 hours)
Help Age International- Evolution, objectives, programmes, health and Nutrition, protection of elderly consumers, Housing and environment, Family, Social Welfare, income security and employment, education, recommendations for implementation. International Federation on Aging, WHO and old age.
Unit IV OLD AGE CARE (15 hours)
Crisis Intervention-medical (skilled care) versus non-medical (social care), Promoting independence in old age and improving mobility. Assessing and planning health care surgery, communicable diseases.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
VHDL DESIGN, SIMULATION, SYNTHESIS & FGPA IMPLEMENTATION OF
- Logic gates
- Adders and Subtractors
- 4-bit multiplier
- ALU
- Flip Flops
- Logic gates
- Adders and Subtractors
- 4-bit multiplier
- Flip Flops
- Shift registers
- Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters
- Moore and Mealy FSM
- RAM and ROM memories
- 4-bit RISC CPU
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; eachcarrying16 Marks 80MarkS
|
SPYA1203 |
Open Elective 2 - Health Psychology |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
100 |
Unit I : Introduction (15 Hours)
Mind-body relationship Health: Meaning – definition – Health Psychology: Definition - History of health psychology – adopting health related behavior – seeking medical attention – receiving healthcare care. Functions and need of health psychologists; Biopsychosocial Model
Unit II: Stress and Coping (15 Hours)
Theories of stress (Selye and Lazarus) - Stress and health: Sources of Chronic Stress - Stress related illness (PTSD and Acute stress disorder - Digestive system disorders – Asthma - Recurrent Headaches) Psychoneuro-immunology - Moderators of the stress experience - Coping with Stress
Unit III : Pain (15 Hours)
Psychological factors and pain - Individual differences in reactions to pain - Types of Pain - Assessment of Pain - Pain Control Techniques
Unit IV: Chronic illness and Management(15 Hours)
Cardiovascular diseases - Cancer - AIDS.Living with chronic illness, Quality of life, Emotional response to chronic illness, Rehabilitation,psychological interventions
Unit V : Health and Behavior (15 Hours)
Health compromising behaviors: Smoking, Alcoholism and substance abuse.Health enhancing behavior: Weight control, Diet, Exercise, Yoga
References:
1.Taylor, S.E. (2006) . Health Psychology. New Delhi : Tata Mc Graw-Hill
2.Sarafino, E.P. & Smith, T.W. (2012). Health Psychology :Biopsychosocial interventions. New
Delhi : Wiley
3.Linda Brannon and Jesse Feist, (2007): Introduction to Health Psychology, New
Delhi: Akash Press
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH COMPOSITE WALL
2. MEASUREMENT OF SURFACE EMMISSIVITY
3. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH LAGGED PIPE
4. HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH NATURAL CONVECTION
5. COUNTER FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER
6. PARALLEL FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER
7. THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF METAL ROD

HISTORY OF ART AND FASHION
Over the years, art and fashion have enjoyed a rich relationship, sometimes bold Equally, designers may have more subtle influences from an art,This subject is to initiate the students into the contextual basis of study of art ,costume, fashion and design in the history of different civilizations.
UNIT I (9Hrs)
Introduction to Art and Design History - Basic parameters for historical study of art, design and fashion, Influence of Design Aesthetics on art and fashion, Evolution the category of designer as distinct from the artist, craftsman and technologist.Timeline- prehistoric, ancient, middle, renaissance, early modern, modern and now.
UNIT II (9Hrs)
Emergence of Institutions like the Museum, Department Store and the Corporation. Objects of desire- Design and Society since 1750.Culture and Society. Twentieth Century Design, Design History.
UNIT III (9Hrs)
Design, the Industrial Revolution, Colonialism and the Coming of Modernity. Colonial design: Ideology, Economy & Patronage.
UNIT IV (9Hrs)
Design and Nationalism: The Case of India. Design Movements: Influences and Inspirations. Sustainable expressions.
UNIT V (9Hrs)
Products and Styles in other fields-Ceramics, Furniture, Interiors, Graphics etc. Arts and crafts Movement 1850-1900, Art Nouveau 1890-1905, The Machine Aesthetic 1900-1930. Art Deco 1925-1939, Streamlining-Consumerism and Style 1935-1955, Pop - Age of Affluence 1955-1975, Modernism, Post Modernism/Retro and Vernacular, Street Influence,Contemporary Thoughts in design.
Max.45 Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to
CO1 Understand the relationship between art and fashion
CO2 Develop inspiration from contemporary designs
CO3 Elaborate the Design and Nationalism
CO4 Build the essential knowledge in history of Art and Craft
CO5 Explore and generate ideas on subjects of art and fashion
TEXT/ REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Clothing art, the visual culture of fashion, 1600-1914 yale university press; 1 edition. 2017.
2. Fashion: the definitive history of costume and style, dk; 1st edition edition , 2012.
3. Fashion and art, adam geczy, vicki karaminas, 2012

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
To understand the tradition and culture of various region of India and their adaptation in interiors.
To develop an insight into the evolution of interiors in Chinese, Japanese and Islamic culture.
To introduce the evolution of interiors in Nordic culture.
To impart the design practices of the contemporary interiors.
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: Juvilasri Vignesh
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To explore the diverse factors that shaped the built forms during Neolithic, bronze and Iron Age.
- To understand the planning principles and the construction techniques adopted in the Early Iron Age.
- To understand the space development and structural quality in roman architecture.
COURSE OUTCOME:
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Outline the role of tangible and intangible factors that influenced the architecture during the Neolithic and bronze age.
CO2 Appraise the salient characteristics of Greek architecture.
CO3 Comprehend the other factors influencing architecture in India.
CO4 Analyze the contributing factors for the design development of different styles.
CO5 Compare and Contrast various styles on the basis of the contributing factors responsible for their development.
CO6 Discuss the influence of factors in determining the architectural character and features from Neolithic to late iron age.

- Teacher: Swetha N.M
Scope: This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge of the structure and functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
1. Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human body.
2. Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
3. Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of the human body.
4. Perform the haematological tests like blood cell counts, haemoglobin estimation, bleeding/clotting time etc and also record blood pressure, heart rate, pulse and respiratory volume.
5. Appreciate coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system
6. Appreciate the interlinked mechanisms in the maintenance of normal functioning
(homeostasis) of the human body
- Teacher: Harini R R
Anatomy is the Basic Science subject reveals the introduction to the basic structures, surfaces, and terminology of the Human body and their clinical significance concerned with the scientific study of the causes and effects of oral disease and understanding of which is essential for diagnosis and for the development of rational treatment and preventive plans in dentistry.
One of the most important purposes of Anatomy is to give the student the ability to correctly identify the structures given and their relations. Based on a sound knowledge of anatomy is essential for good clinical practice. The department imparts training in the Gross Anatomy of Head and Neck, Embryology, Histology, and neuroanatomy. The department provides cadaver demonstration and dissection for dental and medical professionals and also involved in research activities.
- Teacher: Tamil Selvi Palaniappan
Human genetics is the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings. Human genetics encompasses a variety of overlapping fields including: classical genetics, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, population genetics, developmental genetics, clinical genetics, and genetic counseling.

- Teacher: Madan Kumar Arumugam
On completion of the course, student will be able to -
CO1 - Understand the working of different configuration of electric vehicles.
CO2 - Understand the hybrid vehicle configuration.
CO3 - Differentiate electric and hybrid vehicles.
CO4 - Understand the properties of batteries and its types.
CO5 - Understand the electric vehicle drive systems and hybrid electric vehicles.
CO6 - Design of solar cell and fuel cell.
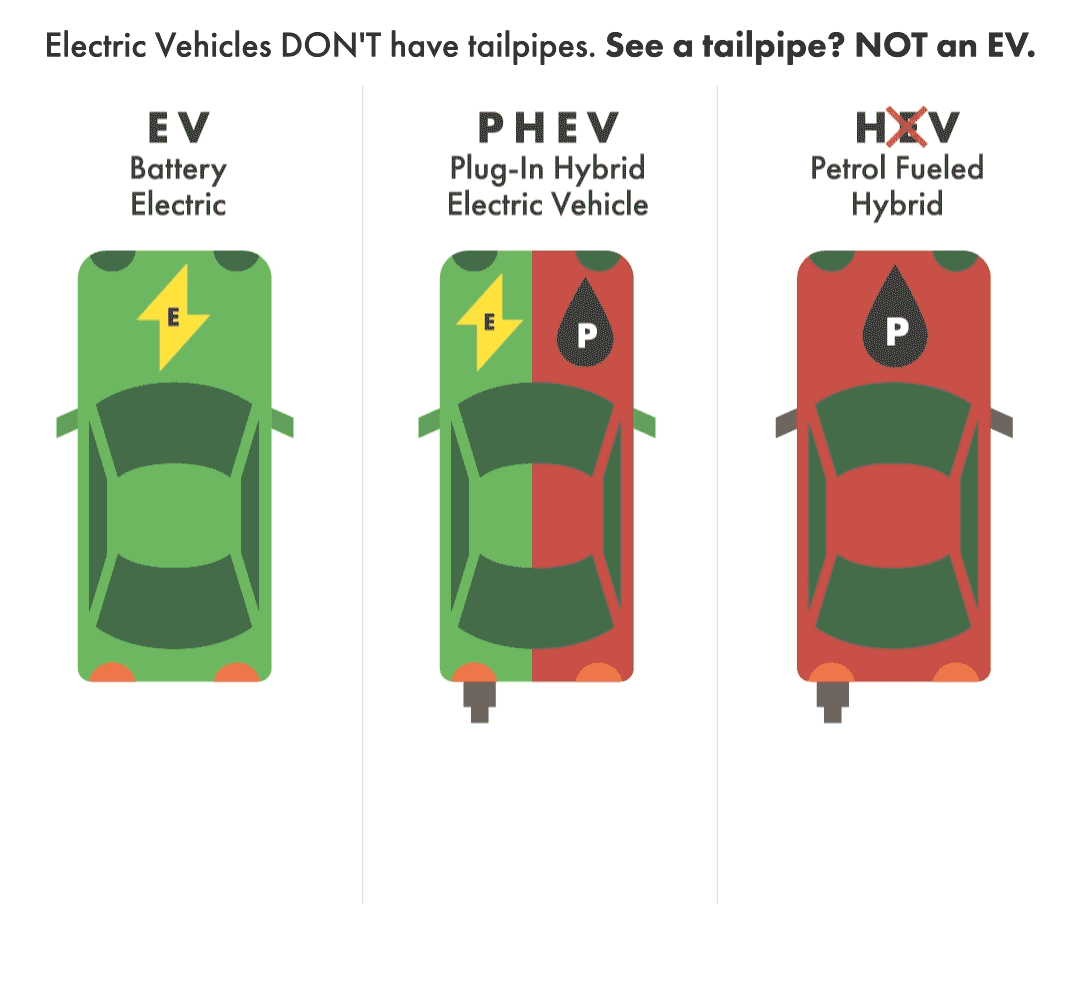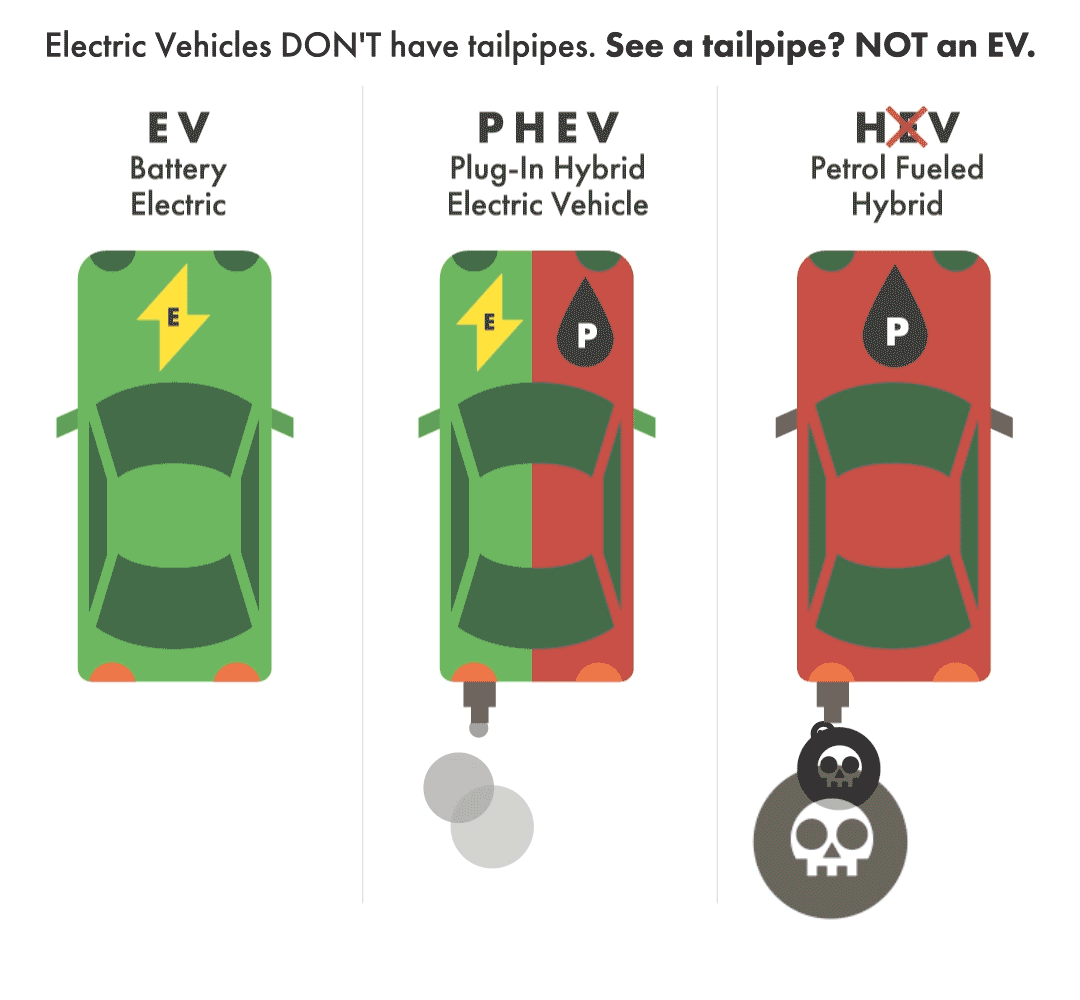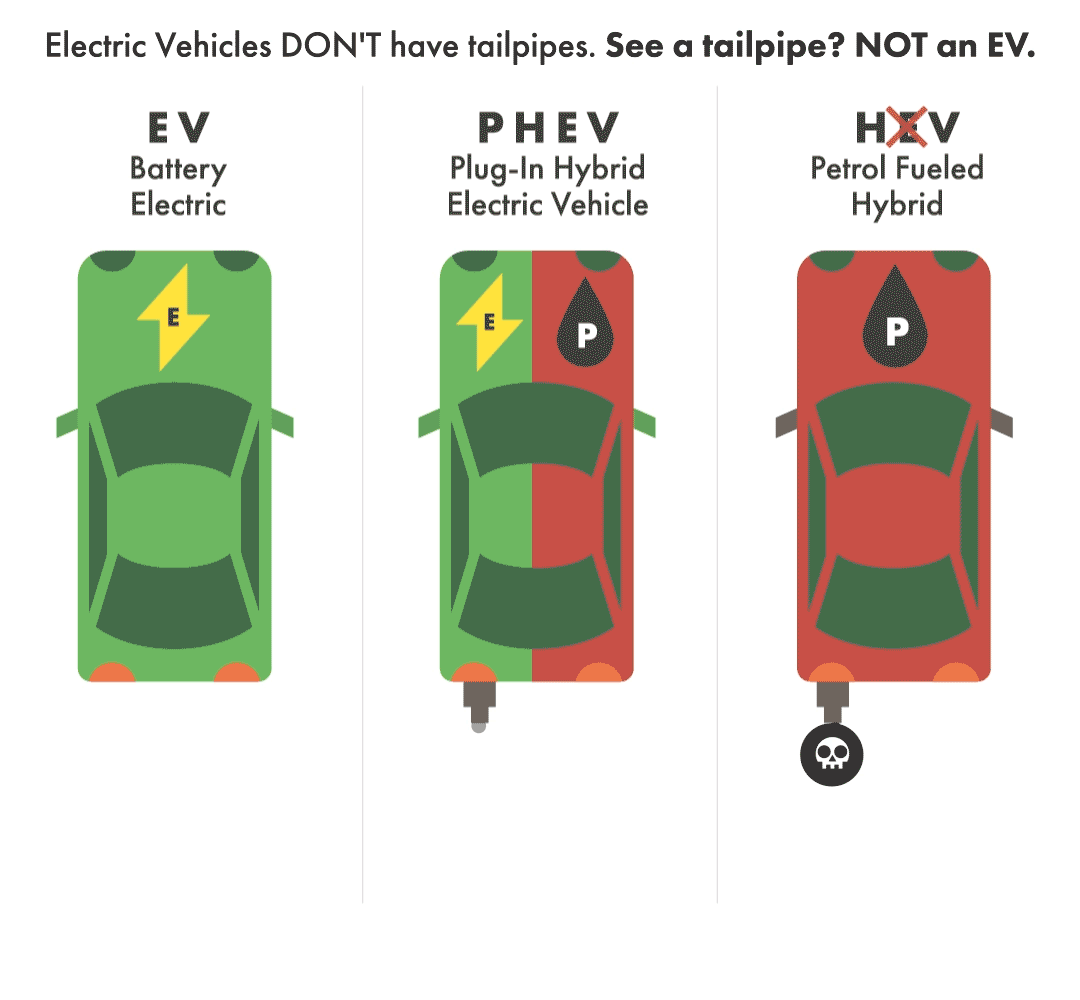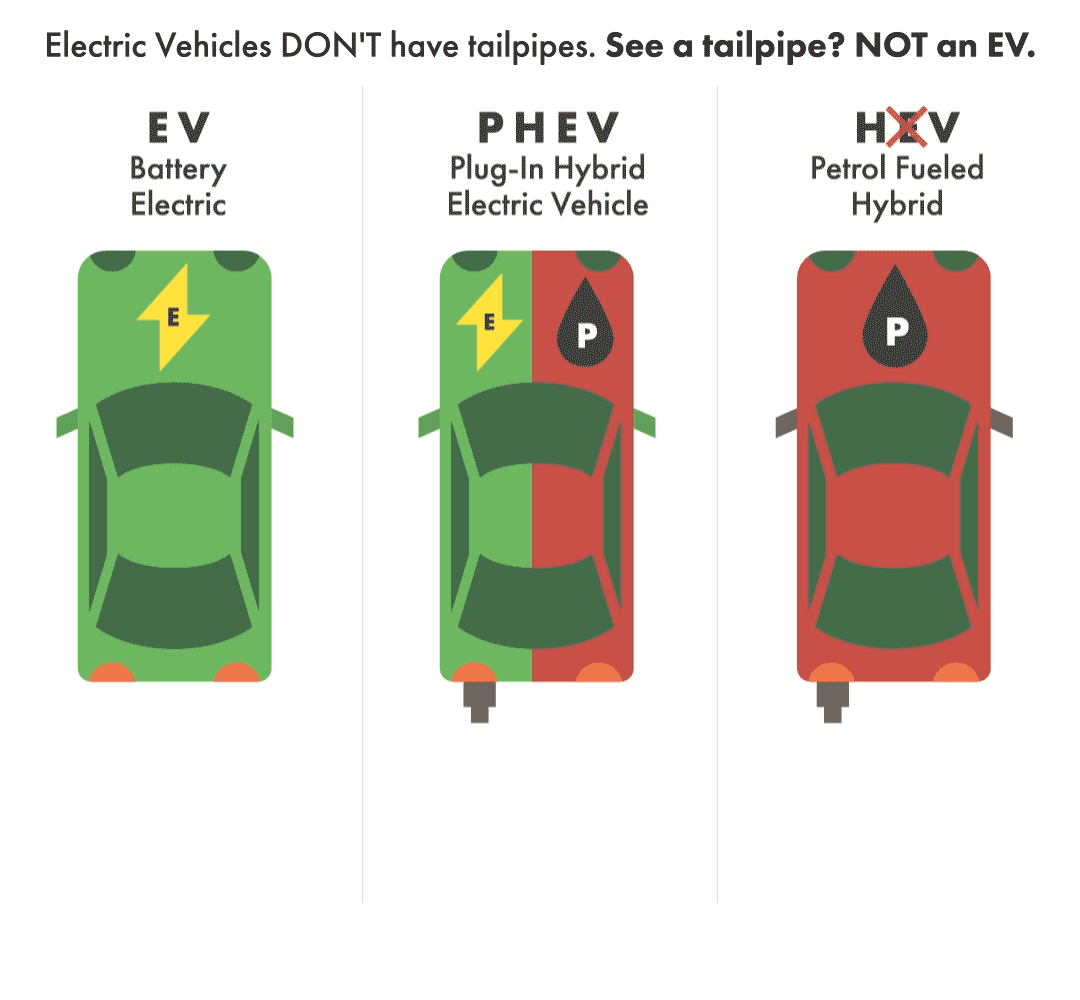
- Teacher: Dr. Ashwin Jacob
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
To introduce the students to the basic elements of poetry, including the stylistic and rhetorical devices employed in poetry, and to various genres of poetry.
LEARNER OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, the students will be able to - • Analyze literature using appropriate terminology and common rhetorical figures.
• Inculcate a sense of appreciation of English Poetry in students.
• Refresh the existing knowledge of the students concerning social, political, historical, philosophical and cultural characteristics of the Victorian and Modernist period.
• Train students in various perspective readings in poetry like gender, race, caste, ethnicity, religion, region, environment and nation etc.
• Enable to correlate their own sensibilities with the literary expressions in the text.
• Exhibit a vast panorama of literary devices used to create poetic world.

- Teacher: Amutha Monica
COURSE DESCRIPTION:
The course provides students with an overview of select women’s writing from the history.
Students are exposed to different genres from around the world. This course builds upon students' existing writing skills through textual analysis, dialogue based on reading assignments
Course Objectives: The objectives of the course is to enable the students to -
• Identify some authors, themes, and genres in women’s writing
• Consider cultural and global contexts in women’s writing
• Differentiate important implications of women’s literature in terms of the study of English literature, and the arts and humanities.
• Compare the developments, themes, and narrative strategies used by women writes expressing in English-language
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
After completing the course students will be able to
• Recall some of the developments, themes, and narrative strategies of English-language feminist fiction
• Analyze literary texts through the perspective of gender
• Identify the central points of a selection of feminist theory to use it as a context for reading literary texts
• Analyze and engage in theoretical and scholarly debates about feminist fiction

- Teacher: Amutha Monica
• To promote learner autonomy and to support various learning styles and strategies
• To support the learners to increase their learning skills through computer technologies
• To improve professional development using the applications of Computers and softwares
At the end of the Course, students will be able
• To promote their knowledge in softwares and computer applications
• To explore technology enhanced learning
• To implement e literacy in their learning process
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
- To learn through an effective blend of theory and practice in translation
- To learn the key concepts of the translation studies and analyse through various texts.
- To implement the diverse approaches and strategies of translation through translation practices and make an oral presentation.
- To broaden and deepen understanding of a variety of issues in relation to translation, such as gender, power relations, and religion and to acquire important transferable skills
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
Course Objectives
• To focus on basics of Industrial Internet
• To modify the various existing industrial systems
• To get an idea about IIoT Architectures
• To acquire the knowledge about various Network Protocols
• To extract the backend Middleware Protocols
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 –Enhance the company’s performance using IoT
CO2 –Demonstrate the different styles of technical and business innovators
CO3 –Examine various IIoT Architectures related to data management system
CO4 –Organize the design of Industrial Internet Systems
CO5 –Select various Software design patterns using API
CO6 –Construct a Middleware software system related to proximity edge networks.
- Teacher: Indhu R
Industrial method of formulations are study about different dosage forms.

- Teacher: Maria Shirley J
- Teacher: Shanmugapandiyan P
This courseis designed to impart fundamental knowledge on pharmaceutical product development andtranslationfromlaboratorytomarket

- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
The aim of Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy is to publish novel, original, peer-reviewed research manuscripts within relevant topics and research methods related to pharmaceutical research and development, and industrial pharmacy. All going to develop more information about the following topics in this semester
- Pilot Plant Scale up techniques
- Technology Development and Transfer
- Regulatory affairs and Regulatory requirements for drug approval
- Quality Management system and Regulatory Management Systems
- Indian Regulatory Requirements
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To enable students understand the fundamentals and the contributing technologies of Industry 4.0.
➢ To make the students evaluate the suitability of Industry 4.0 technologies for the design and manufacturing sectors.
➢ To help the students implement the Industry 4.0 technologies to diverse applications.
UNIT 1 CONTRIBUTING TECHNOLOGIES 8 hrs
Brief introduction to the industrial revolutions. Contributing technologies to Industry 4.0: Additive manufacturing, Digital twin, Internet of things, Smart sensors, AR and VR, Artificial intelligence, Cloud computing, Block chain, Big data and analytics. Challenges and opportunities.
UNIT 2 ADVANCED CAD TECHNOLOGIES 8 hrs
Introduction to CAD. Enabling technologies: Digital twin, AR/VR, AI. Cloud computing, Touch/Voice/Motion enabled CAD, Customized CAD, Cloud based CAD, Digital twin and live simulation.
UNIT 3 SMART MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS 8 hrs
Enabling technologies: AI, Cloud computing, Robotics, IoT. Digital manufacturing: CNC, Cloud based manufacturing, IoT based manufacturing, Advanced CNC programming. Additive manufacturing. Micro electro mechanical systems. Robotics: Robotic automation, Collaborative robots, Autonomous robots, Swarm robots, and Modular robots.
UNIT 4 SMART FACTORY ENABLERS 8 hrs
Enabling technologies. Smart energy: Improving energy efficiency with data, Smart grids. Clean energy. Smart logistics. Smart Inspection. Smart decision making.
UNIT 5 AUTOMOMOUS VEHICLES 8 hrs
Introduction: Traditional mobility versus autonomous driving, Levels of automation, and challenges. Enabling technologies. Self-propelled vehicles, Drones, Unmanned aerial vehicles, Space crafts
UNIT 6 CASE STUDIES 5 hrs
Case studies related to Industry 4.0 applications, such as, transportation, energy, infrastructure, manufacturing, and product design sectors.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
At the end of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Justify how the digitalization technologies are advantageous to the design and manufacturing industries.
CO2: Use the advanced CAD technologies to create the CAD models.
CO3: Use the smart manufacturing technologies to produce the components and products.
CO4: Recommend the enabling technologies to make various factory operations smarter.
CO5: Choose the suitable sensors and technologies to the future autonomous vehicles, drones and space crafts.
CO6: Prepare a report with the challenges faced currently, the enabling technologies to become smarter, and the
steps needed for the effective implementation for the given case study.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Flavio Craveiro, Jose Pinto Duarte, Helena Bartolo and Paulo Jorge Bartolo, “Additive manufacturing as an enabling technology for digital construction: A perspective on Construction 4.0”, Automation in Construction, Vol. 103,pp. 251- 267, 2019.
2. Klaus Schwab, “Fourth Industrial Revolution”, Random House USA Inc, New York, USA, 2017.
3. Oliver Grunow, ”Smart Factory and Industry 4.0. The current state of Application Technologies”, Studylab Publications, 2016
4. Alasdair Gilchrist, “Industry 4.0: Industrial Internet of Things”, Apress, 2016
5. Sang C. Suh, U. John Tanik, John N Carbone, Abdullah Eroglu, “Applied Cyber-Physical Systems”, Springer Publications, New York, 2013.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
To develop an understanding of building services such as water supply, drainage and plumbing system.
To familiarize them with the advanced service integration system and their applications in building.
To choose appropriate systems and integrate the same in their design projects.
- Teacher: ANITHA M
- Teacher: Mohana Gopiraj N
This course aims at understanding the essential metabolic functions of the organism as well as consumption
and storage of energy intermediary metabolism of main biomolecules and its regulatory mechanisms
It seeks to acquaint the reader to the critical approaches that have significantly impacted the study of English Literature.
It attempts to facilitate a chronological overview of critical theories while simultaneously allowing for a quick survey of classical criticism along the way.

- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
Summary
There are several ways of collecting and understanding information and finding answers to your questions – research is one way. The difference between research and other ways of obtaining answers to your questions is that in a process that is classified as research, you work within a framework of a set of philosophies, use methods that have been tested for validity and reliability, and attempt to be unbiased and objective.
Research has many applications. You need to have research skills to be an effective service provider, administrator/manager or planner. As a professional who has a responsibility to enhance professional knowledge, research skills are essential.
The typology of research can be looked at from three perspectives: application, objectives and the enquiry process. From the point of view of the application of research, there is applied and pure research. Most of the research undertaken in the social sciences is
applied, the findings being designed either for use in understanding a phenomenon/issue or to bring change in a programme/situation.
Pure research is academic in nature and is undertaken in order to gain knowledge about phenomena that may or may not have applications in the near future, and to develop new techniques and procedures that form the body of research methodology. A research study can be carried out with four objectives: to describe a situation, phenomenon, problem or issue (descriptive research); to establish or explore a relationship between two or more variables (correlational research); to explain why certain things happen the way they do (explanatory research); and to examine the feasibility of conducting a study or exploring a subject area where nothing or little is known (exploratory research). From the point of view of the mode of enquiry, there are two types of research: quantitative (structured approach) and qualitative (unstructured approach). The main objective of a qualitative study is to describe the variation and diversity in a phenomenon, situation or attitude with a very flexible approach so as to identify as much variation and diversity as possible, whereas quantitative research, in addition, helps you to quantify the variation and diversity. There are many who strongly advocate a combined approach to social enquiries.
These are the two paradigms that form the basis of social science research. Though these may provide values, terminology, methods and techniques for you to apply to your research, it is the purpose of research rather than the paradigm that should determine the mode of enquiry.

- Teacher: Malliga P
- The lab course is designed to train the students in basic techniques of Biochemistry.

- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
Course Objectives
- To understand the origins, structure, and development of language
- To apply linguistics to other areas of humanistic and scientific knowledge.
- To interpret the basic principles of linguistic theories
- To analyze phonological sound system, word structure, and phrase and sentence patterns

- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Murugesan S
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M

- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
To understand the distinctive features of the major ancient literary genres as illustrated in various texts.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
UNIT 1 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
Nuclear radius, charge distribution, spin and magnetic moment – Determination of nuclear mass – Binding energy – Semiempirical mass formula – Nuclear stability – Mass parabolas – Nuclear shell model – Liquid drop model - Optical model – Collective model Nuclear Forces Exchange forces – Yukawa’s meson theory –Yukawa potential – Ground state of deuteron
UNIT 2 RADIOACTIVE DECAYS
Alpha decay – Gamow’s theory – Geiger Nuttal law - Neutrino hypothesis –Fermi’s theory of beta decay-Selection Rules – Non conservation of parity in beta decay – Gamma decay – Selection rules – International conversion – Nuclear isomerism. Detection of Nuclear Radiation Interaction of charged particles and X-rays with matter - Basic principles of particle detectors - Proportional counters and Geiger – Muller counters - Solid state and semiconductor detectors – Scintillation counters.
UNIT 3 NUCLEAR FISSION
Fission process – neutron released in the fission process - Characteristics of fission – Mass and energy distribution of nuclear fragments – Nuclear chain reactions – Four factor formula – Bohr-Wheeler’s theory of nuclear fission – Fission reactors – Power & breeder type reactors Nuclear Fusion Basic fusion processes – Solar fusion – Cold fusion- Controlled thermonuclear reactions – Pinch effects - Laser fusion techniques.
UNIT 4 NUCLEAR REACTIONS
Energetic of reactions – Q-equation - Level widths in nuclear reaction –Nuclear reaction cross sections – Partial wave analysis – Compound nucleus model – Resonance scattering – Breit –Wigner one level formula – Direct reactions – Stripping and pick-up reactions. Scattering Process, scattering cross-section – Scattering amplitude – Expression in terms of Green’s function – Born approximation and its validity – Screened Coulomb potential
UNIT 5 ELEMENTARY PARTICLES
Four types of interactions and classifications of elementary particles – Isospin - Isospin quantum numbers – Strangeness & hyper charge – Hadrons – Baryons – Leptons – Invariance principles and symmetries – Invariance under charge-parity(CP), Time(T) and CPT - CP violation in neutral K-meson decay - Quark model – Gell-Mann-Nishijma formula – Gauge theory of weak and strong interactions – Charm, bottom and top quarks.
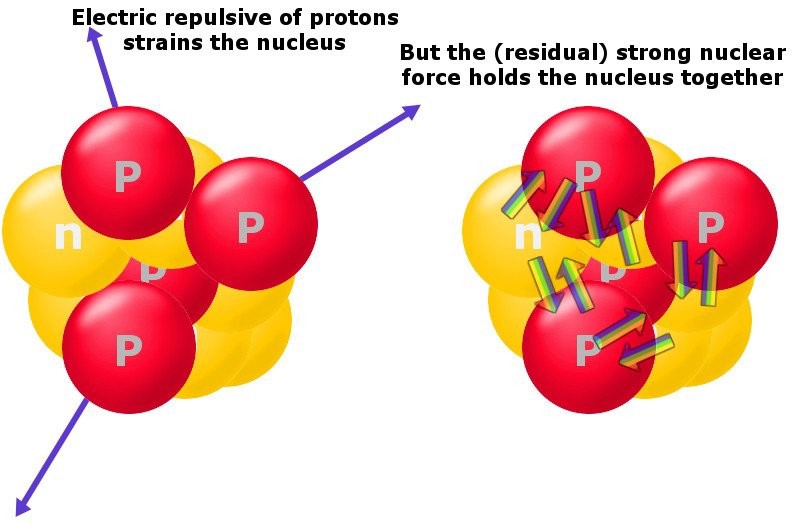
- Teacher: Rameshkumar C
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Understand different metal casting processes, associated defects, merits, and demerits.
CO2 - Compare different metal joining processes.
CO3 - Summarize various hot working and cold working methods of metals.
CO4 - Study the various sheet metal-making processes. CO5 - Distinguish various methods of manufacturing plastic components.
CO6 - Understand the concept of molding process.
- Teacher: Jayaprakash Venugopal
This course would cover the legal aspects of activities like carriage of goods and persons by sea along with concepts of marine insurance and adjudication of marine disputes

- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
: To Impart the Knowledge to the students with MATLAB software to enhances programming knowledge in
Research and Development. To provide a working introduction to the Mat lab technical computing environment. To introduce
students the use of a high-level programming language, Matlab
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
- Teacher: Sathya Bama R
- Teacher: Subapriya V
PAPER I: CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
Examination, diagnosis and treatment plan
Occlusion as related to conservative dentistry, contact, contour, its significance.
Separation of teeth, matrices, used in conservative dentistry.
Dental caries – epidemiology, recent concept of etiological factors, pathophysiology.
Histopathology, diagnosis, caries activity tests, prevention of dental caries and management – recent methods.
Hand and rotary cutting instruments, development of rotary equipment, speed ranges, hazards.
Dental bur and other modalities of tooth reparation – recent developments (air abrasions, Lasers etc)
Infection control procedures in conservative dentistry, isolation equipments etc.
Direct concepts in tooth preparation for amalgam, composite, GIC and restorative techniques, failures and management.
Direct and indirective composite restorations.
Indirect tooth coloured restorations – ceramic, inlays and onlays, veneers, crowns, recent
Advances in fabrication and materials.
Tissue Management
Impression procedures used for indirect restorations.
Cast metal restorations, indications, contraindications, tooth preparation for class 2 inlay, onlay full crown restoration
Restorative techniques, direct and indirect methods of fabrication including materials used for fabrication like inlay wax, investment materials and
Direct gold restorations.
Recent advances in restorative materials and procedures.
Management of non-carious lesion.
Advance knowledge of minimal intervention dentistry.
Recent advances in restoration of endodontically treated teeth and grossly mutilated teeth
Hypersensitivity, theories, causes and management
Lasers in Conservative Dentistry
CAD-CAM & CAD-CIM in restorative dentistry
Dental imaging and its applications in restorative dentistry (clinical photography)
Principles of esthetics
Color
Facial analysis
Smile design
Principles of esthetic integration
Treatment planning in esthetic dentistry
PAPER – II : ENDODONTICS
Rationale of endodontics
Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its implications in endodontic treatment.
Dentin and pulp complex.
Pulp and periapical pathology
Pathobiology of periapex
Diagnostic procedure – recent advances and various aids used for diagnosis –
Orofacial dental pain emergencies: endodontic diagnosis and management
Case selection and treatment planning
Infection control procedures used in Endodontics (aseptic techniques such as rubber dam, sterilization of instruments etc)
Access cavity preparation – objectives and principles
Endodontic instruments and instrumentation – recent developments, detailed description of hand, rotary, sonic, ultra sonic etc.,
Working length determination / cleaning and shaping of root canal system and recent development in techniques of canal preparation.
Root canal irrigants and intra canal medicaments used including non – surgical Endodontics by calcium hydroxide.
Endodontic microbiology.
Obturating materials, various obturation techniques and recent advances in obturation of root canal.
Traumatic injuries and management – endodontic treatment for young permanent teeth.
Pediatric Endodontics – treatment of immature apex.
Endodontic surgeries, recent developments in techniques and devices, endoosscous
Endodontic implants – biology of bone and wound healing.
Endoperio interrelationship, endo + Perio lesion and management
Drugs and chemicals used in Endodontics
Endo emergencies and management.
Restoration of endodontically treated teeth, recent advances.
Geriatric Endodontics
Endo emergencies and management
Biologic response of pulp to various restorative materials and operative procedures.
Lasers in Endodontics.
Multidisciplinary approach to endodontics situations.
Endodontics radiology – digital technology in endodontics practice.
Local anesthesia in endodontics.
Procedural errors in endodontics and their management.
Endodontics failures and retreatment.
Resorptions and its management.
Microscopes in endodontics.
Single visit endodontics, current concepts and controversies.
Paper III:
1. Descriptive and Analysing type question.

- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: PRIYANKA L.S
Part 2:
PAPER I: CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
- Examination, diagnosis and treatment plan
- Occlusion as related to conservative dentistry, contact, contour, its significance.
- Separation of teeth, matrices, used in conservative dentistry.
- Dental caries – epidemiology, recent concept of etiological factors, pathophysiology.
- Histopathology, diagnosis, caries activity tests, prevention of dental caries and management – recent methods.
- Hand and rotary cutting instruments, development of rotary equipment, speed ranges, hazards.
- Dental bur and other modalities of tooth reparation – recent developments (air abrasions, Lasers etc)
- Infection control procedures in conservative dentistry, isolation equipments etc.
- Direct concepts in tooth preparation for amalgam, composite, GIC and restorative techniques, failures and management.
- Direct and indirective composite restorations.
- Indirect tooth coloured restorations – ceramic, inlays and onlays, veneers, crowns, recent
- Advances in fabrication and materials.
- Tissue Management
- Impression procedures used for indirect restorations.
- Cast metal restorations, indications, contraindications, tooth preparation for class 2 inlay, onlay full crown restoration
- Restorative techniques, direct and indirect methods of fabrication including materials used for fabrication like inlay wax, investment materials and
- Direct gold restorations.
- Recent advances in restorative materials and procedures.
- Management of non-carious lesion.
- Advance knowledge of minimal intervention dentistry.
- Recent advances in restoration of endodontically treated teeth and grossly mutilated teeth
- Hypersensitivity, theories, causes and management
- Lasers in Conservative Dentistry
- CAD-CAM & CAD-CIM in restorative dentistry
- Dental imaging and its applications in restorative dentistry (clinical photography)
- Principles of esthetics
- Color
- Facial analysis
- Smile design
- Principles of esthetic integration
- Treatment planning in esthetic dentistry
PAPER – II : ENDODONTICS
- Rationale of endodontics
- Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its implications in endodontic treatment.
- Dentin and pulp complex.
- Pulp and periapical pathology
- Pathobiology of periapex
- Diagnostic procedure – recent advances and various aids used for diagnosis –
- Orofacial dental pain emergencies: endodontic diagnosis and management
- Case selection and treatment planning
- Infection control procedures used in Endodontics (aseptic techniques such as rubber dam, sterilization of instruments etc)
- Access cavity preparation – objectives and principles
- Endodontic instruments and instrumentation – recent developments, detailed description of hand, rotary, sonic, ultra sonic etc.,
- Working length determination / cleaning and shaping of root canal system and recent development in techniques of canal preparation.
- Root canal irrigants and intra canal medicaments used including non – surgical Endodontics by calcium hydroxide.
- Endodontic microbiology.
- Obturating materials, various obturation techniques and recent advances in obturation of root canal.
- Traumatic injuries and management – endodontic treatment for young permanent teeth.
- Pediatric Endodontics – treatment of immature apex.
- Endodontic surgeries, recent developments in techniques and devices, endoosscous
- Endodontic implants – biology of bone and wound healing.
- Endoperio interrelationship, endo + Perio lesion and management
- Drugs and chemicals used in Endodontics
- Endo emergencies and management.
- Restoration of endodontically treated teeth, recent advances.
- Geriatric Endodontics
- Endo emergencies and management
- Biologic response of pulp to various restorative materials and operative procedures.
- Lasers in Endodontics.
- Multidisciplinary approach to endodontics situations.
- Endodontics radiology – digital technology in endodontics practice.
- Local anesthesia in endodontics.
- Procedural errors in endodontics and their management.
- Endodontics failures and retreatment.
- Resorptions and its management.
- Microscopes in endodontics.
- Single visit endodontics, current concepts and controversies.
1. Descriptive and Analysing type question.
- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: SATHYANARAYANAN K
- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Megavarnan R
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
PART-I: Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy of Head and Neck:
• Development of face, paranasal sinuses and the associated structures and their anomalies, cranial and facial bones, TMJ anatomy and function, arterial and venous drainage of head and neck, muscles of face and neck including muscles of mastication and deglutition, brief consideration of structures and function of brain. Brief consideration of all cranial nerves and autonomic nervous system of head and neck. Salivary glands, Functional anatomy of mastication, deglutition and speech. Detailed anatomy of deciduous and permanent teeth, general consideration in physiology of permanent dentition, form, function, alignment, contact, occlusion.
• Internal anatomy of permanent teeth and its significance.
• Applied histology – histology of skin, oral mucosa, connective tissue, bone, cartilage,
blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves, muscles, tongue.
Anatomy and Development of Teeth:
• Enamel – development and composition, physical characteristics, chemical properties, structure.
• Age changes – clinical structure.
• Dentin – development, physical and chemical properties, structure type of dentin,
innervations, age and functional changes and clinical considerations.
• Pulp – development, histological structures, innervations, functions, regressive changes,
clinical considerations.
• Dentin and pulp complex.
• Cementum – composition, cementogenesis, structure, function, clinical considerations.
• Knowledge of internal anatomy of permanent teeth, anatomy of root apex and its
implications in endodontic treatment.
• Periodontal ligament – development, structure, function and clinical considerations.
• Salivary glands – structure, function, clinical considerations.
Applied Physiology:
• Mastication, deglutition, digestion and assimilation, fluid and electrolyte balance.
• Blood composition, volume, function, blood groups, haemostasis, coagulation, blood transfusion, circulation, heart, pulse, blood pressure, shock, respiration-control, anoxia, hypoxia, asphyxia, artificial respiration, and endocrinology – general principles of endocrine activity and disorders relating to pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals
including pregnancy and lactation.
• Physiology of saliva – composition, function, clinical significance.
• Clinical significance of vitamins, diet and nutrition – balanced diet.
• Physiology of pain, sympathetic and Para sympathetic nervous system, pain pathways,
physiology of pulpal pain, Odontogenic and non Odontogenic pain, pain disorders –
typical and atypical.
• Biochemistry such as osmotic pressure, electrolytic dissociation, oxidation, reduction etc.
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and their metabolism, nucleoproteins, nucleic acid and their metabolism. Enzymes, vitamins and minerals, metabolism of inorganic elements, detoxification in the body, anti metabolites, chemistry of blood lymph and urine.
Pathology:
• Inflammation, repair, degeneration, necrosis and gangrene.
• Circulatory disturbances – ischemia, hyperemia, edema, thrombosis, embolism,
infarction, allergy and hypersensitivity reaction.
• Neoplasms – classifications of tumors, characteristics of benign and malignant tumors,
spread of tumors.
• Blood dyscrasias.
• Developmental disturbances of oral and Para oral structures, dental caries, regressive
changes of teeth, pulp, periapical pathology, pulp reaction to dental caries and dental
procedures.
• Bacterial, viral, mycotic infections of the oral cavity.
Microbiology:
• Pathways of pulpal infection, oral flora and micro organisms associated with endodontic diseases, pathogenesis, host defense, bacterial virulence factors, healing, theory of focal infections, microbes relevance to dentistry – strepto, staphylococci, lactobacilli, cornyebacterium, actinomycetes, clostridium, neisseria, vibrio, bacteriods, fusobacteria, spirochetes, mycobacterium, virus and fungi.
• Cross infection, infection control, infection control procedure, sterilization and disinfection.
• Immunology – antigen antibody reaction, allergy, hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis, auto immunity, grafts, viral hepatitis, HIV infections and aids. Identification and isolation of microorganisms from infected root canals. Culture medium and culturing technique
(Aerobic and anaerobic interpretation and antibiotic sensitivity test).
Pharmacology:
• Dosage and route of administration of drugs, actions and fate of drug in body, drug addiction, tolerance of hypersensitivity reactions.
• Local anesthesia – agents and chemistry, pharmacological actions, fate and metabolism of anaesthetic, ideal properties, techniques and complications.
• General anesthesia – pre medications, neuro muscular blocking agents, induction agents, inhalation anesthesia, and agents used, assessment of anesthetic problems in medically compromised patients.
• Anaesthetic emergencies
• Antihistamines, corticosteroids, chemotherapeutic and antibiotics, drug resistance,
haemostasis, and haemostatic agents, anticoagulants, sympathomimitic drugs, vitamins and minerals (A, B, C, D, E, K IRON), anti sialogogue, immunosupressants, drug interactions, antiseptics, disinfectants, anti viral agents, drugs acting on CNS.
Biostatistics:
• Introduction, Basic concepts, Sampling, Health information systems – collection, compilation, presentation of data. Elementary statistical methods – presentation of statistical data, Statistical averages – measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, Normal distribution. Tests of significance – parametric and non – parametric tests (Fisher extract test, Sign test, Median test, Mann Whitney test, Kruskal Wallis one way analysis, Friedmann two way analysis, ANOVA, Regression analysis), Correlation and regression,Use of computers.
Research Methodology:
• Essential features of a protocol for research in humans
• Experimental and non-experimental study designs
• Ethical considerations of research Applied Dental Materials:
• Physical and mechanical properties of dental materials, biocompatibility.
• Impression materials, detailed study of various restorative materials, restorative resin and recent advances in composite resins, bonding- recent developments, tarnish and
corrosion, dental amalgam, direct filling gold, casting alloys, inlay wax, die materials, investments, casting procedures, defects, dental cements for restoration and pulp protection (luting, liners, bases) cavity varnishes.
• Dental ceramics-recent advances, finishing and polishing materials.
• Dental burs – design and mechanics of cutting – other modalities of tooth preparation.
Methods of testing biocompatibility of materials used.
PART-I: Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics
A. Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy:
a. Prenatal growth of head:
Stages of embryonic development, origin of head, origin of face, origin of teeth.
b. Postnatal growth of head:
Bones of skull, the oral cavity, development of chin, the hyoid bone, general growth of head, growth of the face.
c. Bone growth:
Origin of bone, composition of bone, units of bone structure, schedule of Ossification, mechanical properties of bone, roentgen graphic appearance of bone
d. Assessment of growth and development:
Growth prediction, growth spurts, the concept of normality and growth increments of growth, differential growth, gradient of growth, methods of gathering growth data. Theories of growth and recent advances, factors affecting physical growth.
e. Muscles of mastication:
Development of muscles, muscle change during growth, muscle function and facial development, muscle function and malocclusion
f. Development of dentition and occlusion:
Dental development periods, order of tooth eruption, chronology of permanent tooth formation, periods of occlusal development, pattern of occlusion.
g. Assessment of skeletal age.
Physiology:
a. Endocrinology and its disorders:
Growth hormone, thyroid hormone, parathyroid hormone, ACTH.
b. Calcium and its metabolism:
c. Nutrition-metabolism and their disorders:
Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals
d. Muscle physiology:
e. Craniofacial Biology:
Adhesion molecules and mechanism of adhesion
f. Bleeding disorders in orthodontics: Hemophilia
Dental Materials:
a. Gypsum products:
Dental plaster, dental stone and their properties, setting reaction etc.
b. Impression materials:
Impression materials in general and particularly of alginate impression material.
c. Acrylics:
Chemistry, composition physical properties
d. Composites:
Composition types, properties, setting reaction
e. Banding and bonding cements:
f. Wrought metal alloys:
Deformation, strain hardening, annealing, recovery, recrystallization, grain growth,
properties of metal alloys
g. Orthodontic arch wires
h. Elastics:
Latex and non-latex elastics.
i. Applied physics, Bioengineering and metallurgy:
j. Specification and tests methods used for materials used in Orthodontics:
k. Survey of all contemporary literature and recent advances in above mentioned
materials:
Genetics:
a. Cell structure, DNA, RNA, protein synthesis, cell division
b. Chromosomal abnormalities
c. Principles of orofacial genetics
d. Genetics in malocclusion
e. Molecular basis of genetics
f. Studies related to malocclusion
g. Recent advances in genetics related to malocclusion
h. Genetic counseling
i. Bioethics and relationship to Orthodontic management of patients.
Physical Anthropology:
a. Evolutionary development of dentition
b. Evolutionary development of jaws.
Pathology:
a. Inflammation b. Necrosis
Biostatistics:
a. Statistical principles
• Data Collection
• Method of presentation
• Method of Summarizing
• Methods of analysis – different tests/errors
b. Sampling and Sampling technique
c. Experimental models, design and interpretation
d. Development of skills for preparing clear concise and cognent scientific abstracts and
publication
Applied Research Methodology In Orthodontics:
a. Experimental design
b. Animal experimental protocol
c. Principles in the development, execution and interpretation of
methodologies in Orthodontics
d. Critical Scientific appraisal of literature.
Applied Pharmacology
Definitions & terminologies used – Dosage and mode of administration of drugs. Action and fate of drugs in the body, Drug addiction, tolerance and hypersensitive reactions, Drugs acting on the central nervous system, general anesthetics hypnotics, analeptics and tranquilizers. Local anesthetics, Chemotherapeutics and antibiotics. Vitamins: A, D, B – complex group, C & K etc.
Part I Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry
A) Applied Basic Sciences:
Applied Anatomy of Head and Neck:
• Anatomy of the scalp, temple and face
• Anatomy of the triangles of neck and deep structures of the neck
• Cranial and facial bones and its surrounding soft tissues with its applied aspects
• Muscles of head and neck
• Arterial supply, venous drainage and lymphatics of head and neck
• Congenital abnormalities of the head and neck
• Anatomy of the cranial nerves
• Anatomy of the tongue and its applied aspects
• Anatomy and its applied aspects of salivary glands, pharynx, thyroid and parathyroid
gland, larynx, trachea, esophagus
• Autonomous nervous system of head and neck
• Functional anatomy of mastication, deglutition, speech, respiration and circulation
• TMJ: anatomy and function
Applied Physiology:
Introduction, Mastication, deglutition, digestion and assimilation, Homeostasis, fluid and electrolyte balance. Blood composition, volume, function, blood groups and hemorrhage, Blood transfusion, circulation, Heart, Pulse, Blood pressure, Normal ECG,capillary and lymphatic circulation, shock, respiration, control, anoxia, hypoxia, asphyxia, artificial respiration. Endocrine glands in particular reference to pituitary, parathyroid and thyroid glands and sex hormones. Role of calcium and Vit D in growth and development of teeth, bone and jaws.Role of Vit.A, C and B complex in oral mucosal and periodontal health.Physiology and function of the masticatory system. Speech mechanism, swallowing and deglutition mechanism, salivary glands and Saliva
Applied Pathology:
Inflammation and chemical mediators, Thrombosis, Embolism, Necrosis, Repair, Degeneration , Shock, Hemorrhage , Blood dyscrasias, Pathogenesis of Dental Caries, Periodontal diseases, tumors, oral mucosal lesions etc. in children
Applied Microbiology:
Microbiology & Immunology as related to Oral Diseases in Children: Basic concepts, immune system in human body, Auto Immune diseases and Immunology of Dental caries.
Applied Nutrition & Dietics:
• General principles, balanced diet, effect of dietary deficiencies and starvation, protein energy, malnutrition, Kwashiorkor, Marasmus.
• Fluid and Electrolytic balance in maintaining haemostasis
• Diet, digestion, absorption, transportation and utilization
Genetics:
• Introduction to genetics
• Cell structure, DNA, RNA, protein synthesis, cell division
• Modes of inheritance
• Chromosomal anomalies of oral tissues & single gene disorders
Growth & Development:
Prenatal and Postnatal development of cranium, face, jaws, teeth and supporting structures.Chronology of dental development and development of occlusion. Dimensional changes in dental arches. Cephalometric evaluation of growth.
- Teacher: S Aravinthan
- Teacher: MALATHY BALARAMAN RAVINDRRAN
- Teacher: Dr.PRATHIBA GNANASEKARAN
- Teacher: PRIYANKA L.S
- Teacher: MANEESHWARI M
- Teacher: Mirnalini Mirnalini
- Teacher: Dr.Premjanu N
- Teacher: Venkatalakshmi Nagella
- Teacher: Tamil Selvi Palaniappan
- Teacher: Revathy Rajendran
- Teacher: REESHMA RUCKSCHANDA
- Teacher: MOHAMMED MEERA RIYAZ S
- Teacher: Srividya S
- Teacher: Priya Sathish
- Teacher: Dr.Murali Sivakumar
- Teacher: GOUSALYA V
This course is meant to provide learners conceptual knowledge about various electronic measuring instruments and how to choose a specific measuring instrument based on their requirement. There are two types of measuring instruments: one is the type of measuring instruments that show the values on the scale of the meter, and other are type of measuring instruments that displays the waveforms.

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
In chemical engineering and its related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process. For this reason they can be classified in different ways. The first category assigned to UOs is mechanical operations.Mechanical unit operations can be categorized into three:Operations involving particulate solids;Operations involving solid-fluid;Operations involving fluid systems;

- Teacher: Sathish S
|
SMEB1603 |
MECHANICS OF MACHINES |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
The aim of the course is to:
· Provide the insights of the fundamentals of Mechanisms and Cams.
· Understand the basics of Flywheels, Balancing of Rotating and Reciprocating unbalance systems.
· Enhance knowledge of Single degree - Free and Damped Vibrations.
· Provide the detailed overview of Forced Vibrations.
· Discuss the fundamentals of Gyroscopes and Governors.
UNIT I MECHANISMS AND CAMS 9 hrs
Mechanisms – Terminology and definitions – Kinematics inversions of 4 bars and slider crank chain – Kinematic analysis in simple mechanisms. Types of cams and followers - Terminology and definitions – Displacement diagrams – SHM, uniform velocity, uniform acceleration and retardation. Graphical constructions of cam profiles – Disc cam with knife edge follower, roller follower and flat-faced follower.
UNIT II FLY WHEELS AND BALANCING 9 Hrs
Turning moment diagrams – Fluctuation of Energy and speed – Energy stored in Flywheel – Mass of Flywheel – Dimensions of Flywheel. Balancing – Static and Dynamic Balancing of Rotating Masses - Balancing of several masses rotating in same plane and in different planes- Partial Balancing of locomotives – Variation of tractive force, Hammer blow and swaying couple.
UNIT III FUNDAMENTALS OF VIBRATION 9 Hrs
Basic features of vibratory systems - Lumped mass systems - Degrees of freedom - Free vibration of Longitudinal, Transverse and Torsional systems of Single degree of freedom - Equations of motion - Natural frequency – Whirling of shafts and critical speed - Dunkerley’s Method – Torsional vibration of Two and Three rotor system. Damped free vibration - Types of Damping –Critical damping coefficient - Damping Factor – Logarithmic Decrement.
UNIT IV FORCED VIBRATION 9 Hrs
Forced vibration of single degree freedom system with damping - Response to periodic forcing- Harmonic Forcing - Force transmissibility and amplitude transmissibility - Reciprocating and rotating unbalance - vibration isolation and transmissibility - Support motion - self excited vibration with examples
UNIT V GOVERNORS AND GYROSCOPES 9 Hrs
Gyroscopes and gyroscopic effects-Effect of precession motion on the stability of moving vehicles such as motor car, motor cycle, aero planes and ships gyroscopic couple, (Demonstration of models in video). Governors - types and applications - Watt, Porter and Proell governors - Spring loaded governors -Hartnell and Hartung with auxiliary springs. Sensitiveness- isochronisms and hunting.
Max Hours: 45 Hrs
COURSE OUTCOMES:
At the end of the course, the students will be able to:
CO1: Investigate the Mechanisms and Cams.
CO2: Determine the principle of Flywheel, Rotating and Reciprocating masses.
CO3: Analyze the Single degree - Free and Damped Vibrations.
CO4: Evaluate the force transmitted to the foundation for mechanical systems in Forced Vibrations.
CO5: Apply the fundamentals of Gyroscopes.
CO6: Apply the fundamentals of Governors.
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Khurmi R.S& Gupta J.S, “Theory of Machines”, 16th Edition, S.Chand & Company, 2005, Reprint 2016.
2. Singh V.P, “Mechanical Vibrations”, 3rd Edition, Dhanpatrai & Co., 2006.
3. Ghosh A. and Malik A.M, “Theory of Mechanism and Machines”, 4th Edition, Affiliated East West Press (P) Ltd. 2009.
4. Ashok G. Ambekar, “Mechanism and Machine Theory”, First Edition,PHI Learning Private limited, 2009.
5. Rattan S. S, Theory of Machines, 3rd Ed., Tata Mcgraw Hill, 2009.
6. Gordon R Pennock, Joseph E Shigley, “Theory of Machine and Mechanisms SI Edition, 4th Edition, Oxford University Press, 2014
|
END SEMESTER EXAM QUESTION PAPER PATTERN |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
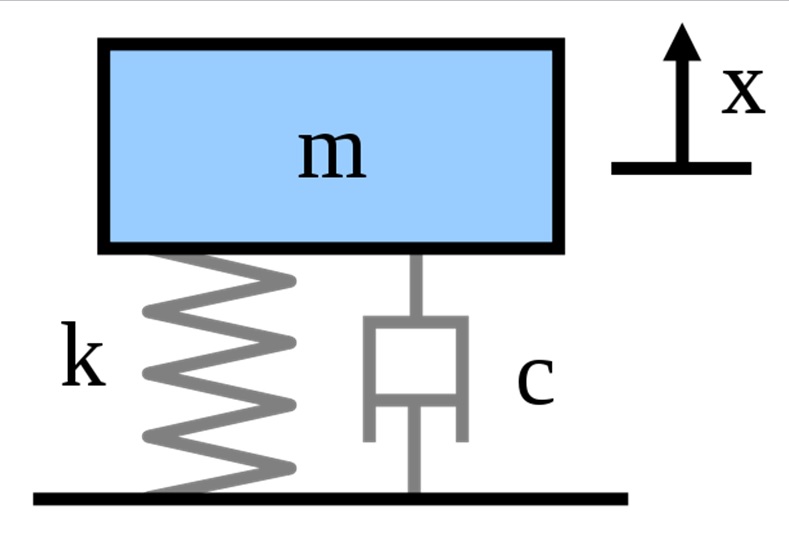
- Teacher: LAKSHMI SANKAR S
The course makes the students to understand the ethics and the principles of Media. The course covers topics on the definition of ethics, values and principles. The learners will identify the relationship between ethics and society. This course will make them to analyze the ethical challenges in the media. Through various case studies, the learners can understand the prevailing laws and ethics especially in cyber space. The course also aims to introduce the concept of cyber crime .

- Teacher: NAZINI N
In Medical Laboratory Techniques course helps students to gain intensive knowledge from basic medical sciences.

- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
- Teacher: MALATHY BALARAMAN RAVINDRRAN
- Teacher: Dr.PRATHIBA GNANASEKARAN
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To give a basic introduction to microcontroller 8085 and 8051.
➢ To provide students knowledge about trivial programs using 8085 and 8051.
➢ To expertise in interfacing of various devices and equipment with 8051.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand 8085 and 8051 chip architecture in real time.
CO2 - Explain the Algorithm for programs in 8085 and 8051.
CO3 - Demonstrate the output of programs in 8085 and 8051.
CO4 - Analyse the performance 8051 in various aspects.
CO5 - Determine the performance of memory chips with 8051.
CO6 - Evaluate the performance of 8051 using various interfaces.
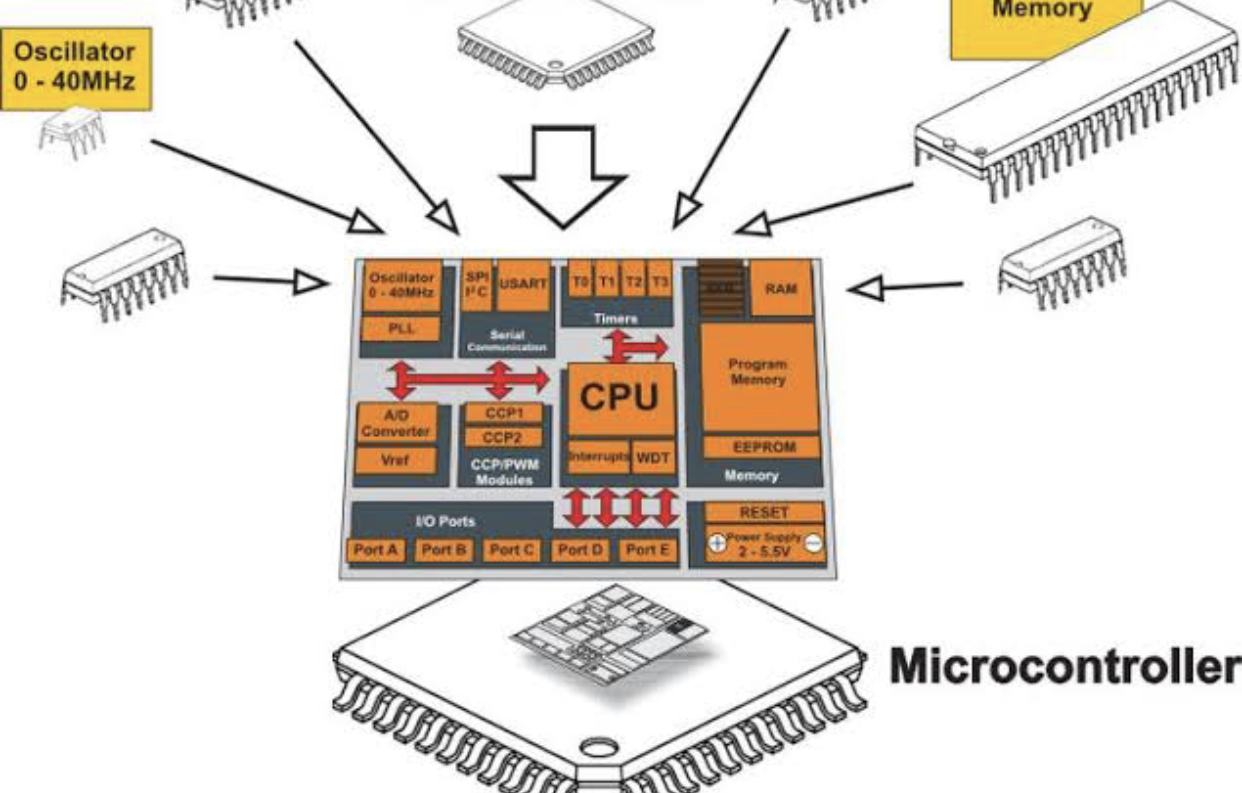
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
- Teacher: Dr. ANNA DEVI E
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Sivagami P
- Teacher: Pandian R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: Nirmal Raj S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
- Teacher: Thaj Mary Delsy T
- Teacher: VINO T
- Teacher: Senthil Nayagam V
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
- Analyze microwave frequencies and microwave components.
- Analysis of microwave systems and assess the impact of microwave component performances on overall system performance.
- Describe the operation and analyze the performance of basic microwave sources and solid state semiconductor devices.
- Analyze, Assess qualitatively and quantitatively the role of optical fiber communication and signal degradation.
- To familiarize on the principle of operation of optical sources, fiber coupling and optical networks
- Teacher: Dr.I.Rexiline Sheeba
MOBILE AND WIRELESS SECURITY
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand the Wireless technology and the threats.
➢ To learn wireless security protocols and cryptography.
➢ To apply the security for wireless devices.
➢ To explore the wireless technologies and applications.
➢ To learn to implement the wireless LANS.

- Teacher: Rajeswari G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To impart the fundamentals concepts of mobile communication systems.
- To introduce various technologies and protocols involved in mobile communication.
- Examine Theory Research in Mobility
- Examine Systems Research in Mobility
UNIT 1 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
Basic cellular systems - Frequency Management and Channel Assignment - Types of handoff and their
characteristics, dropped call rates & their evaluation - MAC - SDMA - FDMA - TDMA - CDMA - Cellular Wireless Networks.
UNIT 2 WIRELESS NETWORKS
Wireless LAN - IEEE 802.11 Standards - Architecture - OFDM Technology - Services - Mobile Ad hoc
Networks- IEEE 802.16 standards, Comparison of 802.11 and 802.16 - Wireless Local Loop - Architecture - WLL Technologies.
UNIT 3 MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
GSM – Architecture - Location tracking and call setup - GSM Mobility management – Handover – Security -GSM SMS - International roaming for GSM - Call recording functions - subscriber and service data management -Mobile Number portability.GPRS – Architecture - GPRS procedures - Attach and detach procedures - PDP context procedure - Combined RA/LA update procedures - Billing.
UNIT 4 MOBILE NETWORK AND TRANSPORT LAYERS
Mobile IP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - Mobile Ad Hoc Routing Protocols - Multicast routing - TCP over Wireless Networks - Indirect TCP - Snooping TCP - Mobile TCP - Fast Retransmit / Fast Recovery – Transmission / Timeout Freezing-Selective Retransmission - Transaction Oriented TCP - TCP over 2.5 / 3G wireless Networks
UNIT 5 APPLICATION LAYER
WAP Model - Mobile Location based services - WAP Gateway - WAP protocols - WAP user agent profile-caching model - Wireless bearers for WAP - WML - WMLScripts - WTA – iMode - SyncML.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Jochen Schiller, “Mobile Communications”, Second Edition, Pearson Education, 2003.
2. William Stallings, “Wireless Communications and Networks”, Pearson Education, 2002.
3. Yi-Bing Lin, Imrich Chlamtac, “Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures”, John Wiley and sons, 2001

- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
- Teacher: Premkumar J
- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R
- Teacher: PRIYADARSHINI M
- Teacher: oviya R.P
Nanobiotechnology lab -explanation with nanosize particles synthesis and chracaterization and invitro studies.
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To give essential knowledge of construction and working of various types of Non-Conventional Energy Systems.
To detail the role of Mechanical Engineers in their operation and maintenance.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the basic concepts of Non-Conventional Power Generation & its importance. CO2 - Apply the basic thermodynamic principles to different renewable energy systems.
CO3 - Analyze and understand solar energy systems, working and its significance.
CO4 - Analyze thermodynamic cycles of Wind, bio & other renewable energy sources.
CO5 - Understand the importance ad necessity of renewable energy sources.
CO6 - Recognize renewable energy production, Distribution & cost estimation.

- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
Unit 1: Properties of Nuclei
Introduction, Classification of Nuclei, Properties of Nuclei - Nuclear size, charge, mass, density, spin, magnetic dipole moment, electric quadrupole moment, binding energy, packing fraction, Nuclear Stability. Nuclear models - Liquid Drop Model (Weizacker Semi Empirical mass formula), Shell Model and magic numbers.
Unit 2: Detectors of Nuclear Radiations
Introduction, Interaction between energetic particles and matter, Ionization Chamber, Solid-State Detectors, Proportional Counter, Geiger-Muller Counter, Photo Multiplier Tube, Scintillation Counter.
Unit 3: Particle Accelerators
Introduction, Van de Graaff Generator, Linear Accelerator, Cyclotron, Synchrocyclotron, Betatron, Electron Synchrotron, Proton Synchrotron (Bevatron).
Unit 4: Radioactivity
Introduction, Natural radioactivity, Alpha Particle – Properties, e/m ratio, charge, range, Geiger-Nuttal law.Measurement of Range of Alpha particle by Bragg - Kleeman method, Geiger - Nuttal method.Beta Particle – Properties, e/m ratio, Pauli’s Neutrino Hypothesis, Neutrino theory of Beta decay, Detection of Neutrino. Gamma Particle – Origin, determination of wavelength by Du Mond Curved Crystal Spectrometer, Nuclear Isomerism, Internal Conversion, Mossbauer effect with experiment.
Unit 5: Elementary Particles
Introduction, Classification of elementary particles (Baryon and Leptons), Particles and Anti-Particles, Antimatter, Fundamental Interactions, Elementary Particle Quantum numbers – Baryon, Leptons, strangeness, Hypercharge and Isospin. Conservation Laws – Parity, Charge Conjugation
- Teacher: Jayalakshmi D.S
This course deals with cell structure and its organelles and their composition. The students will get an insight into the biomolecules responsible for the various biochemical reaction taking place inside the cell. Also will get knowledge about various metabolic disorders related to it.
- Teacher: Dr.Premjanu N
- Teacher: Preetha Wilma Dawson
Research Content: The Dissertation is an individual research project that is a major piece of work undertaken by the students.The aim is to prepare state of art report on the chosen topic and develop hypothesis to be tested through the research methodology designed for the purpose. Students are required to test their outcome proposals through various methods, including questionnaire surveys and case studies. It is encouraged that students identify topics for the Dissertation work which can be further developed into a Thesis Project with research in the next semester for more in-depth research. Alternatively, this Dissertation Project can be an independent research topic. Students must create an innovative insight on the specific issues.
Research Process: Dissertation work includes processes such as: Research area identification; hypothesis of research
topic; literature sourcing and search; aim and objective definition; formulation of methodology; field study planning; survey
data collection, analysis and result presentation; literature study; conceptual an empirical :compilation and inference drawing;
research study validation through case studies, field application and simulation models; discussion of findings of research
findings; study conclusion and recommendation formulations
Area of Research: Some of the area for Dissertation are land use and planning, financial management, lean construction,
quality control and safety procedures, real estate regulations and laws, advanced technologies, project management
knowledge areas, PPP projects and business environment.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
. Understanding the essence of ‘alternative building materials and technology’, ‘rematerial oriented design’, ‘super use’ ‘opportunistic architecture’ need for alternative building materials and building technology, alternative natural building materials - building materials with recycled content
UNIT 2 ALTERNATIVE BUILDING MATERIALS. Locally available building materials and their usability – applications of bamboo in building construction – flooring – roofingceiling – trusses Mud as building and building materials - field tests for identification of suitable soil for mud construction – techniques of mud stabilization –techniques of mud construction – finishes and protective treatments – production of mud blocks Innovative techniques for walls – lato blocks- cellular concrete blocks – hollow concrete blocks – hollow clay blocks – stone masonry blocks – sand lime bricks Use of industrial, agricultural, construction wastes and post-consumer wastes - Survey of such materials development by research organizations like CBRI, SERC etc.
UNIT 3 ALTERNATIVE BUILDING TECHNOLOGY Innovative techniques for roofing/flooring - Filler slabs, Composite beam panel roofs, Masonry vaults and domes – funicular shells – precast reinforced concrete channel units – pre stressed concrete hollow cored units- precast RCC joints – ferro cement ribbed slabs – folded plates, Foundations - Use of arches in foundation, alternatives for walls constructions – composite masonry, confined masonry, cavity walls, rammed earth, rat trap bond - Ferro cement and ferro-concrete building components Materials and specifications, Properties. Top down construction, Fast track construction methods - building examples Alternative practices - windows and door - panels and frames, flooring, handrails, partitions, staircases - Staircase - Methods of construction of staircases (timber, steel, glass, composite materials) - basic principles, finishes for staircases
UNIT 4 EMERGING MATERIALS .
Current developments in the use of Nano materials in construction industry – various types of nano fibers like nano silica, nanoTitania, carbon nano tubes, carbon nano fibers - applications - advantages and disadvantages
UNIT 5 SUGGESTIVE ASSIGNMENT
Case studies of buildings constructed with alternative building materials and technology for substructure and superstructure
in Indian context

Research Content: The intent of pre thesis is to initiate the selection of Thesis topic in the beginning of the third semester itself. The students shall work three alternative topics by studying and analysing the published research papers of their interest area and give justification for the selection of the topics which will be assigned to him / her to proceed to the next phase.
Research Process: Each student will prepare the Pre-Thesis with regular reviews by the faculty of the department. . It is encouraged that students identify topics for the Pre Thesis work which can be further developed into a Thesis Project with research in the next semester for more in-depth research. . The Pre Thesis will be presented in the accepted form of a Pre-thesis report duly supported by copious references, sketches, graphs, proposed statistical data, proposed details of survey, tools and techniques and methodology to be adopted and detailed account of experimental analytical procedures to be adopted. Each student is required to defend his/her Pre-Thesis at a Viva Voce Examination by jury. The Pre-Thesis shall consist of literature, survey on the topic chosen in the relevant field, theoretical and or experimental work based on the literature and discussion.
Area of Research:
The subject for special study may be conceptual or practical but should pertain to building design and construction
management like BIM, construction management procedures, land use and planning, financial management, lean
construction, quality control, value engineering and safety procedures and construction Laws
UNIT 1 TRADITIONAL APPROACH AND NETWORK ANALYSIS
. Traditional Management System - Gantt’s approach - load, progress and bar charts - limitations & overcoming - Project programming - work breakdown structure. Introduction to PERT & CPM -Introduction to network concepts, network elements and inter-relationships-Network techniques -Network logic - activity interrelationships - development of CPM network - Identification of critical path - Different float computations - Early start, early finish, late start, and late finish- worked out examples-Network control (updating): Introduction, process of updating, data required for updating, when to update, method of updating, examples.
UNIT 2 PROBABILITY ANALYSIS
PERT Network - Introduction to theory of probability and statistics - Probabilistic time estimates of activities - Analysis of PERT network.
UNIT 3 PROJECT COST & RESOURCE ALLOCATION
. Introduction to two-dimensional network analysis - activity cost information - cost time relationship - crashed estimates for activities - compression potential-cost slope - Project direct cost and indirect cost- crashed program, Network compression - least cost, least time, optimum solutions. Resource allocation - Resource levelling and smoothing - Simple examples.
UNIT 4 SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS .
Introduction to Project Management software’s - Applications - Detailed planning of a simple project - Scheduling using
M.S. project and Primavera.

Course Objectives:
● To introduce the students to the body of literary writings that stands evergreen in the regions of Kenya, Africa,
Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Pakistan.
● To acquaint the students the various genres.
● To acquaint the students with different authors relating to different regions and literature.
● To make the students approach selected texts for their literary value and cultural importance.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
|
Develop a C++ program to implement a class, object creation, member function invocation concept. |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement the various constructors |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement a friend function, |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement an operator overloading concept. |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement a function overloading concept. |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement the inheritance Single ,multiple |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement the inheritance multilevel & hierarchy |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement the Abstract class |
|
Develop a C++ program to implement a Virtual function. |
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
- To introduce the students to the body of literary writings that stands evergreen in the regions of Kenya, Africa, Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Pakistan.
● To acquaint the students the various genres.
● To acquaint the students with different authors relating to different regions and literature.
● To make the students approach selected texts for their literary value and cultural importance.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide an understanding of the concepts, functions and techniques of managing people.
To understand the HRM practices, in terms of HRP, Training and Development, Compensation, etc
To understand enterprise issues and the changing role of Human Resource and Industrial Relations.
- Teacher: JOHN BRITTO M
Objective:
• To understand the fundamental concepts of object oriented programming.
• Be familiar with concepts like abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism.
• To understand the concept of Classes
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand data, analyze trends, forecast, and plan to drive accurate insight.
To help the organization find new opportunities, improve efficiency, and minimize risk.
To make smarter decisions and to deliver business results.

- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
- To understand the basic statistical tools for analysis & interpretation of qualitative & quantitative data
- To introduce basic concepts of Statistics and to provide statistical techniques for business data analysis.

- Teacher: PRIYADARSHINI E
- Teacher: Subhashini N
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To know the different sources and methods of data collection and different methods of data presentation
Ø To understand the significance of advanced concepts of Statistics
Ø To understand methods of correlation and regression

- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
*To understand the concept of Marketing
*To impart knowledge on the marketing frame work
*To familiarize with marketing strategy formulation and implementation
- Teacher: Dr Sasirekha K
- Teacher: Kaavya K
An Office Management course is designed to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge required to efficiently manage the operations of an office environment. It typically covers a range of administrative, organizational, and managerial responsibilities. Here’s an overview of what such a course might include:
Key Topics in an Office Management Course:
1. Administrative Skills:
• Time management
• Filing and record-keeping systems
• Scheduling and calendar management
• Correspondence and communication handling (emails, phone calls)
2. Organizational Skills:
• Office layout and design
• Workflow optimization
• Inventory and supply management
• Event planning and coordination
3. Technology Proficiency:
• Office software (e.g., Microsoft Office, Google Workspace)
• Database management
• Basic IT troubleshooting
• Use of office equipment (printers, scanners, etc.)
4. Leadership and Interpersonal Skills:
• Team coordination and collaboration
• Conflict resolution
• Staff supervision and motivation
• Communication skills (written and verbal)
5. Financial and Budgeting Skills:
• Managing office budgets
• Expense tracking
• Procurement and vendor management
6. Legal and Ethical Practices:
• Workplace ethics
• Compliance with office and employment laws

- Teacher: SANDHYA V
Local Anesthesia - Mode of action and Clinical action of individual agents.
Inferior alveolar nerve block
ENDOCRINE EMERGENCIES IN DENTAL OFFICE
MEDICAL EMERGENCIES- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
STERILISATION AND DISINFECTION
MAXILLARY NERVE BLOCKS
List of Experiments 1. Develop a C++ program to implement a class, object creation, member function invocation concept.
2. Develop a C++ program to implement the various constructors and destructor concept.
3. Develop a C++ program to implement a friend function, Inline function.
4. Develop a C++ program to implement an operator (Unary & Binary) overloading concept.
5. Develop a C++ program to implement a function overloading concept.
6. Develop a C++ program to implement a run time polymorphism.
7. Develop a C++ program to implement the following inheritance types. a. Single b. Multiple c. Multilevel d. Hierarchical e. Hybrid
8. Develop a C++ program to implement an Abstract class concept.
9. Develop a C++ program to implement a Virtual function.

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
Course Objectives
- To introduce the principles of light propagation through optical fibers.
- To understand signal distortion mechanisms in the fiber.
- To introduce optical transmitters and receivers for fiber /free space links and the fiber optic couplers, connectors involved.
- To introduce optical network concepts and components involved and its applications.
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1-Apply the mathematical concepts to compare different types of optical fibers, modes and configuration
CO2-Analyze the transmission characteristics of optical fibers
CO3-Examine the optical sources and detectors for use in optical communication system
CO4-Construct launching and coupling of optical fibers
CO5-Design high speed optical communication networks
CO6-Design wireless communication system using Li-Fi

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
Optics lab
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. To determine the refractive index of the given liquid forming liquid lens by parallax method 2. To determine the focal length and radius of curvatures of a convex lens. 3. To draw i-d curve and to determine the angle of minimum deviation and the angle of the prism from it and hence to calculate the refractive index of the material of the prism. 4. To determine the focal length and radius of curvatures of a concave lens by displacement method. 5. To standardize the diffraction grating and hence to determine the wavelength of mercury spectral lines by normal incidence method using spectrometer. 6. To determine the radius of curvature of a lenst by Newton‟s rings method. 7. To determine the refractive index of the prominent spectral lines of mercury by spectrometer. 8. To determine the refractive index of a liquid using hollow prism. 9. To determine the dispersive power of the material of the prism by finding the refractive indices of different pairs of mercury spectral lines. 10. To determine the Cauchy‟s Constant of a prism using spectrometer.
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
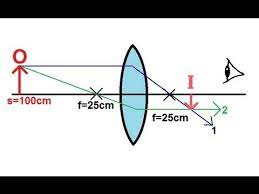
- Teacher: Kanimozhi D
- Teacher: Jayalakshmi D.S
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Jemmy Christy H
Broad outline of theoretical, clinical and practical courses. 1, Study of special and applied pathology of oral tissues as well as relation of local pathologic and clinical findings to systemic conditions. 2. Oral microbiology and their relationship to various branches of dentistry. 3. Oral microbiology affecting hard and soft tissues. Study of clinical changes and their significance to dental and oral diseases as related to oral pathology. 4. Forensic odontology. 5. Maintenance of records of all activities.

In this course participants will learn
Functional group and its significance.
IUPAC nomenclature of different functional groups.
Mechanism for substitution, elimination and addition reactions.
Synhthesis and properties of alkyl halides, alcohols, carbonyl and carbohydrate compounds.

- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
To discuss the concept of organo-nitrogen compounds.
To understand the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds containing O, N, S.
To understand the synthesis, properties and reactivity of carboxylic acids.
To develop the practice of learning molecular rearrangements along with their mechanism.
To discuss the importance of active methylene groups in organic synthesis.

- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
In this course participants will learn the
Concepts of aromaticity, reactivity and stability of organic compounds.
The preparation and properties of reactive intermediates i.e. Carbocations, Carbanions and Carbenes.
To appreciate the concept of substitution, addition
and elimination reactions and their reaction mechanism
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
- Teacher: PAPIYA SAHA
Pathophysiology is the study of causes of diseases and reactions of the body to such disease producing causes.This course is designed to impart a thorough knowledge of the relevant aspects of pathology of various conditions with reference to its pharmacological applications, and understanding of basic pathophysiological mechanisms. Hence it will not only help to study the syllabus of pathology, but also to get baseline knowledge required to practice medicine safely, confidently, rationally and effectively
- Teacher: Vigneshwaran P
- Teacher: Amudha S
Periodontology is the specialty of Dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the Periodontium, which includes the Gingiva, Periodontal Ligament, Alveolar Bone, and Cementum. A branch of dentistry which deals with Gingival, Periodontal and Peri Implant diseases, Diagnosis and Treatment Planning.

- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Yamini R
- Teacher: Dr. Sumathi H Rao
- Teacher: Chella Priya RM
- Teacher: Dr Gayathri S
- Teacher: Shifa Fathima Shajahan
- Teacher: Geetha T
Periodontics is a speciality branch of Dental sciences which deals with the study of health and diseaes of Periodontium. Which Involes Gingiva, Periodontal ligament, Cementum and Alveolar Bone. Placement of Dental Implants, Laser dentistry , periimplant diseases, Regenerative periodontics and Periodontal microsurgery and involved in this specialed branch of Periodontics.

- Teacher: Krithika Krithika
- Teacher: Yamini R
- Teacher: Dr. Sumathi H Rao
- Teacher: Chella Priya RM
- Teacher: Dr Gayathri S
- Teacher: Shifa Fathima Shajahan
- Teacher: Geetha T
- Teacher: VIJAYA KUMAR VOLETI
Enlightens about the methods and other practical aspects of pharmaceutical formulations.
Pharmaceutics-II is a study of different type of Dosage forms and Cosmetics available in Pharmacy.
- Teacher: ARUN SUNDAR M
This course will provide a knowledge on various types of Pharmaco-vigilance and Safety monitoring techniques and their analysis.

- Teacher: Madan Kumar Arumugam
This course provides basic knowledge about different classes of drugs
available for the pharmacotherapy of common diseases. The indications for use,
dosage regimen, routes of administration, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics,
and contraindications of the drugs discussed in this course are vital for successful
professional practice.
- Teacher: Muralikrishna .
- Teacher: SAI HARINI S
The main purpose of the subject is to understand what drugs do to the living organisms and how their effects can be applied to therapeutics. The subject covers the information about the drugs like, mechanism of action, physiological and biochemical effects (pharmacodynamics) as well as absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (pharmacokinetics) along with the adverse effects, clinical uses, interactions, doses, contraindications and routes of administration of different classes of drugs

- Teacher: Vigneshwaran P
- Teacher: Monisha S
PHARACEUTICAL LAW -It has been related to the act, rules, regulation and functions for decades of year.
Deals with the following act such as pharmacy act, Drug and Cosmetic act, medicinal toilet preparation, narcotic act, drug magic remedies act, Prevention of cruelty to animal act etc. Which help the public to know about the drugs and new drug formulation that brings the public awareness in the society.

- Teacher: PADMAPRIYA V
- Monitor drug therapy of patient through medication chart review and clinical review
- Obtain medication history interview and counsel the patients
- Identify drug related problems detect and assess adverse drug reactions
- Interpret selected laboratory results (as monitoring parameters in therapeutics) of specific disease states
- Know pharmaceutical care services
Physical Pharmaceutics deals with the physico-chemical principles involved in the practice of pharmacy. The principles are essential for the preparation of stable and efficacious pharmaceutical formulations.
The course deals with the various physica and physicochemical properties, and
principles involved in dosage forms/formulations. Theory and practical
components of the subject help the student to get a better insight into various
areas of formulation research and development, and stability studies of
pharmaceutical dosage
- Teacher: Dr. Joan Vijetha R

- Teacher: Malliga P
Unit-I: 9 hours
Introduction to Robots-Laws of Robotics-Zeroth law- Law 1-Law 2-Law 3-History of Robotics-First industrial robots-mechanism-Five Basic Principles of Developmental Robotics-The Principle of Embodiment-The Principle of Subjectivity-The Principle of Grounding-The Principle of Gradual Exploration-Medical and Industrial Applications of Robots.
Unit-II: 9 hours
Applications of Quantum Physics: photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, photons, De Broglie waves and the wave-particle duality of matter and light. Introduction to wave mechanics: Schrödinger's equation, wave functions, wave packets, Heisenberg uncertainty principle and zero-point energies. Solutions to Schrödinger's equation in one dimension: Energy Eigen values and eigen functions, Schrödinger's equation in three dimensions: central potentials and introduction to hydrogenic systems. Particle in a 1-D box, Tunneling Effect (Qualitative), Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM)
Unit-III: 9 hours
Sensors: Introduction-measurement of sensor, Basic concepts, Types, mechanism-working principle- classification of sensor-internal sensors: position and velocity sensors:-Types of Robot Sensors: Light sensor-Touch sensor, vision sensor, radar, sonar, ultrasonic sensors-sound sensor-Temperature sensor
Unit-IV: 9 hours
Smart materials for soft Robots: Classification of building materials for Robots: Wood, metal: Aluminum, steel, bronze, brass and copper: Synthetic materials: PVC, Glass, composite materials: Manufacturing-compression molding method-Polymer composite materials-Aluminum alloys, Piezo materials, Shape memory alloys.
Unit-V: 9 hours
Nanophysics of Nono-Robotics: Nanorobotics theory – The origins of nano technology- Manufacturing of nanorobots using chips and nubots- working of nanobots, Types of nano robots, Medical Applications of Nanorobotics (nanobots),Fractal robots-features, self repair in fractal robots, applications of fractal robots.

- Teacher: Malliga P
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
COURSE OBJECTIVE
The objective of the course is to provide knowledge on fundamentals, structures, photosynthesis, metabolism of
nitrogen compounds and about molecular mechanisms of signalization and regulation in plants.
- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on different types of power semiconductor devices and its switching characteristics.
To study the operation, characteristics and performance parameters of controlled rectifiers.
To understand the operations of choppers and inverters.
To get acquainted with the applications of power electronics converters.
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J

- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
On completion of the course, student will be able to
|
CO1 |
Acquire familiarity towards Evolution of Management, principles of F.W.Taylor’s & Henry Fayol, Organizational structures and basics of management including concepts of MBO & MBE |
|
CO2 |
Gain knowledge on the types of business organization, designing a layout for a plant, and the safety measure to overcome industrial accidents. |
|
CO3 |
Recognize the importance of studying individual and group behavior at workplace and its effect on performance in organization |
|
CO4 |
Develop expertise knowledge on the impact of Leadership Communication and Group dynamics in industry |
|
CO5 |
Learn the basics of ethical behavior and corporate social responsibility practiced in industries |
|
CO6 |
Solve cases business, to do a role play based on the knowledge gained from the subject and also apply the gained knowledge in industries in real life situations |

- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S

- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: SAGARIKA S.R
COURSE OBJECTIVE
• To expose of the important legal aspects and legislations practice and profession. To make students to understand the important laws and act relevant to architecture.
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO ARCHITECTURAL PROFESSION 8 Hrs. Importance of Architectural Profession - Role of Architects in Society - Career options open for Architects-Prerequisites for Private Practice - Types of practices (Partnership/ Proprietary Concern /Associate - Architect’s office and its management - Location, Infrastructure requirement - organizational structure, Basic accounts - Legal requirements, Registration of Firm, Tax Liabilities, Relationship with clients, contractors, Associate consultants and product Manufacturers.
UNIT 2 CODE OF CONDUCT AND ETHICS 8 Hrs. Role of Professional Body (The Indian Institute of Architects) History, Objectives, its relevance - Architects Act 1972 (Background, intent, objectives)- Council of Architecture (role and function with regard to Architectural practice) - Registration of Architects - Importance of Ethics - guidelines prescribed for professional code of conduct -punitive action for professional misconduct.
UNIT 3 STATUTORY PROVISIONS GOVERNING ARCHITECTURAL PROVISIONS 8 Hrs. Important Acts and Regulations governing the design of buildings- (Town & Country Planning Act, Consumer Protection Act, Copy Right Act, Persons with Disabilities Act, Coastal Regulation Zone Act, Heritage Act, Land Acquisition Act, Factories Act, Cinema Act)-Master Plan Provisions and Development regulations with reference to CMDA -Planning norms and Building Rules-Role of Planning Authority and local body - Building Approval process.
UNIT 4 EMERGING TRENDS 6 Hrs.
Meaning of GATS - Globalisation and its impact on architectural profession - Entry of Foreign Architects and their
impact in Indian Architectural practice - Information Technology and its impact -specialisation in the field of architecture
-Green Buildings and the governing laws.
. Max. 30 Hours

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To learn the fundamental programming concepts and methodologies which are essential to building good C/C++ program.
To demonstrate a thorough understanding of modular programming by designing programs which require the use of programmer-defined functions.
To impart the knowledge about pointers which is the backbone of effective memory handling.
To perform Inheritance, Overloading of operators, functions,constructors and File Handling
To demonstrate adeptness of object oriented programming in developing solutions to problems demonstrating usage of data abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance.
- Teacher: ANU BARATHI
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi K
To develop programs in C using basic constructs.
For develop applications in C using strings, pointers, functions, structures.
To develop applications in C using file processing.
To make the student learn a programming language.
To learn problem solving techniques.
To teach the student to write programs in C and to solve the problems
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To develop programs in C using basic constructs.
- To develop applications in C using strings, pointers, functions, structures.
- To develop applications in C using file processing.
- To make the student learn a programming language.
- To learn problem solving techniques.
- To teach the student to write programs in C and to solve the problems.
- COURSE OUTCOMES
- On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Develop C programs for simple applications making use of basic constructs, arrays and strings.
- CO2 - Develop C programs involving functions, recursion, pointers, and structures.
- CO3 - Design applications using sequential and random access file processing.
- CO4 - Read, understand and trace the execution of programs written in C language.
- CO5 - Implement Programs with pointers and arrays, perform pointer arithmetic, and use the pre-Processor.
- CO6 - Write programs that perform operations using derived data types

APPLIED PSYCHOLOGY
PLACEMENT: I SEMESTER
THEORY: 3 Credits (60 Hours)
DESCRIPTION: This course is designed to enable the students to develop understanding about basic concepts of
psychology and its application in personal and community life, health, illness and nursing. It further provides students
opportunity to recognize the significance and application of soft skills and self-empowerment in the practice of nursing.
COMPETENCIES: On completion of the course, the students will be able to
1. Identify the importance of psychology in individual and professional life.
2. Develop understanding of the biological and psychological basis of human behaviour.
3. Identify the role of nurse in promoting mental health and dealing with altered personality.
4. Perform the role of nurses applicable to the psychology of different age groups.
5. Identify the cognitive and affective needs of clients.
6. Integrate the principles of motivation and emotion in performing the role of nurse in caring for emotionally sick client.
7. Demonstrate basic understanding of psychological assessment and nurse‘s role.
8. Apply the knowledge of soft skills in workplace and society.
9. Apply the knowledge of self-empowerment in workplace, society and personal life.
| Unit | Time (Hrs) | Learning Outcomes | Content | Teaching/ Learning Activities | Assessment Methods | |
| I | 2 (T) | Describe scope, branches and significance of psychology in nursing | Introduction Meaning of Psychology Development of psychology – Scope, branches and methods of psychology Relationship with other subjects Significance of psychology in nursing Applied psychology to solve everyday issues | Lecture cum Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| II | 4 (T) | Describe biology of human behaviour | Biological basis of behavior –Introduction Body mind relationship Genetics and behaviour Inheritance of behaviour Brain and behaviour. Psychology and sensation – sensory process – normal and abnormal | Lecture Discussion | Essay Short answer | |
| III | 5 (T) | Describe mentally healthy person and defense mechanisms | Mental health and mental hygiene Concept of mental health and mental hygiene Characteristic of mentally healthy person Warning signs of poor mental health Promotive and preventive mental health strategies and services Defense mechanism and its implication Frustration and conflict – types of conflicts and measurements to overcome Role of nurse in reducing frustration and conflict and enhancing coping Dealing with ego | Lecture Case discussion Role play | Essay Short answer Objective type | |
| IV | 7 (T) | Describe psychology of people in different age groups and role of nurse | Developmental psychology Physical, psychosocial and cognitive development across life span – Prenatal through early childhood, middle to late childhood through adolescence, early and mid-adulthood, late adulthood, death and dying Role of nurse in supporting normal growth and development across the life span Psychological needs of various groups in health and sickness – Infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and older adult Introduction to child psychology and role of nurse in meeting the psychological needs of
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay Short answer |
| V | 4 (T) | Explain personality and role of nurse in identification and improvement in altered personality | Personality Meaning, definition of personality Classification of personality Measurement and evaluation of personality – Introduction Alteration in personality Role of nurse in identification of individual personality and improvement in altered personality | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VI | 16 (T) | Explain cognitive process and their applications | Cognitive process Attention – definition, types, determinants, duration, degree and alteration in attention Perception – Meaning of Perception, principles, factor affecting perception, Intelligence – Meaning of intelligence – Effect of heredity and environment in intelligence, classification, Introduction to measurement of intelligence tests – Mental deficiencies Learning – Definition of learning, types of learning, Factors influencing learning – Learning process, Habit formation Memory-meaning and nature of memory, factors influencing memory, methods to improve memory, forgetting Thinking – types, level, reasoning and problem solving. Aptitude – concept, types, individual differences and variability Psychometric assessment of cognitive processes – Introduction Alteration in cognitive processes | Lecture Discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type | |
| VII | 6 (T) | Describe motivation, emotion, attitude and role of nurse in emotionally sick client | Motivation and emotional processes Motivation – meaning, concept, types, theories of motivation, motivation cycle, biological and special motives Emotions – Meaning of emotions, development of emotions, alteration of emotion, emotions in sickness – handling emotions in self and other Stress and adaptation – stress, stressor, cycle, effect, adaptation and coping
| Lecture Group discussion | Essay and short answer Objective type |
| VIII | 4 (T) | Explain psychological assessment and tests and role of nurse | Psychological assessment and tests – introduction Types, development, characteristics, principles, uses, interpretation Role of nurse in psychological assessment | Lecture Discussion Demonstration | Short answer Assessment of practice |
| IX | 10 (T) | Explain concept of soft skill and its application in work place and society | Application of soft skill Concept of soft skill Types of soft skill – visual, aural and communication skill The way of communication Building relationship with client and society Interpersonal Relationships (IPR): Definition, Types, and Purposes, Interpersonal skills, Barriers, Strategies to overcome barriers Survival strategies – managing time, coping stress, resilience, work – life balance Applying soft skill to workplace and society – Presentation skills, social etiquette, telephone etiquette, motivational skills, teamwork etc. Use of soft skill in nursing | Lecture Group discussion Role play Refer/Complete Soft skills module | Essay and short answer |
| X | 2 (T) | Explain self empowerment | Self-empowerment Dimensions of self-empowerment Self-empowerment development Importance of women‘s empowerment in society Professional etiquette and personal grooming Role of nurse in empowering others | Lecture Discussion | Short answer Objective type |
- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Jayaprakash Venugopal
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable the student to understand the modern mechatronics components.
To present the underlying principles and alternatives for mechatronics systems design.
To provide the student with the opportunity for hands-on experience with the related components of the technology for diverse domains of application.
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquaint students with core knowledge in visual information processing and learning.
CO2 - Implement Digital Image Processing Mechanisms.
CO3 - Analyze and design Digital Image Generation Mechanisms.
CO4 - Representation of geometry and subdivision methods.
CO5 - Describe the Learning Methods in Vision.
CO6 - Comprehend the concepts related three dimensional object representations.
- Teacher: CHITRA P
To acquire basic understanding of concepts and laws of thermodynamics, volumetric properties of fluids and thermodynamic properties of fluids
- Teacher: Annam Renita A
Course Objective:
To learn to appreciate the programming language that can be used for a wide variety of programming tasks and
to expose the student to the standard scripting language. At the end of the course, the student will be developing
adequate skills in programming and will be known to understand the implementation of various applications using
a powerful assortment of built-in types in python.
Course Outcome:
The students will be able to

- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
- Teacher: oviya R.P
Python is a high-level, interpreted, interactive and object-oriented scripting language. ... Python is a Beginner's Language − Python is a great language for the beginner-level programmers and supports the development of a wide range of applications from simple text processing to WWW browsers to games.

- Teacher: Dr.R PUGALENDHI -
- Teacher: Dr.R PUGALENDHI -
Course Objectives:
· To make the learners aware of the social, cultural and psychological implications of the Neo-classical.
· To familiarize the students with the evolution of the genre of fiction in Britain.
· To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
· To provide knowledge on the Romantic age of British Literature.

- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
- Teacher: Berlin Mary S

Course Objectives:
• To introduce students with the works of significant critics
• To encourage students to undertake further reading in critical movements and critical theory
• To enable the students to apply principles of criticism to literary texts
• To make them aware of theories from Romantics to the present era

- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
For students who have completed pre-clinical years and successfully entered into the clinical years of the course. Learning to clinically examine and process removable partial denture. The course describes the principles behind the designing and the laboratory and clinical techniques in fabrication of removable partial prosthesis.
- Teacher: Haribabu R
- Teacher: Sankarakrishnan S
- Teacher: M V SRIKANTH
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Comprehend the different types of conventional energy recourses.
CO2 - Design a suitable solar energy conversion system for real world.
CO3 - Design the suitable Wind Energy conversion system for real world application.
CO4 - Design a smart grid for uninterrupted power supply from non conventional energy resources.
CO5 - Justify, the suitability of fuel cells for addressing the energy problems of the modern world
CO6 - Justify, the suitability of Thermo Electric and Thermionic Power Conversion system for addressing the energy
problems of the modern world.
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Ø To comprehend the need, role and importance of research in Architecture.
Ø To understand and synthesize process of research.
Ø To give an insight to report writing and publishing research work in journals.

- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Arulmalar Ramaraj
|
SPYA1303 |
Research Methodology – I |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To understand the basic principles that governs psychological research.
· To understand the variables, sample, and various methods in research
· To be familiar in writing research report
Unit I: Introduction (15 hours)
Meaning of research - Objectives of research- Various steps in research - Types of research - Significance of research - Research methods versus methodology - Review of literature - Problems encountered by researchers in India - Ethical consideration in psychological research.
Unit II: Measurement and Scaling Techniques (15 hours)
Measurement in research - Measurement scales - Source of errors in measurement – Scaling -meaning of scaling - Scale construction techniques - Test development and standardization - Reliability - Validity.
Unit III: Variables and Methods of data collection (15 hours)
Meaning of variable – Various types of variables - Observation methods - Survey method - Questionnaire methods - Interview method –types of interview – Checklist - Rating scales.
Unit IV: Sampling fundamentals and Methods of Psychological Research (15 hours)
Sample - Sample size and its determination – types of sampling - Estimation and estimating population proportion - Testing of hypothesis - Experimental - Quasi-experimental - Case studies.
Unit V: Interpretation and Report Writing (15 hours)
Meaning of interpretation - Precaution in interpretation - Mechanics for writing a research report steps involved in writing research report - Precaution in writing research reports.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Understand the fundamentals of research including research problem, literature review, and hypothesis and so on.
2. Understand the different types of research design used in psychological research and be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of different designs.
3. Apply knowledge of statistics and methodology to undertake various key steps (e.g., design, data collection, screening, preparation, analysis of data, and write-up of research results) to create research of a high quality in an area of psychology.
4. Apply knowledge of research methodology in further study and professional practice.
References:
1. Michael Smithson, (2000), Statistics with Confidence: An Introduction for Psychologists, sage publications.
2. David C. Howell (2012), Statistical Methods for Psychology Cengage Learning.
3. Guilford, J.P. (1973), Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and Education,.McGraw Hill Kogakusha.
4. Ferguson, George, A. (1976), Statistical Analysis in Psychology & Education, McGraw Hill, Kogakusha.
5. Mangal, S. K. (2004), Statistics in Psychology and Education. 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, Delhi
6.Kothari, C. R. (2007). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques. 2nd ed. New Age International Publishers.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To learn the fundamental concepts of Robotics automation process
➢ To introduce basic concepts of various dynamics processes
➢ To understand the effect of various power sources and sensors.
➢ To impart knowledge on the manipulators, grippers and robot dynamics
➢ To implement a real time Robot with the support of available programming languages
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
Course Objective:
• Introduce principles and techniques of VLSI design.
• Teach the use of hardware descriptive languages for VLSI.
• Provide knowledge on VLSI fabrication processes.
• Explore the impact of Al on VLSI design.
• Examine Al applications in VLSI technology.
• Introduce optimization strategies for 3D ICs.
• Teach predictive analysis using machine learning in VLSI.
• Focus on Al-based routing algorithms for VLSI circuits.
Course Outcome
Ability to design and implement VLSI systems.
- Proficiency in using hardware descriptive languages for VLSI circuits
- Understanding of the VLSI fabrication process.
- Ability to evaluate Al's impact on VLSI design.
- Capability to implement Al applications in VLSI.
- Skills in applying optimization techniques for 3D ICs.
- Competence in using machine learning for predictive analysis in VLSI.
- Skills in designing Al-based routing algorithms for VLSI.
- Teacher: Shamini G I
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: MATHAN N
An aptitude is a component of a competence to do a certain kind of work at a certain level. Aptitude tells about the mental stability and analytical skills of an individual.
In this Skill Enhancement course, students are trained on
- Quantitative Aptitude Skills
- Reasoning Ability
- Logical Reasoning
- Visual Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Verbal Abilities & Language Comprehension
- General Awareness & General Knowledge

- Teacher: IMMANUEL Y
- Quantitative aptitude is a measure of an individual’s numeric ability and problem-solving skills. This sort of aptitude is highly valued in fields like computer science, engineering, and mathematics because it usually correlates with success in those fields. However, there is a push to further this understanding in qualitative fields like journalism and the digital arts too.

COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To give the opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
- While upholding the standards of both national and international benchmarking in fashion design each student is required to design an individual collection reflecting originality creative flair with in-depth conceptualization and implementation of the design process combined with impeccable technical strength and quality.
- The focus is on global design with an Indian flavor that is an ideal blend of creativity with function and marketability.
- The Fashion Design Project will have to be carried out by each student in the eighth semester. The project will give ample opportunity to the design student to come out with a minimum of 5 ensembles. The project will be the culmination of various inputs imbibed by the students over the previous semesters ranging from creative exposure and sensitization to technical expertise.
The guidelines for reference to develop design collection:
- The Fabric: Development and exploration of traditional resources (materials and techniques) towards contemporary expressions.
- The Image: Kaleidoscopic images encapsulated in time or space (History) to more globalized aspirations.
- The Attitude: From rejuvenation to revivalism- from transformation to transmutation- from the concrete to the sublime.
- The students may choose to specialize in any of the areas focusing on either women’s wear- menswear or children's clothing. Textiles may be combined with knits leather or any other suitable material while ensuring that the focus is on the extensive and prime usage of woven fabric.
The collection could fall in any one of the categories:
- . Sportswear
- Eveningwear
- Ethnic collection or Fusion
- Kids Wear
- Avant-Garde
- Theatre costume
- Institutional clothing or
- Any other category approved by the mentor

- COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Understand control structures, functions and Arrays in C.
- Construct modules for real time applications using Functions in C.
- Comprehend pointers and file handling mechanisms
CO2 - Build simple solution for any given problem statement using various components of problem solving techniques and measure its efficiency in terms of time and space.
CO3 - Infer and examine the roots and foundation of C programming‘s key concepts like data types, operators.
CO4 - Devise and correlate the use of different core concepts such as arrays and functions in C language.
CO5 - Formulate real time solutions through programs using structure and union in C language.
CO6 - Design and develop various application oriented program for solving real time societal problems.
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand the basic concepts of C/C++ programming.
Ø To demonstrate the techniques for implementing engineering applications using computer programs.
Ø To equip students with sound skills in C/C++ programming language.
Ø To Identify, formulate and solve problems by using computer programming Language.
Ø To write diversified solutions using C language.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the students will be able to
CO1 - Apply good programming design methods for program development.
CO2 - Construct programs that demonstrate effective use of C features including arrays, structures, pointers and files.
CO3 - Develop Recursive Programs.
CO4 - Write programs that perform explicit memory management.
CO5 - Develop programs in object oriented programming.
CO6 - Apply generic programming techniques to solve practical engineering problems.

- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- Teacher: Sivagami P
- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
COURSE OBJECTIVES
• To study the concept of data types
• To study basics of python programing
• To study GUI programing
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the concept of Data types, conditional statements and looping in Python programming
CO2 Apply functions in Python for real time problems.
CO3 Analyze the use of List, Tuples and Dictionaries in Python programming
CO4 Develop python programming for web applications using regular expression
CO5 Design GUI in Python for various applications
CO6 Develop solution in Python for any specific real time problem

- Teacher: Bharathi R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
• To study the concept of data types
• To study basics of python programing
• To study GUI programing
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the concept of Data types, conditional statements and looping in Python programming
CO2 Apply functions in Python for real time problems.
CO3 Analyze the use of List, Tuples and Dictionaries in Python programming
CO4 Develop python programming for web applications using regular expression
CO5 Design GUI in Python for various applications
CO6 Develop solution in Python for any specific real time problem

- Teacher: LAKSHNA A
- Teacher: Gracelydiaphoebe M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
• To study the concept of data types
• To study basics of python programing
• To study GUI programing
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the concept of Data types, conditional statements and looping in Python programming
CO2 Apply functions in Python for real time problems.
CO3 Analyze the use of List, Tuples and Dictionaries in Python programming
CO4 Develop python programming for web applications using regular expression
CO5 Design GUI in Python for various applications
CO6 Develop solution in Python for any specific real time problem

- Teacher: M Subramoniam .
- Teacher: Allan Dino J
- Teacher: BAVYA L
- Teacher: Somasekar M
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Nandhitha N M
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: PARUTHI ILAM VAZHUTHI P
- Teacher: Bharathi R
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: Surender R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: PURUSHOTHAMAN S
- Teacher: REVATHY V
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
➢ To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semi-conductors.
➢ To familiarize on the principle of operation, capabilities and limitation of various advanced semiconductor devices and its practical application.
➢ To design practical circuits with alternate electronic devices.
➢ To study Nano devices.

- Teacher: annieangelinepreethi .
- Teacher: Rajasekar B
- Teacher: Dr. SUMATHI M
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: Indhu R
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
* To acquaint the students with the construction, theory, and operation of the basic electronic devices such as PN junction diode, Bipolar and Field-effect Transistors, Power control devices, LED, LCD, and other Optoelectronic devices.
*To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semiconductors.
* To familiarize on the principle of operation, capabilities, and limitations of various advanced semiconductor devices and its practical application.
* To design practical circuits with alternate electronic devices.
* To study about the display devices and power semiconductors.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Apply the knowledge of basic semiconductor materials and understand fabrication processes.
CO2 - Analyse the characteristics of various electronic devices like diode, transistor etc.
CO3 - Classify and analyse the various circuit configurations of Transistor and MOSFETs.
CO4 - Illustrate the qualitative knowledge of Power electronic Devices.
CO5 - Become Aware of the latest technological changes in Display Devices.
CO6 - Apply the knowledge of basic semiconductor materials and understand fabrication processes.
- Teacher: Bhuvana B P
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: YOKESH V
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1- Minimize Boolean functions for computationally less complex implementations
CO2- Apply K map and tabulation method for minimization of Boolean functions
CO3 - Implement combinational logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO4 - Implement sequential logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO5 - Analyze the performance of various logic families
CO6 - Implement memory units with Programmable logic devices
- Teacher: Dr.Divya A
- Teacher: Bhuvana B P
- Teacher: Sharanya C
- Teacher: JEGAN G
- Teacher: SOWMIYA G
- Teacher: ANBARASI K
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: BAVYA L
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
- Teacher: Kanimozhi M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Bhavani R
- Teacher: VINO T
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To familiarize the student with the design and analysis of Rectifiers and power supplies.
Ø To understand different Transistor biasing circuits.
Ø To understand Small signal analysis of FET and MOSFET amplifiers.
Ø To understand working of feedback amplifiers, oscillators, tuned amplifiers and multivibrators
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand basic construction, equivalent circuits and characteristics of basic electronics devices.
CO2 - Understand basic linear electronics circuits and their working principle.
CO3 - Design and analyze DC Power supplies.
CO4 - Design and analyze multistage amplifiers.
CO5 - Design negative feedback amplifier circuits and oscillators.
CO6 - Analyze and design solid state power amplifier circuits.
- Teacher: Bhuvaneswari C
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To widen capability for analyzing the needs of analogue and digital communication systems
Ø To comprehend various analogue and digital modulation techniques for generation and detection.
Ø To acquire theoretical knowledge of each block in AM, FM transmitters and receivers
Ø To be familiar with sampling and quantization principles
Ø To understand the various band pass signaling schemes
Ø To know the fundamentals of spread spectrum modeling and speech coding.

- Teacher: Sharanya C
- Teacher: RAJESWARI D
- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
- Teacher: Surender R
- Teacher: Dr.I.Rexiline Sheeba
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
|
Course Outcomes On completion of the course, the student will be able to CO1 - Analyze LTI Discrete Time Systems using DFT and FFT CO2 - Design of digital filters like FIR and IIR Filter CO3 - Evaluate the effect of finite word length while designing a digital filter CO4 - Employ signal processing strategies in multirate signal processing CO5 - Apply the signal processing technique in speech signal and image processing CO6 - Build filter design algorithm in DSP processor |
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To study the basics of Embedded System.
- To explain the various development tools in embedded System.
- To get a knowledge in embedded programming and acquire a knowledge in embedded system application

- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
COURSE OUTCOMES :
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Analyze the architecture and functional operations of 8051 microcontroller.
CO2 – Apply the 8051 microcontroller for addressing the Engineering problems.
CO3 - Analyze the architecture, functionalities of PIC 16F877A Microcontroller and apply for addressing the Engineering problems.
CO4 - Analyze the suitability of various interfacing bus devices for applications.
CO5 -.Analyze the operation of the real time operating system (RTOS) for embedded applications.
CO6 - Evaluate the concept of RTOS in real time embedded system.

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: V SIVAPRAKASH
- Teacher: AROCKIA SUTHAN
Heat Transfer course demonstrates the three modes of heat transfer through conduction, convection and radiation. Along conduction the heat flow through steady state and unsteady state systems were elaborated in detail through the access of one, two and three dimensional systems. Convection highlights the fluid flow under the influence of various flows accustomed with the applications of various flow equations. The radiation mechanisms were described through the application of various electromagnetic laws. Design of Heat transfer equipment such as heat ex-changers and evaporation units were also well discussed using the fundamental and derived equations governing heat transfer process.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Compare the amino acid sequence and structure of proteins relating this information to the function of proteinsCO2 - Analyze several techniques used for isolation and characterisation of proteins
CO3 - Appraise protein databases as a storehouse for the latest information in protein research
CO4 - Analyse the protein sequence for their structural properties
CO5 - Apply appropriate tools to predict the structure of proteins
CO6 - Appraise enzymes and different protein design strategies used to design completely new proteins tailored to specific tasks
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Compare the amino acid sequence and structure of proteins relating this information to the function of proteinsCO2 - Analyze several techniques used for isolation and characterisation of proteins
CO3 - Appraise protein databases as a storehouse for the latest information in protein research
CO4 - Analyse the protein sequence for their structural properties
CO5 - Apply appropriate tools to predict the structure of proteins
CO6 - Appraise enzymes and different protein design strategies used to design completely new proteins tailored to specific tasks
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Gracelydiaphoebe M
- Teacher: Muthulakshmi A
S614BLH38 - CYBER FORENSICS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To learn about the Cyber Crime and to Understand the concepts of open source tools
To learn about Cyber Forensics and to identify and report the forensic on disk level
To learn about Cyber Investigation and to Implement forensic concepts in network level
To learn about Evidence Management and to Analyze Virtual machine forensic
To learn about Cyber Laws and Authorities and Analyze various cloud forensic

- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: Jemmy Christy H
- Teacher: Theboral J
To give students a broad and challenging experience that will formulate their thought process by in-depth investigation, analysis and critical review of relevant materials.
To enable their understanding, cognitive and communicative skills, critic the existing practices in Sustainable Architecture based on the current practices, new trends and technologies.
To provide students an opportunity to cultivate specialization in the areas of their own interest and undertake academic research or develop specific sustainable design independently
Dissertation work includes processes such as: Research area identification; hypothesis of research topic; literature sourcing and search; aim and objective definition; formulation of methodology; field study planning; survey data collection, analysis and result presentation; literature study; conceptual an empirical :compilation and inference drawing; research study validation through case studies, field application and simulation models; discussion of research findings; study conclusion and recommendation formulations.

- Teacher: Catherine S
To identify an area of research and design interest related to sustainable architecture and develop a thesis synopsis
To facilitate the independent research skills of students
To acquire a fresh approach in formulating an effective methodology that will help in the flow of the research
The intent of pre thesis is to initiate the selection of thesis topic in the beginning of the third semester itself. The students shall work three alternative topics by studying and analyzing the published research papers of their interest area and give justification for the selection of the topics which will be assigned to him / her to proceed to the next phase.
The subject for special study shall be conceptual or practical but pertaining to sustainable building and environment design practices.

- Teacher: Catherine S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To channelize the knowledge constructed on ‘sustainable principles in architecture’ and successful integration in the identified typology
The project provides students an opportunity for academic research to cultivate specialization in the areas of their own interest under the overall guidance of the faculty.
The objective of the seminar work is to train the students to prepare state of art report by assimilation of concepts / ideas on a chosen topic in the area of Sustainable Architecture.

- Teacher: Kavitha S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To undergo professional training in a firm to get experience of handling various environmental design practice, Sustainable developments and learn latest software trending in the market.
To utilize the forum to discuss key issues in the projects, keep track of the different sustainable approaches, communicate with the stakeholders and get an overall view of the contract administration.
The final project report will comprise of an in-depth research and analysis of activities in the form of drawings & relevant details, schematic charts & reports, photographs, documentation of the project, comments, suggestions, etc to appraise the efficiency in progress of work.
To undergo professional training in a firm to get experience of handling various environmental design practice,
Sustainable developments and learn latest software trending in the market.
➢ To utilize the forum to discuss key issues in the projects, keep track of the different sustainable approaches,
communicate with the stakeholders and get an overall view of the contract administration.
➢ The final project report will comprise of an in-depth research and analysis of activities in the form of drawings & relevant
details, schematic charts & reports, photographs, documentation of the project, comments, suggestions, etc to
appraise the efficiency in progress of work.

- Teacher: Catherine S
This Course is Research Oriented and Pre-thesis is taken prior to the final semester of the M.Arch program. The goal of pre-thesis is to lay the foundation for the successful and timely accomplishment of your final project. Pre-thesis course include Identifying research area, Literature reviews, Case study, Analysis and Site selection.
Course Objectives
· Learn the principles of meal planning.
· Acquire knowledge on planning meals for different age groups
- Teacher: KANYA S
Nutrition and health in National development
Nutritional disorders
Methods of assessing nutritional status
Improvement of nutrition of a community
Nutritional and infection relationship
Food borne infection and intoxication diseases
National and International agencies in uplifting the nutritional status
Community nutrition programme planning

- Teacher: Roshni M
Course Objectives
This course will enable the students to –
- Know the factors affecting the nutrient needs during different stages of life cycle & the RDA for various age groups.
- Gain knowledge of dietary modification for weight management.
Course Outcomes
On completion the student will be able to
- Develop a philosophy of why meal preparation and consumption at the family table is an important component in development and stability of families.
- Plan attractive meals with consideration for nutritional adequacy, income level, social, cultural, psychological, palatability, and aesthetic factors.
- Employ sanitation standards and safety procedures in food handling and in the use and care of kitchen utensils, equipment, and food storage.
- Demonstrate an understanding of factors affecting food habits, meal consumption patterns, and trends in food cost.
- Utilize managerial skills and available resources in food purchasing, and meal planning, preparation, and service
- Differentiate the meal menu between different age groups

- Teacher: KANYA S
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: Roshni M
- Teacher: Priya S
- Teacher: Priya S
- Teacher: Roshni M
Clearly understand the working of different types of low and speed wind tunnels and water tunnels and their specifications. Know about horizontal buoyancy, flow angularities, and other calibration parameters. Know about aerodynamic measurements and three and six component external and internal balances for steady and unsteady force measurements. Get a clear idea about the surface and flow field flow visualization of incompressible and compressible flows

- Teacher: Venkatesh S
About Airframe Main

COURSE OBJECTIVE
To know about the airport planning, airport design and air traffic control
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 10 Hrs.
Significance of Air Transport -Economic Significance - - History Of Aviation - Air Transportation In India – Indian Airlines Corporation - Air India - International Corporation - International – Airport Authority Of India - (IAAI) – Civil Aviation – Open Sky Policy – Airport Terminology - Component Parts Of Airplane – Characteristics Of The Jet Aircraft – Civil And Military Aircrafts Classification Of Aerodromes . Classification Of Airports – Flying Activities - Aircraft Characteristics - Dimensional Standards - Landing Gear Configurations - Aircraft Weight - Engine Types - Wind Speed And Direction - Payload And Range -Runway Performance - Air Traffic Management - Flight Service Stations - Airspace Classifications And Airways - Area Navigation - Air Traffic Separation Rules - Longitudinal Separation - Lateral Separation In The Airspace - Navigational Aids - Ground-Based Systems
UNIT 2 AIRPORT PLANNING 10 Hrs.
The Airport System Plan - Master Plan - Project Plan - Continuing Planning Process - Levels Of Forecasting - Forecasting Methods - Time Series Method - Market Share Method - Econometric Modeling - Airport Design Standards – ICAO Standards - FAA Standards - Airport – Surveys –types Of Surveys - drawings - Capacity – Improving –Traffic Forecast – Planning – Airport Site Selection – Different Conditions - Zoning Laws – Airport Architecture - Environmental- Factors - Runway Orientation - Head Wind, - Cross Wind - Component- Wind rose – Runway Length – Corrections - Geometric Design Of Runways - Balanced Field - Concept - Airport Capacity – Runway – Patterns- Runway Types - Geometric Design Of Runway Intersection – Layout Of Taxiways Arrangement, Geometric Standards For Taxiway - Gradient - Exit Taxiways Air Traffic Control – Angle Of Turn, Compound Curve - Occupancy Time – Shape Of Taxiway – Loading Aprons – Holding Aprons - Configuration - Entry Runway - Holding Bays - Location – Peak Demands – Simple Problems - Capacity And Delay - Formulation Of Runway Capacity Through - Formulation Of Ultimate Capacity - Hourly Capacity -Parameters Required For Runway Capacity - Computation Of Delay On Runway Systems -Graphical Methods For Approximating - Simulation Models - Gate Capacity - Analytical Models For Gate Capacity.
UNIT 3 TERMINAL AREA DESIGN 9 Hrs.
Terminal Building Design Objectives – Passenger Flow – Parking – Size Of Apron – Hangars - Jet Blast – Typical Airport Layouts-Military Layouts – Types Of Pavements – Design Factors – Design Of Flexible, Rigid Pavements – LCN Method – Pavement failures – Maintenance ,Evaluation Of Airport Pavements – The CBR test - The Plate Bearing Test - Young’s Modulus (E Value) - Effect Of Frost On Soil Strength -Subgrade Stabilization - FAA Pavement Design Methods –Aircrafts-Pavement Classification – Joints In Cement Concrete Pavements - Pumping – Design –Pavements – Drainage – Importance Of Grading –Basic Requirements Of Airport Drainage- Surface Drainage – Design Procedure – Subsurface Drainage – Types Of Pipes
UNIT 4 AIRPORT LIGHTING, MARKING, AND SIGNAGE 8 Hrs.
The Requirements For Visual Aids - The Airport Beacon - The Aircraft Landing Operation - Alignment Guidance - Height Information - Approach Lighting -Visual Approach Slope Aids - Visual Approach Slope Indicator Precision Approach Path - Threshold Lighting - Runway Lighting - Runway Edge Lights - Runway Centerline And Touchdown Zone Lights - Runway Stop Bar - Runways - Runway Designators -Runway Threshold Markings – Different Types Of Markings - Taxiway Guidance Sign System - Signing Conventions - Sign Operation
UNIT 5 AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL 8 Hrs.
Importance – Air Traffic Control – Flight Rules - Meaning,- Responsibility – Type Of Control – Air Traffic Control Network –Control - Towers – Flight Service Stations - Air Traffic Control Aids –– GPS Air Traffic Control-Free Flight Types - Heliports- Stolports – Planning Of Heliport Ports – Characteristics of Stolports- Planning of StolPorts
Max. 45 Hours TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Airport Engineering ,Rangwala , Charotar Publishing House Pvt. Ltd . Anand 388 001 India , 14th Edition ,2014
2. Planning And Design Of Airports, Fifth Edition Robert Horonjeff, Francis Mckelvey, William Sproule, Seth Young ,McGraw Hill Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2013
3. Airport Engineering: Planning, Design And Development Of Development Of 21st Century Airports, Norman J. Ashford, Saleh
4. Mumayiz, Paul H. Wright - 2011 - - 4th Edition,
5. Airport Planning &Design ,S. K. Khanna, M. G. Arora , NemChand Publishers ,New Delhi ,1999
6. Airport Engineering: Planning And Design ,Subhash Chandra Saxena , Alkem Company (S) Pte Limited, 2009.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G

- Teacher: GokulNath R
Aerodynamics is the study of forces and the resulting motion of objects through the air. Because aerodynamics involves both the motion of the object and the reaction of the air, there are several pages devoted to basic gas properties and how those properties change through the atmosphere.

This subject deals with solid mechanics and its behaviors at different conditions . it is related to aircraft structures

- Teacher: Dr. ANAND T
UNIT 1 PREREQUSITES TO EVALUATE AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Properties of earth’s atmosphere and standard atmosphere, Forces and moments acting on a flight vehicle - Equation of motion of a rigid flight vehicle- Different types of drag – estimation of parasite drag co-efficient by proper area method- Drag polar of vehicles from low speed to high speeds.
UNIT 2 ENGINE CHARACTERISTICS 9 Hrs. Variation of thrust, power with velocity and altitudes for air breathing engines – specific fuel consumption of piston engine and jet engine – ideal efficiency of engines- power plants for flight vehicles – limitations of power plants with Mach number and altitude.
UNIT 3 EVALUATION OF UN - ACCELERATED FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Airplane performance in steady level flight - Power available and power required curves. Maximum speed in level flight - Conditions for minimum drag and power required - steady climb descent and glide performance. Climb and Glide Hodograph, Range and Endurance. .
UNIT 4 ACCELERATED AND MANOEUVERING FLIGHT PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Accelerated level flight - Climbing and gliding flight, Maximum rate of climb and steepest angle of climb, minimum rate of sink and shallowest angle of glide –Take off – Landing-Turning performance. Bank angle and load factor – limitations on turn - V-n diagram.
UNIT 5 FLIGHT TESTING METHODS TO EVALUATE PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs. Flight - testing: Altitude definitions, Speed definitions, Air speed, altitude and temperature measurements. Errors and calibration. Measurement of engine power, charts and corrections. Flight determination of drag polar. Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the need for ISA.
CO2 - Analyze the flight performance with variations of pressure and density with altitude.
CO3 - Estimation of total drag and drag polar that influence the performance.
CO4 - Analyze the performance in un-accelerated flight conditions.
CO5 - Determination of speed limit, load limit, landing and takeoff distances of the aircraft.
CO6 - Know different testing methods to evaluate aircraft performanc

- Teacher: KEVIN BENNETT S
- Teacher: Dr. ANAND T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concepts of applying Aero thermodynamics to non air breathing propulsion.
To familiarize the student's ability to analyze the concepts of Advance Propulsion.
To understand the basics of Solid Propellant, Liquid Propellant and Cryogenics.
To understand the basics of Micro propellants.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF ROCKET PROPULSION 9 Hrs.
History and evolution of rockets - Rocket principle and Rocket equation - Classification of rockets - Mass ratio of rocket- Rocket Nozzles - Classifications - Nozzle Performance - Nozzle area ratio - Mass flow rate Characteristic velocity - Thrust coefficient-Performance parameters and Efficiencies of rocket - Staging and Clustering.
UNIT 2 SOLID PROPELLANT ROCKET 9 Hrs.
Hardware components and its functions - Mechanism of burning - Ignition system and igniter types- Propellant grain configuration and its applications - Burn rate - Factors influencing burn rates-Burn rate index for stable operation - Action time and burn time - Design of Solid Propellant rocket.
UNIT 3 LIQUID AND CROGENIC PROPELLANT ROCKET 9 Hrs.
Classifications - Hardware components and its functions-Propellant feed systems and Turbo pump feed system - Injectors and types - Thrust chamber and its cooling-Cryogenic propulsion system, Special features of cryogenic systems. Thermophysical Properties of Cryogenic Propellants; Geysering Phenomenon.
UNIT 4 ADVANCE PROPULSION TECHNIQUES 9 Hrs.
Hybrid propellant rocket and gelled propellants - Electrical rockets - Electro-thermal, Electro-static and Electro-magnetic propulsion system- Arc-jet thruster - Ion thruster - Hall Effect Thruster - Magneto plasma dynamic thruster- Nuclear rockets -Solar sail.
UNIT 5 MICRO PROPULSION SYSTEM 9 Hrs.
Recent Micro Spacecraft Developments; Micro propulsion Options; Primary Set of Micro propulsion Requirements; Chemical Propulsion Options; Review of Electric Propulsion Technologies for Micro and Nano- satellites; Emerging Technologies: MEMS and MEMS- Hybrid Propulsion System.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the working principles of non air breathing engine.
CO2 - Comprehend the sound foundation in the design principles of solid propellants.
CO3 - Learn the operation of Liquid and Cryogenic Propellant Rocket.
CO4 - Understand the concept of Advance Propulsion Techniques.
CO5 - Understand the principle and performance of. Micro propulsion system.
CO6 - Applying the importance of Advance Propulsion in Aerospace.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. George P. Sutton and Oscar Biblarz. “Rocket Propulsion Elements” 9th Edition, Wiley Publication, 2016.
2. Ramamurthi.K: “Rocket propulsion” Macmillan Publishing Co, India. 1st Edition. 2010.
3. Hill.P.G. and Peterson.C.R: “Mechanics and thermodynamics of propulsion” 2nd Edition .Pearson Education, 1999.
4. V.Ganesan., “Gas Turbines”, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 3rd Edition, 2010.
5. Philip Hill and Carl Peterson, “Mechanics and thermodynamics of propulsion”, Pearson India, 2nd Edition, 2010.
6. Cohen.H, Rogers.G.F.C. andSaravanamuttoo.H.I.H, “Gas turbine theory”. Pearson education, 5th Edition, 2001.
7. Saeed Farokhi, “Aircraft Propulsion”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc ., 2009.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: GokulNath R
- Teacher: GokulNath R
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
To understand the concepts of air vehicle design.
To estimate aerodynamic, propulsive and gravitational forces for design.
To select airframe components and power plant.
To analyze the performance, stability and control of the airplane.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 9 Hrs.
Introduction, Aircraft Design Requirements, specifications, role of users, Aerodynamic and Structural consideration, Airworthiness requirements and standards-classifications of airplanes, relative merits and demerits. Special features of modern airplane, Weight-estimation based on mission requirements.
UNIT 2 AERODYNAMIC DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE 9 Hrs.
Basics of Wing Design, Selection of airfoil selection, influencing factors. Span wise load distribution and Planform shapes of airplane wing. Wing drag estimation. High lift devices, Air Loads in Flight, Symmetrical measuring loads in flight, Basic flight loading conditions, Load factor, Velocity - Load factor diagram, gust load and its estimation.
UNIT 3 STRUCTURAL DESIGN 9 Hrs.
Structural aspects of design of airplane, Bending moment and shear force diagram. Design principles of all metal stressed skin wings for civil and military application, features of light airplanes using advanced composite materials.
UNIT 4 INTEGRATION OF WING, FUSELAGE, EMPENNAGE AND POWER PLANT 9 Hrs. Estimation of Horizontal and Vertical tail volume ratios. Choice of power plant and various options of locations, considerations of appropriate air -intakes. Integration of wing, fuselage, empennage and power plant. Estimation of center of gravity.
UNIT 5 ADVANCED DESIGN CONCEPTS 9 Hrs.
Supercritical Wings, relaxed static Stability, controlled configured vehicles, V/STOL aircraft and, rotary wing vehicles. Layout peculiarities of supersonic aircraft – optimization of wing loading to achieve desired performance – loads on undercarriages and design requirements. Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Understand the concepts of design through preliminary design.
CO2 - Estimate the gross weight of the aircraft using statistical data.
CO3 - Evaluate aerodynamic and performance parameters for design.
CO4 - Understand the Structural aspects of airplane design.
CO5 - Analyze the stability and performance by CG calculation and engine characteristics. CO6 - Understand the advanced design concepts.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. D.P. Raymer, “Aircraft Conceptual design”, AIAA Series, 2012.
2. G. Corning, “Supersonic & Subsonic Airplane Design”, II Edition, Edwards Brothers Inc., Michigan 2010.
3. E.F. Bruhn, “Analysis and Design of Flight Vehicle Structures”, Tristate Offset Co., U.S.A., 2011.
4. E. Torenbeek, “Synthesis of Subsonic Airplane Design”, Delft University Press, London, 1976.
5. A.A. Lebedenski, “Notes on airplane design”, Part-I, I.I.Sc., Bangalore.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To know about the airport planning, airport design and air traffic control
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1: Describes the structure of the Airport and its infrastructure coming under AAI and IAAI.
CO2: Construct the Airport infrastructure as per FAA and ICAO standards.
CO3: Design of the airport terminal infrastructure as per FAA Pavement design methods and joints in cement concrete pavements.
CO4: Design of the runway lightning, marking centerline and sign operation for aircraft taxiway guidance system.
CO5: Develop the Air Traffic Control by Network control method in airports for landing the aircrafts in touch down point.
CO6: Develop the Air Traffic Control by Tower control Flight service station for landing and takeoff the aircrafts.
UNIT 1 AIRPORT PLANNING 9 Hrs.
Air transport characteristics-airport classification-air port planning: objectives, components, layout characteristics, socioeconomic characteristics of the Catchment area, criteria for airport site selection and ICAO stipulations, Typical airport layouts, Case studies, Parking and circulation area.
UNIT 2 AIRPORT DESIGN 9 Hrs.
Runway Design: Orientation, Wind Rose Diagram – Runway length – Problems on basic and Actual Length, Geometric design of runways, Elements of Taxiway Design – Airport Zones – Passenger Facilities and Services.
UNIT 3 DESIGN OF AERODROME PAVEMENT 9 Hrs.
Procedure for pavement design (Aircraft Classification Number (ACN) - Pavement Classification Number (PCN) method), Elements of pavement Evaluation, USA practices: design of flexible and rigid pavements, design examples (FAA method, FAAR FIELD method).
UNIT 4 DESIGN OF VISUAL AIDS 9 Hrs.
Operational factors, operating approach slope marking, visual indicators system (T- VASIS, PAPI), runway and taxiway lighting, surface movement guidance and control requirements, additional marking of pavement shoulders, apron marking, taxiway edge system, Signs, Frangibility.
UNIT 5 SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 9 Hrs.
Introduction to State Safety Program - Introduction to Safety Management System. Airport drainage: Purpose, determination run-off (FAA method), typical drainage layout, sub-surface drainage.
Max. 45 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Airport Engineering ,Rangwala , Charotar Publishing House Pvt. Ltd . Anand 388 001 India , 14th Edition ,2014
2. Planning And Design Of Airports, Fifth Edition Robert Horonjeff, Francis Mckelvey, William Sproule, Seth Young ,McGraw Hill Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2013
3. Airport Engineering: Planning, Design And Development Of Development Of 21st Century Airports, Norman J. Ashford, Saleh
4. Mumayiz, Paul H. Wright - 2011 - - 4th Edition,
5. Airport Planning &Design ,S. K. Khanna, M. G. Arora , NemChand Publishers ,New Delhi ,1999
6. Airport Engineering: Planning And Design ,Subhash Chandra Saxena , Alkem Company (S) Pte Limited, 2009.

- Teacher: GokulNath R
SAEA3017 MANNED SPACE MISSIONS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Know the advanced concepts of manned space missions to the engineers.
Understand the space and environment and its conditions.
Apply the concept of life supporting devices.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF SPACE MISSIONS 9 Hrs.
The physics of space, Current missions: space station, Moon mission and Mars missions, Engineering challenges on Manned vs. unmanned missions, Scientific and technological gains from space programs, Salient features of Apollo and Space station missions, space shuttle mission.
UNIT 2 SPACE VS EARTH ENVIRONMENT 9 Hrs.
Atmosphere: Structure and Composition, Atmosphere: Air Pressure, Temperature, and Density, Atmosphere: Meteoroid, Orbital Debris & Radiation Protection, Human Factors of Crewed Spaceflight, Safety of Crewed Spaceflight, Magnetosphere, Radiation Environment: Galactic Cosmic Radiation (GCR), Solar Particle Events (SPE), Radiation and the Human Body, Impact of microgravity and g forces on humans, space adaptation syndrome.
UNIT 3 LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS AND COUNTERMEASURES 9 Hrs.
Life Support Systems and Space Survival Overview, Environment Controlled Life Support Systems (ECLSS), Human / Machine Interaction, Human Factors in Control Design, Crew Accommodations.
UNIT4 MISSION LOGISTICS AND PLANNING 9 Hrs.
Group Dynamics: Ground Communication and Support, Space Resources and Mission Planning ‐ Space Mission Design: Rockets and Launch Vehicles ‐ Orbital Selection and Astrodynamics , Entry, Descent, Landing, and Ascent, Designing and Sizing Space elements, Transfer, Entry, Landing, and Ascent Vehicles, Designing, Sizing, and Integrating a Surface Base, Planetary Surface Vehicles.
UNIT 5 SUBSYSTEMS 9 Hrs.
Spacecraft Subsystems: Space Operations, Space Architecture, Attitude Determination and Control‐ Designing Power Systems, Extravehicular Activity (EVA) Systems, Space Robotics, Mission Operations for Crewed Spaceflight ‐ Command, Control, and Communications Architecture.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the working principles of basic control system.
CO2 - Comprehend the sound foundation in the various subsystems.
CO3 - Learn the advanced concepts of manned space missions to the engineers.
CO4 - Understand the space and environment and its conditions.
CO5 - Understand the the principle and performance of various subsystems.
CO6 - Applying the importance of the mission logistics and planning.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Larson, W. J. and Pranke, L. K., Human Spaceflight: Mission Analysis and Design, McGraw‐Hill Higher Education,Washington, DC , 1999 2. McNamara, Bernard. 2010.
2. Into the Final Frontier: The Human Exploration of Space (BrooksCole Publishing), 2012.
3. Connors, M.M., Harrison, A.A., and Akins, F.R. 2005. Living Aloft: Human Requirements for Extended Spaceflight, University Press of the Pacific, Honolulu, Hawaii: ISBN: 1‐4102‐1983‐6 4 Eckart, P. 1996. Spaceflight Life Support and Biospherics.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
UNIT1 BASIC PROPERTIES OF ATMOSPHERE 9Hrs.
Heat, Temperature, and Temperature Scales - The Electromagnetic Spectrum - Composition of the Atmosphere - Layers in the atmosphere are defined by temperature profiles, How pressure varies in the atmosphere - Principal weather instruments – Earth’s Radiation Belts.
UNIT2 CLASSIFICATION OF AEROSPACE VEHICLES 9Hrs.
Fixed wing Aircraft – Classification of Aircraft, Aircraft as a Space Launcher assistance – Rotorcraft – Classification of Rotorcraft – Missiles – Classification of Missiles, Missile technology missions – Space Vehicles – classification of space vehicles.
UNIT3 SATELLITE MISSION AND CONFIGURATION 9Hrs.
Mission Overview – Requirements for different missions – Spacecraft configuration - Spacecraft Bus–Payload–Requirements and constraints– Initial configuration decisions and Trade-offs–Spacecraft configuration process– Broad design of Spacecraft Bus–Subsystem layout–Types of Satellites–Constellations– Applications
UNIT4 FUNDAMENTALS OF MISSILE SYSTEMS 9Hrs.
History of guided missile for defence applications- Classification of missiles– The Generalized Missile Equations of Motion- Coordinate Systems- Lagrange’s Equations for Rotating Coordinate Systems-Rigid-Body Equations of Motion-missile system elements, missile ground systems.
UNIT5 SPACE ENVIRONMENT 9Hrs.
Peculiarities of space environment and its description– effect of the space environment on materials of spacecraft structure and astronauts- manned space missions – effect on satellite life time
Max.45Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
CO1: Describe the layers in the atmosphere and earth’s radiation belts.
CO2: Classify the space launchers, missiles, rotorcraft and aircrafts for different applications.
CO3: Categorize the satellite mission configuration and types of satellites required for different applications.
CO4: Estimate the missile equations of motion in static and rotating coordinate system
CO5: Analyse the rigid body equation of motion for missile systems.
CO6: Synthesize the effect of the space environment on materials of spacecraft structures and astronauts.
TEXT/REFERENCEBOOKS
1. Cornelisse, J.W., “Rocket Propulsion and Space Dynamics”, J.W. Freeman &Co.,Ltd, London, 1982
2. Siouris, G.M. "Missile Guidance and control systems", Springer, 2003.
3. James R.Wertzand WileyJ.Larson,” Space Mission Analysis and Design”, (Third Edition),1999.
4. Charles D.Brown, “Spacecraft Mission Design”, AIAA Education Series, Published by AIAA, 1998
5. Van de Kamp, “Elements of astromechanics”, Pitman Publishing Co., Ltd., London, 1980.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: Dr. ANAND T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To gain in-depth knowledge of the fundamentals of Aircraft Engineering tools and to study the various measurement tools for aircraft production.
To discuss conventional and non-conventional machine tools used in Aircraft production.
To understand Lathe and Special purpose machines.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the basic concepts of various measurement tools in aircraft production.
CO2 - Recognize various Aircraft Engineering tools.
CO3 - Understanding the basics of various machining operations used in the lathe.
CO4 - Understanding the working principle of various conventional and non-conventional machines.
CO5 - Understanding the casting and metal joining process used in aircraft production.
CO6 - Understanding Surface Finishing and Protective Coating in Aircraft Production

- Teacher: KEVIN BENNETT S
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concepts of mass, momentum and energy conservation relating to aerodynamics.
To make the student understand the concept of vorticity, irotationality, theory of airfoils and wing sections.
To introduce the basics of viscous flow.
UNIT 1 REVIEW OF BASIC AERODYNAMICS 9 Hrs.
Atmosphere- Air speeds- Aerodynamic definitions Types of Drag- General Aerodynamic characteristics of airfoil sections-Complex potential-Singularities-Equations of Vortex-doublet and Rankine oval - Lift and Drag on cylinder and Aero foil.
UNIT 2 LOW SPEED FLOW 9 Hrs.
Models of the fluid: control volumes and fluid elements. Continuity, Momentum and energy equations. Substantial derivative, incompressible Bernoulli’s equation.
UNIT 3 AIRFOIL AND CONFORMAL TRANSFORMATION 9 Hrs.
Airfoils Nomenclature and NACA series, Airfoil Characteristics, Vortex sheet, Kelvin Circulation theorem Thin aerofoil theory and its applications. Joukowski transformation and its application to fluid flow problems.
UNIT 4 WING THEORY 9 Hrs.
Introduction to Finite wing, Downwash and Induced Drag, Biot -Savart law and Helmhotz’s theorems, Horse shoe vortex, Prandtl’s Classical Lifting line theory and its limitations.
UNIT 5 VISCOUS FLOW 9 Hrs.
Derivation of Navier-Stokes equation for two-dimensional flows, boundary layer approximations, laminar boundary equations and boundary conditions, Blasius solution, qualitative features of boundary layer flow under pressure gradients, Integral method, aspects of transition to turbulence, turbulent boundary layer properties over a flat plate at low speeds. Separation of flow over bodies stream lined and bluff bodies, Lift and Drag on cylinder and Aero foil.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Apply aerodynamics concepts.
CO2 - Develops mathematical modelling ability.
CO3 - Differentiate between ideal and real flows.
CO4 - Model flow over wing.
CO5 - Understand the real time viscous flow.
CO6 - Understand the Boundary Layer behaviour.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Aerodynamics for. Engineering Students. Sixth Edition. E.L. Houghton. P.W. Carpenter. Steven H. Collicott. Daniel T. Valentine, 2013 Elsevier, Ltd.
2. Bertin, John J., Aerodynamics for Engineers, Pearson Education Inc., 2002.
3. John J. Bertin, Russell M. Cummings, “Aerodynamics for Engineering students”, Sixth Edition,Pearson,2013.
4. Anderson J.D., “Fundamentals of Aerodynamics”, Sixth Edition , McGraw Hill Book Co., NewYork,2017.
5. Schlichting H., “Boundary layer theory” , Seventh Edition, McGraw Hill, NewYork 2014.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: MATHIYARASI M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concepts of compressibility.
To make the student understand the theory behind the formation of shocks and expansion fans in Supersonic flows.
To introduce the methodology of measurements in Supersonic flows.
UNIT 1 CONCEPTS OF COMPRESSIBLE FLOW 9 Hrs.
Basic concepts of compressible flow, Review of continuity, energy and momentum equations. One dimensional inviscid flow; Stagnation quantities; Isentropic conditions. Speed of sound and Mach number; Isentropic relations; Area-velocity relation. Flow through constant area duct.
UNIT 2 COMPRESSION AND EXPANSION WAVES 9 Hrs.
Normal shock –Prandtl equation and Rankine–Hugonoit relation .Oblique shock and supersonic compression by turning. Weak shocks and Mach waves; Super sonic expansion by turning. Prandtl-Meyer expansion fan; Reflection and intersection of shocks. Shock detachment and bow shock; Shock Expansion theory with application to thin airfoils.
UNIT 3 AIRFOIL IN HIGH SPEED FLOWS 9 Hrs.
Small perturbation potential theory, solutions for supersonic flows, Mach waves and Mach angles, Prandtl-Glauert rule - affine transformation relations for subsonic flows, linearized two dimensional supersonic flow theory - Lift, drag, pitching moment and center of pressure of supersonic profiles.
UNIT 4 TRANSONIC FLOW OVER WING 9 Hrs.
Lower and upper critical mach numbers, Lift and drag divergence, shock induced separation, characteristics of swept wings, Effects of thickness, camber and aspect ratio of wings, Transonic area rule, Tip effects.
UNIT 5 EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES FOR HIGH SPEED FLOWS 9 Hrs.
Blow down, indraft and induction tunnel layouts and their design features. Transonic, supersonic and hypersonic tunnels and their peculiarities. Helium and gun tunnels, Shock tubes, Optical methods of flow visualization.
Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquire knowledge on the basic concepts of compressible flowCO2 - Distinguish the compression and expansion waves on arbitrary bodies and open deflected conduits. CO3 - Solve the lift, drag and center of pressure of supersonic airfoils.
CO4 - Differentiate the transonic flow effects over Wings and wing fuselage compartment.
CO5 - Understand the different types of tunnel layouts and their design features.
CO6 - Analyse the shock tube effect and application of flow visualization in it.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Radhakrishnan, Ethirajan., Gas Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons,2010.
2. Anderson J. D., Jr., Modern Compressible Flow with Historical Perspective, McGraw Hill Publishing Co.,2004.
3. H W Liepmann and A Roshko, Elements of Gas Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons.
4. Shapiro, A.H., "Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Compressible Fluid Flow", Ronold Press.
5. Zucrow, M.J. and Anderson, J.D., "Elements of gas dynamics", McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York.
6. Clancy,L,J., “Aerodynamics”, Pitman, Shroff Publishing co.,2006.

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
|
SAEB2301 |
SIMULATION LAB |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
2 |
100 |
||
|
COURSE OBJECTIVES Ø To make students learn the steps involved in quadcopter simulation. Ø To introduce the knowledge about fidelity models. Ø To impart practical knowledge to students on determining the visualization techniques. Ø To find the waypoint follower and orbit follower in drones. Ø To impart practical knowledge to students about different simulators of drone and flight
|
|||||||
|
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS |
|||||||
|
1. Quadcopter 3D Simulation 2. Fixed Wing Low Fidelity Model 3. Multi Rotor Low Fidelity Model 4. Depth and Semantic Segmentation Visualization 5. Waypoint follower, Orbit follower 6. Packet delivery 7. Drone Simulation pattern Square, circle clockwise and Anti-clock wise 8. Drone Simulation pattern spiral takeoff and Landing, Shape Eight 9. Aircraft simulation Take off 10. Aircraft simulation Landing
|
|||||||
|
Max. 45 Hrs. COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Acquire simulation experience of a Quadcopter. CO2 - Impart the knowledge on Fidelity models for fixed wing and multi rotor. CO3 - Visualize the depth and semantic segmentation of the drones. CO4 - Compute the waypoint follower and orbit follower for drones CO5 - Get practical experience on flying of various drones CO6 - Get practical experience on flying of Aircrafts
|
|||||||

- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OBJECTIVE
- To study the various types of communication techniques and their analysis based on Fourier transform and to provide fundamental knowledge of pulse modulation techniques and their types.
UNIT 1 SIGNAL ANALYSIS
Fourier transform of gate functions, delta functions at the origin – Two delta function and periodic delta function – properties of Fourier transform – Frequency shifting – Time shifting – Convolution theorem – Frequency convolution theorem – Sampling theorem.
UNIT 2 PULSE MODULATION AND COMMUNICATION
Pulse amplitude modulation – Natural sampling -Instantaneous sampling Transmission of PAM signals – Pulse width modulation – Time division multiplexing and frequency division multiplexing – Band width requirements for PAM signals – Pulse code modulation – Principles of PCU – Quantizing noise – Generation and demodulation of PCM – Effects of noise – Advantages and application of PCM – Differential PCM (DPCM) – Delta modulation.
UNIT 3 BROAD BAND COMMUNICATION
Coaxial cable circuit -Parallel wire line circuit – Computer communication – Digital data communication – Modems – Microwave communication links – LOS links – Tropospheric scatter microwave links – Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) – Architecture – Broadband ISDN – Local Area Network (LAN) – LAN topologies – Private Branch Exchange (PBX).
UNIT 4 SATELLITE COMMUNICATION
Introduction – Communication satellite systems – Transmitting and receiving earth station – Satellite orbits – Satellite frequency bands – Satellite multiple access formats – FDMA – CDMA – Satellite channel, Power flow – Polarization antenna gain – Parabolic dish antenna – Power loss – Rainfall effect – Receiver noise –satellite system power budget: EIRP, received power Carrier to noise ratio, G/T ratio. – Satellite link analysis – Up link – Down link – Cross link – Direct Home TV broadcasting – Satellite transponders.
UNIT 5 RADAR SYSTEMS AND OPTICAL FIBER
Introduction, Basic Radar systems, Radar systems – Radar range – Pulsed radar system – A Scope – Plan Position Indicator (PPI) – Search Radar – Tracking Radar – Moving Target Indicator (MTI) – Doppler Effect – MTI principle – Digital MTI – Radar Beacons. Optical Fiber: Introduction to light, optical fiber and fiber cables, optical fiber characteristics and classification, losses, Fiber optic components and systems, Installation, testing and repair.
Course Outcomes:
By the end of this course students will be able to
CO1: Design, operation, and troubleshoot of electronic systems
CO2: Solve electronic devices and systems using mathematical concepts.
CO3: Analyze electronics devices and circuits using computer simulations.
CO4: Analyze components associated with digital and analog electronic/communication systems.
CO5: Analyze basic wireless and communication circuits using computer simulations

- Teacher: KEVIN BENNETT S
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is the ongoing automation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices, using modern smart technology.
SAIC4001 Industry 4.0
UNIT 1 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY AND MATERIALS
Advanced electro-optical sensing technology-active, passive multi-spectral and hyper spectral imaging; electronic beam steering; vacuum technology, surface and coating technology, health care technology, Nanotechnology- Nanomechanics, Nano optoelectronics; energy storage technology-next generation Li-based Batteries, Hydrogen storage, solar photovoltaic’s, Flexible electronics. Intellectual Property Rights - case studies governing/pertaining to Materials/Technology.
UNIT 2 TRANSFORMING TECHNOLOGIES IN BIOENGINEERING
Establishment of smart biotechnology factory, Artificial intelligence in Bioprocess technology, Omics – Big data analysis through automation, 3D bio printing for tissue engineering. Simulation tools, RSM and Box model. Cyber physical system based telemedicine, diagnosis and therapeutics through real time biosensors. Bionanotechnology. Case studies –Intellectual Property rights infringement in Biology.
UNIT 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN SUSTAINABLE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
Introduction – Technological developments in Architectural, Engineering and Construction (AEC) - Building Information Modelling (BIM) using Cloud computing technology and Internet of things (IoT) – Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, sensors – Additive manufacturing in construction – Concrete 3D printing - Materials used - Lightweight and functionally graded structures - Net Zero Energy buildings, Bioswales, Biofiltration pond, Ecosan systems- Recent developments in Waste water Management, Air pollution control, waste disposal, public health issues-improving water management in surface and overhead irrigation- Integration of energy, water and environmental systems for a sustainable development.
UNIT 4 SMART MANUFACTURING
Smart factories and interconnection, Smart Manufacturing – automation systems, Additive Manufacturing, Smart grids, Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Stealth technology, Metal Finishing, Self propelled vehicles, e mobility, Green fuels, drones – unmanned aerial vehicles(UAVs), aerodynamics. Robotic Automation and Collaborative Robots – Augmented reality and haptics, engineering cybernetics and artificial intelligence (AI), Disruptive Technologies – Frugal Innovations – Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): Case Studies.
UNIT 5 SMART WORLD
Smart Sensors and IIOT, Smart grid, Hybrid renewable energy systems, Electronics in Smart city, Integration of Sensors in Robots and Artificial Intelligence, 5G Technology, Communication protocols, Human-Machine Interaction, Virtual Reality, Quantum Computing: Changing trends in transistor technology: Processor, Intellectual Property Rights- Case Studies.
UNIT 6 CYBER PHYSICAL SYSTEMS
Introduction to Cyber Physical Systems (CPS), Architecture of CPS, Data science and technology for CPS, Prototypes of CPS, Emerging applications in CPS including social space, crowd sourcing, healthcare and human computer interactions, Industrial Artificial Intelligence, Networking systems for CPS applications, Wearable cyber physical systems and applications, Domain applications of CPS: Agriculture, Infrastructure, Disaster management, Energy, Transportation, Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) : Case Studies.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. William D. Callister,“Materials Science and Engineering, An Introduction”, John Willey and Sons Inc. Singapore, 2001.
2. V. Raghavan, “Physical Metallurgy: Principle and Practice”, Prentice Hall India Pvt Ltd, 2006.
3. Flavio Craveiro, Jose Pinto Duarte, Helena Bartolo and Paulo Jorge Bartolo, “Additive manufacturing as an enabling
technology for digital construction: A perspective on Construction 4.0”, Automation in Construction, Vol. 103,pp. 251-267, 2019.
3. Klaus Schwab, “Fourth Industrial Revolution”, Random House USA Inc, New York, USA, 2017.
4. Oliver Grunow, ”SMART FACTORY AND INDUSTRY 4.0. The current state of Application Technologies”, Studylab Publications, 2016.
5. Alasdair Gilchrist, “INDUSTRY 4.0: Industrial Internet of Things”, Apress, 2016.

- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan

- Teacher: Dr.T. AMBIKA
This course is designed to help students to understand the nature and challenges of Indian welfare state and to acquaint the students to the changing dimensions and perspectives on working with vulnerable sections of society. It will equip the students for a career in social sector like NGOs, Corporate Social Responsibility and Government welfare agencies.

- Teacher: Dr. N. SOFIA
The primary emphasis of the present work is to synthesis all major provisions of the Constitutional law which come across with every Indian from day to day life and which are the very basic provisions of the Constitutional Law including but not limited to the purpose of Constitutional Law, formation of Constitutional Law, key provisions, Preamble, Union of India, Citizenship, Fundamental Entitlements, Directive Principles of the State Policy, Fundamental Duties, President of India, Prime Minister, Attorney General of India, Parliament of India, Powers of House of the People and Council of States, Parliamentary Committees, Sessions of Parliament, Comptroller and Auditors General of India, Supreme Court of India and High Court jurisdiction, Pertains between the Union and the States, Entitlement to property Elections, Emergency provisions.
The primary emphasis of the present work is to synthesis all major provisions of the Constitutional law which come across with every Indian from day to day life and which are the very basic provisions of the Constitutional Law including but not limited to the purpose of Constitutional Law, formation of Constitutional Law, key provisions, Preamble, Union of India, Citizenship, Fundamental Entitlements, Directive Principles of the State Policy, Fundamental Duties, President of India, Prime Minister, Attorney General of India, Parliament of India, Powers of House of the People and Council of States, Parliamentary Committees, Sessions of Parliament, Comptroller and Auditors General of India, Supreme Court of India and High Court jurisdiction, Pertains between the Union and the States, Entitlement to property Elections, Emergency provisions.
- Teacher: Yuva Poornima A
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
OBJECTIVES
to understand the concept and classification of property as well as principles governing transfer of immovable property and easements.
-
To study about the concept of ‘Property’, the ‘nature of property rights’ and the general principles governing the transfer of property.
-
To gain knowledge about the substantive law relating to particular transfers, such as sale, mortgage, lease, exchange, gift and actionable claims
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Monisha S
- To understand Cyber Space and Information Technology Act, 2000
- To learn multifarious changes brought in to substantive and Procedural changes
- To know various facets of Cyber Laws and its impact on the modern world
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
- Teacher: S B Reshma John
The course provides an introduction to basic human rights philosophy, principles,
instruments and institutions, and also an overview of current issues and debates in the field
with focus on the problems specific to Bulgaria.
This course aims to explore some aspects of the diverse and increasingly complex body of
international law of human rights that has both national and international application. The
course also seeks to analyze the ways in which allegations of human rights violations are
dealt with in the Bulgarian courts and the impact of human rights discourse on international
politics and relations.

- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Vinaya G
Labour law also known as employment law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their organisations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions, employers and employees. In other words, Labour law defines the rights and obligations as workers, union members and employers in the workplace.
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: Vinaya G
Labour law also known as employment law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their organisations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions, employers and employees. In other words, Labour law defines the rights and obligations as workers, union members and employers in the workplace.
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
Labour law also known as employment law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and
precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their
organisations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions,
employers and employees. In other words, Labour law defines the rights and obligations as workers,
union members and employers in the workplace.
- Teacher: Madhana B
Labour law also known as employment law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their organisations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions, employers and employees. In other words, Labour law defines the rights and obligations as workers, union members and employers in the workplace.
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
This course is an introduction to Public International Law for Students of International Relations. Emphasis throughout the course is both on the substantive rules of the law and on historical episodes that illustrate the various issues. By the end of the course, students should have a good understanding of the legal structures underpinning international relations.

- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: SAGARIKA S.R
Property Law
- To understand the concept and classification of property as well as principles governing transfer of immovable property and easements
- To study about the Concept of 'Property', 'the nature of Property rights' and the general principles governing the transfer of property
- To gain knowledge about the substantive law relating to particular transfers, such as sale, mortgage, lease, exchange, gift and actionable claims etc.

- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: SELMA G.S
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
Intellectual Property Rights defend investments in innovation by granting the ground breaker a short lived monopoly on the utilization of the innovation. This prevents speedy imitation that would take the innovator's returns and reduce the inducement to pioneer. Intellectual property rights (IPRs), such as patents and copyrights, are an important means used by researchers to help protect their investments in innovation. IPRs inherently embody a policy conflict between the target of providing an incentive to technological innovation and therefore the objective of encouraging the speedy diffusion of latest technology and therefore the accumulation of technological knowledge. These competing objectives can be achieved on a difficult path. It is vital to notice during this regard that IPRs are primarily a matter of national jurisdiction (i.e., the protection offered to an innovation is governed by the laws of the state during which the innovation is created, used, or sold). Thus, for example, a patent obtained from India provides protection only within the territory. If a corporation is doing business in another country, it must file for and obtain IPR protection in that country. Moreover, the protection offered by that country's laws in many cases is not as strong as Indian IPR protection. Some of the foremost important rising technologies—including those within the areas of data, electronics, communications, and the new biotechnology do not fit neatly within existing categories of intellectual property rights. They may force a valuation of current approaches in obtaining grant and for protection at national and international levels.
This apparent paradox reflects the complexities, conflicts, and uncertainties surrounding IPR issues as they pertain to science and technology and includes complicated and time consuming procedures. This Course is about the legislative frame work, challenges relating to Intellectual Property Rights.

- Teacher: Amirdha Varshini C
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
- Teacher: Dr.DILSHAD SHAIK
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan

- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Yuva Poornima A
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: Vinu Sree G
- Teacher: SELMA G.S
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Monisha S
Administrative law is the law that governs the administrative actions. As per Ivor Jennings- the Administrative law is the law relating to administration. It determines the organisation, powers and duties of administrative authorities. It includes law relating to the rule-making power of the administrative bodies, the quasi-judicial function of administrative agencies, legal liabilities of public authorities and power of the ordinary courts to supervise administrative authorities. It governs the executive and ensures that the executive treats the public fairly.

- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: SELMA G.S
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan

- Teacher: Yuva Poornima A
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: Dr.DILSHAD SHAIK
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Preethi A
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: SHALMA J
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: MOHANAPRIYA M
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: SHYAM SRINIVASAN K
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
- Teacher: SELMA G.S
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: KRISHNA R
- Teacher: S B Reshma John
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: SHALMA J
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: KAVIYA R
- Teacher: KRISHNA R
- Teacher: Yuva Poornima A
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: SHALMA J
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: ANANTHAGOMA M
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Monisha S
- To introduce the basic concepts and principles in Personal laws
- To impart knowledge about various sources of Personal laws
- To endow the students with knowledge of both the codified portions of Personal laws

- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Preethi A
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Sanjay K
This subject is to provide a general Penal Code for India. Though this Code consolidates the whole of the law on the subject and is exhaustive on the matters in respect of which it declares the law, many more penal statutes governing various offences have been created in addition to this code.

- Teacher: SAHANA ASHOKUMAR
- Teacher: Sanjay K
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: S B Reshma John
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
The primary emphasis of the present work is to synthesis all major provisions of the Constitutional law which come across with every Indian from day to day life and which are the very basic provisions of the Constitutional Law including but not limited to the purpose of Constitutional Law, formation of Constitutional Law, key provisions, Preamble, Union of India, Citizenship, Fundamental Entitlements, Directive Principles of the State Policy, Fundamental Duties, President of India, Prime Minister, Attorney General of India, Parliament of India, Powers of House of the People and Council of States, Parliamentary Committees, Sessions of Parliament, Comptroller and Auditors General of India, Supreme Court of India and High Court jurisdiction, Pertains between the Union and the States, Entitlement to property Elections, Emergency provisions.
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: SHALMA J
- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: Dr.T. AMBIKA
This course is an introduction to Public International Law for Students of International Relations. Emphasis throughout the course is both on the substantive rules of the law and on historical episodes that illustrate the various issues. By the end of the course, students should have a good understanding of the legal structures underpinning international relations.

- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: RAGAVI P.J
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: JEEVITHA M

- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: Lumina S

- Teacher: Dr.T. AMBIKA
- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: SAGARIKA S.R
This course aims to understand the cyber space and the Information Technology Act, 2000, also to learn multifarious changes brought into substantive and procedural legislations. Understanding about recent cyber laws developments under the Information Technology Act,2000 and under international dimensions.

- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: Anusha Patnaik
- Teacher: KRISHNA R
Intellectual Property Rights defend investments in innovation by granting the ground breaker a short lived monopoly on the utilization of the innovation. This prevents speedy imitation that would take the innovator's returns and reduce the inducement to pioneer. Intellectual property rights (IPRs), such as patents and copyrights, are an important means used by researchers to help protect their investments in innovation. IPRs inherently embody a policy conflict between the target of providing an incentive to technological innovation and therefore the objective of encouraging the speedy diffusion of latest technology and therefore the accumulation of technological knowledge. These competing objectives can be achieved on a difficult path. It is vital to notice during this regard that IPRs are primarily a matter of national jurisdiction (i.e., the protection offered to an innovation is governed by the laws of the state during which the innovation is created, used, or sold). Thus, for example, a patent obtained from India provides protection only within the territory. If a corporation is doing business in another country, it must file for and obtain IPR protection in that country. Moreover, the protection offered by that country's laws in many cases is not as strong as Indian IPR protection. Some of the foremost important rising technologies—including those within the areas of data, electronics, communications, and the new biotechnology do not fit neatly within existing categories of intellectual property rights. They may force a valuation of current approaches in obtaining grant and for protection at national and international levels.
This apparent paradox reflects the complexities, conflicts, and uncertainties surrounding IPR issues as they pertain to science and technology and includes complicated and time consuming procedures. This Course is about the legislative frame work, challenges relating to Intellectual Property Rights.

- Teacher: SELMA G.S
- Teacher: Manas Unnikrishnan
- Teacher: SHALMA J
- Teacher: Lumina S
- Teacher: Ugarthi Shankalia M
- Teacher: V. POOJASREE
- Teacher: KRISHNA R
- Teacher: JANVIASHIKA G
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: P.S.S. GOWRISHANGAR
- Teacher: S B Reshma John
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: Madhana B
- Teacher: Yazhini Kuppusamy
- Teacher: Sathiya Priya M
- Teacher: Dr.DILSHAD SHAIK
- Teacher: MADHUMITHA C. L.
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: Anjana Lakshmi .
- Teacher: Dhanushyadevi S
- Teacher: Monisha S
- Teacher: Sudhakar T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To identify the practices
essential for blood transfusion
To implement the procedures in maintaining blood bank
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
Course Objectives:
· To learn the basic histological and cytological procedures
· To understand the diagnostic applications of histological and cytological methods
List of Experiments
1. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining
2. PAP staining
3. Embedding
4. Microtome: Uses, care, and parts
5. PAS stain
6. Pearls stain
7. Reticulin stain
8. Giemsa stain
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 Demonstrate proficiency and expertise in the proper use of the light microscope in examining histological specimens on glass slides
CO2 Understand the basic concepts of tissue fixation, dehydration, embedding, sectioning, staining, and mounting of slides for histological examination, immunofluorescent staining, and electron microscopy
CO3 Differentiate the characteristics of tissues of the body (epithelium, connective, muscle, nerve) and their relationships in the various organ systems of the human body
CO4 Identify the histological features of selected tissues/organ systems resulting from disease processes
CO5 Examine how certain diseases can be diagnosed using histological and cytological methods
CO6 Demonstrate common histology procedures such as embedding tissue in paraffin, tissue sectioning, and mounting, or routine staining of tissue sections
- Teacher: James John
COURSE OBJECTIVES :
To learn the basic procedures
in coagulation studies
To apply techniques in the storage and handling of blood specimens
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
SATHAYBAMA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY REGULATIONS 2023
SAMB2501
ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES &
BIOINSTRUMENTATION-LAB
L T P Credits Total Marks
0 0 4 2 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Acquire practical knowledge about laboratory instrumentations.
Acquire knowledge about applications of centrifugation and electrophoretic methods in
laboratory.
Demonstrate the use of spectroscopic techniques.
Attain knowledge to use chromatographic techniques in research.
Apply molecular techniques in analysis & research.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Centrifugation techniques Lab-Separation of blood WBC using fycoll reagent.
2. Chromatographic techniques Lab Demonstration of Paper chromatography.
3. Electrophoretic techniques- Demonstration of Agarose gel electrophoresis.
4. Electrophoretic techniques-Immunoelectrophoretic in agarose gel to see Ag-Ab reactions.
5. Molecular techniques- Demonstration of DNA extraction and quality check.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to know
CO1 - Understand the basic instrumentation and their use in laboratory.
CO2 - Identify instruments and their uses.
CO3 - Recognize the types of separation techniques and their uses in lab diagnosis.
CO4 - Apply the practical knowledge and understanding to usage of instruments.
CO5 - Bridge the gap between clinical and theory during practice of instruments
CO6 - To acquire knowledge about various laboratory techniques
- Teacher: James John
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Aimstoprovideabasicunderstandingofthecoreprinciplesandtopics ofBiochemistry
andtheirexperimentalbasis.
To enable to perform routine as well as special investigative procedures in different specialties
of Medical LaboratoryTechnology.
UNIT 1 Chemistry, metabolism & Clinical pathology of Carbohydrate 12 Hrs.
Chemistry of carbohydrates & their related metabolism - Introduction, definition, classification,
biomedical importance Brief outline of metabolism: Glycogenesis & glycogenolysis (in brief), Glycolysis,
citric acid cycle & its significance, HMP shunt & Gluconeogenesis, Diabetes mellitus, gestation diabetes
mellitus, Hyperglycemia & hypoglycemia and its causes.
UNIT 2 Chemistry of Amino acids and Protein- Protein Metabolism and its clinical pathology 12
Hrs.
Amino acids -Definition, classification, essential &non-essential amino acids. Chemistry of Proteins -
Introduction, definition, classification, structure, and its biomedical importance, Transformation,
Decarboxylation, Ammonia formation & transport, Urea cycle, metabolic disorders in urea cycle,
catabolism of amino acids especially Phenylalanine, Tyrosine & Tryptophan, Creatinine, Proteinuria.
UNIT 3 Chemistry of Lipids, Lipids metabolism & clinical Pathology 12 Hrs.
Introduction,definition, classification, biomedical importance, essential fatty acids. Non-essential fatty
acids, Brief out line of metabolism: Beta oxidation of fatty acids, fatty liver, Ketosis, Cholesterol & it's
clinical significance, Lipoproteins in the blood composition & their functions in brief, Atherosclerosis
UNIT 4 Enzymes and its clinical significance 12 Hrs.
Introduction, definition, classification, coenzymes, isoenzymes, properties, factors affecting enzyme
action, enzyme inhibition, diagnostic value of serum enzymes - Creatinine kinase, Alkaline
phosphatase, Acid phosphatase, LDH, SGOT, SGPT, Amylase, Lipase, Carbonic anhydrase etc
UNIT 5 Acid base balance concepts & disorders 12 Hrs.
Water metabolism, Distribution of fluids in the body, ECF, ICF, dehydration. - pH, Buffers, Acidosis,
Alkalosis
Max. 60 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to know
CO1 - Attain knowledge about the basics of biochemistry and the its importance.
CO2 - Attain knowledge on carbohydrates, proteins, fats and their functions in the body.
CO3 - Attain knowledge on the basic principles of metabolism and its regulation
CO4 - Understand the role of enzymes and its importance in diagnosis of various diseases.
CO5 - Understand the role of pH, buffer system and water balance in the body.
CO6 - Understand and access various
biochemical parameters and its relation to disease and dysfunction of organs.
- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
Course Objectives:
• To be able to fix, process, embed tissues and make sections for micro section studies
• To be competent to make routine cytological preparation
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Identify the basic structure of cells, tissues and organs and describe their contribution to normal function.
CO2 Interpret light- and electron-microscopic histologic images and identify the tissue source and structures.
CO3 Demonstrate common histology procedures such as embedding tissue in paraffin, tissue sectioning and
mounting, or routine staining of tissue sections
CO4 Describe common histology laboratory procedures used to prepare stained slides from tissue samples.
CO5 Outline the principles of histochemistry, and types of microscopies utilized in histology
CO6 Understand professional procedures in museum display, collections, care and preservation
1. Bancroft's Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques by John D Bancraft /Edition 8 (2018)
2. Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Techniques: Including Museum Techniques / edition 3 (1974) by C. F. A. Culling
3. Hand book of Medical laboratory technology, 2nd edition by Robert H Carman, Christian Medical Association of India
(publishers)
4. Textbook of Medical Laboratory Technology/ edition 3 (2020) b
- Teacher: Premkumar J
- Teacher: James John
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
- Teacher: Dr. Mohmmad Ashaq Sofi
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: D. JASMINE PRIYA
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
- Teacher: Dr. Mohmmad Ashaq Sofi
- Teacher: James John
SATHAYBAMA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY REGULATIONS 2023
SAMB3003
LABORATORY AUTOMATION &
QUALITY CONTROL
L T P EL Credits Total Marks
3 0 0 0 3 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To introduce the concept of quality management, to apply the significances of analysers in
automation.
To apply the significances of analyzers in automation and to introduce the concept of quality
management.
UNIT 1 AUTOMATION 9 Hrs.
Introduction to automation, study on the instrumental concepts and definition of batch analysis,
sequential analysis, discrete analysis etc. Detailed study on the steps in automated analysis, reagent
handling, chemical reaction phase, reaction vessels, cuvettes in discrete analyzers and measurement
using absorbance, electrochemical measurements and transmittance photometry.
UNIT 2 AUTO ANALYZERS 9 Hrs.
Continuous flow analyzers, discrete and Centrifugal analyzers auto analyzers-advantages, Dry
chemistry analyzers, Random access analyzers (RAA), Micro particle enzyme immunoassay, Immulite
automated immunoassay analyzers.
UNIT 3 CELL COUNTERS 9 Hrs.
Study on the different type of cell counters, available and their principle of operation, basic principle in
estimating each parameter. Brief study on the operation and quality control of automated laboratory
analyzers.
UNIT 4 INTRODUCTION TO QUALITY CONTROL 9 Hrs.
Demonstration of various methods of quality control, Preparation of Quality control charts, a) Levy-
Jennings and b) Cusum charts. Demonstration of various methods of quality control- Westgard Rules to
verify trends, biases, or errors in quality controls.
UNIT 5 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAMME 9 Hrs.
External quality control, Internal Quality control, Proficiency testing, Total quality management
framework, Quality laboratory processes, Quality assurance, Quality assessment, Current trends in
laboratory accreditation, ISO certificate, Quality planning and Quality improvement.
Max. 60 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to know
CO1 - Understand the principles of automation.
CO2 - Identify role of automation in flow analyzers.
CO3 - Recognize the types of analyzers and their significance.
CO4 - Apply the theoretical understanding to practical usage.
CO5 - Recognize the latest trends and quality practices.
CO6 - Bridge the gap between clinical and industry in theory and and practice of automation.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Laboratory management Quality in Laboratory diagnosis Candis A Kinkus, Demos medical
publishers, 2011.
2. Quality control in Laboratory Gaffar Sarwar Zamman, Intech open publishers, 2011.
3. Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods, Henry 23rd edition, 2016.
- Teacher: James John
• To develop an understanding of the role of the endocrine system in maintaining homeostasis and health.
• To understand the integrative workings of the human body by studying this signaling systemsOn completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 Explain the roles of the endocrine system in maintaining homeostasis, integrating growth and development,
responding to environmental insults and promoting successful reproduction
CO2 Investigate how the secretion of hormones is regulated, including the principles of negative and positive
feedback mechanisms
CO3 Apply endocrinological principles to determine the pathophysiological basis and consequences of specific
endocrine disorders
CO4 Understand the role of tumor markers for diagnosis, management and therapeutic selection.
CO5 Correlate the presence of a tumor marker with its associated affected organ system
CO6 Differentiate between carbohydrate-rich tumor markers, protein-rich tumor markers, enzymatic tumor markers,
and oncofetal antigens
- Teacher: James John
|
SAMB4002 |
DIAGNOSTIC MOLECULAR BIOLOGY |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
C |
Total Marks |
|
4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To provide a good foundation in molecular biology where importance is laid on the master molecule.
Ø Subject is an emerging discipline with a broad conceptual approach that transcends all sections of anatomic and clinical pathology.
UNIT 1 BASIC PRINCIPLES IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS 12 Hrs.
Organizations of molecular diagnostic laboratory-Bio-membranes and the sub-cellular organization of eukaryotic cells.
UNIT 2 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF GENES AND CHROMOSOMES 12 Hrs.
Organization of cellular DNA into chromosomes –morphology and functional elements of eukaryotic chromosomes –chromosomal organization of genes and non-coding DNA.
UNIT 3 STRUCTURE OF DEOXY NUCLEIC ACIDS (DNA) 12 Hrs.
ABZs of DNA Secondary Structure, Denaturation and Renaturation of DNA, Supercoils and Cruci forms: Tertiary Structure in DNA. DNA replication –repair-recombination –mutation – Regulation of the eukaryotic cell cycle-gene control in development-Cellular energetics.
UNIT 4 RIBONUCLEIC ACID 12 Hrs.
Types and function of RNA. Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Structure of RNA. The role of RNA in protein synthesis-stepwise formation of proteins on ribosome.
UNIT 5 THE SYNTHESIS OF MACROMOLECULES AND THE GENETIC CODE 12 Hrs.
synthesis of biopolymers- nucleic acid synthesiss. Molecular oncology including DNA assay for T and B-cell rearrangement- analysis for translocation, oncogene analysis -translocation gene mutation in various cancer, Molecular histocompatibility testing, forensic identity testing by DNA analysis.
Max. 60 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Apply knowledge of cellular structure and function, especially DNA and RNA.
CO2 - Understand the DNA replication, repair and recombination in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes.
CO3 - To know about RNA synthesis and processing and function of different types of RNA.
CO4 - To know about protein synthesis and inhibition factors of protein synthesis.
CO5 - Apply the knowledge of molecular testing to the most commonly performed applications in the clinical laboratory.
CO6 - To learn about molecular diagnostic procedures and their clinical uses.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Albert B. Bray D and Lewis J Molecular biology of the cells, 2nd edition New York. Garland Publications 1989.Brown, T.A. (1999). Gene Cloning. 3rd edition. Chapman and Hall Publications, U.S.A.
2. Burrel, M.M. (1993). Enzymes of Molecular Biology, Humana Press.
3. Chirikjian, J.G. (1995). Biotechnology – Theory and Techniques, Vol. II, Jones and Burtlett Publishers.
4. Lewin, B. (2000). Genes VII. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
5. Antony, J.F., Griffiths, Gilbert, W.M., Lewontin, R.C. and Miller, J.H. (2002). Modern genetic analysis, Integrating Genes and Genomes, 2nd edition, WH Freeman and Company, New York.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A : 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PART B : 5 Questions from each unit with internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
- Teacher: James John
UNIT 1 MANUFACTURED BUILDING MATERIALS - STEEL 6 Hrs.
Iron: brief study on manufacture, composition, properties and uses of cast iron, wrought iron, pig iron - Steel: Composition, Properties, anticorrosive measures, mechanical and heat treatment of steel - Market forms of steel : Steel for Reinforcement - Hot rolled bars, CTD Bars, TMT bars , Welded wire fabrics; Steel for Pre stressed concrete; Structural steel; Stainless steel, steel alloys, current developments.
UNIT 2 STEEL DOORS/ WINDOWS/ VENTILATORS &TRUSSES 8 Hrs.
Different types of doors and windows (open able, sliding etc., methods of construction using steel)- Design and detailing of steel rolling shutter. Design and detailing of steel roof trusses (north-light, tubular, butterfly truss etc.,) including construction methods for roof covering using steel, FRP, polycarbonate, cement fibre sheets etc. Visit to steel structure fabrication site.
UNIT 3 LONG SPAN STRUCTURES 8 Hrs.
Long span roofs using different types and materials (stadium and auditoriums) .Methods of construction using cable structure- principle of cable stayed bridges -space frame structures. Methods of construction using Shell structures and folded plates - various forms and classification of shells and types of folded plates.
UNIT 4 ARCHITECTURAL DETAILING - LARGE GATHERING SPACES 8 Hrs.
Architectural Detailing in public spaces - Fundamentals Geometry Simple Types: Complex Types: Natural Lighting Envelope Landscaping Thermal Control Thermal Control Pressurization and Air Balance Fire Protection/Smoke Control.

- Teacher: Catherine S
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: RAJESH KANNAN S
- Teacher: SHOBANA SUBRAMANIAN
A subject that is meant to ensure the students of 4th year Architecture, understand the meaning and purpose of Landscape, as a natural process, then Landscape Architecture, as a driving force behind and within Architectural design process and all the details of the design process and how different it is from Architectural design. Ofcourse with the strong touch of history and evolution of the field from Horticultural and Botanical field to a site management tool.
- Teacher: VIJENDRANATH R

COURSE OBJECTIVE
• To introduce the fundamentals of Architectural photography.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
Introduction to architectural photography, interpretation and creation, Recording mediums - film and digital, specialist hardware for image capture, black and white, colour photography, basics of composition.
UNIT 2 FUNDAMENTAL OF PHOTOGRAPHY
Fundamentals- focal length, aperture, exposure, aperture, shutter speed, recording medium, exposure meters, automatic & Techniques, film speed, contrast, Characteristics of lenses-viewing angle, Types of lenses, depth of field, resolution and distortion, multiple exposures.
UNIT 3 EXTERNAL LIGHTING
Understanding light and photography, External lighting- Direction of lighting - front, side, back, shadows, texture, and effects of clouds, light modification, psychological effects, and types of artificial lighting, combined daylight and flash.
UNIT 4 FRAMING VIEWS
Single point and two-point perspective- examples, distortions, emphasizing architectural elements, effect of the camera to subject distance, oblique angles, three-point perspective- applications in interiors and exteriors - composition, symmetric composition, applying the law of thirds - examples, image capture to publication.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
To expose the students on services and facilities to be provided to urban communities and train them to deal with the challenges posed in the design of multi-functional public community building in an urban setting
FOCUS
Design of simple medium rise buildings in smaller sites with exploration of form integrated with function incorporating barrier free environment principles.
METHODOLOGY PROPOSED
To expose the students to the issues involved through visits to similar typologies / special lectures / orientation on urban challenges (limitation of land / regulations). Students will be encouraged to approach the problem with a three dimensional approach using study models, 3d sketches, etc. Students will work on manual presentations only.
DESIGN INTEGRATION
Students would be exposed to deal with different projects.
SUGGESTED TYPOLOGIES:
· Shopping arcades / malls / bazaar
· Auditorium / performing centres / museums / gaming parlour / club house
· Marriage halls / community halls / memorial complexes
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1: Developing an inclination to identify and analyse suitable literature and live case studies appropriate to the design typology
CO2: A thorough understanding of the important local bye laws and Standards applicable to the specific typology
CO3: Developing an appropriate design intent based on notions, ideas with the three dimensional perception as part of design process.
CO4: Integration of the structural grid, parking, services and landscape in architectural design.

- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: SHOBANA SUBRAMANIAN
The main objective of the course is to impart and train rigorously the students for human resources and materials involved in construction projects and their planning and management.

Evolving methodologies for site responsive design and integration between built and natural environment.
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar

COURSE OBJECTIVE
To understand the basic principles of physics of electricity and light and to enable them to understand the electrical layout with appropriate cross section of wires and luminance.

- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand the physics of sound, its characteristics & behavior both indoors and outdoors.
Ø To learn the principles of design with particular reference to acoustics in performing spaces.
Ø To explore the types of mechanical transportation systems and their usage in built environment along with the design parameters.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1: Knowledge on Science of Sound including different types of acoustic materials, their properties and design factors
In the built environment based on the function.
CO2: Comprehend principles of acoustic design and its application in outdoor environment.
CO3: Art and Science of designing performing spaces and broadcasting studios with particular reference to acoustics
CO4: Methods to avoid sound transmission in interior spaces.
CO5: Judicial use of mechanical transportation devices in built environment.
CO6: Total
understanding of design standards of diverse mechanical transportation systems
like elevators and
escalators.

- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To introduce the basic concepts of manufactured building materials and their applications in built environment including the techniques of thermal and sound insulation.
➢ To get an understanding on the terminology and materials used in false ceiling along with details for incorporating lighting and air conditioning.
➢ To familiarize the students with the methods of construction for a staircase using various materials like timber, steel, glass and composite materials.

SAR1304_Materials and Construction - IV
Ar. Ramkumar, Ar. Juvila, Ar. Selvendiran, Ar. Madhumitha
- Teacher: Ramkumar R
- To introduce the importance of specification for quality control in design and construction.
- This course is a field oriented course and contains easy simple examples for better understanding
- Helping the students in preparation of bill of quantities for the quantity estimate in construction, the calculation of rough and detailed estimation for the budgeting in construction projects.
- After successful completion of this course, you will be able to Estimate Any Building Project (From Foundation To Finishing)

- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
To give an introductory and over all understanding of the relationship between Architecture and urban and regional planning
To construct knowledge on various aspects involved in the planning and development of cities and regions
To explore the holistic understanding of regional planning in Indian context.

- Teacher: Juvilasri Vignesh
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To introduce the skills and knowledge relevant to the practice of professional journalism.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
Introduction to journalism, Subfields within Journalism, Key concepts and objectives of Journalism - Introduction to architectural journalism, skills needed, reporting, writing, editing, photography, columnists, public relationships, criticism.
UNIT 2 TECHNOLOGIES IN JOURNALISM
Environment, Social Change, Persuasion Interviewing techniques, Argument and debate as a technique in the investigation of social problems; evidence, proof, refutation, persuasion; training in argumentative speaking, theories of journalism, Introduction to architectural software needed in journalism and photography, Video coverage, walkthrough of buildings, production of contemporary architectural journalism. Understanding the individual demands in the context of newspapers, radio, film, and television.
UNIT 3 PRESENTATION TECHNIQUES
Text preparations, Mode of presentation, Standards and Guidelines for documentation, Code of ethics, Basic knowledge on Press laws, Press Council of India, Public Debate, Navigating Information Networks for Mass Media with relevance to searches on Architectural topics, User generated contents for analysis of various issues on Architecture, creating an online forum and platform for exchange of ideas and information, to critically contrast outputs of selected individual pieces of journalism.
UNIT 4 IMPLICATIONS FOR ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
Regional, National and International discussion forums, Changes in contemporary and historical design practices, Discussions on topics needed in an architectural journal and current issues- types of journals, works of key architectural journalists, Public Discourse on the Internet, Mass Media and Public Opinion critically appraise selected individual pieces of journalism.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
In this course, we will be looking at what low-energy design means, specific strategies to be considered while designing a energy efficient building, through the basic energy efficiency principles, building materilas, technologies and policies.This course will give an in-depth understanding of the different steps involved in achieving Energy efficient design. Detailed examples from the world over will further reinforce understanding of the concept.

- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
SAR1613 - Steel in Architectural Design
This is one of the Common elective at University level, where students from across departments can register and benifit
This course gives an insight into 'research,' 'types of research,' 'research in architectural domain.' Novices are expected to build knowledge on approaches, strategies, and data collection methods relating to research. Numerous open ended assignments enable them to unravel and demystify the various phases of research critically.
- Teacher: Arulmalar Ramaraj
This course will help the student understand the concept and types of innovation in a wider context, it will appraise the diverse strategies adopted by diverse architects with a focus on the competing logics of sustainable architecture. The course will formulate unique strategies to achieve sustainability in architectural design.

COURSE OBJECTIVES :
- To construct knowledge on the fundamentals of art and its reflection in culture, theories and solutions related to society and culture.
- To understand the basic concepts / theories of formation of society, role of architecture in the built environment and the relationship between man and the environment.
- To familiarize the students with the community, various factors influence various communities in a society and its impact on the environment.
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Understand the cultural contexts, development of various art forms and their representation during different time periods.
CO2 Comprehend the relationship between society, culture and the environment.
CO3 Understand the evolution of social groups over time and human habitat related to various contexts and culture.
CO4 Appraise the relationship of construction with respect to society and their culture and also the emergence of the Architect.
CO5 Summarize the different cultural context and analyze their relationship with the design of built forms.
CO6 Relate the role of culture and human behavior in a society and their response to the environment.

COURSE OBJECTIVES:
⮚ To explore the architectural marvels constructed during the modern era.
⮚ To comprehend the philosophies of the master architects during the 19th century.
⮚ To study in detail the different post-modern directions in architecture.
COURSE OUTCOME:
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1 Outline the planning principles and the construction techniques adopted during the indosaracenic era.
CO2 Summarize the architectural exemplars during the Neo Classicism era.
CO3 Outline the salient features and construction techniques adopted in the industrial exhibitions.
CO4 Explain the manifestations of art movements in architecture.
CO5 Discuss the philosophies of master architects with examples
CO6 Explain the transition observed in exemplars of architecture during the modern era.

- Teacher: Shruthi Natarajan
- Teacher: Arhannaraju .
- Teacher: Sindhumeenaatchi .
The objective of the course is to introduce and disseminate the knowledge about project management and their
application during the pre- construction and construction phase of a large construction project life cycle. To provide the basic understanding about the various project management methodologies used in various phases
like initiation, feasibility, design phase, bid and award phases, construction and closeout phases of a project.

- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Dr.Annamalai S
The Course is designed to provide an understanding of the basic principles of water supply and sanitation. It also enables the architect by providing exposure to planning, design and execution aspects of water supply and sanitation systems. Further the course offers an insight on the various water supply and sanitary systems for residence & high-rise structures

- Teacher: Arhannaraju .
To realize the role of climate in shaping a climate responsive built form.
To understand the need and importance of ventilation, day lighting, shading devices in building design towards the approach of climate responsive built environment.
To familiarize on passive design strategies for architecture of different climatic zones.
- Teacher: ANITHA M
- Teacher: Catherine S
Vernacular Architecture - Approaches and concepts in different regions, Vernacular Architecture in tropics, deserts and hills

- Teacher: Brindha K
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
⮚ To recommend ‘psychology’ as an integral prospect of Architectural study.
⮚ To broaden the understanding about various theories illustrating the relationship between man and environment.
⮚ To enhance thinking and examine various concepts that connect communal living and an urban environment
- Teacher: Catherine S
The term 'professional practice & Ethics' refers to the conduct and work of someone from a particular profession.
Professions are occupations that require a prolonged period of education and training. They are often overseen by professional bodies who may accredit educational establishments and qualified professionals.
Professional bodies may set standards of ethics, performance, competence, insurance, training and so on that must be met to remain within the profession. These are typically set out in a code of conduct.
Professions will have specific practices and standards that they value, but in construction there are some general principles common to most professionals:
- Act with integrity.
- Adopt an ethical approach.
- Provide a high standard of service.
- Only undertake work for which there is appropriate competence.
- Have appropriate insurance.
- Ensure that terms of appointment are clear.
- Act in a way that promotes trust in the profession.
- Do not discriminate against parties on any grounds.
- Demonstrate a commitment to continuing professional development.
- Offer a dispute resolution service.

- Teacher: Sindhumeenaatchi .
- Teacher: Kavitha S
Course objectives:
- Gain knowledge on Building Management System (BMS) and Automation.
-Be familiarized with various transducers and sensors in BMS.
-Be exposed on Control panel and CommunicationCOURSE
OUTCOMES On completion of the course the
student will be able to CO1: Understand Building Management
system and Automation. CO2: Describe various Sensors and
Transducers - Automation components in BMS CO3: Explain control panel and
communication such as HVAC.

- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
- Teacher: Brindha K
- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
This Course will provide a holistic understanding of the effect of various climatic parameters on built form, help to synthesis the relationship between climate and architecture. You will get familiarized with the evolution of climate responsive architecture in the tropics and this course will enable you to choose the appropriate approaches adopted to develop environmental conscious designs in the tropics.

- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
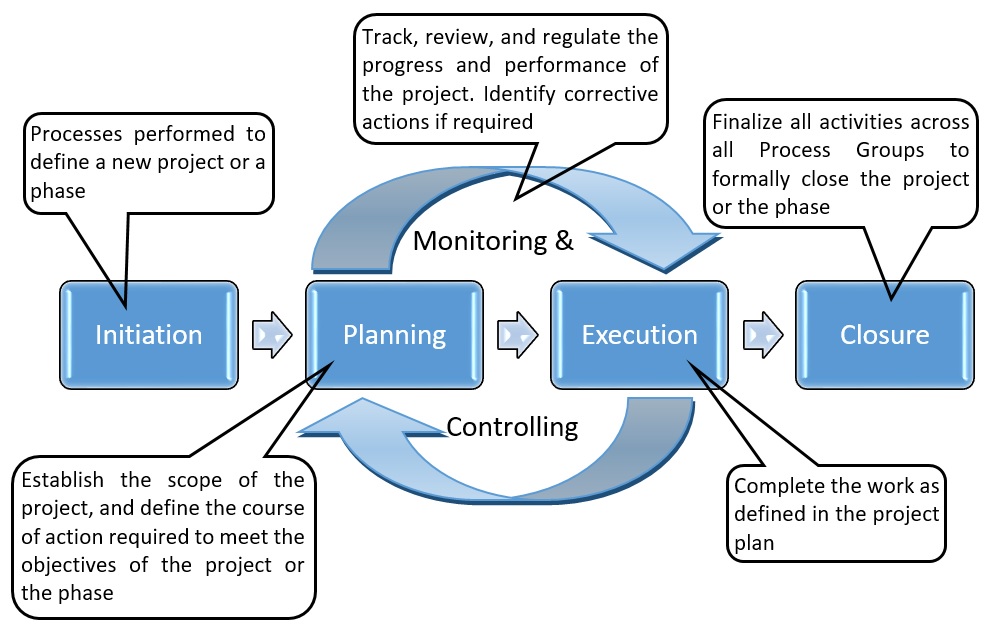
- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
This Course is structured to enable the student understand the dynamic interaction between building physics and climatic elements and explore the impact of climate on occupant comfort and environment.
Students shall learn to interpret the effect of climate on building envelope and building components and learn calculations specifically pertaining to heat loss, heat gain in a building
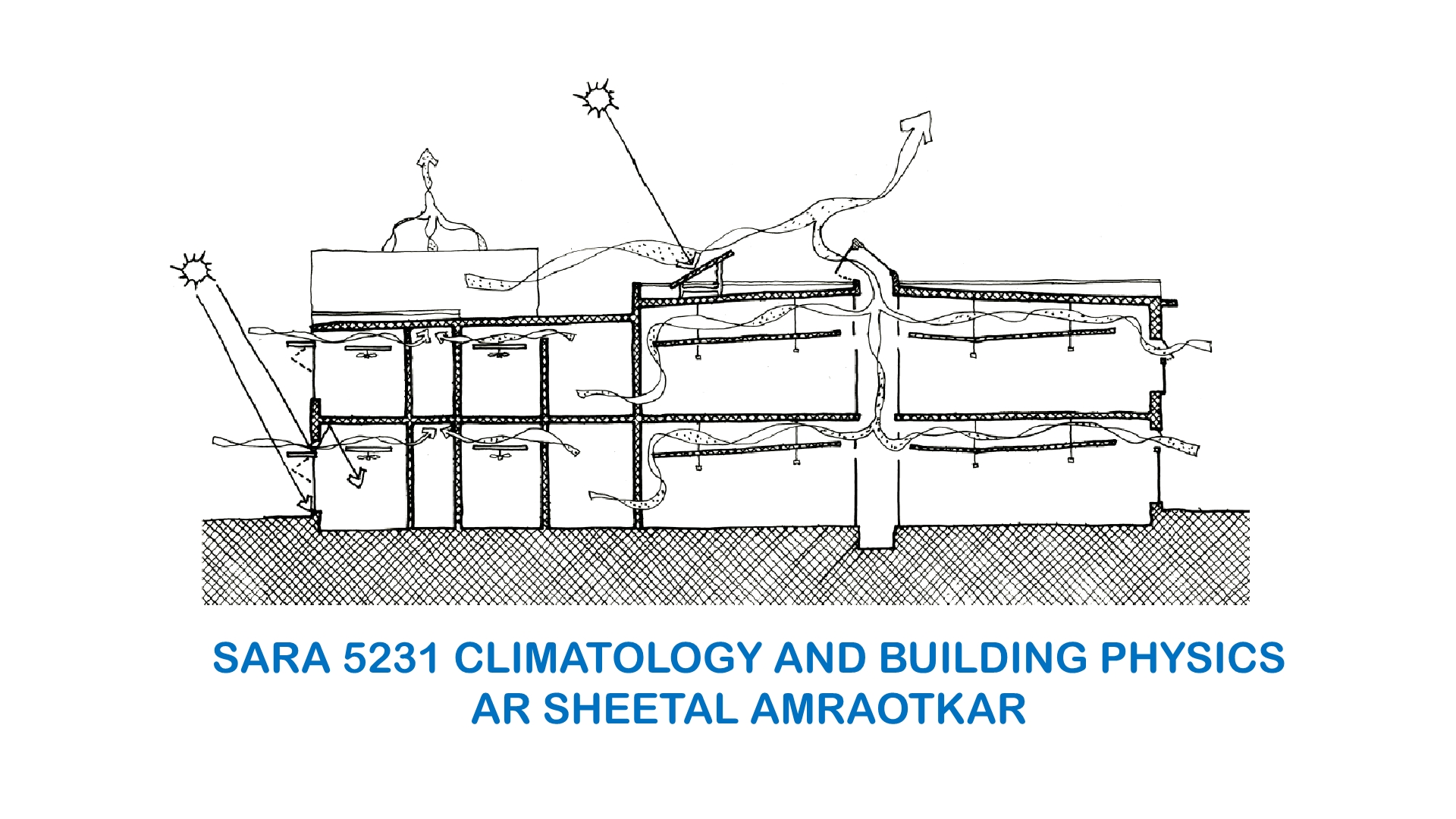
- Teacher: Kavitha S
- Teacher: SHOBANA SUBRAMANIAN
- Teacher: Guruji V
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To understand the various aspects of natural and mechanized ventilation.
- To give a comprehensive introduction and the principles of natural and artificial lighting.
- To explore the fundamentals of integrating services in buildings.

- Teacher: Dr. Devyani Gangopadhyay
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
This course talks about vital
competencies in Construction related production, operations & distribution management, concepts of operations management & new
techniques in the area of operations management.

- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
- Teacher: Catherine S
In this course the software related to project management will be taught and it will be explored by students with the projects
- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
To familiarize the fundamentals of landscape ecology, landscape planning and management.
Objectives
to impart knowledge on the landscape ecology process, structure and function.
to understand the various parameters involved in sustainable landscape planning.
to explore landscape design strategies to achieve a sustainable environment.

- Teacher: VIJENDRANATH R
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
⮚ Develop sketching and visual representation in different media of different 2-dimensional art forms, painting and interior
decoration of walls and floors.
⮚ Correlate three-dimensional art and craft forms, natural forms, structure and learn to model the same in different media.
⮚ Investigate the properties and appropriate use of materials in different craft forms.
- Teacher: Dr. Amudhan J
SARA9701 - Design Studio VII
Ar. Ramkumar / Ar. Brinda, Ar. Yusufchiniwala / Ar. Juvila

- Teacher: Ramkumar R
- Teacher: Kavitha S
Exposing to issues, challenges in the design of industrial buildings and large built forms involving alternative construction materials and technology. Orienting the students on the need for creating sustainable environment through sound Green building principles.

- Teacher: Brindha K
- Teacher: Surya Rajkumar
To introduce the fundamental concepts of form and space.
To explore spatial relationships, visual perception, and ordering principles.
To analyze the impact of scale, proportion, and materiality in design.
To understand how space is defined, articulated, and perceived.
- Teacher: EVELYN JENY V
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
- Teacher: Ramesh Kumar NA
- Teacher: Lokesh Kumar Boopathy .
- Teacher: Thiyagarajan Gopal .
This Value Added Course on Preclinical Animal Research provides knowledge on basic research and the ethics in handling Lab animals for Research.
- Teacher: Lokesh Kumar Boopathy .
- Teacher: Saravanan Durai .
- Teacher: Thiyagarajan Gopal .
Course Objectives:
The students should be able to
1. Acquire the knowledge of Electrical and Electronics engineering concepts.
2. Understand the construction and applications of Electrical and electronics components in various automotive electrical circuits.
3. Understand the construction and working of various automotive electrical systems and components.
4. Identify, demonstrate and compare the various components and systems of Auto
electrical systems.
Course Outcomes
CO1 : Enumerate the construction, characteristics and maintenance of battery, lighting system and different accessories in a typical automobile after careful inspection.
CO2 : Explain the construction, characteristics and maintenance of starting and ignition system and diagnose the ignition system fault of any vehicle.
CO3 : List out the principles and characteristics of charging system components and demonstrate their working with suitable tools.
CO4: Describe the principles and architecture of electronics systems and its components present in an automobile related to instrumentation, control, security and warning systems.
CO5: Enumerate the principles, application, construction and
specification of different sensors and actuators usable in typical
automobile by suitable testing.

- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
Vehicle Dynamics is the study of a vehicle behavior during motion which plays a vital role in finding out the right balance between driver feel, comfort and safety of passengers and and the wow factor which we all experience during driving.
Automotive aerodynamics is the study of the aerodynamics of road vehicles. The main concerns of automotive aerodynamics are reducing drag, reducing wind noise, and preventing undesired lift forces at high speeds. For some classes of racing vehicles, it may also be important to produce desirable downwards aerodynamic forces to improve traction and thus cornering abilities.
Course Objective
- Defines the Vehicle Aerodynamics, through its coupling to energy efficiency, is important in the creation of a sustainable society.
- Understand the coupling between the fundamental theories of Fluid Dynamics and Vehicle Aerodynamic applications.
- Explain the criteria/conditions for achieving good Aerodynamic design of passenger- and commercial vehicles.
- Recognize the strengths and limitations of the different tools used to optimize and evaluate Aerodynamic performance.
- Be able to evaluate aerodynamic properties of a vehicle, by analyzing wind tunnel and CFD results, as well as suggest improvements to an existing design.
- Recognize implications of Aerodynamics on other vehicle attributes such as Thermal Management, Aeroacoustics, Contamination, and Climate Comfort.
This course enable the students
- To understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics
- To understand the air standard cycles and working principles of four stroke and two stroke engines
- To familiarize with the types of air compressors and their working principle
- To understand the working principles of refrigeration and air conditioning systems
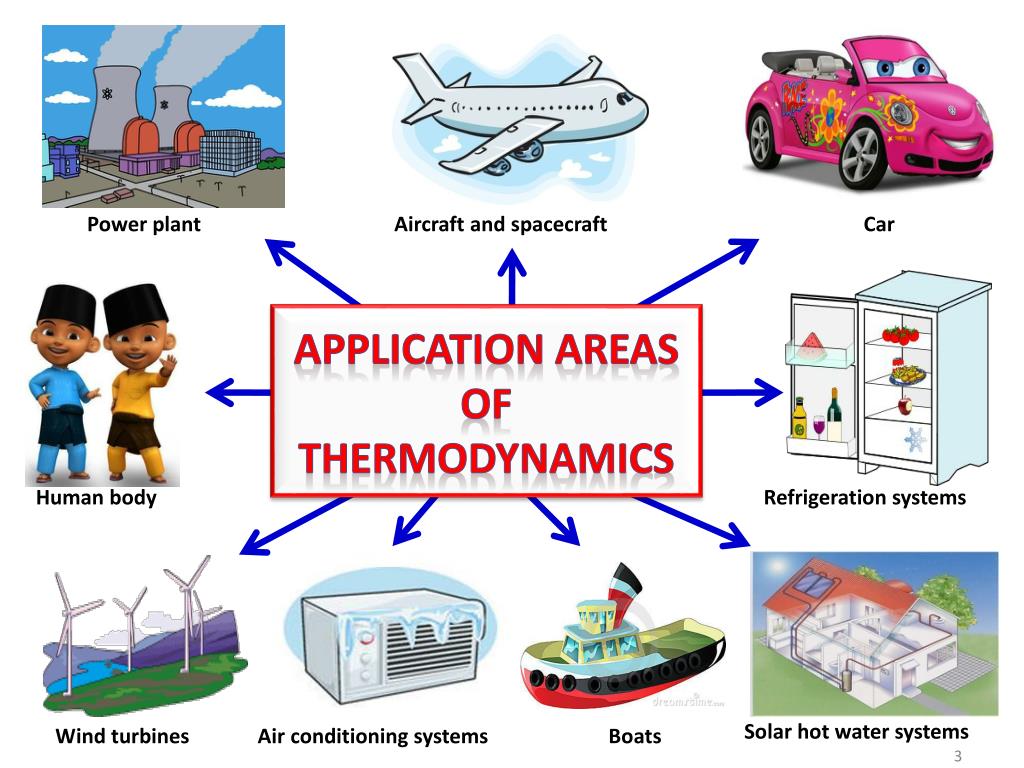
- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
- Teacher: Bupesh Raja V.K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the refining process of petroleum.
- To develop understanding about various types of fuels, lubricants and their properties
- To understand the importance of Alternate fuels available.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
SAUA1702 VEHICLE MAINTENANCE
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know about the various methods of maintaining vehicles and their subsystems.
To impart knowledge on engine maintenance – repair and overhauling.
To understand step by step procedure for maintain the various automotive sub systems.
UNIT 1 MAINTENANCE, WORKSHOP PRACTICES, SAFETY AND TOOLS 9 Hrs.
Maintenance – need, importance, primary and secondary functions, policies - classification of maintenance work - vehicle
insurance - basic problem diagnosis, automotive service procedures – workshop operations – workshop manual .safety –
personnel, machines and equipment, vehicles, fire safety - first aid, basic tools – special service tools – measuring
instruments – condition checking of seals, gaskets and sealants, scheduled maintenance unscheduled maintenance
services – service intervals - towing and recovering, reports, log sheets, trip sheets and other forms.
UNIT 2 ENGINE AND ENGINE SUBSYSTEM MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
General engine service- dismantling of engine components- engine repair- working on the underside, front, top, ancillariesservice
of basic engine parts, cooling and lubricating system, fuel system, intake and exhaust system, electrical system -
electronic fuel injection and engine management service - fault diagnosis- servicing emission controls.
UNIT 3 TRANSMISSION AND DRIVELINE MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Clutch- general checks, adjustment and service- dismantling, identifying, checking and reassembling transmission,
transaxle- road testing- removing and replacing propeller shaft, servicing of cross and yoke joint and constant velocity jointsrear
axle service points removing axle shaft and bearings- servicing differential assemblies- fault diagnosis.
UNIT 4 STEERING, BRAKE, SUSPENSION, WHEEL MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Inspection, maintenance and service of hydraulic brake, drum brake, disc brake, parking brake, bleeding of brakes.
inspection, maintenance and service of mc person strut, coil spring, leaf spring, shock absorbers, dismantling and assembly
procedures, wheel alignment and balance, removing and fitting of tyres, tyre wear and tyre rotation, inspection, maintenance
and service of steering linkage, steering column, rack and pinion steering, recirculating ball steering service-worm type
steering, power steering system.
UNIT 5 AUTO ELECTRICAL AND AIR CONDITIONING MAINTENANCE 9 Hrs.
Maintenance of batteries, starting system, charging system and body electrical -fault diagnosis using scan tools,
maintenance of air conditioning parts like compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator - replacement of hoses- leak
detection- AC charging- fault diagnosis, vehicle body repair like panel beating, tinkering, soldering, polishing, painting.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Gain knowledge about vehicle operation and maintenance, service schedules etc.
CO2 - Apply the concepts of scheduling.
CO3 - Understand Maintenance of engine sub system and Repair
CO4 - Understand maintenance procedures like repairing, overhauling
CO5 - Describe the basic concepts of steering, brake, suspension and wheel maintenance.
CO6 - Analyze the testing methods for checking battery, starter motor, charging systems, ignitions system.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Ed May, “Automotive Mechanics”, Volume 1 and 2, 8th edition, McGraw Hill Publications, 2009.
2. Vehicle Service Manuals of reputed manufacturers.
3. Bosch Automotive Handbook, Tenth Edition, 2017.
4. Automotive Mechanics W.H. crouse.2010.
5. James D Halderman, “Advanced Engine Performance Diagnosis” 6 edition, Pearson, 2015
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 questions of 2 marks each - No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
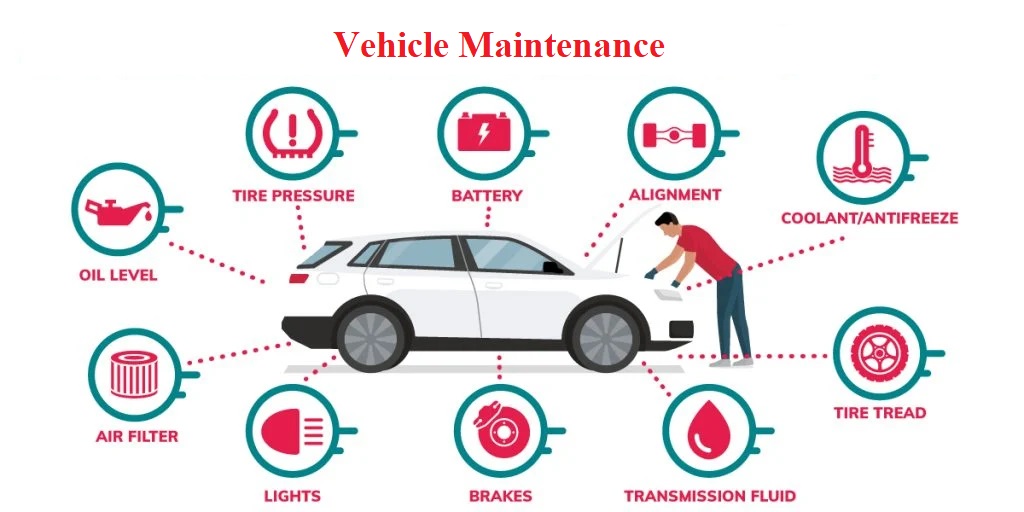
- Teacher: RAM PRAKASH S
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
The main objective of this course is
- To impart knowledge in automotive pollution control.
- The detailed concept of formation and control techniques of pollutants like UBHC, CO, NOx, particulate matter and smoke for both SI and CI engine
- The instruments for measurement of pollutants and emission standards will also be introduced to the students.
At the end of the course the students will have command over automotive pollution and control.

- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
Automotive safety is the study and practice of design, construction, equipment and regulation to minimize the occurrence and consequences of traffic collisions involving motor vehicles. The course gives an introduction to safety and vehicle structural crashworthiness and crash testing, types of impacts, and impact with rebound, driver assistance systems in automobiles, concept of crumble zone,characteristics of vehicle structure, role of safety systems in automobiles, importance of ergonomics in automotive safety.

- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the importance of vehicle safety and explain different vehicle collision and its effects.
CO2 - Explain different types of safety concept and understand the deformation behaviour of vehicle body during collision.
CO3 - Explain the operation of different safety equipment and understand various collision warning system.
CO4 - Understand vehicle ergonomics system and psychological factors in man machine system.
CO5 - Explain different types of mirror and their location and working principle of central locking system garage door opening system.
CO6 - Explain rain sensor system and environment information system
- Teacher: MANOJ E
- Teacher: Dr. Ashwin Jacob
This Course is designed
1.To create an understanding on the basic concepts of Business Management.
2.To familiarize about the various forms of organization, need for industrial safety and the importance efficient plant layouts in business organizations.
3.To give exposure towards the importance of studying human behaviour at work place .
4.To extend students knowledge in the importance of leadership and communication and its impact on the performance of individuals.
5.To create awareness towards the basic ethics followed in business and corporate social responsibilities of business organizations.

- Teacher: JOHN BRITTO M
- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
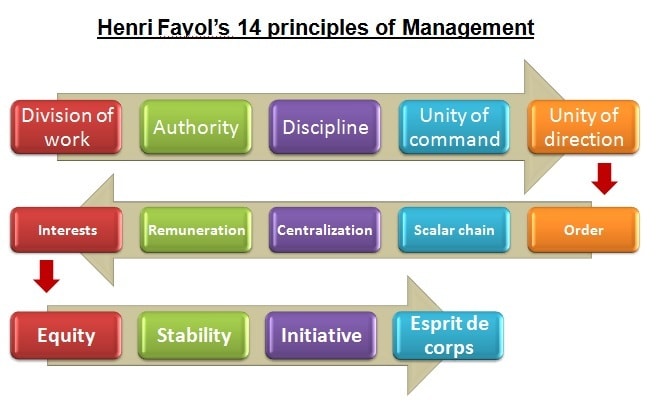
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Comprehend various management principles and practices followed in industries
- CO2 - Analyze the types of business organization, plant layout and its safety measures.
- CO3 - Develop appropriate behavior as an individual and as a team to excel in industries. CO4 - Develop expertise knowledge on the impact of Leadership Communication and Group dynamics in industry
- CO5 - Comprehend the basics of ethical behaviour and corporate social responsibility practiced in industries
- CO6 - Investigate business cases by applying the ethical guidelines in industrial real-life situations.

- Teacher: Sivagami P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand the Principles of Economics in Business.
- To gain knowledge of Micro and Macro Economic environment.
- To analyze the different market structures.

Operations Research offers
scientific methods for better decisions. The idea is to develop and use
mathematics and informatics tools to solve complex organization
problems.At the end of this course,
students should be able to
solve optimization problem.

- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable students to develop cognizance of the importance of human behavior.
To provide insight on individual and group behavior.
To familiarize with organizational culture, change and development processes.

- Teacher: DR. RANI J
- Teacher: JOHN BRITTO M
- Teacher: Shahinabegum M
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
This is a course will help the students to identify the key elements of costing and pricing of product or service. This will used to analyse the value and importance of essential resources of business such as material, manpower and other cash transactions. It brings the worthiness of each and every elements in business segment by preparing cost sheet which mainly support to prepare the budget for business organisation. This will also brief the basic functions and services of bank along with its different classification.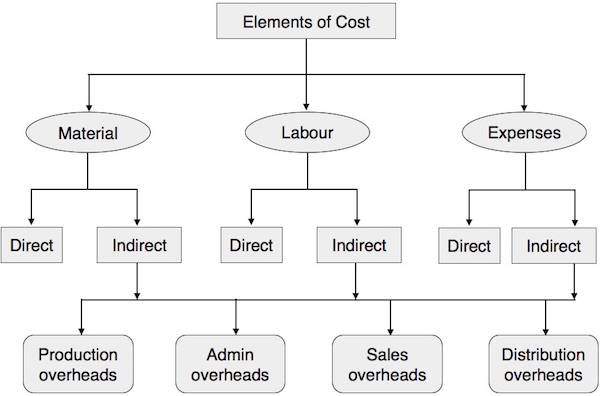

- Teacher: Saranya J

- Teacher: Rathnakumar A
- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: Dr. Moli Ghosh
- Teacher: LAVANYA M
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
- Teacher: NAMASIVAYAM SHEEBA
Income Tax is a specified subject which helps to Assess the Income of the person and to calculate the amount of TAX for corresponding assessment year. It gives the macro and micro knowledge on Income tax and gives the opportunity to become a TAX professional in all kind of industries.

- Teacher: Kaavya K
Course Objectives:
1) To gain the basic knowledge of Management Accounting Concepts.
2) To enable the students to prepare budgets.
3)To interpret the financial data for managerial planning, control and decision making.

- TEACHER: Kaavya K
- TEACHER: THAMILSELVAN R
To gain the basic knowledge of Management Accounting concepts
To enable the students to prepare Budgets
To interpret the financial data for managerial planning, control and decision making

- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: SANDHYA V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
¨ To understand the concept of risk.
¨ To acquire specialized knowledge of law and practice relating to Insurance.
¨ To know about the regulatory environment
FACULTY NAME: Dr.M.LAVANYA

- Teacher: Rathnakumar A
- Teacher: Bhavya B
- Teacher: JAYASEELY M
- Teacher: Nikkath Fathima G
- Teacher: DR. RANI J
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
CO1 - Describe the evolution and development of management concepts.
CO2 - Understand the functions of management.
CO3 - Apply the concepts and develop key competencies for managing human resources.
CO4 - Analyze appropriate management techniques for Controlling and Reporting.
CO5 - Evaluate the various aspects of decision making and demonstrate critical thinking.
CO6 - Elaborate the importance of the ethical dimension in workplace
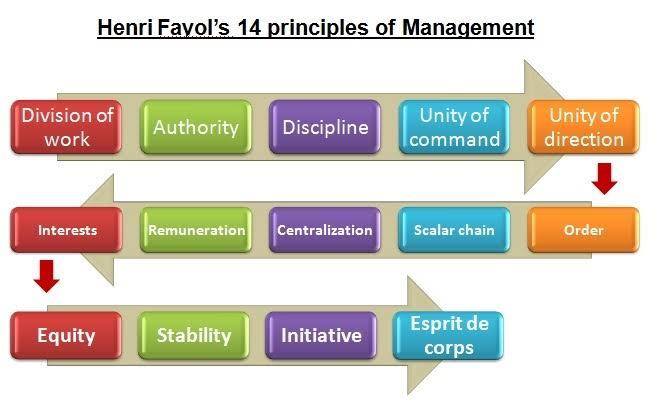
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
This Course will helps you in the following ways:
(i) To understand management accounting tools and techniques.
(ii) To analyze and interpret financial statements.
(iii) To recognize the roles of budgets variance as tools of planning and control.

- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: THAMILSELVAN R
- Teacher: NAMASIVAYAM SHEEBA
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
COURSE NAME :SBAA5301 GLOBAL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
BATCH :MBA 2019-2021
FACULTY NAME: DR TR. KALAI LAKSHMI

- Teacher: Bhavya B
- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: Nivedhitha K.S
Strategic financial management (SFM) integrates the financial management function in to the corporate strategy. It applies financial tools and techniques in devising strategic decision plan for maximizing return on investment. This course will help you make value-creating financial decisions for the firm. You will be able to comprehend the implications of financial decisions of a company on shareholder value.

- Teacher: Meera A
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: Yamuna D
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
Course Objectives :
- To know the fundamentals of Information System
- To study about Management Information System
- To understand the concepts of Knowledge Management System, Strategic Information System
The course is divided in to Five Units as follows:
- Unit 1 – Introduction to Information system
- Unit 2 – Structure and Classification of Information System
- Unit 3 – Management Information System
- Unit 4 – Strategic Information System
- Unit 5 – Knowledge Management System
On completion of the course, student will be able to :
- Understand the concepts of Information system.
- Identify the structure and classification of Information System.
- Generalize MIS concepts.
- Evaluate Strategic Information System, security and ethics in MIS.
- Analyze the concepts of DSS and KMS.
- Compile the concepts of Information system.

- Teacher: PALANI A
- Teacher: Jeya Rani R
- Teacher: Agila S
This is course will help to identify the key factors in successful marketing of business. This will highlight the emerging trends in marketing channels, process, segments, tools etc. This will mainly used to identify the customer's need and satisfaction for customer relationship management.
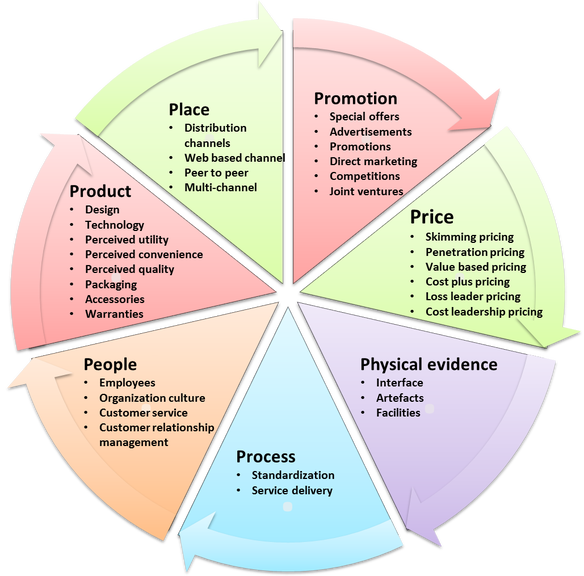

- Teacher: Raja M
- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
- Teacher: NAMASIVAYAM SHEEBA
- Teacher: SANDHYA V
- Teacher: Jeya Rani R
- Teacher: Dr. Moli Ghosh
- Teacher: LAVANYA M
- Teacher: Jeya Rani R
- Teacher: VIGNAESWERAN P
- Teacher: AROCKIAMARY R
- Teacher: GANESH V
1. To develop an entrepreneurial mindset, understand the concept of entrepreneurship and identify personal strengths and weaknesses
2. To understand the design thinking process and apply design thinking to real-world problems
3. To identify problems and opportunities and develop ideas for new ventures by assessing market potential
4. To develop a value proposition, business model canvas, build MVP to create sustainable differentiation for the venture with a well-structured business plan, unit economics, go-to-market strategies and funding plan for managing business growth
5. To build an idea pitch and deliver it with confidence to potential stakeholders

- Teacher: Rathnakumar A
- Teacher: JOYCE S
- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To assist the students in understanding basic laws affecting the operations of a business enterprise.
To identify the fundamental legal principles behind contractual agreements
To acquire knowledge and skills related to business law

- Teacher: PALANI A
- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: LAVANYA M
- Teacher: Dr.Dhanya M.M.
- Teacher: HARIPRASAD RACHETTY
Students develop a basic understanding of business finance which deals with how organizations effectively manage their operating and fixed assets and fund them with an optimal mix of debt and equity financing. This course will also explain financial tools and techniques, which can be used to help firms maximize value by improving decisions relating to capital budgeting, capital structure, and dividend.

- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: Yamuna D
- Teacher: THAMILSELVAN R
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
- Teacher: Rathnakumar A
- Teacher: Yamuna D
- Teacher: P HAMEEM KHAN
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: HARIPRASAD RACHETTY
- Teacher: MD DANISH RAZA
- Teacher: Dr Kishore Raaj S
COURSE: SBAB7014ADVERTISING MANAGEMENT AND SALES PROMOTION
FACULTY : DR. TR. KALAI LAKSHMI
BATCH : MBA 2023-2025

- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
- Teacher: NIVIN JOY
- Teacher: UMAMAHESWARI S
In this course the students will learn different areas of cellular biology including the structure and functions of celL.
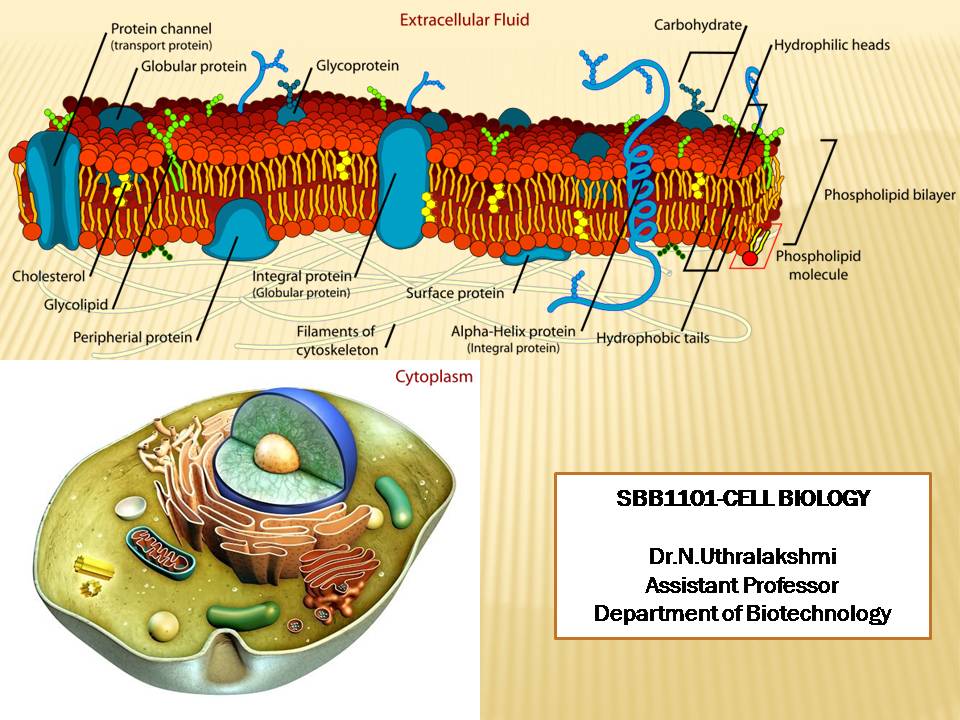
Culturing of animal cells and preservation and revival of celllines
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
SBBA 1203 INTRODUCTION OT BIOCHEMISTRY L T P Credits Total Marks 5 0 0 3 100
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
This course is aimed give an understanding of the basics of biochemistry dealing carbohydrates, Amino acids, Lipids, nucleic acid and vitamins.
UNIT 1: CARBOHYDRATES 12 Hrs. Carbohydrate – Definition, Classification, biological significance, structure of glucose, digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
UNIT 2: PROTEINS 12 Hrs. Amino acids – structure, classification (Essential and non-essential, protein and non-protein amino acids). Proteins – definition, classification and structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary).
UNIT 3: LIPIDS 12 Hrs. Lipids – definition, classification and biological significance. Structure, properties and functions of fatty acids.
UNIT 4 NUCLEIC ACIDS 12 Hrs. Nucleic acids – Structure of DNA and its functions. Different forms of DNA. Different types of RNA and its functions.
UNIT 5 VITAMINS 12 Hrs. Vitamins – Source, biological function, daily requirement and deficiency symptoms of fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K) and water soluble vitamins (Ascorbic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, niacin, pantothenic acid, lipoic acid, biotin, folic acid and vitamin B12).
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry-David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox, Macmillan Worth Publishers.
2. Harper―s Biochemistry-Rober K. Murray, Daryl K. Grammer, McGraw Hill, Lange Medical Books. 25th edition.
3. Fundamentals of Biochemistry-J.L. Jain, Sunjay Jain, Nitin Jain, S. Chand & Company.
4. Biochemistry-Dr. Amit Krishna De, S. Chand & Co., Ltd. END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION
PAPER PATTERN Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 questions of 2 marks each - No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks

The course aims to give an overview on application of biotechnology in agriculture. It also aims to understand
the basic concepts in plant tissue culture and transgenic plants

- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Hartiha S
COURSE OBJECTIVE
The
experiments provide hands-on experience in operating various analytic
instruments thereby developing skill in handling them which will be a
pre-requisite for research work
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 – Learning how to handle laboratory instrumentation for anti-microbial, anti-fungal studies
CO2 – Preparing necessary reagents and solvents for cell culture studies
CO3 – Separation of cells and cellular components through centrifugation techniques.
CO4 – Understanding the principles of various calorimetric types and its importance in various chemical reactions.
CO5 – Understand the absorbance and transmittance of light in solution by spectrophotometer.
CO6 – Learning how to separate macromolecules and nucleic acids by SDS and agarose electrophoresis techniques.
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Jesia Persis Preethi
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: Arjita Ghosh
- Teacher: Dr. HARI RAJ K
- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
- Teacher: Jesia Persis Preethi
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
Genetic Engineering course explores the manipulation of DNA using various tools and methods for its diverse application in the field of industry, medicine, plant and animal Biotechnology.
- Teacher: KUNTHAVAI P.C.
- Teacher: Jancy Mary E
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Devi B
- Teacher: Hartiha S
- Teacher: Prabhakar Singh
|
Course objectives This course is aimed give an understanding about the basics of microbiology dealing types of microbes, classification & characterization |
- Dr.S.Usha Nandhini: Usha Nandhini S
|
Course objectives This course is aimed give an understanding about the basics of microbiology dealing types of microbes, classification & characterization |
- Teacher: Jayashree S
Students can get wide knowledge on Basic concepts of clinical Biochemistry in relation to basic Laboratory analysis of Hematology, Disorders of all metabolic reactions in the body, and a variety of Organ function laboratory tests and its methodologies advantages followed by Isoenzymes and their role discussed.

- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
COURSE OBJECTIVE
Developing of general understanding how physical laws govern biological processes.
Acquire basic knowledge about how physical methods can be applied to understand biological processesCOURSE
OUTCOMES On completion
of the course, student will be able to CO 1: Understand the fundamental principles and
thermodynamics that drive biomolecules. CO:2: Emphasize profound knowledge on cell
structure, function and dynamics of inter-intra cellular processes. CO 3:
Explore various basic and advanced sophisticated biochemical and biophysical
techniques for analyzing macromolecules CO 4: Comprehend clear understanding on various
cellular metabolic pathway mechanism and its applications in biological system. CO 5. The application of mathematical tools to
calculate thermodynamic. CO 6: The students familiar about the inorganic
halogen compounds, coordination compounds and transition elements.

- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
- Teacher: Theboral J
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
COURSE OBJECTIVE
➢ To understand experimental enzyme techniques
with a problem-oriented approach.
SUGGESTED
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS - ENZYMOLOGY
1. Standard Maltose Curve
2. Isolation of Alpha/Beta Amylase
3. Determination of enzyme activity
4. Construction of Protein standard curve by Folin’s Lowry method and Determination of specific activity of enzyme.
5. Effect of substrate concentration on Enzyme kinetics and determination of Km and Vmax
6. Effect of temperature on Enzyme kinetics
7. Effect of enzyme concentration on Enzyme kinetics
8. Effect of pH on Enzyme kinetics
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 – to build a strong foundation on basic techniques in enzymatic reactions
CO2 – determine various parameters affecting an enzyme reaction
CO3 – breakdown the fundamentals of handling laboratory equipemnts and reagents
CO4 – apply the concepts of enzyme kinetics
CO5 – discuss the use of idenitifation of enzyme reactions
CO6 – recognize the kinetics behind a chemical reaction.

- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: PRAVDA CHIDAMBARANATHAN
- Teacher: Daflin Femi F
- Teacher: NANDHINI GANESAN
- Teacher: SAI CHARAN K.V
- Teacher: MELODY KHWAIRAKPAM
- Teacher: PRIYANKA M
Dental Anatomy, Oral Histology, Oral Physiology and Embryology
DENTAL ANATOMY, EMBRYOLOGY, ORAL HISTOLOGY
Dental Anatomy including Embryology and Oral Histology - a composite of basic Dental Sciences & their clinical applications
SKILLS
The student should acquire basic skills in :
1. Carving of crowns of permanent teeth in wax.
2. Microscopic study of Oral tissues.
3. Identification of Deciduous & Permanent teeth.
4. Age estimation by patterns of teeth eruption from plaster casts of different age groups.
OBJECTIVES
After a course on Dental Anatomy including Embryology and Oral Histology,
1. The student is expected to appreciate the normal development, morphology, structure & functions of oral tissues & variations in different pathological/non-pathological states.
2. The student should understand the histological basis of various dental treatment procedures and physiologic ageing process in the dental tissues.
3. The students must know the basic knowledge of various research methodologies.
I. TOOTH MORPHOLOGY (31hrs)
1. Introduction to tooth morphology: (5hrs)
♦ Human dentition, types of teeth, & functions, Palmer's & Binomial notation systems, tooth surfaces, their junctions - line angles & point angles, definition of terms used in dental morphology, geometric concepts in tooth morphology, contact areas & embrasures - Clinical significance.
2. Morphology of permanent teeth : (17hrs)
• Description of individual teeth, along with their endodontic anatomy & including a note on their chronology of development, differences between similar class of teeth & identification of individual teeth.
• Variations & Anomalies commonly seen in individual teeth.
3. Morphology of Deciduous teeth : (8hrs)
♦ Generalized differences between Deciduous & Permanent teeth.
♦ Description of individual deciduous teeth, including their chronology of development, endodontic anatomy, differences between similar class of teeth & identification of individual teeth.
4. Occlusion : (2hrs)
♦ Definition, factors influencing occlusion - basal bone, arch, individual teeth, external & internal forces & sequence of eruption.
♦ Inclination of individual teeth - compensatory curves.
♦ Centric relation & Centric occlusion - protrusive, retrusive & lateral occlusion.
♦ Clinical significance of normal occlusion.
♦ Introduction to & Classification of Malocclusion.
II. ORAL EMBRYOLOGY (12hrs)
1. Brief review of development of face, jaws, lip, palate & tongue, with applied aspects. (4hrs)
2. Development of teeth : (4hrs)
♦ Epithelial mesenchymal interaction, detailed study of different stages of development of crown, root & supporting tissues of tooth & detailed study of formation of calcified tissues.
♦ Applied aspects of disorders in development of teeth.
3. Eruption of deciduous & Permanent teeth : (2hrs)
♦ Mechanisms in tooth eruption, different theories & histology of eruption, formation of dentogingival junction, role of gubernacular cord in eruption of permanent teeth.
♦ Clinical or Applied aspects of disorders of eruption.
4. Shedding of teeth : (2hrs)
♦ Factors & mechanisms of shedding of deciduous teeth.
♦ Complications of shedding.
III. ORAL HISTOLOGY (48hrs)
1. Detailed microscopic study of Enamel, Dentine, Cementum & Pulp tissue. Age changes & Applied aspects (Clinical and forensic significance) of histological considerations - Fluoride applications, transparent dentine, dentine hypersensitivity, reaction of pulp tissue to varying insults to exposed dentine ; Pulp calcifications & Hypercementosis. (16hrs)
2. Detailed microscopic study of Periodontal ligament & alveolar bone, age changes, histological changes in periodontal ligament & bone in normal & orthodontic tooth movement, applied aspects of alveolar bone resorption. (9hrs)
3. Detailed microscopic study of Oral Mucosa, variation in structure in relation to functional requirements, mechanisms of keratinization, clinical parts of gingiva, Dentogingival & Mucocutaneous junctions & lingual papillae. Age changes & clinical considerations. (8hrs)
4. Salivary Glands : (4hrs)
♦ Detailed microscopic study of acini & ductal system.
♦ Age changes& clinical considerations.
5. TM Joint : (3hrs)
♦ Review of basic anatomical aspects & microscopiuc study & clinical considerations.
6. Maxillary Sinus : (3hrs)
♦ Microscopic study, anatomical variations, functions & clinical relevance of maxillary sinus in dental practice.
7. Processing of Hard & soft tissues for microscopic study : (2hrs)
♦ Ground sections, decalcified sections & routine staining procedures.
8. Basic histochemical staining patterns of oral tissues. (3hrs)
IV. ORAL PHYSIOLOGY (14hrs)
1. Saliva : (2hrs)
♦ Composition of saliva - variations, formation of saliva & mechanisms of secretion, salivary reflexes, brief review of secretomotor pathway, functions, role of saliva in dental caries & applied aspects of hyper & hypo salivation.
2. Mastication : (2hrs)
♦ Masticatory force & its measurement - need for mastication, peculiarities of masticatory muscles, masticatory cycle, masticatory reflexes & neural control of mastication.
3. Deglutition : (2hrs)
♦ Review of the steps in deglutition, swallowing in infants, neural control of deglutition & dysphagia.
4. Calcium, Phosphorous & fluoride metabolism : (2hrs)
♦ Source, requirements, absorption, distribution, functions & excretion, clinical considerations, hypo & hypercalcemia & hyper & hypo phosphatemia & fluorosis.
5. Theories of Mineralization : (1hr)
♦ Definition, mechanisms, theories & their drawbacks.
♦ Applied aspects of physiology of mineralization, pathological considerations - calculus formation.
6. Physiology of Taste : (1hr)
♦ Innervation of taste buds & taste pathway, physiologic basis of taste sensation, age changes & applied aspects - taste disorders.
7. Physiology of Speech : ( 2hr)
♦ Review of basic anatomy of larynx & vocal cords.
♦ Voice production, resonators, production of vowels & different consonants - Role of palate, teeth & tongue.
♦ Effects of dental prosthesis & appliances on speech & basic speech disorders.
PRACTICALS (250HRS)
1. Carving of crowns of permanent teeth in wax. (140hrs)
2. Microscopic study of Oral tissues. (80hrs)
3. Identification of Deciduous & Permanent teeth. (20hrs)
4. Age estimation by patterns of teeth eruption from plaster casts of different age groups. (10hrs)
RECOMMENDED TEXT BOOKS
1. Orban's Oral Histology & Embryology - S.N.Bhaskar
2. Oral Development & Histology - James & Avery
3. Wheeler's Dental Anatomy, Physiology & Occlusion - Major.M.Ash
4. Dental Anatomy - its relevance to dentistry - Woelfel & Scheid
5. Applied Physiology of the mouth - Lavelle
6. Physiology & Biochemistry of the mouth - Jenkins
- Teacher: Murali Balasubramaniam Arunachalakannan
- Teacher: ANUSHA M.N
- Teacher: Saranya Ramsridhar
- Teacher: Indu Bharkavi S K
- Teacher: Rajkumari Sriraman
Course Objectives:
To learn to appreciate the programming language that can be used for a wide variety of programming tasks and
to expose the student to the standard scripting language. At the end of the course, the student will be developing
adequate skills in programming and will be known to understand the implementation of various applications using
powerful assortment of built-in types in python.
Course Outcome:
The students will be able to

- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
The student will be able to understand the basics of programming and use the Perl and its strengths in biomolecular sequence manipulation and analysis.
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Manisha Koyimadatha
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
This course is devoted to the of biological sequence analysis techniques...

- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Dr. Mahalakshmi R
The branches of science known informally as omics are various disciplines in biology whose names end in the suffix -omics, such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, metagenomics and transcriptomics. Omics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of pools of biological molecules that translate into the structure, function, and dynamics of an organism or organisms.

- Teacher: Alex Anand D
To enable the student to understand the modelling methods, such as supervised classification and clustering along with the application of probabilistic graphical models for knowledge discovery, as well as deterministic and stochastic heuristics for optimization.

- Teacher: Alex Anand D
Systems Biology Lab deals with construction, visualization and analysis of complex biological networks.
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Manisha Koyimadatha
- Teacher: Swetha Sunkar
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Amit Kumar .
- Teacher: Swetha Sunkar
To enable the student to understand the modelling methods, such as supervised classification and clustering along with the application of probabilistic graphical models for knowledge discovery, as well as deterministic and stochastic heuristics for optimization.

- Teacher: Dr. Mahalakshmi R
- Teacher: Swetha Sunkar
- Teacher: Swetha Sunkar
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1: Understand the basics of analog and digital communication systems
CO2: Acquire knowledge to process the transmission techniques for analog and digital signals
CO3: Apply the acquired knowledge to process the bio signals on telemetry systems
CO4: Analyze the various transmission techniques using analog and digital signals
CO5: Investigate the results of various transmission techniques for the signals
CO6: Develop the system to analyze the real time bio signals for digital transmission

- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
To introduce extensive knowledge in cell structure, functions, cell signaling pathways and transfer across membranes in cells.
To learn about the transmission, distribution, arrangement, and alteration of genetic information and how it
functions and is maintained in populations.
- Teacher: Krishnakumar S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To gain in depth knowledge of fundamentals of operational amplifier circuits and to study the various applications using operational amplifiers
- To discuss filters and circuits and introduce the application of signal conditioning in biomedical field
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- Design and implement linear and non-linear applications of operational amplifiers
- Implement waveform generation using operational amplifier
- Analyze and design bio filters and isolation circuits used in signal conditioning
- Design ADC and DAC using Operational Amplifiers
- Describe the basic concepts of Timers and voltage regulators
- Recognize various bio amplifier for Biosignal acquisitions using opamps
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
Course Objectives:
1. To acquire knowledge about the various medical imaging techniques
2. To understand the fundamental principle and working of the medical imaging systems
involved in the diagnosis of health care
3. To apply different classical image processing techniques to different types of medical images
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to–
1. Demonstrate Knowledge and understand the basic image processing concepts such as relationship between pixels, basic transformation and color models
2. Implement image enhancement techniques in spatial and frequency domain for accomplishing image preprocessing task.
3. Evaluate and select image filtering techniques for image restoration process
4. Illustrate the steps involved in segmentation process and Morphological operations to solve a given medical image task.
5. Analyse the performance of image compression methods.
6. Recognize and assess how image processing techniques can be applied across all medical imaging modalities and applications.
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
The prime objective of this course is to introduce to the students the programming skill of Microprocessor Microcontroller and Arduino.
The students will be trained with the interfacing and applications microprocessor, microcontroller and
Arduino

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
- Teacher: Senthil Nayagam V
Course Objectives
· The course is designed to provide a brief and basic knowledge to understand musculoskeletal, neuromuscular, sensory disorders, prosthetics and orthotics and their applications
· The main aim is to provide the basic concept so that students can implement their knowledge for higher studies in developing innovative and effective rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1: Apply the various principles involved in rehabilitation.
CO2: Support rehab engineers in designing orthotic and prosthetic devices.
CO3: Compare the types of wheelchairs and assist disabled persons
CO4: Discover new augmentation and substitution devices for visual and hearing impaired.
CO5: Assess the merits of support aids designed for the disabled.
CO6: Develop and design rehabilitation devices cost effectively and purposefully.
- Teacher: Sindu Divakaran
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
COURSE OBJECTIVES ÿ
To enable the student to develop adequate knowledge and mastery of techniques relevant to Hospital Management and hospital management discipline.
To develop awareness of the responsibilities in Hospital Management like healthcare and operational problems at a hospital attachment.
Formulate ideas and develop plan and to take a proactive and self-reflective role in working and to develop
professional expertise.

- Teacher: Premkumar J
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- This course introduces fundamental physical principles of both classical and modern optics as well as principles of optical design used in the engineering of optical systems.
- It also provides exposure to practical aspects of optical materials and devices.
- Its intention is to provide a foundation of basic principles, design methodology, and practical considerations needed to design nor use optical instruments in the biomedical engineering practice
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. With widespread use and required hardware components for designing of medical instruments, this course gives knowledge of the principle of operation and design of biomedical instruments.
2. It attempts to render abroad classification of converters for the biomedical instruments.
3. It provides knowledge of the principle operation and design and the background knowledge of all the hardwires such as amplifiers, filters, converters and interfacing components for designing biomedical instruments and specific applications of biomedical engineering.

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To have adequate knowledge basics of signals and systems.
- It helps to understand the basic definition and classification of continuous time and discrete time signals.
- to study its analysis and its relevance to physiological signal
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To expose the student to gain knowledge on semi conductor devices such as diode, transistor etc.
To understand the analysis of different circuits like amplifier, oscillator etc.

- Teacher: Sindu Divakaran
- Teacher: Dr. P Grace Kanmani Prince
- Teacher: Krishnakumar S
To understand the engineering of genetic material and thereby utilize DNA effectively.
CONTENTS
1. Isolation of genomic DNA from leaf samples - CTAB Precipitation method
2. Estimation of DNA / RNA by UV spectrophotometry
3. Restriction digestion of DNA
4. Construction of restriction map - plasmids
5. DNA ligation
6. Polymerase Chain Reaction - Amplification of DNA of interest/ RAPD
7. Purification of PCR products
8. Southern blotting / Western blotting / northern blotting
9. Cloning of PCR products (competent cell preparation, CaCl2 transformation, blue - white screening of transformants)

- Teacher: Krishnakumar S
- Teacher: Krishnakumar S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To gain in depth knowledge of fundamentals of operational amplifier circuits and to study the various applications using operational amplifiers.
- To discuss filters and circuits and introduce the application of signal conditioning in biomedical field.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the working of linear and non-linear applications of operational amplifiers.CO2 - Analyze waveform generation using operational amplifier.
CO3 - Evaluate the bio filters and isolation circuits used in signal conditioning.
CO4 - Design ADC and DAC using Operational Amplifiers.
CO5 - Examine the construction and working of CMOS and Instrumentation bio amplifiers.
CO6 - Recognize various bio amplifier for Biosignal acquisitions using opamps.
- Teacher: Dr. Bethanney Janney J
SBS1304 - PYTHON PROGRAMMING
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide Basic knowledge of Python
- To learn how to design and program Python applications.
- To learn how to use lists, tuples, and dictionaries in Python programs
Unit I (9 Hrs)
Overview of Programming : Structure of a Python Program, Elements of Python.
Unit II (9 Hrs)
Introduction to Python: Python Interpreter, Using Python as calculator, Python shell, Indentation. Atoms, Identifiers and keywords, Literals, Strings, Operators(Arithmetic operator, Relational operator, Logical or Boolean operator, Assignment, Operator, Ternary operator, Bit wise operator, Increment or Decrement operator).
Unit III (9 Hrs)
Creating Python Programs :Input and Output Statements, Control statements(Branching, Looping, Conditional Statement, Exit function, Difference between break, continue and pass.), Defining Functions, default arguments, Errors and Exceptions.
Unit IV (9 Hrs)
Iteration and Recursion: Conditional execution, Alternative execution, Nested conditionals, The return statement, Recursion, Stack diagrams for recursive functions, Multiple assignment, The while statement, Tables, Two-dimensional tables.
Unit V (9 Hrs)
Strings and Lists: String as a compound data type, Length, Traversal and the for loop, String slices, String comparison, A find function, Looping and counting, List values, Accessing elements, List length, List membership, Lists and for loops, List operations, List deletion. Cloning lists, Nested lists.
Text Books:
- Allen Downey, Jeffrey Elkner, Chris Meyers.How to think like a computer scientist learning with Python / 1st Edition,2012
Useful websites:
- http://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/index.html
- http://interactivepython.org/courselib/static/pythonds
- http://www.ibiblio.org/g2swap/byteofpython/read/
- Teacher: Nagarajan G
- Teacher: Asha P
COURSE OBJECTIVES :
- To provide Basic knowledge of Python
- To learn how to design and program Python applications.
- To learn how to use lists, tuples, and dictionaries in Python programs
- To learn syntax of Python language
- To create dynamic applications in Python
- To implement object oriented concepts using Python
COURSE OUTCOMES:
CO1 - To provide Basic knowledge of Python
CO2 - To learn how to design and program Python applications.
CO3 - To learn how to use lists, tuples, and dictionaries in Python programs
CO4 - To learn syntax of Python language
CO5 - To create dynamic applications in Python
CO6 - To implement object oriented concepts using Python

- Teacher: Nagarajan G
- Teacher: Saravanan M
Big data is a phrase(like software development or testing) which describes about capturing, storing, querying, updating and analyzing of huge data sets that are so voluminous and complex that traditional data-processing application software are inadequate to deal with them.
Course Objectives:
- To understand the basics of Hadoop, MapReduce, Pig Latin
- Gain experience looking at analytics from a strategic perspective


- Teacher: Selvi M
- Teacher: VANATHI M
- Teacher: VELVIZHI R
Course Outcomes
1. Classify and
convert the various types
number system,
simplification of Boolean Functions.
addressing modes.
6. State the inter processor communication and
synchronization.

➢ Knowledge of basic SW engineering methods and practices, and their appropriate application.
➢ A general understanding of software process models, role of project management, different software architectural styles and approaches to verification and validation
To Understand the fundamentals of Object Oriented System Development
To understand the object oriented methodologies.
To use UML in requirements elicitation and designing.
To understand concepts of relationships and aggregations.
To test the software against its requirements specification

- Teacher: Ancy A
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
SBSA3009- NETWORK SECURITY
This network security course covers advanced topics such as Public Key Encryption (with a focus on the RSA algorithm), authentication methods such as message encryption and MACs, intrusion detection techniques such as statistical anomaly and rule-based detection, password management strategies, and virus, worm, and other malware protection. Furthermore, it delves into firewall design ideas, characteristics, and configurations for optimal network security.

- Teacher: Ancy A
- Teacher: Saranya P
- Teacher: Rajeshwary S
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: Thulasibala V
- Teacher: ASWINI B
- Teacher: Jesintha J
SBSA3009- NETWORK SECURITY
This network security course covers advanced topics such as Public Key Encryption (with a focus on the RSA algorithm), authentication methods such as message encryption and MACs, intrusion detection techniques such as statistical anomaly and rule-based detection, password management strategies, and virus, worm, and other malware protection. Furthermore, it delves into firewall design ideas, characteristics, and configurations for optimal network security.

- Teacher: Saranya P
- Teacher: GAYATHRI D
- Teacher: Saranya P
- Teacher: Jesintha J
- Teacher: Dr. TAMILSELVI. P
- Teacher: PALANIMEERA J
- Teacher: RAJESWARI R
- Teacher: PALANIMEERA J
- Teacher: RAJESWARI R
- Teacher: Dr. TAMILSELVI. P
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. To understand about the basic classification and biological significance of carbohydrates.
2. To have insight on structure, classification and properties of aminoacids and to study their impact on organizing the structure of proteins.
3. To recite the categorization, structure and various functions of lipids and nucleic acids.
4. To understand the functional mechanism of interaction between enzyme and substrate.
5. To know the mechanism of enzyme kinetics.
6. To know the vital role of vitamins and minerals

- Dr.L.INBATHAMIZH: Inbathamizh L
The course describes the drug development,manufacture processes and its metabolism. The development of Pharmaceutical products and the regulations governing are detailed.

- Teacher: Ramesh kumar V
Plant biotechnology has emerged as an exciting area of plant sciences by creating unprecedented
opportunities for the manipulation of biological systems.

- Teacher: Prakash P
Genetic engineering is the process of using recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology to alter the genetic makeup of an organism. Traditionally, humans have manipulated genomes indirectly by controlling breeding and selecting offspring with desired traits. Genetic engineering involves the direct manipulation of one or more genes. Most often, a gene from another species is added to an organism's genome to give it a desired phenotype.
- Teacher: Devi B
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
Animal biotechnology lab is used to grab knowledge in the field of animal tissue culture.
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To impart knowledge on the issues related to environment and to emphasize the importance of a clean
environment.

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand biosafety and the importance of bioethics.
To be able to distinguish the different IPR and biotechnological patent
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSAFETY 9 Hrs.
Biosafety – definition, need, importance, applications, levels of biosafety and criteria for biosafety levels. NIH guidelines for
biosafety. Regulations specific to biotechnology companies and research institutions. Biosafety guidelines in India. Role of
institutional biosafety committee.
UNIT 2 IMPLICATIONS OF BIOSAFETY 9 Hrs. Guidelines for research with transgenic organisms. Environmental impact of genetically modified organisms (beneficial and hazardous impact), Field trials with GMO, Containment levels. Biosafety protocol, Cartagena Biosafety protocol, Mechanism of implementation of biosafety guidelines. Biosafety and politics. Biosafety database.
UNIT 3 INTRODUCTION TO BIOETHICS 9 Hrs.
Bioethics – need, applications. Impact of bioethics to the environment and society. Bioethical issues pertaining to various
aspects of Biotechnology. Bioengineering ethics, responsible researchers, research ethics, ethical decision making.
Biowarfare and biopiracy.
UNIT 4 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS 9 Hrs. Forms of Intellectual property – patent, copyright, trademark, design, trade secret, domain name and geographical indications. WTO treaties, GATT articles, main features of TRIPS agreement, practical aspects of WIPO. IPR related legislatures in India.
UNIT 5 PATENT 9 Hrs. History of Indian patent system and law. Patenting authority. Different types of patent. Requirements and procedure for patenting. Patentable and Non-patentable things. Patent search and patent co-operation treaty (PCT). Farmer’s right and plant breeders right. Importance, social consequences and controversies on biotechnology patents. Max.45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of course, student will able to
CO1 - Define biosafety, bioethics and intellectual property rights.
CO2 - Discuss the different regulations pertaining to biosafety.
CO3 - Categorize the various forms of IPR.
CO4 - Appraise the importance of bioethics in biotechnology.
CO5 - Elaborate the different patents and the process of patenting.
CO6 - Interpret biotechnological novelty as patents.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Sateesh M.K., Bioethics and Biosafety, I.K. International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., 2013.
2. Fleming D.O. and Hunt D.L., Biological Safety: Principles and Practices, ASM Press, 2006. 3. Goel D. and Parashar S., IPR Biosafety and Bioethics, Pearson Education India, 2013.
4. Pandey N. and Dharni K., Intellectual Property Rights, PHI Learning, 2014.
5. Singh K.K., Biotechnology and Intellectual Property Rights: Legal and Social Implications, Springer India, 2014.
6. Young T.R., Policy I. and Group G.C., Genetically Modified Organisms and Biosafety: A Background Paper for Decision-makers and Others to Assist in Consideration of GMO Issues. IUCN, 2004.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
Part A: 10 Questions of 2 marks each - No choice 20 Marks
Part B: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Mar
|
DAY |
9-10 |
10-11 |
11.15-12.15 |
LUNCH BREAK |
1.15-2.15 |
2.15-3.15 |
|
Monday |
|
|
BBIPR |
|
|
|
|
Tuesday |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wednesday |
BBIPR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thursday |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Friday |
|
|
BBIPR |
|
|
|
|
Saturday |
BBIPR |
|
|
|
BBIPR |
|
- Teacher: BALASANKAR KARAVADI
- Teacher: oviya R.P
- Teacher: Hartiha S
- Teacher: Jayshree Nellore
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To know the marine organisms of interest in biotechnology, their basic functions and role in the marine
ecosystems; to understand the essential elements related to aquaculture and fish genetics and to acquire
knowledge on marine natural products and fishery by-products; and also, to apply biotechnological methods
for the conservation and protection of marine environment
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of course, student will able to
CO1 - Learn the importance of marine ecosystems and microbial biodiversity
CO2 - Develop the aquaculture practices of marine fish, shrimp, crab, lobster, edible oyster, pearl oyster and seaweeds
CO3 - Device the various fish genetic techniques involved in aquaculture
CO4 - Formulate the production methodologies for economically and pharmaceutically important products from marine
organisms
CO5 - Generate the production strategy of various seaweed and fishery by-products and its applications
CO6 - Evaluate the human impacted pollution in the marine environment and the usage of marine microbes to ameliorate
environmental deterioration

- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
Food processing Technology- explaining the food processing technique by industrial-level methodologies are explained
- Teacher: Jayshree Nellore
- Teacher: Usha Nandhini S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To apply bioinformatics tools in designing novel drugs
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of course, student will able to
CO1 - Provide an overview of the basic concepts of molecular modelling and analyse on the different types of input provided to generate 3D models along with the stability of a model based on the energy of the system
CO2 - Enumerate on the various force fields responsible for the energy of a system and assess the significance of energy minimisation for the stability of a system
CO3 - List out the different aspects of drugs like soft drugs and pro drugs and comprehend the various parameters involved in the solubility of the drugs
CO4 - Summarise the steps involved in the development of drugs and ponder on the important aspects of pharmacophore analysis and lead molecule identification in the process of drug design
CO5 - Describe the docking mechanism and analyse its importance in the development of drugs and thereby understand the nuances involved in the development of drugs
CO6 - Look into the various databases of molecules and analyse them by giving the appropriate input system like
SMILES notation and analyse the three dimensional structures of molecules
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
Introduces the basic principles and calculation techniques used in the field of bio-chemical engineering

- Teacher: Sathish S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
The course provided a deep insight on to the various techniques involved in manipulation of DNA for its
exhaustive use in the field of gene characterization, modification, cloning and transgenesis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to CO1 - Review the methods for analyses of gene expression at different levels CO2 - Evaluate the pros and cons of the different gene mapping techniques CO3 - Describe the methods for silencing the gene expression CO4 - Summarize the application of genetic engineering techniques in the field of medicine and transgenesis CO5 - Comment on the controversies on the use of GMO in Bioremediation, medicine, agriculture etc. CO6 - Examine and evaluate the biosafety regulations and legal issues on the use of GMO

- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
Culturing and maintenance of Plant and Animal tissue culture and its applications are discussed.
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
- Teacher: Bavani latha Muthiah
TOPIC: 1 Introduction to Marine ecosystem and Microbial Diversity
Physical and chemical parameter of sea
zonation of sea
Marine ecosystem and biodiversity
Marine microbial diversity
Marine microbial habitat
Factors that Impact Marine microbial diversity
Interaction between marine microbes and other organisms
Assignment
Quiz
TOPIC: 2 AQUACULTURE
Definition, site selection and construction of aquaculture pond
criteria for selecting the candidate species
Types of aquaculture methods: Extensive, Semi-intensive
Intensive culture, Raft culture, Pond culture.
Culture practices of marine fish: Shrimp, Crab,
Culture practices of marine fish: Lobster, Oyster,
Culture practices of Seaweed
Assignment
Quiz
Topic: 3 Economic Importance Of Marine Organisms
Live feed for marine organisms: Culture of microalgae, rotifers,
Culture of Artermia, Biofuel production
Marine enzymes
Production of omega 3 fatty acid acids from marine organisms
Marine Pharmacology: New and novel antibiotics from marine organisms
Secondary Metabolites from marine bacteria
Secondary Metabolites from marine actinomycetes
Secondary Metabolites from marine endophytic fungi
Prebiotics and Probiotics for aquaculture
Assignment
Quiz
Topic: 4 Fish Genetics and Marine Organisms
Andorgenesis, Gynogenesis,Polyploidy
Artificial Insemination, Eye stalk ablation
Cryopreservation of fish gametes
Marine algal by products: Chitin, Chitosan
Marine algal by products: Agar, Alginates
Marine algal by products: Carrageenan and Heparin
Fishery by products: Fish oil, Isinglass, fish glue
Fishery by products : Fish silage, Fin rays
Assignment
Quiz
Topic: 5 Marine Environment Protection
Human Impacts of Marine Microbial diversity
Usage of marine microbes to ameliorate environmental deterioration
Control of oil spills and bioremediation
Effect of bio-fouling and bio-deterioration on marine structures.
Protection methods against corrosion and fouling
Red tides
Causative factors and effects on the organisms of marine environment
Treatment of Aquaculture effluents
Assignment
Quiz

COURSE OBJECTIVES
To discuss the ethical and safety concerns in the Biotechnology field with respect to Global and Indian standards.
To highlight the current trends and issues of intellectual property rights.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Realize the responsibility and follow ethics in handling experimental animals and biological samples.
CO2 - Understand the need and gain knowledge on biosafety levels and biosafety labs.
CO3 - Analyze the impact of Biosafety regulations and committees on Biotechnology work at National and International levels.
CO4 - Explore the basic principles of Intellectual Property Rights and practices followed.
CO5 - Update knowledge on the legal framework of patents.
CO6 - Demonstrate safe and standard operating procedures for Biotechnology research
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Jayshree Nellore
- Teacher: Prakash P
Food processing Technology- explaining the food processing technique by industrial-level methodologies are explained
- Teacher: Usha Nandhini S
- Teacher: Prakash P
Biochemical Engineering is a branch of chemical engineering that mainly deals with the design and construction of unit processes operations make use of microbial, animal and plant cells and components of cells such as enzymes to manufacture new products and destroy harmful wastes.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Thyagarajan Rajendiran
This subject deals with the basic introduction of chemical industries and equipment used in them. This subject also explains the process involved in separating products from raw materials.

- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
BASICS
OF MATLAB
Starting MATLAB,Help, Simple, Functions, Output, Algebra Vectors, Graphs, Interrupting, Syntax, Suppressing Output, Defining Matrices, Size of Matrix, The Identity Matrix, Specialized Matrices ,Diagonal Matrices, The ,Manipulating Matrices, Matrices, matrix Multiplication, String Arrays, Printing Output,MATLAB Scripting Language: M-File MATLAB Search Path, Path Management, and Startup ,File, Function, Errors.
FORMULATION OF PHYSICAL PROBLEMS
Mathematical statement of the problem, Representation of problems, Formulation on extraction in single & multiple stages, Radial heat transfer through a cylindrical conductor, salt accumulation in stirred tank.
INITIAL VALUE PROBLEMS
Initial value problems for ordinary differential equations-Euler’s method, Trapeziodal method, Runge Kutta methods for second and fourth order , interpolation, Newton-cotes integration, Gaussian quadrature.
NUMERICAL OPTIMIZATION AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES
Methods for constrained and unconstrained optimization- Lagrangian methods, Simplex, Newton line search method, Trust region Newton method, Single response linear regression, least square regression, Applications- Fitting a kinetic rate law to time dependent data.
BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS
Introduction to boundary value problems, shooting method, finite difference method, finite volume method, finite element method. Applications of BVP-Chemical reaction and diffusion in a spherical catalyst, finite differences for a convection, diffusion equation.

- Teacher: Venkatesan D
Chemical reaction engineering is that engineering activity concerned with the exploitation of chemical reactions on a commercial scale.
Its goal is the successful design and operation of chemical reactors, and probably more than any other activity it sets chemical engineering apart as a distinct branch of the engineering profession.
Pillars of the temple of chemical reaction engineering

Comprises Optimization Procedure, Methods of optimization, identifying objective and continuous functions, analyzing constrained and unconstrained limit values, employing numerical methods to solve the optimization problems and finally applications of optimization technique to solve chemical engineering problems.
Optimization is an act of achieving the best possible solution for a given problem.
involves objective functions. constraints with equality and inequality symbols,
techniques to solve the equality and inequality constraints, solving the optimization problems through various numerical and analytical methods
application of optimization in chemical engineering process plants
- Teacher: Sathish S
COURSE OBJECTIVE
- Exposing to the techniques and capabilities in MATLAB will enhance your ability to use computing tools and
languages to solve engineering problems

- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
Chemical Engineering Process Simulation is ideal for students, early career researchers, and practitioners, as it guides you through chemical processes and unit operations using the main simulation software’s that are used in the industrial sector. Users can model and simulate chemical reactions, focusing on thermodynamics, equilibrium, kinetics, and acid–base titrations, with accompanying virtual lab exercises.
Applications for this include design studies, engineering studies, design audits, debottlenecking studies, control system check-out, process simulation, dynamic simulation, operator training simulators, pipeline management systems, production management systems. Steady state, Fluid flow and Dynamic process simulator.
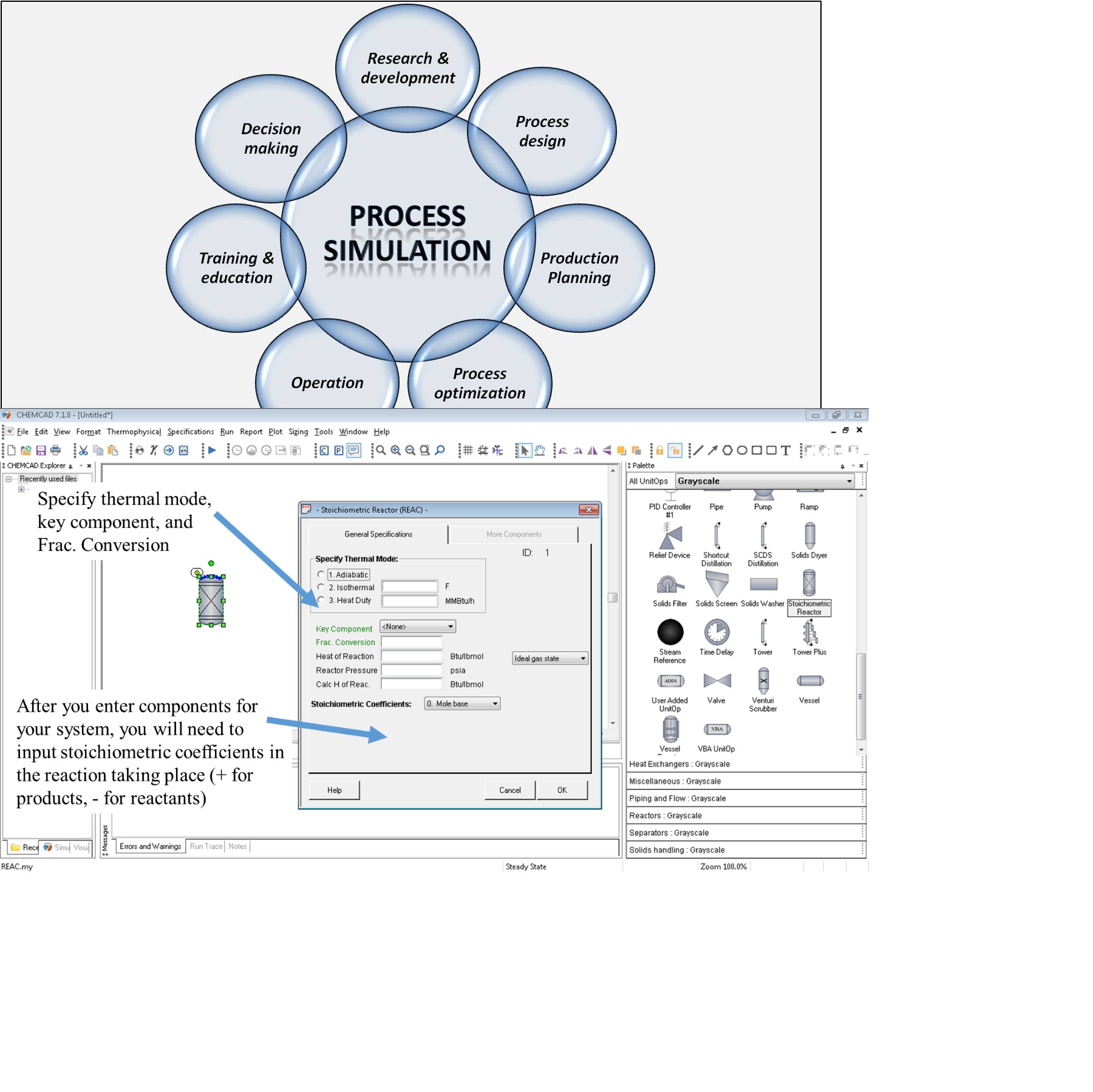
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, civil, chemical and biomedical engineering, geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology.
- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, civil, chemical and biomedical engineering, geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
Fundamental concepts, Units and Dimensions, gas relationship, molarity, molality, normality, partial pressure, pure volume and the related calculations. fundamental concepts of material balance. Material balance in various unit processes and unit operations. Material balance with chemical reactions Energy balance related to various process equipment. Calculation of standard heat of reaction from the heat of formation and heat of combustion, thermochemistry, energy balance in various unit operations, the heat of solutions, the heat of neutralization etc. Fuels and combustion calculation, proximate and ultimate analysis, adiabatic reaction temperature, air to fuel ratio, complex processes calculation.

As chemical engineers, this course will be helpful to understand the processes technologies of various organic and inorganic process industries for manufacturing chemicals and associated troubleshoot. This will give powerful approach in designing new process and product development.

- Teacher: Annam Renita A
Plant Design
Economics Introduction
Time value of money
Depreciation
Balance sheet and income statements

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
The subject deals with transport processes involved in fluid flow acquiring momentum, heat and mass flux. The subject also involves the Kinetics for microbial growth and measurement of the associated parameters through various kinetic models. Also the kinetic diffusion strategies is demonstrated using various equations and measurement techniques. Momentum, heat and mass transport share a very similar mathematical framework for fluid flow processes and the similarities between them are exploited to provide a deep understanding in microbial kinetic evaluations through different model equations.
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
The study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems.
- Teacher: Sathish S
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
Energy engineering or Energy Systems Engineering is a broad field of engineering dealing with energy efficiency, energy services, facility management, plant engineering, environmental compliance, sustainable energy and renewable energy technologies.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: GokulNath R
Energy engineering is a broad field of engineering dealing with energy efficiency, energy services, facility management, plant engineering, environmental compliance, sustainable energy and renewable energy technologies. Energy engineering is one of the more recent engineering disciplines to emerge.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
- Teacher: Karthikeyan M
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
To acquire basic understanding of concepts and laws of thermodynamics, volumetric properties of fluids and
thermodynamic properties of fluids
- Teacher: Annam Renita A
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
Fundamental concepts, Units and Dimensions,gas relationship, molarity, molality, normality, partial pressure, pure volume and the related calculations. fundamental concepts of material balance. Material balance in various unit processes and unit operations. Material balance with chemical reactions Energy balance related to various process equipment. Calculation of standard heat of reaction from the heat of formation and heat of combustion, thermochemistry, energy balance in various unit operations, the heat of solutions, the heat of neutralization etc. Fuels and combustion calculation, proximate and ultimate analysis, adiabatic reaction temperature, air to fuel ratio, complex processes calculation.

- Teacher: Venkatesan D
The science of thermodynamics deals with energy and its transformation. It tells us about the direction in which changes take place in nature. It also determines the conditions under which a proposed change attains a state of equilibrium.
We have seen that the thermodynamic properties of homogeneous pure substances depend only on the state of the system. The relationships developed for pure fluids are not applicable to solutions and need modification. The thermodynamic properties of solutions and heterogeneous systems consisting of more than one phase are influenced by the addition and removal of matter. The term solution includes homogeneous mixtures of two or more components in the gas, liquid or solid phase. The pressure, temperature and the amount of various constituent’s present determine the extensive state of a solution; and pressure, temperature and composition determine the intensive state. We discuss how the thermodynamic properties of a solution are determined and introduce certain concepts that are essential to the study of phase equilibria and chemical reaction equilibria.

- Teacher: Venkatesan D
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes.
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation.

- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
In a scientific sense, a chemical process is a method or means of somehow changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds. Such a chemical process can occur by itself or be caused by an outside force, and involves a chemical reaction of some sort. In an "engineering" sense, a chemical process is a method intended to be used in manufacturing or on an industrial scale (see Industrial process) to change the composition of chemical(s) or material(s), usually using technology similar or related to that used in chemical plants or the chemical industry.
- Teacher: Prabu Deivasigamani
- Teacher: Eshanthini P
HIGHWAY DEVELOPMENT, PLANNING AND ALIGNMENT
MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION PRACTICE
PAVEMENT DESIGN
PAVEMENT EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT

- Teacher: Dr.V.Sampathkumar .

- Teacher: Padmapriya R
- Teacher: Eshanthini P
- Teacher: Eshanthini P
- Teacher: Vanjinathan J
- Teacher: Eshanthini P

Cost accounting is a platform that help to control the cost elements and manage the activity to get the best result by adopting the techniques of costing.

- Teacher: Murthy CMA
- Teacher: MUTHUVALAVAN R
Course Objective
1. To impart basic knowledge of the important business legislation.
2. To comprehend the laws relating to business.
3. To provide awareness on consumer protection.
- Teacher: Rajeswari A
- Teacher: Princy A.S
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: Pujaa D
- Teacher: DR. GANANATH KHILLA
- Teacher: Deepa M
- Teacher: Chinta Shriya
- Teacher: Princy A.S
- Teacher: YASMEEN BANO
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: UMAMAHESWARI S
- Teacher: SANDHYA V
- Teacher: Meera A
- Teacher: Indra Refline Missier C
- Teacher: Lakshmi C
- Teacher: Kaavya K
- Teacher: Sairamya K
- Teacher: JAYASEELY M
- Teacher: NAMASIVAYAM SHEEBA
- Teacher: Priyanka T
- Teacher: Yuvaraj R
- Teacher: KRISHNASWAMI V
- Teacher: JAYASEELY M
To learn the python programming language that can be used for a wide variety of programming tasks and to expose the student to the language.
At the end of the course, the student will be able to develop adequate programming skills to implement various applications using built-in types in python

- Teacher: Kabitha R.J
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi S
- Teacher: Dhanalakshmi S
- Teacher: VELUMONI D
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
Objectives
- Understand the division of network functionalities into layers.
- Be familiar with the components required to build different types of networks.
- Be exposed to the required functionality at each layer.
- Learn the control and congestion control algorithms.
Teacher: Dr. BHARATHI.M.L
T

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
- Teacher: Bharathi M L
- Teacher: Lalithakumari S
The course gives you an overview for programming using C language and also foundation of Data structures using C

- Teacher: Barani S
• Understand and implement the most popular learning algorithms.
• Perform feature selection and experimental set up on real tasks
• Analyze in detail about unsupervised learning, dimensionality concepts and neural networks.
• Evaluate multiple learning algorithms across several Robotic tasks

- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To Implement basic encryption and decryption Techniques.
➢ To Implement discreate logarithm problems.
➢ To understand the concepts of public key Encryption.
➢ To Implement various Identification Protocol.
➢ To Implement different Signature Scheme.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Understand the basic concepts of Encryption and Decryption Techniques.
CO2: Remembering the concepts of Polynomial.
CO3: Able to implement the public key encryption
CO4: Understand the concepts of attacks using hash methods
CO5: Apply the concepts of identification protocol
CO6: Able to apply and implement various signature scheme

- Teacher: RAJASHREE S
- Teacher: DHARANI V
- Teacher: Sivasangari A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand why Python is a useful scripting language for developers and learn how to design and program Python
applications.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1-Describe the Numbers, Math functions, Strings, List, Tuples and Dictionaries in Python.
CO2-Do the decision Making and write functions in Python.
CO3-Explain how to design GUI Applications in Python and evaluate different database operations.
CO4-Design and develop Client Server network applications using Python.
CO5-Ability to design real life situational problems and think creatively about solutions of them.
CO6-Apply the best features of mathematics, engineering and natural sciences to program real life problems.

- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To learn the fundamentals of PST and methodologies which are essential for building good C/C++ programs.
Ø To demonstrate a thorough understanding of modular programming by designing programs which require the use of programmer-defined functions.
Ø To impart the knowledge about pointers which is the backbone of effective memory handling
Ø To demonstrate adeptness of object oriented programming in developing solutions to problems demonstrating usage of data abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance.

- Teacher: SANDHIYA B
- Teacher: ANU BARATHI
- Teacher: Geetha C
- Teacher: hemalatha c
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: MURALI E
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: Joan Niveda J
- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: NAFEES MUNEERA M
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Vaishnnave M P
- Teacher: JEMSHIA MIRIAM
- Teacher: Umasankari N
- Teacher: USHA N S
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: SANTHIYA P
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Gomathi R M
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: Srividhya S.R
- Teacher: Nirmalrani V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand number systems and codes.
➢ To illustrate simplified Boolean expressions using Gates.
➢ To construct combinational logic circuits.
➢ To design sequential logic circuits.
➢ To analyze circuits and latches.
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
- Teacher: Ramya D
- Teacher: Ravi Kumar D N S
- Teacher: Barnabas Paul Glady J
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Poonguzhali S
- Teacher: GOMATHI T
- Teacher: VINO T
Programming in c and c++ is a high level language.

- Teacher: Sundar Rajan G T
- Teacher: Sivagami P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. To learn the fundamental programming concepts and methodologies which are essential to building good C/C++ program.
2. To demonstrate a thorough understanding of modular programming by designing programs which require the use of programmer-defined functions.
3. To impart the knowledge about pointers which is the backbone of effective memory handling.
4. To demonstrate adeptness of object oriented programming in developing solutions to problems
demonstrating usage of data abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Develop simple applications in C using basic constructs.
CO2 - Design and Implement applications using arrays and strings.
CO3 - Develop and Implement applications using memory allocation and File concepts.
CO4 - Use proper class protection to provide security.
CO5 - Describe the reusability of code through Inheritance.
CO6 - Demonstrate the use of virtual functions to implement polymorphism.

Data Structures in C are used to store data in an organised and efficient manner. The C Programming language has many data structures like an array, stack, queue, linked list, tree, etc. A programmer selects an appropriate data structure and uses it according to their convenience.
Data Structure in C Programming Language is a specialized format for organizing and storing data. In General data structure types include the file, array, record, table, tree.. etc.
- Array: Array is collection of similar data type, you can insert and deleted element form array without follow any order.
- Stack: Stack work on the basis of Last-In-First-Out (LIFO). Last entered element removed first.
- Queue: Queue work on the basis of First-In-First-Out (FIFO). First entered element removed first.
- Linked List: Linked list is the collection of node, Here you can insert and delete data in any order.
- Tree: Stores data in a non linear form with one root node and sub nodes.
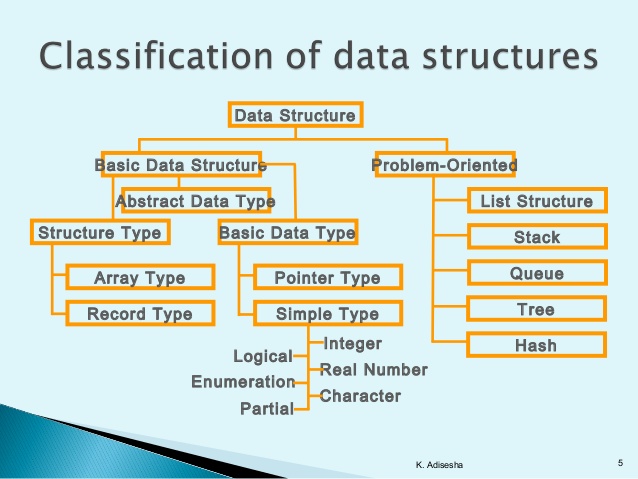
- Teacher: Nirmalrani V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- Software process models and compare their applicability.
- Identify the key activities in managing a software project.
- Concepts of requirements engineering and Analysis Modelling.
- Apply systematic procedure for software design and deployment.
- Compare and contrast the various testing and maintenance.
- Teacher: Pravin A
- Teacher: Ronald Tony A
- Teacher: Yovan Felix A
- Teacher: hemalatha c
- Teacher: Deepa D
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: Albert Mayan J
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Kamalesh Murari Devakannan
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: Aroul Canessane R
- Teacher: Shalini R
- Teacher: Vignesh R
COURSE OBEJCTIVES
• To understand the technologies behind the embedded computing systems
• To acquire knowledge about microcontrollers embedded processors and their applications
• To analyze and develop software programs for embedded systems
• To have knowledge about the working of a microcontroller system and its programming in assembly language
• To provide experience to integrate hardware and software for microcontroller application systems

- Teacher: Sathya K B
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
· To understand the concepts of Internet of Things
· To identify the various elements of an IoT System.
· To understand the various means of communication from Node / Gateway to Cloud Platforms.
· To transfer data from IoT devices to various cloud providers.
· To make students aware of various domain specific applications and challenges while implementing IoT solutions.
- Teacher: Menaka D
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand the fundamentals of Object Oriented System Development.
➢ To understand the object oriented methodologies.
➢ To use UML in requirements elicitation and designing.
➢ To understand concepts of relationships and aggregations.
➢ To test the software against its requirements specification.
- Teacher: Pravin A
- Teacher: SATHIYARAJ A
- Teacher: Yovan Felix A
- Teacher: Ruby Angel
- Teacher: Deepa D
- Teacher: NANCY KIRUPANITHI D
- Teacher: SUBATHRA G
- Teacher: Albert Mayan J
- Teacher: Refonaa J
- Teacher: Dr T Prem Jacob
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: Lakshmanan L
- Teacher: DHARANI M.K.
- Teacher: Kamalesh Murari Devakannan
- Teacher: USHA N S
- Teacher: Abirami R
- Teacher: Aroul Canessane R
- Teacher: Vignesh R
- Teacher: Gomathi R M
- Teacher: Gayathri S
- Teacher: Gowri S
- Teacher: HEMALATHA S
- Teacher: Srinivasulu Senduru
- Teacher: Anandhi T
SCSA1503 - COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To introduce two and three dimensional graphical structure.
- To design 2D and 3D methods and Models.
- To explore the visible surface detection with illumination and color models.
- To understand the concepts involved in multimedia and basis tools.
- To gain knowledge on Multimedia compression and animations.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1 : Identify the various line and circle drawing algorithm.
CO2 : Study the various transformations in 2D and 3D objects.
CO3 : Understand the concepts of curves and surface.
CO4 : Apply transformation and clipping algorithm in 2D and 3D objects.
CO5 : Design Illumination and color models.
CO6 : Implement 2D and 3D Transformation concepts in Real world Applications
SYLLABUS
UNIT 1 BASICS OF COMPUTER GRAPHICS 9 Hrs.
Output primitives- Survey of Computer Graphics- Overview of Graphics System- Line drawing Algorithm (DDA Line Drawing Algorithm, Bresenhams Line Drawing Algorithm)-Circle drawing Algorithm- Curve Drawing Algorithm- Attributes of output Primitives- Antialiasing.
UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 8 Hrs.
2D Transformation and other transformation – 2D and 3D Viewing- Line Clipping(Cohen Sutherland)– Polygon Clipping (Sutherland Hodgeman) – Logical Classification Input Function.
UNIT 3 3D CONCEPTS AND CURVES 10 Hrs.
3D Object: Representation Method- B-Rep- Sweep Representation- 3D Transformation – curve generation – Splines – Beziers – Blending of curves other interpolation techniques- Display Durves and Surface – Shape Description Requirements – Parametric function – 3D Concept Introduction – Fractals and Self Similarity – Successive refinement of Curves – Koch Curves and Paeno Curves
UNIT 4 METHODS AND MODELS 8 Hrs.
Visual Surface detection methods – Illumination models – Halftone Patterns – Dithering Techniques – Polygon Rendering Methods – Ray Tracing Methods – Color methods – Color Applications.
UNIT 5 MULTIMEDIA BASICS AND TOOLS 10 Hrs.
Multimedia Basics and Tools – Introduction to Multimedia – Compression and Decompression – Data and File Format Standards – Digital voice and audio video image animation- Introduction to photoshop- workshop tools- Navigating window – Importing and Exporting Images – Operations on Images – resize, Crop, rotate. Introduction to Flash – Elements of Flash Documents – Flash Environment- Drawing Tools – Flash Animation Importing and Exporting – Adding Sounds – Publishing Flash Movies.
Max. 45 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics C Version, 2 nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006.
2. Fabio Ganovelli, Massimiliano Corsini, Sumanta Pattanaik, Marco Di Benedetto “Introduction to Computer Graphics: A Practical Learning Approach” Taylor and Frainces Group. 2015.
3. Tay Vaughan ,”Multimedia”, 5th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2001.
4. Ze-Nian Li, Mark S. Drew ,”Fundamentals of Multimedia”, Prentice Hall of India, 2004.
5. D.P. Mukherjee , “Fundamentals Of Computer Graphics And Multimedia ” Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, 2006.
6. D. McClelland, L.U.Fuller, ”Photoshop CS2 Bible”, Wiley Publishing, 2005
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: SundaraVelarani K
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: DEVIPRIYA M
- Teacher: SANTHIYA P
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: AMSHAVALLI R S
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: sageengrana s
- Teacher: NITHYA SEKAR
- Teacher: Anandhi T
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Describe and discuss constraints unique to wearable and ubiquitous computing platforms and applications
Design, develop and evaluate a wearable computing application, Apply state-of-the-art hardware and software development tools to computer system design
Communicate both orally and in writing with other members of a team.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 :Understand advanced and emerging technologies
CO2 :Extend the knowledge achieved and apply it to solve real world problems
CO3 :Understanding of different methodologies for research on wearable technology
CO4 : Ability to analyse ethical issues related to the Wearable devices
CO5 : To contribute innovative thinking and innovation processes
CO6 : Ability to integrate several domain through wearable technology
- Teacher: Viji Amutha Mary A
CO1:Address the challenges in Conventional System and to deal with missing and incomplete data.
CO2: Understand the various phases of Data Analytic Lifecycle and its influence over Business Models.
CO3: Analyse distinct techniques for Classification and Clustering.
CO4: Apply the principles of Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic towards advanced data analytics.
CO5: Synthesize knowledge to address Streaming Data Models and Computing.
CO6: Design and Build Real Time Applications with Streaming Data Model

- Teacher: Sethuraman .
- Teacher: GEETHANJALI D
- Teacher: Saravanan M
CO1 : Comprehend machine learning solutions to classification, regression and clustering problems
CO2 : Understand the strengths and weaknesses of many popular machine learning approaches.
CO3 : Interpret the results of the algorithms.
CO4 : Select suitable model parameters for different machine learning techniques.
CO5 : Design algorithms for real world problems using machine learning algorithm.
CO6 : Gain experience of doing independent study and research.

- Teacher: Dr. Santha Sheela A C
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Mary Gladence L
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: Mercy Paul Selvan Paul selvan
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: LAKSHMI PRIYA S
- Teacher: Revathy S
- The Objectives of this course is to explore the principles, algorithms, and data structures involved in the design and construction of compilers. Compiler Design will teach students the fundamental concepts and techniques used for building a simple compiler.
- The course will introduce the theory and tools that can be employed in order to perform syntax-directed translation of a high-level programming language into an executable code.
- This course includes context-free grammars, lexical analysis, parsing techniques, symbol tables, error recovery, code generation, and code optimization.
- At the end of the course, students will understand different considerations and phases of compilation, the impact of language attributes upon the compilation process, the effect of hardware feature on the generated code and the practical fundamentals of compiler implementation.

- Teacher: Mary Posonia A
- Teacher: Ankayarkanni B
- Teacher: Usha Nandini D
- Teacher: Gopika G S
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Selvi M
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Yogitha R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ Identify the problem.
➢ To analyse the various steps in program development.
➢ Evaluate and select the best algorithm to solve the problem.
➢ Deploy suitable methods to get the desired output.
➢ Create the solutions for various Real-World Problems

- Teacher: Geetha C
- Teacher: NAFEES MUNEERA M
- Teacher: SANKARI M
- Teacher: Anto Praveena M D
- Teacher: Vaishnnave M P
- Teacher: Ajitha P
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Yogitha R
- Teacher: Anandhi T
- Teacher: GOWRI MANOHARI V
- Teacher: Nirmalrani V
- Teacher: RAMALAKSHMI D
- Teacher: Jabez J
- Teacher: Vaishnnave M P
- Teacher: Ramya Franklin G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the concepts of Procedure Oriented Programming.
To handle conditional and Looping Statements in different scenarios.
To learn and employ concepts of ADTs.
To apply Linear Data Structures – lists, stacks, and queues in real time applications.
To apply concepts of Non Linear Data structures namely Trees and Graphs.
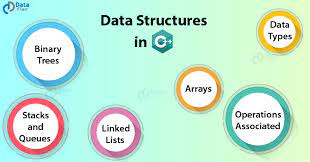
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: SAROJINI PREMALATHA J
- Teacher: Dr.Sridevi N

- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: Devi D
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: VANATHI M
- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: Veena K
- Teacher: RAJASHREE S
- Teacher: MERLIN MARY JENITHA
- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: SARASWATHI S
- Teacher: Jayanthi S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To provide the knowledge of simulation tools for security in IoT.
➢ To familiarize students with different tools for cyber security.
➢ To provide knowledge of deployment of tools for secure data storage.
➢ To capable of using different access control techniques for security in cloud.
➢ To implement the intrusion detection techniques for security in cloud.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand how to implement socket programming.
➢ To be familiar with simulation tools.
➢ To understand how to create applications using TCP and UDP.
➢ To gain Knowledge on various networking protocols.

- Teacher: Suji Helen L
- Teacher: DR.RAJALAKSHMI R
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: Jayanthi S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To configure Big Data Ecosystem.
➢ To work with No SQL Databases.
➢ To process job scheduling.
➢ To analyze and Interpret Data.
➢ To visualize the data insights.

- Teacher: Nagarajan G
- Teacher: DEVIPRIYA M
- Teacher: JEMSHIA MIRIAM
- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: Mercy Paul Selvan Paul selvan
- Teacher: NANCY NOELLA R S
- Teacher: Dhamodaran S
- Teacher: Prayla Shyry S

- Teacher: Annie Michael A
- Teacher: Parveen Akhther A
- Teacher: SAROJINI PREMALATHA J
- Teacher: Sundar R
- Teacher: Nandini S
- Teacher: Malathi V
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquaint students with core knowledge in visual information processing and learning.
CO2 - Implement Digital Image Processing Mechanisms.
CO3 - Analyze and design Digital Image Generation Mechanisms.
CO4 - Representation of geometry and subdivision methods.
CO5 - Describe the Learning Methods in Vision.
CO6 - Comprehend the concepts related three dimensional object representations
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To gain an understanding of how managers use business analytics to formulate and solve business problems and to support managerial decision making.
- To understand the different basic concept / fundamentals of business statistics.
- To become familiar with the processes needed to develop, report, and analyze business data.

- Teacher: Rajeswari G
To learn linear and non linear programming problem.
To understand the concept of queuing model, simulation and decision theory
- Teacher: MOHAMED ISMAIL A
Ø To understand the concept of Internet of Things.
Ø To identify the various elements of an IoT System.
Ø To understand the various means of communication from Node / Gateway to Cloud Platforms.
Ø To understand Cloud Computing & its relevance in IoT.
Ø To identify types of data analytics and data visualization tools.
Ø To make students aware of security concerns and challenges while implementing IoT solutions.
- Teacher: Subhashini R
Greetings of the Day !!!
Green computing, also called green technology, is the environmentally responsible use of computers and related resources.
The goals of Green computing is to manage the power and energy efficiency, choice of eco friendly hardware and software, and recycling the material to increase the product's life. The term Green computing came into existence with the launch of Energy Star program in 1992 by U.S environmental protection agency.
This means that the main benefits of green computing are: reduced environmental impact lower energy costs. longer lasting computing devices. Reduced health risk for computer workers and recyclers.
Join Together Virtually !! We will Learn More !!!
"Stay Home ; Stay safe ;Learn more"" Nothing is Impossible"

COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand and analyze some fundamental data structures, such as binary search trees, disjoint sets, and
self-adjusting lists.
Ø To understand the implementation and complexity analysis of fundamental algorithms such as RSA, primality
testing, max flow, discrete Fourier transform.
Ø To know about algorithmic issues in a variety of areas, including linear programming and game-theory.
Ø To understand and implement linear and non linear data structures in real time.
Ø To analyze the design of algorithms using various performance metrics.
SUGGESTED LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Polynomial Differentiation.
2. Printing the node details level wise.
3. Searching the given element from N*N matrix using Binary search.
4. Knapsack Problem using Greedy Method.
5. Traveling salesman Problem.
6. Binary Tree Traversal.
7. Implementing RED BLACK Trees.
8. Minimum Spanning Tree using KRUSKAL’S Algorithm.
9. Minimum Spanning Tree using FLOYD – WARSHALL Algorithm.
10. Implementing Splay trees.
11. Implementing quad trees.

- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: RAJASHREE S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1.To identify the different technologies and different platforms in IoT
2.To understand how to use sensors and actuators for design of IoT.
3.To learn different protocols used in IOT.
4.To learn the concepts of smart city develop

- Teacher: Sivasangari A
- Teacher: Suji Helen L
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To explore the aspects of classic and public key cryptography.
- To acquire knowledge on standard algorithms used to provide confidentiality, integrity and authenticity.
- To become aware of system security components.
- To know the technological aspects of security. ÿ To explore the vulnerabilities in any computing system.

- Teacher: NANTHINI N
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the various means of communication from Node / Gateway to Cloud Platforms.
To transfer data from IoT devices to various cloud providers and create awareness of various domain specific applications.
To familiarize with the sensors, drive system, control systems and design a robot work cell for
an industrial application.
On Completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand general concepts and recognize various devices, sensors and applications.
CO2 - Analyze various M2M and IoT architectures and design issues in IoT applications.
CO3 - Select the appropriate type of tools and grippers for various applications.
CO4 - Design a robotic arm and to bring a controlled movement in the end effectors.
CO5 - Ability to design robot work cell.
CO6 - Develop robots for real life situational problems and think creatively for solutions.
- Teacher: Nivedha R
- Teacher: Naresh Kumar Thapa
- Teacher: Umasankari N
- Teacher: NANTHINI N
- Teacher: Umasankari N
SCSB1611 COMPUTATIONAL
INTELLIGENCE
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To study the basic principles of fuzzy logic and fuzzy operators.
To understand the concept of fuzzy logic controller and its applications.
To comprehend the concepts of swarm intelligence algorithms.
To study and analyse various methodologies for training multi-layer network.
To acquire knowledge about SOM and special networks.
To illustrate the concepts of Genetic Algorithms& Evolutionary strategies.
UNIT 1 FUZZY LOGIC INTELLIGENCE 9 Hrs.
Classical set- operations and properties -Fuzzy Set-operations and properties-problems, Classical
Relations-Operations and Properties, Fuzzy Relations-Operations and Properties -Compositions-Maxmin, Max-Product-Problems, Membership function- features of membership functions-types, α cuts,
Linguistic Hedges.
UNIT 2 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL SYSTEM 9 Hrs.
FLCS- Fuzzy logic control system-Need for FLCS-Assumptions in FLC design. Fuzzification –
Defuzzification. Fuzzy decision making, Fuzzy Rule Based System- Knowledge Base System. Mamdani
and sugeno FLC architectures, Introduction to ANFIS- Architecture. Fuzzy cognitive maps. Applications
- speed control of induction motor, automatic train control.
UNIT 3 SWARM INTELLIGENC 9 Hrs.
Introduction – Particle swarm optimization algorithm – Bat algorithm and its variants – Artificial Fish swarm
optimization algorithm – Cockoo search algorithm and its variants – Firefly algorithm and its variants –
Flower pollination algorithm – Artificial Bee colony optimization algorithm – real world applications of
swarm intelligence algorithms.
UNIT 4 MULTILAYER AND ADAPTIVE ARCHITECTURES 9 Hrs.
BPN-Algorithm, Application, CPN-Training, Applications, Mexican Hat, Kohonan SOM, vector
quantization, - Associate memory - Bidirectional Associative Memory (BAM) - Architecture – Hopfield –
Discrete & Continuous types, Algorithm- Energy function, Adaptive Resonance Theory - ART1, ART2-
training. Probabilistic neural network, Applications - Fault diagnosis, Motion control in robo

- Teacher: Ashok Kumar K
- Teacher: KALAIVANI A
- Teacher: Saravanan D
- Teacher: Sheema D
- Teacher: DAPHINE DESONA CLEMENCY C A
- Teacher: VINOTHINI E
- Teacher: Muthulakshmi A
- Teacher: Dr. Usama Abdur Rahman
- Teacher: GEETHANJALI D
- Teacher: Sonia Jenifer Rayen
- Teacher: BALAPRIYA S
- Teacher: G Kalaiarasi
- Teacher: Selvi M
This
course enables the students to understand the second and third laws of
thermodynamics and their applications; the concepts and applications of
electromotive force; the kinetics and mechanisms of chemical reactions; about
adsorption, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis and the laws and kinetics
of photochemical reactions.

- Teacher: Krithiga T
SCYA1102- ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY (CSE SPECIALIZATION,ECE, EEE, MECH, MECHATRONICS, AUTO, AERO, CIVIL)
This course is designed for the budding engineers to understand the significance of chemistry which forms the basic foundation of engineering. The course comprises of five units dealing with all the aspects of material science. Bonds to bands explains the fundamentals involved in the bond formation to the band theory of materials which finds significant applications in engineering. Molecular spectroscopy involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with materials in order to produce an absorption pattern from which structural or compositional information can be deduced. Functional materials deal with charge transport carriers such as soliton, polaron and bipolaron in conducting polymers that are utilized in engineering molecular devices. Carbon materials emphasize the structure, properties, production of fullerenes, graphene, CNT’s and their applications in the field of health, stealth and energy. Engineering materials covers the importance of Phase rule, Fuels and nanoparticles in the engineering and medicinal field.
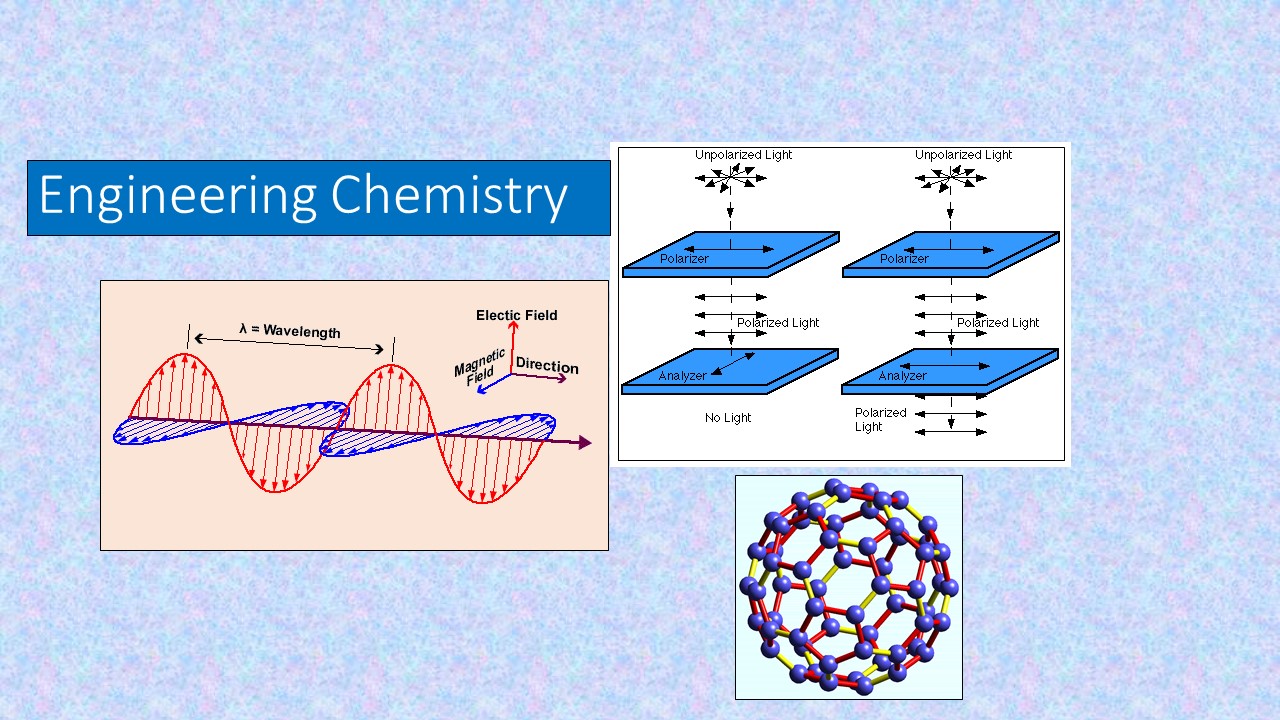
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Supriya S
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Anand T
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Kavitha V
This course is designed for the budding engineers to understand the significance of chemistry which forms the basic foundation of engineering. The course comprises of five units dealing with all the aspects of material science. Bonds to bands explains the fundamentals involved in the bond formation to the band theory of materials which finds significant applications in engineering. Molecular spectroscopy involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with materials in order to produce an absorption pattern from which structural or compositional information can be deduced. Functional materials deal with charge transport carriers such as soliton, polaron and bipolaron in conducting polymers that are utilized in engineering molecular devices. Carbon materials emphasize the structure, properties, production of fullerenes, graphene, CNT’s and their applications in the field of health, stealth and energy. Engineering materials covers the importance of Phase rule, Fuels and nanoparticles in the engineering and medicinal field.
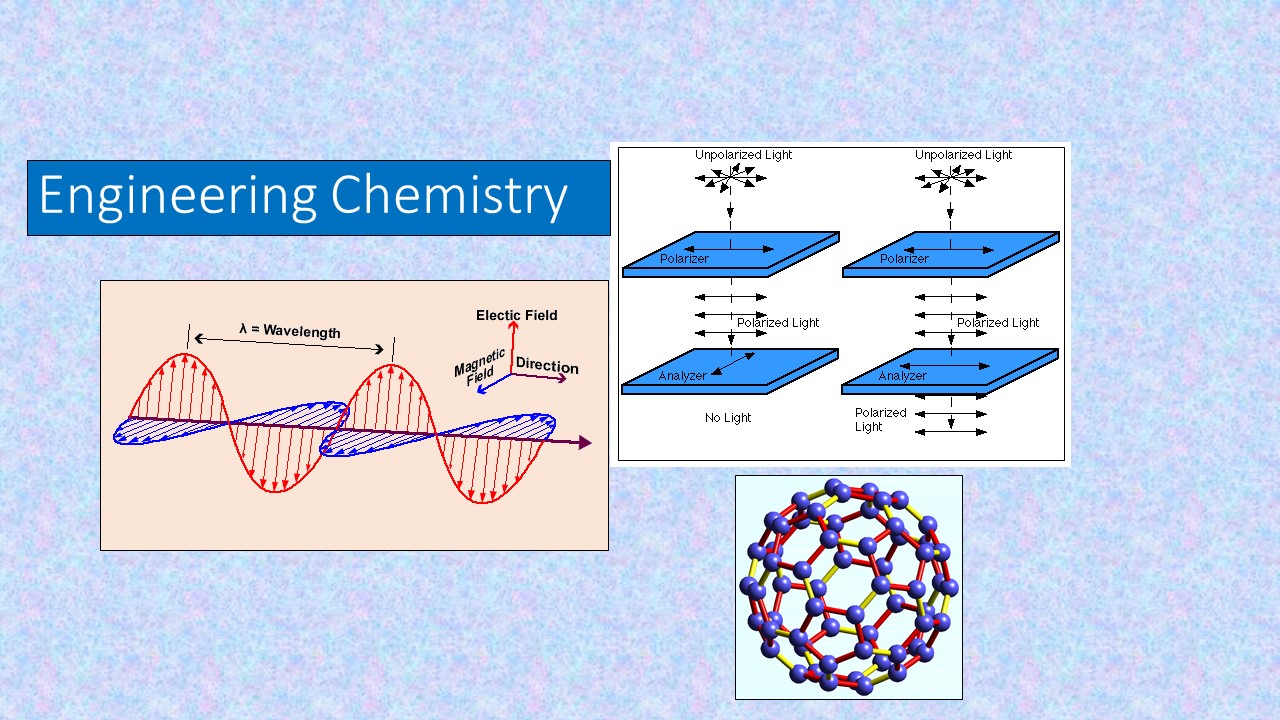
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Supriya S
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for under graduate students in chemistry to give an insight into the general aspects of organic reactions. The students will be able to understand the significance of functional groups, reactivity of the compounds and the types of reactions. On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1: Analyze the structure and reactivity of aromatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon
CO2: Apply the nucleophilic substitution and elimination mechanism of alkyl and aryl halides
CO3: Examine the structure and reactivity of alcohols and phenols
CO4: Examine the physical and chemical properties of ethers and epoxides
CO5: Apply the nucleophilic addition and electrophilic substitution mechanism to carbonyl compounds
CO6: Evaluate the basic concept of chemistry to real world applications
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is intended for undergraduate students in chemistry with an insight into organic compounds preparations and synthesis. The course will provide a platform in understanding the molecular rearrangements which pave way in their industrial applications. At the end of the course, the participants will be able to
To understand the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds containing O, N, S.
To synthesize the carboxylic acids along with their reactivity nature.
To develop the practice of learning molecular rearrangements along with their mechanism.
To discuss the importance of active methylene groups in organic synthesis.

- Teacher: Subhenjit Hazra .
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course is framed for undergraduate chemistry students to bridge the conceptual ideas in analytical chemistry with practical experiment for better understanding. The course will create a platform for the students to undergo hands-on training in preparing the solutions with safe handling of chemicals and glasswares. The course promotes analytical skills among the students in quantitative and qualitative analysis. At the end of the course, the students will be able to
Acquire analytical skills in handling equipments , glassware and chemicals.
Compile, Analyze and interpret the volumetric data for calculation with greater accuracy and precision.
The course is framed for undergraduate chemistry students to bridge the conceptual ideas in analytical chemistry with practical experiment for better understanding. The course will create a platform for the students to undergo hands-on training in preparing the solutions with safe handling of chemicals and glasswares. The course promotes analytical skills among the students in quantitative and qualitative analysis. At the end of the course, the students will be able to
Acquire analytical skills in handling equipments , glassware and chemicals.
Compile, Analyze and interpret the volumetric data for calculation with greater accuracy and precision.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Jyoti Gahtori
- Teacher: Anand T
- Teacher: Krithiga T
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Ramanjaneya Reddy G
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course will give an insight in understanding the strategies involved in designing a chemical reaction. and highlights the importance of oxidizing and reducing agents in functional group conversion reactions. It provides an platform in understanding the name reactions and molecular rearrangement in organic chemistry. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1) Construct a single step retrosynthetic pathway for organic reaction.
2) Interpret and design the products in organic chemical reactions.
3) Formulate and predict the products based on Metal-mediated organic chemical reactions.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course will give an insight in understanding the strategies involved in designing a chemical reaction. and highlights the importance of oxidizing and reducing agents in functional group conversion reactions. It provides an platform in understanding the name reactions and molecular rearrangement in organic chemistry. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1) Construct a single step retrosynthetic pathway for organic reaction.
2) Interpret and design the products in organic chemical reactions.
3) Formulate and predict the products based on Metal-mediated organic chemical reactions.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
The course will give an insight in understanding the strategies involved in designing a chemical reaction. and highlights the importance of oxidizing and reducing agents in functional group conversion reactions. It provides an platform in understanding the name reactions and molecular rearrangement in organic chemistry. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1) Construct a single step retrosynthetic pathway for organic reaction.
2) Interpret and design the products in organic chemical reactions.
3) Formulate and predict the products based on Metal-mediated organic chemical reactions.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: Sunitha S
This course deals with the fundamentals of quantum chemistry in sub-atomic level such as wave properties, Uncertainty principle, de-Broglie hypothesis, Schrodinger equation, operators and eigen functions. Applications of quantum chemistry to one-dimensional harmonic oscillator, three-dimensional hydrogen atom, angular momentum and spin angular momentum, quantum numbers, shapes of atomic orbitals are discussed. Approximation methods- Perturbation and variation methods and its application to helium atom is dealt in a simplified manner. The latter part of the course covers the mathematical treatment of symmetry elements and point groups of molecules in predicting the chirality, chemical bonding, polarisability, molecular orbitals and spectroscopic transitions.
- Teacher: Krithiga T
This course enables the students to elucidate the use of chemical kinetics in understanding reaction mechanisms and kinetics of fast reactions; to understand adsorption phenomena and enable the learners to understand the importance and significance of heterogeneous catalysis and to learn the kinetics of polymerization and experimental methods of determination of molar masses of polymers.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry consists of five units. The first unit deals with the study of stability of metal complexes based on EAN rule. Interpretation of structure and geometry of metal carbonyls through hybridization enhances the knowledge of synthesis of highly stable organometallic complexes by the selection of ligands for complexation. The second unit discusses the various chemical reactions involving metal carbonyls as reactants. The third unit deals with the various catalytic applications of metal carbonyls in different organic conversion reactions. The fourth unit discusses the involvement and role of transition metal ions in biological molecules and also includes their mechanism of action. The last unit give strong insight to different types of nuclear reactions and the applications of radioisotopes in different fields.
This course will facilitate to explain theories of inter-ionic interactions, the concept of activity coefficient; to derive Butler-Volmer equations; to describe the structure of electrified interface and to explain electrochemical analytical techniques such as cyclic voltammetry, Tafel plots, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; and also to explain the fascinating area of solid state chemistry; the preparative methods of solids.
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Krithiga T
On successful completion of the course, student
will be able to
CO1- Understand the systematic identification of
mixtures containing two compounds
CO2- Separation and identification simple binary
mixtures having acidic, basic and neutral components by chemical methods
CO3- Preparation of
the identified compound derivatives
CO4- Recognize the
chemical reactions in identifying the chemical compounds
CO5- Identify the compounds containing one or more functional
groups
CO6
- Acquire the separation skills for binary
mixtures
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
This practical course enables the students to understand the construction binary and ternary phase diagrams; to gain practical knowledge in the synthesis of nanomaterials; to know about the practical applications of uv-visible spectrophotometer; and to learn the use of Ostwald’s viscometer for molecular mass determination.
- Teacher: Krithiga T
On completion of the course the student will be able to
Elaborate on structural elucidation and chemical synthesis of alkaloids.
Discuss on structural determination and stereochemistry of terpenoids and carotenoids.
Explain on classification and properties of proteins and lipids.
Design the synthesis of proteins.
Analyze and compare the synthesis and properties of five, six and fused ring heterocyclic compounds.
Predict the structural activity of antibiotics and vitamins
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
This course introduces the fundamentals of molecular spectroscopy and the principles of various spectroscopic methods such as UV-Vis, IR, NMR, ESR, Mossbauer and Mass spectrometry techniques. The key role of the course facilitate the learner to interpret the spectra of various spectroscopic methods and in elucidating the structure of compounds.
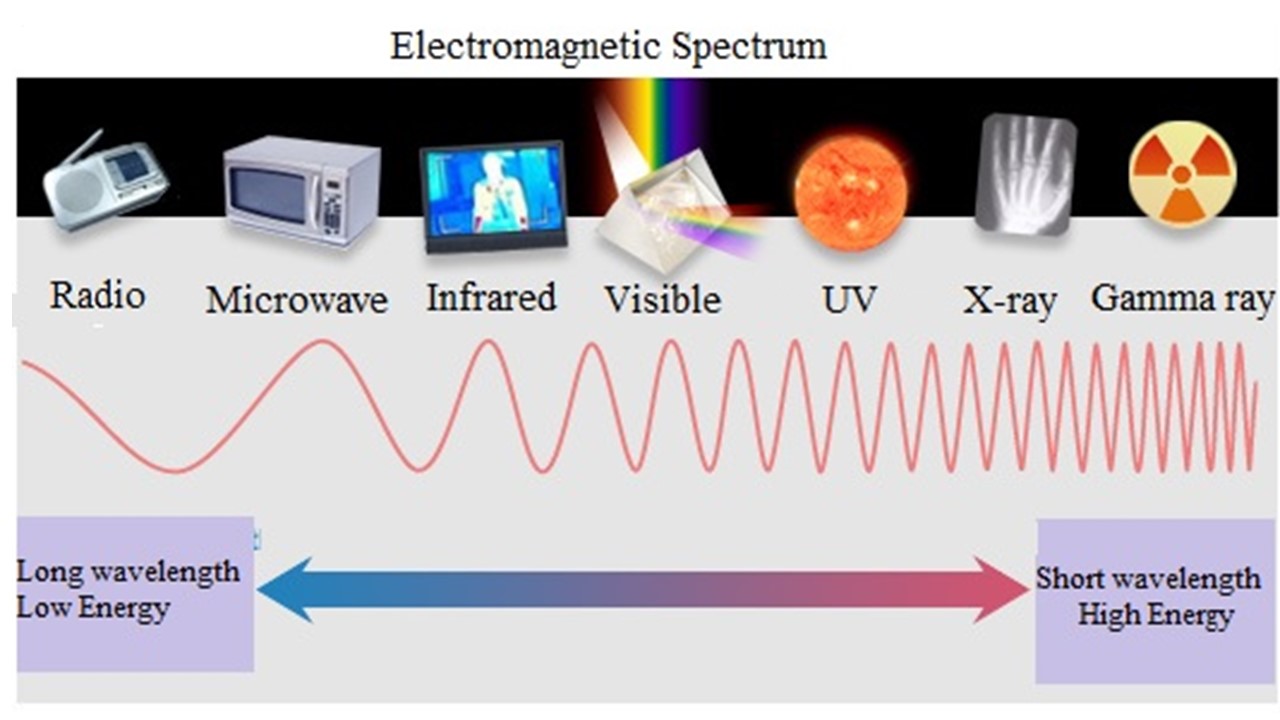
- Teacher: Krithiga T
The course is intended for post graduate student s in chemistry to give an insight into the industrial aspects of designing the products. The students will be able to understand the significance of stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective asymmetric synthesis in aldol formation, hydrogenation, hydroformylation reactions. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
1)Categorize and analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions.
2) Propose and predict a strategic reaction pathway in synthesizing a stereo, regio, enantiomeric chiral product.
3)Choose and predict the organometallic reagents in organic reaction
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Jyoti Gahtori
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Anand T
- Teacher: Shirley Auxilia L
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
The students can enable to learn the principles
of separation and purification techniques and to understand the principles of various
chromatographic techniques. The techniques for separation of
metal ions using different chromatographic methods can be constructed. The students can develop the skill of learning by thermal methods and to discuss the basic principle of polarimetry
and amperometry methods.

- Teacher: Sayantani Bhattacharya
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
- Teacher: Surya CP
- Teacher: Jyoti Gahtori
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
- Teacher: Shirley Auxilia L
- Teacher: Amrita Pal
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Supriya S
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
- Teacher: Anand T
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: Shirley Auxilia L
- Teacher: Dr. S Gayathri
The course is framed for undergraduate chemistry students to bridge the conceptual ideas in analytical chemistry with practical experiment for better understanding. The course will create a platform for the students to undergo hands-on training in preparing the solutions with safe handling of chemicals and glasswares. The course promotes analytical skills among the students in quantitative and qualitative analysis. At the end of the course, the students will be able to
Acquire analytical skills in handling equipments , glassware and chemicals.
Compile, Analyze and interpret the volumetric data for calculation with greater accuracy and precision.
Provides a preparative skills in the synthesis of inorganic complexes .

- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Kavitha V
1 To enable the student to develop analytical skill in organic qualitative analysis
2. Systematic identification of compounds containing one functional groups like acidic, basic and neutral
3. Develop the skill in analyzing the special elements like N, Cl, Br, S present in the organic substances.
4. Discuss the aliphatic and aromatic nature of the organic substances.
5. Develop the derivatives of the functional group for a given organic substance.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
This is an Organic Qualitative Analysis lab in which the students will identify the various functional groups including nitrogen and non-nitrogen substances. And also perform the various preliminary test as well as confirmation test to identify the nature of the functional group. Students will also prepare derivative and melting point for the corresponding functional group.

- Teacher: Sunitha S
- Teacher: Krithiga T
This course is aims to give a fundamentals of polymer characteristics and classification involved in a polymer reaction.This course is elaborated what are the types of polymerization reaction,mechanisms and properties. moulding process of polymers.
- Teacher: Dr. Y. Sasikumar
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the structure, isomerism, and bonding in coordination complexes.
CO2 - Deduce the crystal field splitting diagram for different geometries.
CO3 - Characterize the electronic spectra of metal complexes based on correlation diagrams.
CO4 - Evaluate the mechanistic pathway of metal complexes.
CO5 - Determine the stability of metal complexes using conventional methods. CO6 - Interpret the spectrum of different metal complexes with different geometries.
- Teacher: Karthikeyan Jayabalan
- Teacher: Anju K
This course deals with the fundamentals of quantum chemistry in sub-atomic level such as wave properties, Uncertainty principle, de-Broglie hypothesis, Schrodinger equation, operators and eigen functions. Applications of quantum chemistry to one-dimensional harmonic oscillator, three-dimensional hydrogen atom, angular momentum and spin angular momentum, quantum numbers, shapes of atomic orbitals are discussed. Approximation methods- Perturbation and variation methods and its application to helium atom is dealt in a simplified manner. The latter part of the course covers the mathematical treatment of symmetry elements and point groups of molecules in predicting the chirality, chemical bonding, polarisability, molecular orbitals and spectroscopic transitions.
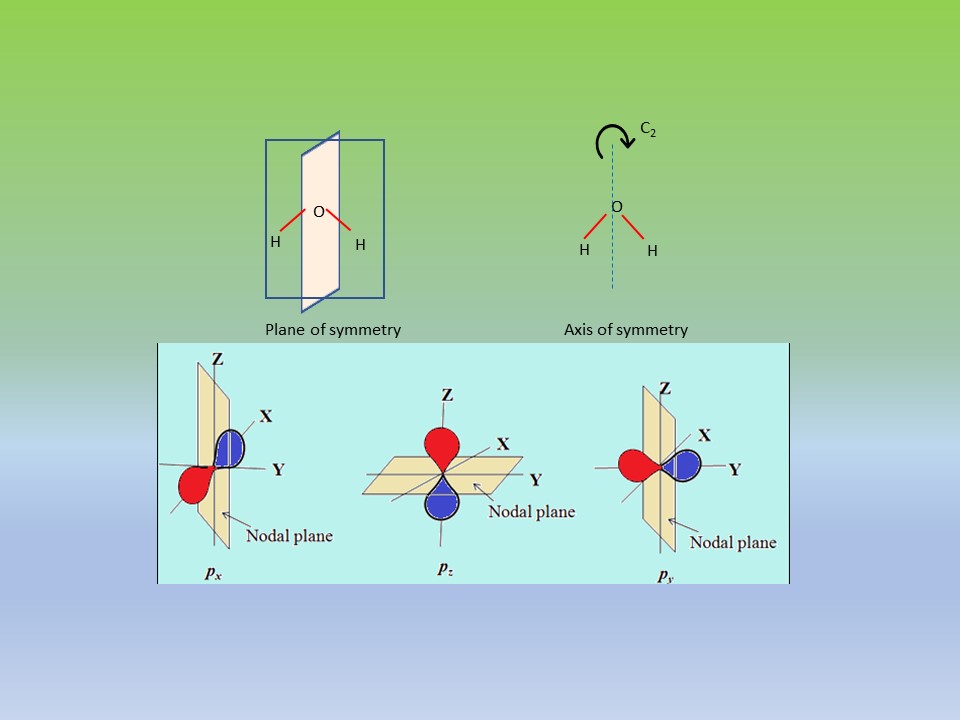
- Teacher: Krithiga T
This course deals with the fundamentals of Stereochemistry such as elements of symmetry, chirality, projection formula, optical purity, racemization, resolution, conformational analysis etc. The stereo, enantio, regio and chemo selective reactions such as Hydrogenation, Reduction of ketones, Epoxidation of Allylic alcohols, Dihydroxylation of alkenes, hydroboration etc are discussed. The latter part of the course covers the Asymmetric Synthetic principles and selective reactions such as Asymmetric Oxidations: Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols: Sharpless Epoxidation - Selective opening of 2, 3 epoxy alcohols by metallic hydride and organometallic reagents - Asymmetric Diels Alder Reaction: Intramolecular and Retro Diels Alder Reaction etc. are detailed with suitable examples.
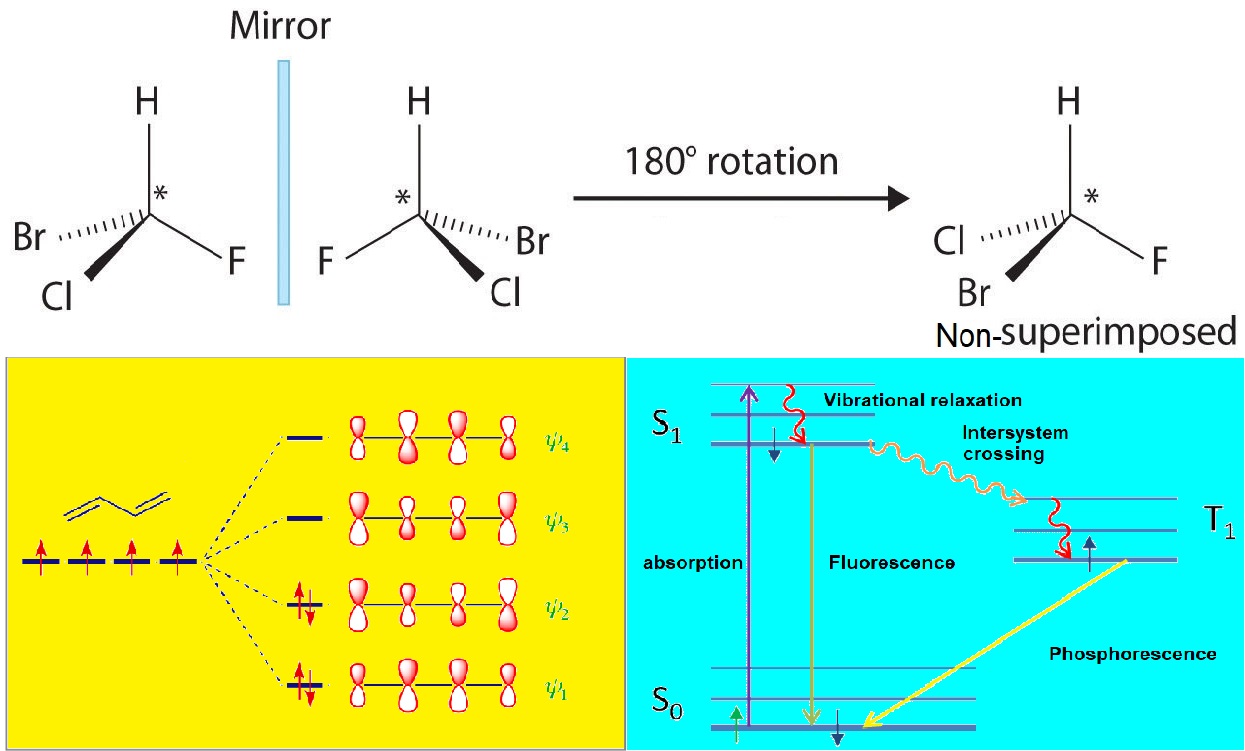
- Teacher: Krithiga T
- Teacher: Sayantani Bhattacharya
- Teacher: K CHENNAKESAVULU
The course is designed for postgraduate students in chemistry to understand the organic reactions in natural systems and bio systems. At the end of the course, the student will be able to
- Analyze the mechanism involved in basic organic reactions
- Elaborate on structural elucidation and chemical synthesis of alkaloids, terpenoids
- Understand the role of Supramolecules and their significance.
- Assess the importance of proteins and enzymes.
- Examine the action of drugs.
- Propose the structural activity for natural products.
- Teacher: Kavitha V
- To introduce various concepts related to the study of society and culture.
- To develop an understanding of art, craft, and design in a variety of contexts with respect to space, function, and climate.
- To expose the students to the principles of Vastushastra and Feng shui and their applications in interior design.

- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To understand the process of evolution from program and conditions to concept, design and graphical representation of the process.
To comprehend the fundamentals of small functional spaces understanding the anthropology as well as sensitivity to materials- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: Mohana Gopiraj N
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To reinforce the concepts of 3D modelling.
- To enable them to experiment with forms, mapping, rendering and presentation techniques.
- To prepare the student for mass production of furniture for various classes of people with the parameters of economy and culture
SYLLABUS:
UNIT 1 MATERIAL AND PROCESSES IN DESIGN
Material Deposition Processes Laser Deposition, Micro-Plasma Powder Deposition, Chemical vapour Deposition, Micro Welding, Powder Casting Metal 3D Printing, Powder Deposition 3D printing;
UNIT 2 SUBTRACTIVE MANUFACTURING
Subtractive Processes Electrochemical machining, Electro-Discharge machining, Ultrasonic Machining, Laser Beam Machining, Water jet machining, Abrasive Jet Machining, Plasma Arc machining; Cutting and Removal Water Jet Cutting, Plasma Cutting, Laser Cutting, Electro-Discharge Wire Cutting; Abrasive Jet Cutting
UNIT 3 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Additive Extrusion Processes Extruded Filament 3D printing, Clay 3D printing, Stereo lithography; Special Purpose Manufacturing processes- Rot molding, Layer Compression, Sheet contouring, Friction Welding
UNIT 4 SURFACE TREATMENT PROCESSES
Surface Treatment Processes Laser Etching, Acid/Base Etching, Electro Chemical Etching, Sand Blast Etching, Ultraviolet Etching, Photochemical Machining Electro Chemical Polishing
UNIT 5 CONSTRUCTIVE ASSIGNMENTS
Demonstrate comprehensive understanding through accompanying assignments, group discussions, and site visits.
COURSE OUTCOME:
- Understand the various subtractive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Compare the various new technologies being incorporated into manufacturing processes
- Comprehend the various subtractive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Discuss the various additive manufacturing processes frequently used in Interior and furniture design.
- Analyse the various surface treatment processes in the manufacturing of interior design elements.
- Develop systematic design approach and space planning through manufactured furniture as elements of design.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To introduce students to the basic elements of design, its principles, visual aspects, along with preparation, design vocabulary
and thereby the application of these in design.
To strengthen the students understanding of human factors and dimensions while designing interior spaces and accessories.
To enable students to explore the design process by identifying the design parameters and formulating concepts while
emphasizing function and aesthetics.
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
⮚ To outline the basic principles of drafting and rendering techniques.
⮚ To understand plane and solid geometry, isometric and axonometric view.
⮚ To familiarize with simple objects and building components through measured drawing.
COURSE OUTCOME:
CO1 Understand the concepts and fundamentals of architectural drawing.
CO2 Develop representation skills and to generate geometrical forms and its projections.
CO3 Ability to represent various solids and its sectional projection.
CO4 Measure real objects and represent them graphically.
CO5 Create three-dimensional solids and combination of solids
CO6 Develop graphical skill to represent real time objects.

The aim of this course is to make the students understand the relationship between INTERIORS and the built form. They will be introduced to various concepts and principles to design spaces of two different scales.

- Teacher: Esther Kiruba J C
- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
To develop a sensitivity to design the interiors of public spaces incorporating services and the principles of place making.

- Teacher: Catherine S
The aim of this course is to make the students understand the relationship between INTERIORS and the built form. They will be introduced to various concepts and principles to design office interiors.

- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
- Teacher: Juvilasri Vignesh
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
➢ To understand the tradition and culture of various region of India and their adaptation in interiors.
➢ To develop an insight into the evolution of interiors in Chinese, Japanese and Islamic culture.
➢ To introduce the evolution of interiors in Nordic culture.
➢ To impart the design practices of the contemporary interiors.
- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To develop methods for critical thinking and analysis.
- To help the students develop opinions on various design-related topics.
- To develop new platforms and formats for their writing.\
- To examine how space is conceived and conceptualised
- To evaluate texts
- To investigate “visual language”, symbolism, and some of the pictorial devices, materials, and techniques employed by designers to tell stories visually
COURSE OUTCOMES:
- CO1 Explore innovative ways of researching and writing about contemporary design and culture.
- CO2 Create valid arguments and to argue for and against ideas
- CO3 Analyse structure of oral and written arguments
- CO4 Critically evaluate design ideas.
- CO5 Understand and apply various spatial representations for their own designs.
- CO6 Produce a booklet of the ideas and themes discussed.
SYLLABUS:
UNIT 1 COMMUNICATION PRINCIPLES
Process of Communication. Transmission of ideas, facts & figures from one person to another. Kinds of Communication: Oral and Written, Verbal and Non-Verbal. Levels of Communication: Intrapersonal, Interpersonal, Group, Mass Communication.
UNIT 2 READING DESIGN
Reading skills: Model of reading to learning, reading tactics and strategies, reading purposes – associated apprehensions, reading for meaning, reading outcomes; Reading Space and its qualities; Presentations and writings of great design theorists
UNIT 3 DESIGN STORYTELLING AND NARRATIVES
Elements of a good story: facts, situation, characters, plot and resolution of a design project; Building context in the design process: Emotional, Environmental, Social context; Organising ideas- Personas, storyboards, and flowcharts; Documenting processes through writing
UNIT 4 REPRESENTATION OF SPACE
Innovation with orthographic drawings- beyond the plan, elevation, section; Perspectives and Montages; Maps and Models; Interior space and its occupation, experience and perception; Constructing and interpreting layers of meaning within interior spaces.
- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Ø To identify the components of a building including the structural systems.
Ø To understand the properties and uses of varied natural, synthetic materials and the internal service elements.
Ø To introduce the fundamentals and components of plumbing and electrical systems.
COURSE OUTCOME:
CO1 Understand the properties and uses of natural materials like wood and fabrics, synthetic materials like glass and plastics and their appropriate application techniques.
CO2 Select and specify materials based on the its properties and requirements
CO3 Understand the components of a building and methods of construction including foundation, plinth, superstructure, floorings, openings, roofs and finishes.
CO4 Get familiarized with the varied forms of roofs and the types of roofing systems.
CO5 Able to design interior elements that go with the existing architectural and structural components
CO6 Have an overview of the plumbing and electrical systems in a building.

- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: VIJENDRANATH R
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Ø To introduce the building materials and the construction techniques used for the walls and floors.
Ø To comprehend the various types of timber joinery adopted in the movable and fixed barriers in the external walls.
COURSE OUTCOME:
CO1 Gain comprehensive knowledge on various types of masonry walls.
CO2 Design temporary as well as permanent elements for enclosing spaces both physically and visually.
CO3 Explain the treatment of timber the various applications in buildings.
CO4 Demonstrate the types of joinery adopted in doors, windows and furniture
CO5 Classify and understand the different materials for floor finishes in interior design.
CO6 Select and specify flooring materials based on its properties and intended use.

- Teacher: Seetha Visalakshi K
- To introduce students to the basic elements of design, its principles, visual aspects, along with preparation, design vocabulary and thereby the application of these in design.
- To strengthen the students understanding of human factors and dimensions while designing interior spaces and accessories.
- To enable students to explore the design process by identifying the design parameters and formulating concepts while emphasizing function and aesthetics.
Exercises to Hand-on Product designs through carpentry, glass painting & other model making techniques.3D sculptures involving platonic
solids, wooden sculptures applying different types of carpentry joints, design and execution of POP made objects such as: cornices,
moldings, brackets, etc., Metal and terracotta sculptures.

COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To get an insight into various products and accessories used in Interior Spaces.
- To understand relevant products designed according to user’s needs.
- To know about the role of accessories in interiors. Integration of accessories in interior design and stylistic development.
- To learn about the practical aspects of product design processes
COURSE OUTCOMES:
- CO1 Understand the role of product design and designers in our everyday environment.
- CO2 Analyse the various approaches to Product and accessories design for Interior Environments.
- CO3 Apply various human factors in the design of products and accessories.
- CO4 Develop approaches to design keeping practical aspects in mind.
- CO5 Approach towards Product Design in relation with various spaces
- CO6 Distinguish various design trends in the Indian and Global markets.
SYLLABUS
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
A brief introduction to Product Designing – Various elements – History of Product Design – Definition of Product Design, understanding of Product Design - Purpose of Product Design – Role of Product Designers. Design approaches in product and lifestyle accessories design with a focus on functionality, ergonomics, aesthetics, multiple usages etc.
UNIT 2 HUMAN FACTORS
Application of human factors data. Human activities, their nature and effects. Human response to climate. Visual, Auditory, Tactual, Olfactory human mechanisms, Physical space and arrangement. Evolving the strategy of design with integration of technical complexities and lifestyle influences. Development of the design of products and accessories to specific interiors and prevailing trends.
UNIT 3 DESIGN APPROACH
Design approach with limited constraints inherent in accessory products. Broad-based approach towards innovative design and application to multi products and multi-materials in manufacturing interior products and lifestyle accessories. Study of materials and processes adopted in accessories design. Stylistic development of interior products from the past to present with insight into technological advances and the influences of social, economic and political factors on their design. Form, Colour, Texture, Symbols, User-specific criteria, Material, Technology and recyclability, Packaging. Multiple Utility oriented approaches to Product Design.
UNIT 4 PRACTICAL ASPECTS
Consumer Motivations Identification of user needs and Driving Factors; Emotional Design, Sensibility, Social Ethics and Concerns; Market Gaps, Market-Oriented Innovation; Business Evolution Product Planning for the future, Disruptive Innovation; Basic understanding of construction principles, modelling, rapid prototyping, with broad orientation to the socio-cultural and historical context of the sector. Orientation to Indian as well as global context of interiors, trends and market.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To acquaint students with the basic elements/principles of design and visual art.
- Understanding the basic characteristics of different techniques, mediums and its practical applications.
- To develop a perspective of artistic and creative expression through experimentation with different tools, techniques and medium in two and three-dimensional visual art forms
UNIT 1 CONCEPT AND MEANING OF VISUAL ARTS
Definition and meaning of Visual Art; Categorization of Visual Art- Fine art, Contemporary arts, Decorative arts and crafts, Applied arts
UNIT 2 ELEMENTS AND PRINCIPLES OF VISUAL ARTS
Elements of Visual Art: color, form, line, shape, space, texture, and value; Principles of Composition of Visual Art: balance, emphasis, harmony, movement, pattern, proportion, repetition, rhythm, unity, and hierarchy.
UNIT 3 2 DIMENSIONAL ARTS AND FORMS
2D Methods & techniques; Drawing and Painting, Still life, Life drawing, Composition, Collage, Print making, Photography, Wall painting, Posters, Folk art forms, etc.
UNIT 4 3 DIMENSIONAL ARTS AND FORMS
3D Methods & techniques; Sculpture, Clay modelling, Terracotta, Carving and relief work, Paper Mache, Mask making, Construction (using waste materials), Pottery, Installations, Folk art forms, etc.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course the student will be able to:
CO1: Understand the categorizations of visual art.
CO2: Apply elements (line, shape, form, texture, color, value, and space) and principles (repetition, variety, rhythm, proportion, movement, balance, emphasis, and unity) in work that effectively communicates their ideas.
CO3: Identify and discriminate between types of shape (geometric and organic), colors (primary, secondary, complementary, intermediates, neutrals, tints, tones, shades, and values), lines (characteristics, quality), textures (tactile and visual), and space (background, middle ground, foreground, placement, perspective, overlap, negative, converging lines positive, size, color), and balance (symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial)
CO4: Interpret and analyse the use of proportion, rhythm, variety, repetition, and movement in their work and the works of others.
CO5: Comprehend the various three dimensional art forms.
CO6: Develop and apply skills using a variety of two dimensional and three dimensional media, tools, and processes to create works that communicate personal meaning.

- Teacher: Ramkumar R

- Teacher: Deepalakshmi S
SDE 1106 |
PSYCHOLOGY OF INTERIORS |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To expose the students to the role of users’ psychology and the relationship in interior design.
To give an overview of psychological impact of colour and lighting in the interior spaces.
To understand the role of space design on the psychology of the human and their behavior.
COURSE OUTCOME:
CO1 |
Understand the various psychological attributes in interiors. |
CO2 |
Articulate the coexistence of more than one psychological aspect and to determine which of the aspects play a dominant role. |
CO3 |
Inculcate the role of colours, patterns and psychological impacts in the interior environment. |
CO4 |
Comprehend the importance of natural and artificial light, their application and perception in interior design. |
CO5 |
Design interiors incorporating the emotions and aesthetic values. |
CO6 |
Apply psychological aspects in their own design. |
- Teacher: MADHU VARSHINI P
- Teacher: VIJENDRANATH R
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To enable the students to elarn the concept of space in interior design
- To Understand the importance of space planning and its impact in design.
- To communicate the interior design in accurate and professional grpahics.

- Teacher: Vignaeshwar C
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSHINI S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
⮚ To provide the student of Interior Design a foundation in the techniques of drafting using a computer as a tool.
⮚ To introduce computer operation principles and explore image editing through a visual composition using graphics.
⮚ To impart training in computer-aided 2D drafting and 3D modelling.
⮚ To expose the students to visual composition using computer tools.
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 2D DRAFTING
Understanding on model workspaces –setting up limits – setting drafting units – understanding on drawing tools and objects..
Introduction to scale command – Filter command- Advantages of segregating layers using filter command –Functions of insert
command Revision cloud – Detail drawings. paper setting –plot manager – plot styles setting -layout properties –plot manager –
plot styles – understanding on ctb files – Introduction to presentation techniques. Preparation of drawings using layouts and
viewports. Understanding page setup and Scale in layouts.
UNIT II INTRODUCTION MODIFY AND EDITING COMMANDS
Introduction to layers , layer editing -Line type- Line thickness - line weight –Match properties - Draw order – Trim –move –copy –
rotate –Block - mirror – array commands –Area calculation - Hatching commands . Introduction setting up annotations –
Dimensioning and its properties –match properties - Leader commands. - Introduction to scale command – Filter command-
Introduction to Plot Styles and layout settings. Preparation of drawings using layouts and viewports. Understanding page setup
and Scale in layouts.
UNIT III INTRODUCTION TO 3D MODELLING
Introduction to 3d modelling – Sketch up tool set – understanding on workspace and template settings – unit settings. –Import and
export settings. Introduction to drafting tools – Navigation 3d model – accuracy modelling.-Orbit commands –Insight in modelling
space.
UNIT IV INTRODUCTION TO MATERIAL EDITOR
understanding on material palate – materials editing – define pattern - painting tools and other tools.
UNIT V INTRODUCTION TO PRESENTATION TECHNIQUES 15 Hrs.
Introduction to image editing & plugins – understanding on v-ray – Introduction to render – walkthrough render setting .Introduction
to Adobe Photoshop –Introduction to basic tools used for image editing for presentation.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course the student will be able to
CO1: Achieve proficiency in the basic computer skills relevant in the architectural profession
CO2: Construct 2D orthographic projections in CAD
CO3: Visualize design concepts in-the-round and make simple and complex 3D objects
CO4: Retrieve and present drawings and visualizations appropriately for multiple usages across various platforms
CO5: Develop diagrams and visuals to express architectural ideas and concepts.
CO6: Process images and create photo montages for presentation visualizations.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Introduction to AutoCAD 360 .Beginners 2020 & 2022
2. Introduction to Trimble Sketch up .Beginners 2020 & 2022
3. Introduction to Adobe Photoshop Beginners 2020 & 2022
4. Introduction to V-ray 2022
- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
- Teacher: Kaavya K
- Teacher: Yamuna D
- Teacher: Pujaa D
- Teacher: Sairamya K
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
Analyze the architecture of 8051 microcontroller and its memory organization
Apply the knowledge of Instruction sets to develop the assembly language programs
Analyze the architecture of PIC microcontroller, addressing modes, instruction sets, timers and
interrupts
Comprehend the requirements, trends and applications of Embedded systems
Explain the software development tools in embedded systems
Develop programs using microcontrollers for various applications
- Teacher: Pandian R
On completion of this course, students are able to
CO1 Describe the fundamentals of 8085 and 8086
CO2 Apply addressing mode and instruction set to program 8085 microprocessor
CO3 Develop the interfacing concepts of Peripheral IC’s
CO4 Create assembly language programs using 8051 microcontroller
CO5 Examine the applications of microprocessor and microcontroller
CO6 Design and develop microprocessor and microcontroller based systems

- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
To impart the knowledge of 8085 and 8086 processor.
To develop assembly language program in 8085/8086 processor.
To introduce the peripheral devices.
To acquire the knowledge of interfacing and hardware implementation.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To learn the various synchronization schemes.
To discuss about the spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To acquaint the students with the architecture, theory and operation of telecommunication systems, issues related to telecommunication systems and the services rendered by the system to the end users.
On completion of this course, the students will,
Acquire basic knowledge on telecommunication and various signaling related to it
Acquire knowledge on traffic in telecommunication systems
Acquire knowledge about QoS and various impairments

- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
COURSE OUTCOMES
|
CO1 |
Describe the overall cellular concepts |
|
CO2 |
Describe the step by step evolution of 1G to 5G networks |
|
CO3 |
Explain the 2G, 3G and B2G systems |
|
CO4 |
Describe the functional Architecture and Protocol of Bluetooth, ZigBee and RFID |
|
CO5 |
Explain the Functional architecture of GSM and GRPS |
|
CO6 |
Implement the testing of Cognitive Radios |

- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. Understand the microwave frequencies and derive the scattering parameter for the microwave network and to study and analyse the microwave system and components.
2. To study the characteristics of couplers and power dividers.
3. To study the microwave sources and solid state devices.
4. To measure the RF parameters and to study the functions of RF analyzers.
5. To study the system aspects of MIllimeter wave systems.
On completion of the course, students are able to
CO1 - Identify and formulate S matrix of microwave junctions.
CO2 - Explain couplers and power dividers.
CO3 - Classify the microwave tubes and explain their principle of operation.
CO4 – Perform microwave measurements and analyze the parameters.
CO5 - Analyze the basic radio receiver architecture.
CO6- Develop millimeterwave radio links for microwave transmission
SEC1406 Programming in HDL
After the completion of course student will be able to
|
CO1 |
Understand the requirements of VHDL design flow |
|
CO2 |
Interpret the Verilog language elements and its relevance to digital design |
|
CO3 |
Apply the Modelling Styles for Simulation, Synthesis and Test Bench Creation. |
|
CO4 |
Analyze the Performance Study of Combinational and Sequential logic design using Verilog |
|
CO5 |
Evaluate State Machine and Memory designs by Verilog |
|
CO6 |
Create and realize the system in FPGA using Verilog |

- Teacher: VINO T
COURSE OBJECTIVE
· To impart knowledge on various types of Binary logic
· To design a binary logic circuit for an arithmetic expressions
· To understand the usage of registers and counters used in various digital circuits
· To understand the design of memory devices used
· To get an exposure about the electronics behind design of Basic digital logical elements
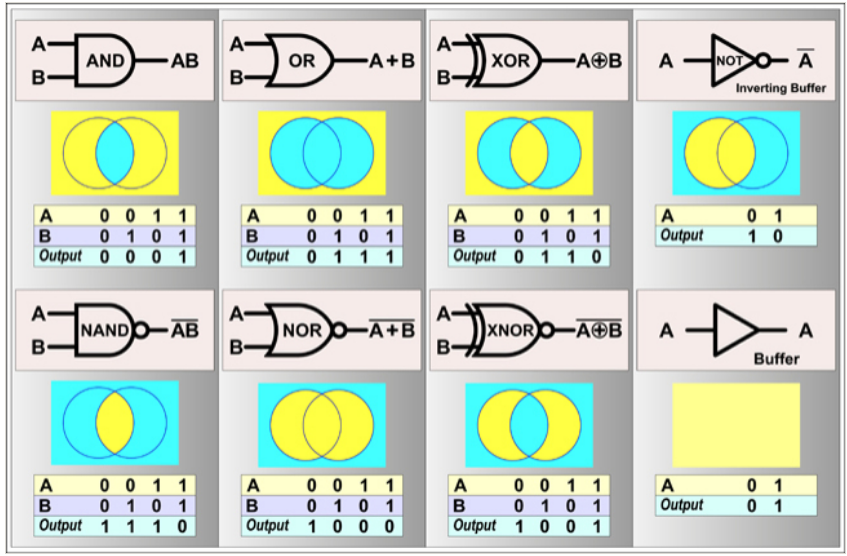
- Teacher: Thaj Mary Delsy T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To acquaint the students with the construction, theory and operation of the basic electronic devices such as PN
junction diode, Bipolar and Field effect Transistors, Power control devices, LED, LCD and other Opto-electronic
devices, display devices and power semiconductors.
Ø To understand the mechanisms of current flow in semi-conductors and special semiconductor devices.
Ø To understand the method of biasing transistors.
Ø To familiarise the students with the analysis and design of Multistage Amplifier circuits.
Ø To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits of amplifiers and oscillators.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the method of biasing transistors.
To familiarize the students with the analysis and design of basic transistor Amplifier
circuits.
To acquire the knowledge of equivalent circuits.
To understand the frequency response of amplifiers.
To provide foundation and confidence to the students to troubleshoot and fault
analysis of power supplies and power amplifiers.
To develop current mirrors and differential operations.
UNIT 1 BIASING OF BJT AND FET 9 Hrs.
BJT– Need for biasing – Various biasing methods of BJT- Bias Circuit Design- DC Load Line –
DC analysis of Transistor circuits-AC Load Line- AC analysis of Transistor Circuits- Quiescent Point
–
Thermal stability - Stability factors - Biasing of JFET - Various biasing methods of JFET - JFET Bias
Circuit Design - MOSFET Biasing-Two port network.
UNIT 2 EQUIVALENT MODEL OF BJT AND FET AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Hybrid model- Analysis of CE, CC and CB amplifiers using Hybrid equivalent circuits to obtain
gain, input impedance and output impedance--Small Signal Amplifiers – Analysis of CE, CC and CB
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits to obtain gain, input impedance and output
impedance. Small Signal equivalent circuit of FET and MOSFET - Analysis of CS, CD and CG JFET
amplifiers using small signal equivalent circuits- Analysis of CS, CD and CG MOSFET amplifiers
using small signal equivalent circuits.
UNIT 3 MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIERS AND FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF BJT AND FET
AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Multistage Amplifiers- Methods of Coupling- RC Coupled- Transformer Coupled – Direct
Coupled Amplifiers- Amplifier frequency response – Miller effect- Frequency response of transistor
amplifiers with circuit capacitors – BJT frequency response – Low and High frequency analysis of
CE, CB, CC -Frequency response of FET - Low and High frequency analysis of CS, CG, CD JFET
& MOSFET.
UNIT 4 POWER SUPPLIES AND POWER AMPLIFIERS 9 Hrs.
Linear mode power supply - Rectifiers - Half-Wave Rectifier - Full-Wave Rectifier - Filters-L, C,
LC, CLC Filter- Regulators - Zener Diode regulator- Linear series, shunt voltage Regulators -
Switched mode power supply (SMPS) – Large Signal Amplifiers – Class A, Class B, Class C, Class
D- Distortion in power amplifiers.
UNIT 5 CURRENT MIRRORS AND DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS. 9 Hrs.
Current sources for biasing – Current steering circuits – Current mirror with improved performance
(Cascode mirror, Wilson, Widlar). Large and small signal operation of Differential pair circuit
Differential pair with active load - Frequency response of the Differential amplifier
Max. 45 Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Acquire knowledge of simple BJT circuits design and implement circuits with transistor
biasing design.
CO2 - Draw the equivalent circuits of BJT and FET.
CO3 - Understand the working principles, Frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET.
CO4 - Compare the frequency response characteristics of BJT and FET amplifiers.
CO5 - Design and troubleshoot simple power supplies and analyse the performance parameters of
power supplies. Understand and identify the performance level in power amplifiers and checking its
distortion levels.
CO6 – Design the differential amplifier and study the performance of current mirrors
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Millman J and Halkias C., “Integrated Electronics”, TMH, 2nd Edition, 2017.
2. S. Salivahanan, N. Suresh Kumar and A. Vallavaraj, “Electronic Devices and Circuits”, TMH,
2 nd Edition, 2017.
3. Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C.Smith, “Microelectronic Circuits”, Oxford University Press, Sixth
Edition, 2009.
4. Behzad Razavi, “Fundamentals of Microelectronics”, 1st edition, wiley publication, 2008.
5. Donald. A. Neamen, “Electronic Circuits Analysis and Design”, McGraw Hill Education (India)
Private Ltd., 3rd Edition, 2010.
6. Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nasheresky, ”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Pearson
Education, 11th Edition, 2013.
7. Floyd, “Electronic Devices”, Pearson Education, 9th Edition, 2012.
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To give a basic introduction to electronic components.
Ø To provide students knowledge about semiconductor diodes.
Ø To design the feedback amplifier circuits.
Ø To design the importance of digital circuits.
Ø To design the importance of PSPICE.
SECA1201-Digital Logic Circuits
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To impart knowledge on various types of Binary logics.
- To design a binary logic circuit for an arithmetic expressions.
- To understand the usage of registers and counters used in various digital circuits.
- To understand the design of memory devices used.
- To get an exposure about the electronics behind design of Basic digital logical elements.
- Teacher: VINO T
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To discuss and understand fundamental concepts of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques.
Ø To understand the concepts of Frequency Modulation and De-Modulation techniques and compare with AM and PM.
Ø To understand the concepts of Analog Pulse modulation and De-Modulation techniques (PAM, PDM/PWM and PPM) & Multiplexing techniques and classifications.
Ø To apply different multiplexing techniques for AM, FM, PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
Ø To understand the various noises and their effect on Analog modulation systems.
Ø To discuss the working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Explain the Functional blocks of communication system, modulation techniques and Various noise sources and types.
CO2 - Analyse AM, FM, PM, PAM, PDM, PPM and PCM using mathematical equations and demonstrate their modulation and demodulation techniques.
CO3 - Illustrate sampling theorem and explain the importance of various multiplexing techniques.
CO4 - Demonstrate the working of AM and FM transmitters, Receivers and communication Systems.
CO5 - Performance evaluation and selection of appropriate modulation technique for real time applications.
CO6 - Working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
- To discuss and understand fundamental concepts of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques.
- To understand the concepts of Frequency Modulation and De-Modulation techniques and compare with AM and PM.
- To understand the concepts of Analog Pulse modulation and De-Modulation techniques (PAM, PDM/PWM and PPM) & Multiplexing techniques and classifications.
- To apply different multiplexing techniques for AM, FM, PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
- To understand the various noises and their effect on Analog modulation systems.
- To discuss the working of Analog Communication Receivers and Telephone and Television Systems.

- Teacher: SAHAYA ANSELIN NISHA A
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
Electronic Devices and Circuits, deals with the design and applications of electronic devices and circuits such as passive components, diodes, triodes and transistors, rectification and power supplies,amplifying circuits, electronic instruments, and oscillators.

- Teacher: Nirmal Raj S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
➢ To understand operational principles and characteristics of semiconductor electronic devices.
➢ To learn about analog electronic circuits such as rectifiers, regulators and amplifiers.
➢ To learn about Boolean algebra and basic building blocks of digital systems.
➢ To learn about optimized implementation of combinational and sequential digital circuits and systems.
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
- Teacher: VINO T
On completion of the course, student will be able to
Design and analyze the Feedback amplifiers.
Design and analyze the Oscillators.
Analyze the performance of Tuned Amplifiers.
Analyze the types of Multivibrators.
Develop the application using Time Based Generator.
Develop the application using Blocking Oscillator.
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
** To understand the concepts of Feedback amplifiers.
** To identify the design and analysis of Oscillators.
**To familiarize with the performance of Tuned Amplifiers.
**To learn the types of Multi-vibrators.
** To focus on Time Based Generator and Blocking Oscillator.
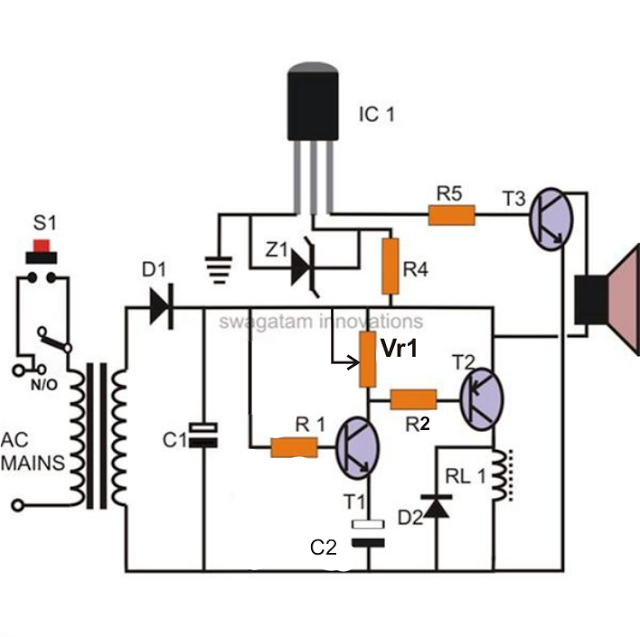
- Teacher: annieangelinepreethi .
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: Lalithakumari S
- Teacher: Mary Sajin Sanju
- Teacher: Magthelin Therase
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Discuss the fundamental concepts of wave propagation in Transmission Lines and Wave Guides.
CO2 - Analyze the line parameters and various losses in transmission lines.
CO3 - Apply smith chart for line parameter and impedance calculations.
CO4 - Evaluate the characteristics of parallel plane and rectangular wave guides.
CO5 - Evaluate the characteristics of Circular waveguides.
CO6 - Evaluate the characteristics of resonators.

- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
To know the principles of sampling & quantization.
To understand the various Base Band signaling schemes.
To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of baseband signals.
To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding.
To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes.

- Teacher: Vijayakumar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To know the principles of sampling and quantization
- To understand the various base band signalling schemes
- To introduce the basic concepts of digital modulation of base band signals
- To get introduced to the basics of source and channel coding/decoding
- To understand the basics of spread spectrum modulation schemes

- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- To learn the basic antenna parameters.
- To understand the radiation mechanism from the dipole antennas.
- To explore the various antenna arrays and calculate the maxima, minima and half power directions.
- To discuss the characteristics of travelling wave radiators and high frequency antennas.
- To study antenna measurements techniques.

- Teacher: Magthelin Therase
The primary objective of this course is to provide a thorough understanding and working
knowledge of design, implementation and analysis DSP systems.
On completion of this course, students are able to
CO1 Apply various transforms for different types of signals
CO2 Design IIR & FIR filter using various filter approximations
CO3 Make use of the concept of finite word length effects and its applications in signal
processing
CO4 Elaborate the concept of Multirate signal processing
CO5 Explain the perception of Multirate signal processing in real time applications
CO6 Develop real time applications with DSP hardwares
- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
- Teacher: Allan Dino J
- Teacher: Jagan K
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: LAKSHMI S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To impart the knowledge of 8085 and 8086 processor.
- To develop assembly language program in 8085/8086 processor.
- To introduce the peripheral devices.
- To acquire the knowledge of interfacing and hardware implementation.
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Have clear understanding on the basics of 8085/8086 microprocessor, working and signals and Familiarize the entire instruction set of 8085/8086 microprocessors.
CO2 - Ability to analyse the computational complexity of the developed algorithms through timing diagrams/T-states
CO3 - Familiarize the peripheral devices.
CO4 - Ability to provide solutions to the problems related to processor program development.
CO5 - Design and develop interfacing circuits for real time applications.
CO6 - Feasibility of developing user defined circuits for the left out flip flops in the flag registers of 8085/8086 processors

- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To study the basics of Embedded System.
- To explain the various development tools in Embedded System.
- To acquire knowledge in Embedded Networking.
- To get a knowledge in Embedded programming.
- To acquire knowledge in embedded system testing and its application.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the fundamentals and areas of applications for the Embedded System.
CO2 - Analyse the various architectures for embedded software development.
CO3 - Classify and analyse the various standards and protocols used for embedded interfaces.
CO4 - Demonstrate the knowledge of programming for embedded system through various high level language.
CO5 - Examine the various types of software unit testing necessary for embedded system design.
CO6 - Develop knowledge and skills necessary to develop a real time embedded system.

- Teacher: Kanchana D
- Teacher: Pandian R
- Teacher: SAKTHI PRABHA R
- Teacher: JOANY R M
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
On completion of the course, student will be able to
Apply the knowledge of basic microwave components and understand the scattering parameters differences between low and high frequency processes.
Analyses the characteristics of various microwave sources and solid state devices.
Classify and analyze the various microwave measurements and EMI/EMC measurements
Demonstrate the qualitative knowledge of optical communication and types of optical fibers, its losses and signal degradation
Become Aware of the latest optical sources, launching and coupling of optical fibers
Examine the theoretical concepts of optical Networks.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Remember the pin details, specifications, register configurations and explain the internal operations of 8051
microcontroller.
CO2 - Explain the addressing modes, Instruction sets and able to write assembly language programs based on 8051
microcontroller.
CO3 - Remember the pin details, specifications and register configurations and explain the internal operations of PIC
16F877A Microcontroller.
CO4 - Categorize and compare the suitability of various interfacing bus devices for applications.
CO5 - Understand the basics of RTOs.
CO6 - Explain the concepts of RTOs in real time embedded system.
List of Experiments
1.
Verification of KCL
& KVL. 2.
Verification of
Thevenin’s & Norton’s Theorem. 3.
Series and Parallel Resonance. 4.
Constant K filters (both LPF & HPF). 5.
M-Derived filters
(both LPF & HPF). 6.
Attenuators. 7.
Equalizers. 8.
Matching Networks. 9.
Twin T Network as
Notch filter. 10. Verification of reciprocity theorem. 11. Verification of compensation theorem. 12. Study of composite m-derived filters.
- Teacher: Ramya D
To understand the characteristics of diodes, transistors, LDRs, SCR, DIAC, Triac.
To understand the theorems for electrical circuit analysis.

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide knowledge for understanding of digital signal processing through hands-on experience that is sufficient to enable them to apply DSP to real-world problems.
- To understand the process of convolution, correlation, DFT, IDFT, Signal smoothing, filtering of long duration signals, and Spectral analysis of signals
CO1 - Understand the handling of discrete signals using MATLAB.
CO2 - Learn to represent real world signals in digital format and understand transform-domain representation of the signals.
CO3 - Analyse the spectral parameters of window functions.
CO4 - Design of IIR and FIR filters using butter worth and chebyshev approximation.
CO5 - Perform the convolution and correlation of two signals.
CO6 - Design the signal processing algorithm using MATLAB.
- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To introduce the history and the terms of telecommunication systems.
Ø To study the various signalling techniques used in the telecommunication system.
Ø To acquire knowledge on traffic in telecommunication systems.
Ø To introduce the service engineering and the protocols used in telecommunication services.
Ø To study the various impairments in telecommunication.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Tell the history and terminologies of the telecommunication
systems.
CO2 - Explain the classical signaling to the advanced signaling
techniques in telecommunication systems.
CO3 - Choose the Supporting protocols for various applications.
CO4 - Analyze the traffic in the telecommunication networks using
various models.
CO5 - Interpret the importance of Service engineering.
CO6 - Discuss the impairments in telecommunication systems.
- Teacher: Dr. SUMATHI M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To acquaint the students with the architecture, theory and operation of telecommunication systems, issues related to telecommunication systems and the services rendered by the system to the end users.
On completion of this course, the students will,
Acquire basic knowledge on telecommunication and various signaling related to it
Acquire knowledge on traffic in telecommunication systems
Acquire knowledge about QoS and various impairments

- Teacher: Aranganathan A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To obtain the knowledge about quantum physics and principle.
- To learn about properties of semiconductor and Nano Technology.
- To acquire the knowledge of Nanoscale devices and properties.
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the electronic properties of materials at the nanoscale quantum devices and principles.
CO2 - Know the various properties of Nano devices.
CO3 - Design the nanoscale based circuits with simulation tools.
CO4 - Understand the sensors and memory devices.
CO5 - Understand the various types of Nano sensors.
CO6 - Analyse various nanoscale memory devices.
- Teacher: JEGAN ANTONY MARCILIN L
Course Objectives
• To learn about wireless mobile communication standards and co-existence of 4G and 5G.
• To learn 5G network architecture, components, features and their benefits.
• To learn channel access methods, modulation and spectrum sensing techniques used in 5G wireless systems.
• To understand advanced wireless concepts such as Massive MIMO, Virtualized RAN and Network Slicing.
• To learn about mmWave communication systems and its use cases.
Course Outcomes:
On Completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1 - Distinguish major mobile communication standards such as 3G, 4G and 5G
CO2 - Analyze various modulation and multiplexing techniques like OFDM, NOMA etc.
CO3 - Design system level architecture of 5G communication systems.
CO4 - Analyze spectrum sensing and sharing techniques in 5G systems.
CO5 - Assess the potential of mmWave spectrum for 5G applications.
CO6 - Apply the concepts of green communications in real life applications.

- Teacher: Dr. KRUTI DEEPA
- Teacher: Karthikeyan K.V
- Teacher: MATHAN N
- Teacher: Kalaipriya O
Course Objectives :
To explore the fundamental concepts of verilog
To understand systemVerilog data types and capabilities
To enumerate system Verilog RTL and abstraction
To analyze dynamic types and arrays for behavioral modeling
To evaluate System Verilog Assertions for design and verification
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1: Understand the digital system designs skills using VERILOG HDL based on IEEE-1364 standards and managed by Open Verilog International (OVI)
CO2: Model digital systems in Verilog HDL at different levels of abstraction
CO3: Know the simulation techniques and test bench creation.
CO4: Demonstrate the skill on writing test-benches for design of digital systems and connecting them with the design.
CO5 Verify and Analyze the complete systems through robust verification methods such as assertion based verification.
CO6 Design and verify the digital systems such as FIFOs, memories, ATM interfaces, etc. using the learnt methods and demonstrate the skills.

- Teacher: MATHAN N
UNIT I IoT FOR HEALTHCARE
Architecture of IoT for Healthcare , IoT based Health Monitoring System using Arduino, Healthcare monitoring Technique for Diabetes Patients, Remote Patient Monitoring- IoT Heart Rate Monitoring, remote monitoring of physiological parameters, ECG, EEG, and BP.
UNIT II IoT ENABLED SMART CITIES
Smart Energy meters, Smart home powered by IoT, Smart Lightining, Smart Traffic Control ,Smart Grid and Solar Energy Harvesting, Intelligent Parking System.
UNIT III IoT FOR SMART AGRICULTURE
Smart Agriculture, IoT Based Agriculture, Animal Intrusion detection in farms, soil moisture detection and Irrigation system, Livestock monitoring system, IoT based Greenhouse Environment Monitoring and controlling
UNIT IV IoT BASED INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION
IoT based gas leakage monitoring system, Temperature and liquid level monitoring in boilers, Wireless video surveillance robot, Automatic Solar Tracker, IoT in Logistics Sector
UNIT V IoT FOR SOCIETY
Medical Waste Management, Weather update system with IoT, Women security system,wearable glove to enable sign to speech conversation, IoT based air pollution meter, Improved productivity of staff and reduced human labor

- Teacher: M Subramoniam .
- Teacher: DIGANTA DAS
- Teacher: Dr. ANNA DEVI E
- Teacher: SRILATHA K
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: VINO T
Course Objectives
• To Recognize Different Key Paradigms For Machine Learning Concepts
• To Familiarize With Various Classifiers Used For Machine Learning
• To Understand And Differentiate Among Various Supervised Learning Concepts
• To Become Familiarize With Data Reduction And Feature Extraction Methods
• To Apply Suitable Machine Learning Algorithms For Simple Engineering Problems

- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
Course Objectives
• To explore the fundamental concepts of Image Processing
• To become conversant with various Image Enhancement and restoration techniques
• To study and understand various Morphological and segmentation concepts and techniques
• To analysis the pattern classifier techniques for image understanding
• To design Artificial Intelligence (AI) based image classification systems
Course Outcomes
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1- Apply Suitable Mathematical Concepts For The Measurement Of Quality In Digital Images.
CO2-Analyze the Performance of Image enhancement and image restoration techniques.
CO3-Analyze Various Morphological Image Processing and Segmentation Techniques.
CO4-Identify Suitable Pattern Classifier for Object Classification Problems.
CO5-Implement AI Based Image Classification Systems.
CO6-Solve Real World Problems Using AI
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: CHITRA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand and gain complete knowledge about the fundamentals of MATLAB programming.
To develop and translate mathematical concepts to MATLAB code.
To provide data analytic skills by processing and visualization of data’s.
To design and develop Simulink and MATLAB models for specific engineering applications
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Recall and recollect the basic programming fundamentals
CO2 - Understand various array arithmetic procedures
CO3 - Analyze and develop different control structures using MATLAB
CO4 - Evaluate different interactive plotting methods
CO5 - Identify the need for GUI based operations for real time programming.
CO6 - Design and demonstrate applications based on communication systems, controllers etc.
- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: Poonguzhali S
Course Objectives:
- To Present the mathematical, statistical, and computational challenges of building neural networks
- To study the concepts of deep learning
- To introduce dimensionality reduction techniques
- To enable the students to know deep learning techniques to support real-time applications
- To examine the case studies of deep learning techniques
- Teacher: Ishwarya C
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Gomathi V
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
Course Outcomes
Co1 – Articulate Ehealth And Its Regulations
Co2 – Explore Medical Data Analytics And Records
Co3 – Appraise Digital Transformation In The Field Of Medicine
Co4 – Analyze Ai In Health Care Systems
Co5 – Design System Level Architecture For Health Information Systems
Co6 – Deploy Android Application On Devices

- Teacher: Naresh Kumar Thapa
- The Internet of Things (IoT) involves the internet-connected devices we use to perform the processes and services that support our way of life.
- This Course provides an overview of Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud Computing concepts, infrastructures and capabilities.
- The course emphasises on the architecture, programming languages for IoT systems, different communication protocols and standards governing the system implementation and the migration of the data to the Cloud platforms for processing.
- Students will gain practical experience in the development of Cloud-based IoT systems and exposure to appropriate hardware and software platforms that underpin such development.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Design and interfacing of microcontroller-based embedded systems. High-level languages are used to interface the microcontrollers to various applications.

- Teacher: MEGALAN LEO L
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, the student will be able to
CO1 - Describe the components of embedded system and different communication protocols.
CO2 - Describe the differences between the general computing system and embedded system, also recognize the classification of embedded systems.
CO3 - Attain expertise with embedded system development and debugging tools.
CO4 - Apply the interrupt service mechanism in the design of embedded system.
CO5 - Design of real time embedded systems using the concepts of RTOS.
CO6 - Articulate the role of embedded systems in industry and provide feasible design solutions for given problem
statement.
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
To impart knowledge about the fundamental difference between general purpose and real time operating systems and thereby to learn the scheduling algorithms, porting and configuration of Real Time Operating System
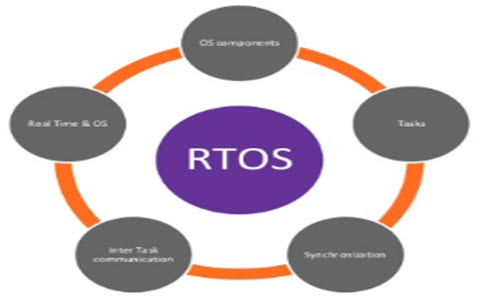
- Teacher: karthikeyan S
This course cloud computing is specially framed for the students who are learning Embedded and IoT domain. On completion of the course, student will be able to articulate the main concepts, key technologies, strengths, and limitations of cloud computing. Identify the architecture and infrastructure of cloud computing, including SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, public cloud, private cloud, etc. They could able to demonstrate how storage and virtualization are used in the cloud platform and apply this in practice and also analyse the core issues of cloud computing such as security, privacy, and interoperability and evaluate various cloud computing solutions. They could able to suggest relevant cloud computing solutions according to the applications and also apply the fundamental principles of multi-tier web applications and services in a cloud environment.
This course covers Embedded-C programming of 8-bit & 32-bit microcontrollers and
IoT applications development using Python.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Real-Time Embedded Systems has to meet the severe time constraints imposed by critical applications. Real Time Operating Systems (RTOS) serve as a powerful and convenient software tool to develop time-critical embedded systems.
This Laboratory course provides a foundation for understanding the principles of RTOS and apply the concept of task scheduling, memory allocation and resource management in developing real-time systems.
- Teacher: SUGADEV M
Course Objectives
· To explore the fundamental
concepts of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
· To assess the applicability,
strengths, and weaknesses of the basic knowledge representation
· To impart machine learning
techniques
· To understand various CNNs
· To develop the solutions
for real-world problems using AI
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To explain how digital circuit of large complexity can be built in a methodological way to acquire the knowledge about memory architectures.
- To illustrate how the concepts presented in the lectures are applied in practice, and how the need to accommodate different practically motivated trade-offs can lead to alternative implementations.
- To teach fundamental concepts of hardware description languages.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Apply the steps for state table reduction and state assignment, ASM chart and ASM tables for the design of synchronous sequential design.
CO2 Determine the Real Time Challenges in the design of Asynchronous sequential circuits.
CO3 Elaborate the feasibility of sequential circuit design using PLA.
CO4 Evaluate the testing algorithms and perform the comparison study for digital circuits.
CO5 Design the Combinational logic circuits using VHDL.
CO6 Construct the low power sequential circuit using VHDL.

- Teacher: AISHWARYA K
- Teacher: EMIMAL M
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: GEETHA P
- Teacher: Balamurugan Velan
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1- Minimize Boolean functions for computationally less complex implementations
CO2- Apply K map and tabulation method for minimization of Boolean functions
CO3 - Implement combinational logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO4 - Implement sequential logic circuits for Real World Problems
CO5 - Analyze the performance of various logic families
CO6 - Implement memory units with Programmable logic devices
- Teacher: JEGAN G
• Understand and implement the most popular learning algorithms.
• Perform feature selection and experimental set up on real tasks
• Analyze in detail about unsupervised learning, dimensionality concepts and neural networks.
• Evaluate multiple learning algorithms across several Robotic tasks

- Teacher: LUBNA KALAM
- Teacher: NIVETHA S
COURSE OUTCOMES :
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Model various parameters in communication channels.
CO2 - Analyze the suitability of IEEE standards for specific applications.
CO3 - Correlate ISO-OSI and TCP/IP reference models.
CO4 - Develop suitable error detection and error correction techniques for reliable communication.
CO5 - Analyze various transport layer protocols for Real Time Applications.
CO6 - Develop suitable routing and congestion control algorithms for Real World Problems.

- Teacher: GOMATHI T
- Teacher: SUDHA R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To categorize the sensors and transducers according to its applications
- To introduce virtual instrumentation and LabVIEW
- To focus on the advanced features of smart sensors
- To summarize the characteristics and operating principles of various types of transducers
- To familiarize with Arduino programming
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 Infer the needs of sensors and transducers in industrial automation.
CO2 Evaluate the unique characteristics of Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive transducers.
CO3 Investigate different types of advanced sensors and its principles of operation.
CO4 Apply virtual instrumentation techniques for complicated process handling.
CO5 Monitor the environmental parameter variations using smart sensors.
CO6 Analyze the real time problems with Arduino programming.
- Teacher: Pandian R
Course Outcomes
On
completion of the course, the student should be able to
CO1-Apply the mathematical concepts to compare
different types of optical fibers, modes and configuration.
CO2-Analyze
the transmission characteristics of optical fibers.
CO3-Examine
the optical sources and detectors for use in optical communication system.
CO4-Construct
launching and coupling of optical fibers.
CO5-Design
high speed optical communication networks.
CO6-Design wireless
communication system using Li-Fi.
- Teacher: JEGAN G
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: ANU SUDHA T.A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To understand and gain complete knowledge about the fundamentals of MATLAB
programming.
- To develop and translate mathematical concepts to MATLAB code
- To provide data analytic skills by processing and visualization of data’s.
- To design and develop Simulink and MATLAB models for specific engineering
applications.
- Teacher: M Subramoniam .
- Teacher: MOHANA PRIYA G
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: AISHWARYA K
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Nandhitha N M
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: CHITRA P
- Teacher: GEETHA P
- Teacher: Krishnaprasanna R
- Teacher: Barani S
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
· To study the fundamental concepts of robotics.
· To impart knowledge on various sensors & actuators.
· To acquire the concept of kinematics and inverse kinematics.
· To understand basics of deep learning and reinforcement learning
· To learn about applications of AI in robotics
COURSE OUTCOMES
After Completion of the course the students will be able to:
CO1: Classify robots based on their geometrical configurations
CO2: Analyse Robot Motion using forward and inverse kinematics
CO3: Apply Deep Learning techniques for robotic perception
CO4: Analyse the performance of DLNN in localization strategies of Robots
CO5: Apply Reinforcement Learning techniques for Robotics Motion Control
CO6: Formulate AI algorithms for given automation task.
- Teacher: RAJSHREE A
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: PRIYADHARSINI R
- Teacher: POORNAPUSHPAKALA S
- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
1. To reinforce the mathematical foundation with advanced topics.
2. To enable the student to appreciate the engineering aspect of mathematics.
3. To equip the student with tools to confront continual mathematical.
4. To understand probabilistic models and their applications.
5. To expose the students to different Transform techniques.
- Teacher: KAVIPRIYA P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To Understand the Architectural Overview of IoT
To Understand the IoT Reference Architecture and Real-World Design Constraints
To Understand the various IoT Protocols
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Choose appropriate hardware components for implementation of IoT applications.
CO2 - Analyze various IoT Application layer Protocols.
CO3 - Implement IoT-based systems for real-world problem
CO4 - Demonstrate state of the art methodologies in data representation and analysis.
CO5 - Apply appropriate IP based protocols and Authentication Protocols for IoT communication.
CO6 - Analyze security issues in IoT Communication
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Pandian R
To have a knowledge on basics of cloud
To provide students basic understanding and virtualization.
To discuss some scenarios of clouds in organizations
COURSE OUTCOMES On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Articulate the main concepts, key technologies, strengths, and limitations of cloud computing CO2 - Analyze the core issues of cloud computing such as security, privacy, and interoperability.
CO3 - Develop applications based on public cloud and private cloud architectures.
CO4 - Demonstrate how storage and virtualization is carried out in the cloud platform.
CO5 - Create virtual machine based applications for real world problems.
CO6 - Apply the fundamental principles of multi-tier web applications and services in a cloud environment.

- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: MATHAN N
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
- CO1 - Identify the main challenges associated with machine-to-machine communications with respect to the status quo in networking today.
- CO2 - Describe the standards, protocols and algorithms that are used to address the challenges in M2M communications.
- CO3 - Develop an understanding of edge and fog computing for data aggregation, filtering and detecting anomalies
- CO4 - Design and build a network based on the client server, as well as how to publish/subscribe to connect, collect data, monitor and manage assets.
- CO5 - Develop device, gateway and server-side scripts and apps, enabling them to aggregate and analyze sensor data
- CO6 - Analyze and suggest suitable application-layer protocols and web services architectures for a seamless integration of various components within an IoT ecosystem.
- Teacher: MATHAN N
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To learn about the security issues in IoT and cloud computing.
Ø To learn about the cryptography solutions and issues in IoT.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF IoT ECOSYSTEM
IoT security issues, how to design an IoT system, Hardware, software and network security related to IoT systems. Basics of cryptographic solutions to IoT systems.
UNIT 2 OVERVIEW OF CLOUD COMPUTING AND ITS SERVICES
Cloud Computing Fundamental: Cloud computing definition, private, public and hybrid cloud.
Cloud types; IaaS, PaaS, SaaS.
UNIT 3 CHALLENGES IN CLOUD COMPUTING
Benefits and challenges of cloud computing, public vs. private clouds, Role of virtualization in enabling the cloud.
UNIT 4 SECURITY CONCEPTS IN CONTEXT TO IoT DEVICES
Security Concepts: Confidentiality, privacy, integrity, authentication, non-repudiation, Virtualization.
UNIT 5 IoT SECURITY THREATS AND COUNTER MEASURES
System-Specific Attacks: Guest hopping, attacks on the VM (delete the VM, attack on the control of the VM, code or file injection into the virtualized file structure), VM migration attack, hyper jacking.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. David Etter, “ IoT Security: Practical guide book “ Create Space, 1st Edition, 2016.
2. Drew Van Duren, Brian Russell, “Practical Internet of Things Security”, Packt, 1st Edition, 2016.
3. Sean Smith, “The Internet of Risky Things”, O'Reilly Media, 1st Edition, 2017.
4. Brian Russell, Drew Van Duren, “Practical Internet of Things Security: Design a security framework for an Internet connected ecosystem”, 2nd Edition, 2018.

- Teacher: JEGAN G
Power System Analysis is a blueprint of Power Systems. It discuss with per unit computations, Equivalent Circuit representations of all power system components, Impedance Diagram, Reactance Diagram, Symmetrical Components and Sequence Networks. It deals with the study of Power flow Analysis, Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical short Circuit Analysis, Stability Analysis.
Course Objectives
To impart knowledge in modelling of power system elements
To implement Numerical methods in power flow problem
To analyze the system in various faulted conditions.
To have a knowledge in stability and security of power systems
Course Outcomes
CO1: Model Impedance, Reactance networks and develop bus admittance matrix.
CO2: Examine load flow in a power grid using bus admittance matrix.
CO3: Examine fault currents and post fault voltages in symmetrical short circuit using bus impedance matrix.
CO4: Estimate fault currents and post fault voltages in unsymmetrical short circuit using symmetrical components.
CO5: Evaluate the stability conditions in power grid for minor and major disturbances.
CO6: Develop the mathematical solution for achieving stability in power grid during transient state.
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
- Teacher: Kavitha M
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
To understand the various applications of electronic devices for conversion and control of the electrical power.
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ÿ To analyze the electromechanical system.
ÿ To impart knowledge in construction details, principle operation and performance characteristics of DC machines and transformer.
ÿ To evaluate the different losses and performance of DC machines and transformer using different testing methods.
ÿ To analyze the performance characteristics of DC machines.
ÿ To impart knowledge in three phase transformer connection.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the concept of magnetic circuits.
CO2 - Explain the principle, types, effect of armature reaction and commutation of DC generator.
CO3 - Analyze the performance characteristics of DC motor using various testing methods.
CO4 - Understand the principle, equivalent circuit and performance of a single phase transformer.
CO5 - Compare the saving of copper of auto transformer with a two winding transformer.
CO6 - Analyze the various transformer connection for specific application.
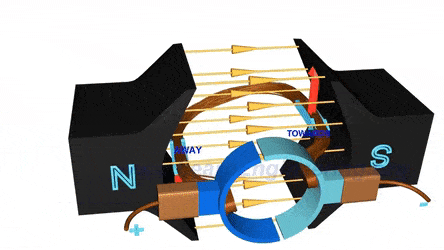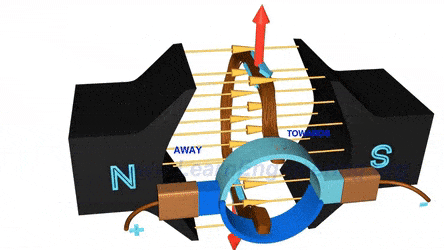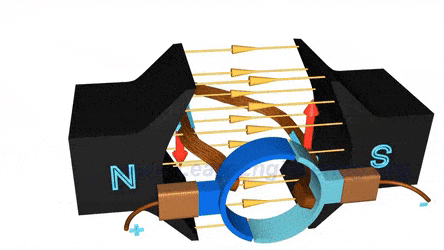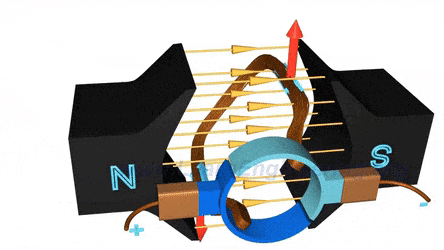
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge about the basic ideas and principles of Electrical Engineering.
To provide knowledge for the analysis of basic DC, AC and magnetic circuits.
To determine the response of electrical circuits using various network theorems.
To gain knowledge about the working of various machines.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Analyze electrical circuits using Kirchoff’s Laws and its application
CO2 - Compare the behavior of R, L and C and their combinations in AC circuits.
CO3 - Apply various network theorems for the analysis of electrical circuits
CO4 - Understand the basic concepts of magnetic circuits
CO5 - Describe the construction and working principle of DC and AC machines
CO6 - Demonstrate the various types of stepper motor.
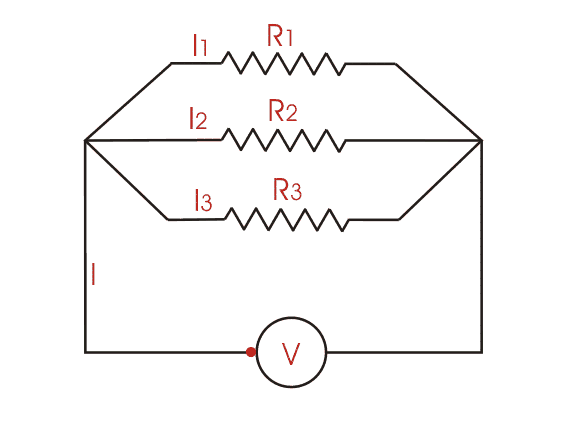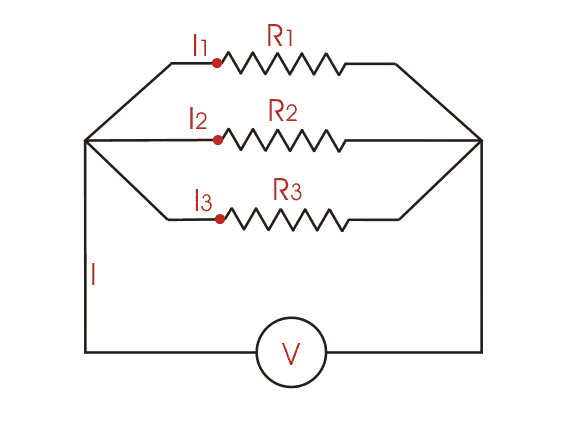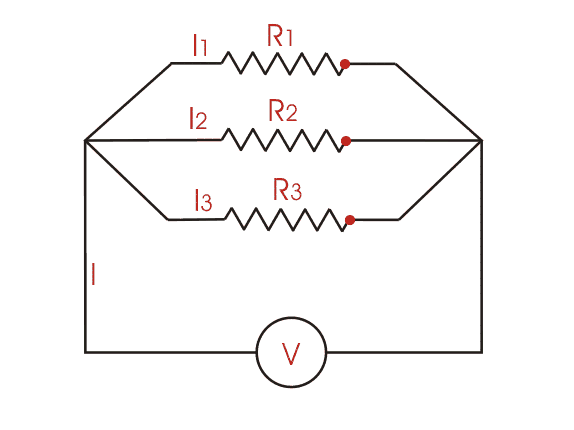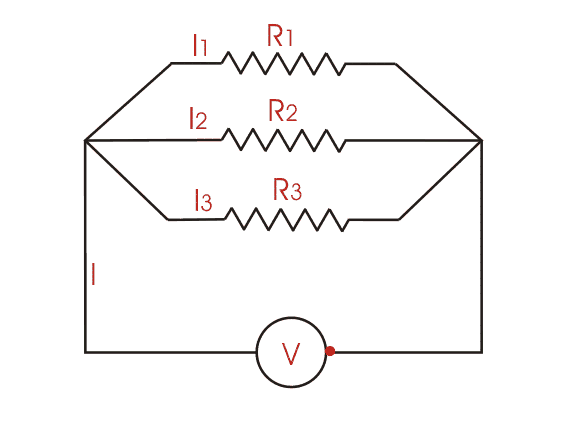
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on Construction and principle operation of Asynchronous and Synchronous machines.
To impart knowledge on not self-starting AC machines.
To convey knowledge on speed control of three-phase induction motors.
To analyze performance characteristics of Synchronous and Asynchronous machines.
To convey knowledge on synchronized operation of an Alternator with an Infinite bus bar.
UNIT
1 SYNCHRONOUSGENERATORS 10 Hrs.
Constructional features - EMF Equation - Armature Reaction - Synchronous Reactance - Voltage Regulation -Synchronous Impedance Method - MMF and Potier Methods - Synchronising & Parallel Operation - Two Reaction Theory - Determination of Xd and Xq (Slip test).
UNIT 2 SYNCHRONOUS MOTORS 9 Hrs.
Principle of Operation - Starting Methods - Effect of Increased Load with Constant Excitation - Effect of Changing Excitation on Constant Load - Different Torque - Power flow equation - Phasor diagram - V and inverted V curves - Hunting and suppression methods.
UNIT 3 THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTORS 9 Hrs.
Construction - Types of 3- Phase Induction Motors - Rotating Magnetic Fields - Torque Equation – Condition for Maximum Torque - Slip, Torque Slip Characteristics - Power Stages in Induction Motors - Losses and Efficiency - Plugging - Cogging and Crawling - Concept of Induction Generator.
UNIT 4 CIRCLE DIAGRAM AND CONTROL METHODS OF 3- PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 9 Hrs.
No load and Blocked rotor tests - Equivalent circuit - Construction of Circle diagram - Starting methods - Speed control - Double cage Induction motor.
UNIT 5 SINGLE PHASE AC MOTORS 8 Hrs.
Double Field Revolving Theory - Types of Single Phase Induction Motor - Equivalent Circuit (Qualitative) -Repulsion Motor - Series Motor - Universal motor, AC Servomotor, Linear Induction Motor, Hysteresis motor. Max. 45 Hrs.
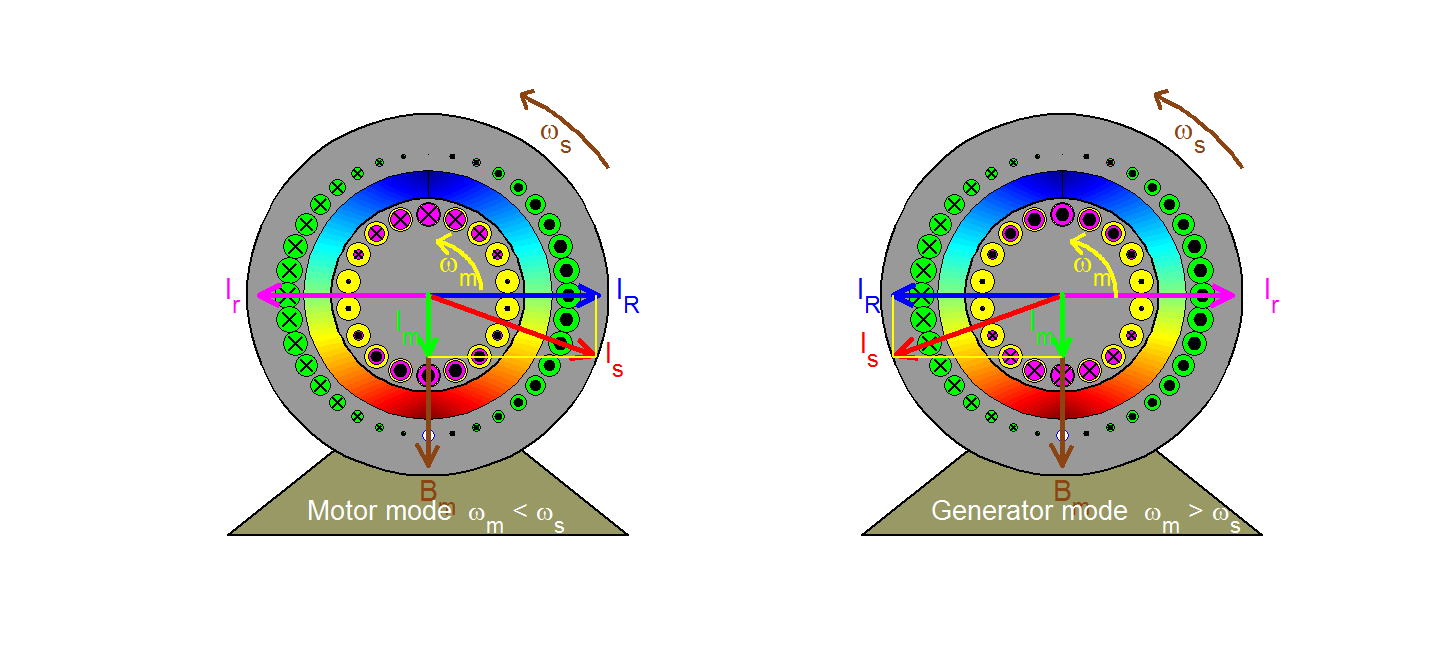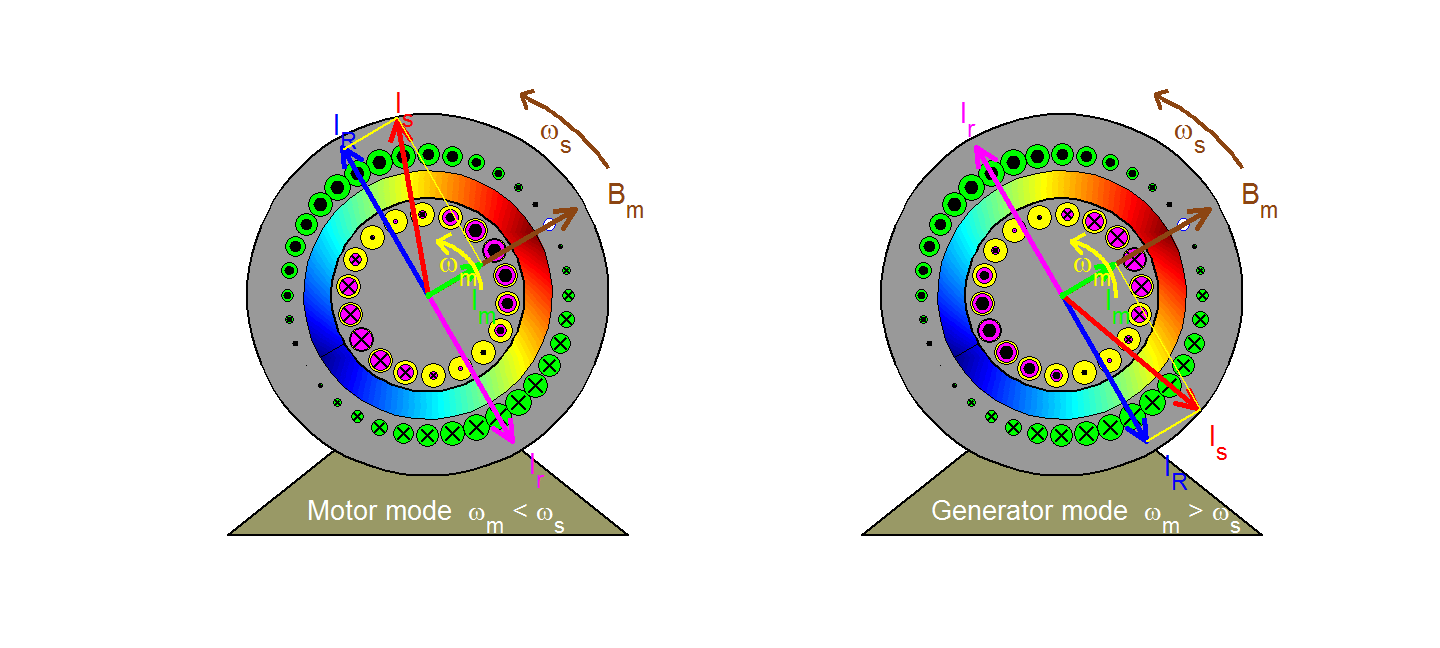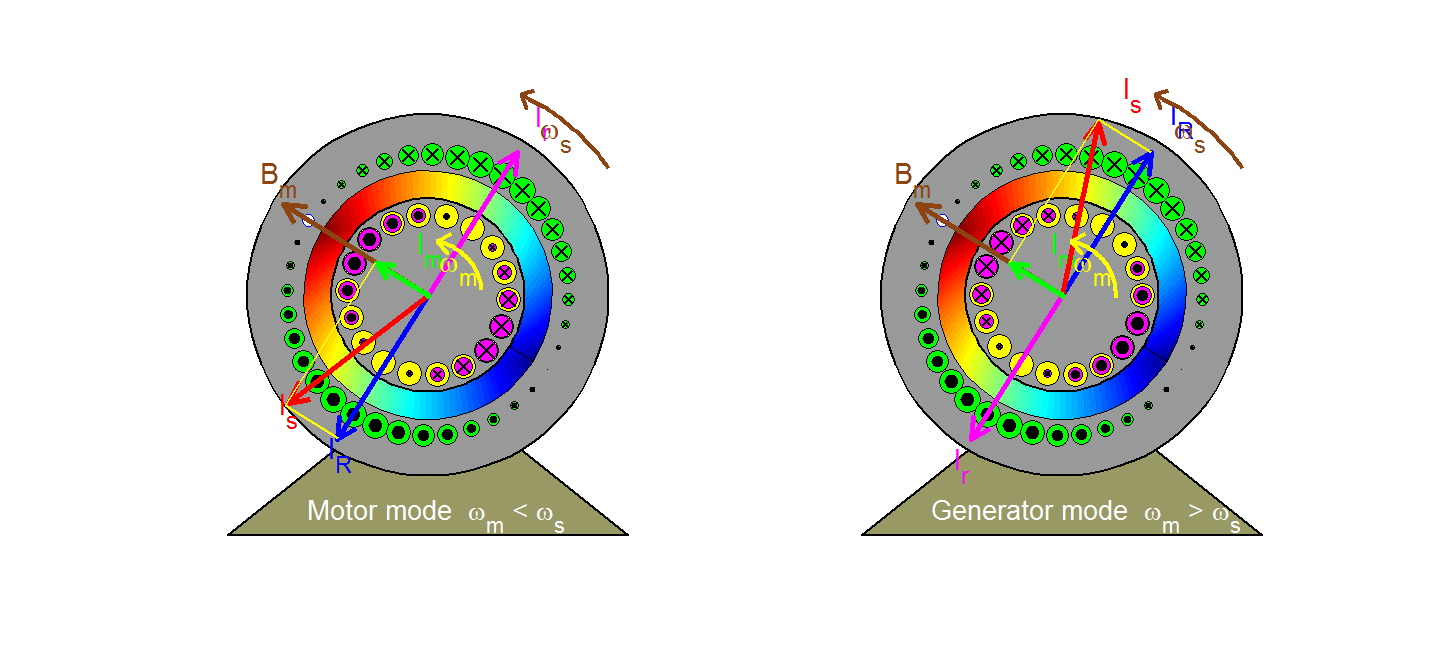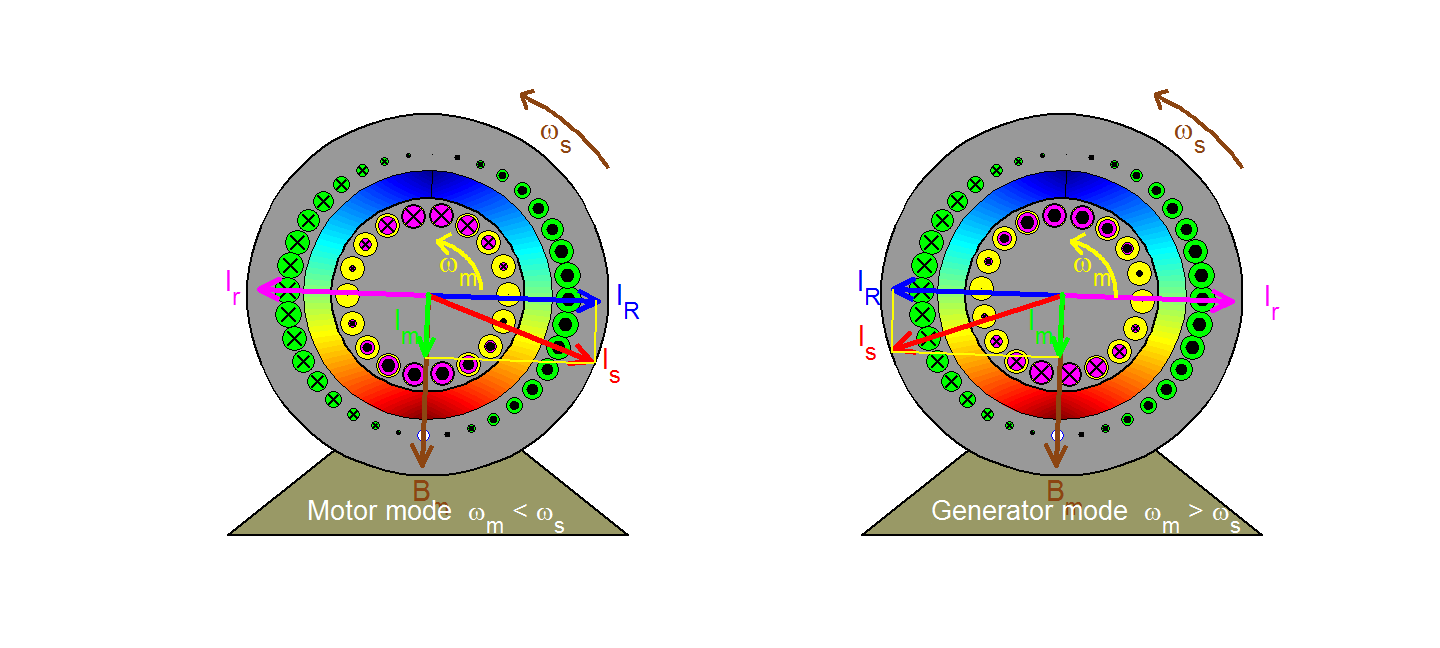
- Power electronics is a technology that deals with the conversion and control of electrical power with high-efficiency switching mode electronic devices for a wide range of applications.
- Power electronics is ushering in a new kind of industrial revolution because of its important role in energy conservation, renewable energy systems, bulk utility energy storage, and electric and hybrid vehicles, in addition to its traditional roles in industrial automation and high-efficiency energy systems.
- Power electronics has recently emerged as a complex and multidisciplinary technology after the last several decades of technology evolution.
- The technology embraces the areas of power semiconductor devices, converter circuits, electrical machines, drives, advanced control techniques, computer-aided design and simulation, and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), as well as artificial intelligence (AI) techniques.

- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- Teacher: Sivachidambaranathan V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge about engineering materials, calculation of mmf for air and iron path for rotating machines.
To impart knowledge in design of armature and field system of DC machines.
ÿ To impart knowledge in design of core, yoke, windings and cooling systems of transformer.
To impart knowledge in design of stator and rotor of induction machines.
To impart knowledge in design of stator and rotor of synchronous machines

- Teacher: Sivagami P
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To gain knowledge in the designing of state space analysis.
- To obtain the state transition matrices and the solution of state equations.
- To design a state observer using the concept of controllability and observability.
- To have a clear understanding in Digital Data Systems.
- To have an exposure in different stability analysis of Nonlinear Systems

- Teacher: Meenakshi V
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Abitha Memala W
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
- Teacher: Senthil Nayagam V
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the fundamental electrical concepts.CO2 - Analyze simple DC circuits using appropriate techniques.
CO3 - Apply phasor analysis techniques to solve AC circuits.
CO4 - Demonstrate the characteristics of various semi-conductor devices.
CO5 - Analyze characteristics of switched mode power supply.
CO6 - Design power supply unit using regulator IC.
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To analyze the electromechanical system.
To impart knowledge in construction details, principle operation and performance characteristics of DC machines and transformer.
To evaluate the different losses and performance of DC machines and transformer using different testing methods.
To analyze the performance characteristics of DC machines.
To impart knowledge in three phase transformer connection.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the concept of magnetic circuits.
CO2 - Explain the principle, types, effect of armature reaction and commutation of DC generator.
CO3 - Analyze the performance characteristics of DC motor using various testing methods.
CO4 - Understand the principle, equivalent circuit and performance of a single phase transformer.
CO5 - Compare the saving of copper of auto transformer with a two winding transformer.
CO6 - Analyze the various transformer connection for specific application.
- Teacher: Jaya Prakash S
- Teacher: Sundar Singh Jebaseelan S D
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the fundamental electrical concepts.CO2 - Analyze simple DC circuits using appropriate techniques.
CO3 - Apply phasor analysis techniques to solve AC circuits.
CO4 - Demonstrate the characteristics of various semi-conductor devices.
CO5 - Analyze characteristics of switched mode power supply.
CO6 - Design power supply unit using regulator IC.
- Teacher: Meenakshi V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on Construction and principle operation of Asynchronous and Synchronous machines.
To impart knowledge on not self-starting AC machines.
To convey knowledge on speed control of three-phase induction motors.
To analyze performance characteristics of Synchronous and Asynchronous machines.
To convey knowledge on synchronized operation of an Alternator with an Infinite bus bar.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the principle and predetermine the regulation of a Synchronous Generator.
CO2 - Analyze the operation of synchronous motor under various excitation conditions.
CO3 - Explain the principle, characteristics and losses of three phase induction motor.
CO4 - Realize the various methods of starting and testing of three phase induction motor.
CO5 - Explain the principle, types and equivalent circuit of single phase induction motor.
CO6 - Appreciate and select a suitable AC motor for particular application.

- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
- Teacher: Sivagami P
To understand the various applications of electronic devices for conversion and control of the electrical power.
- Teacher: Ramesh Babu A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
i) To impart knowledge about engineering materials, calculation of mmf for air and iron path for rotating machines.
ii) To impart knowledge in design of armature and field system of DC machines.
iii) To impart knowledge in design of core, yoke, windings and cooling systems of transformer.
iv) To impart knowledge in design of stator and rotor of induction machines.
v) To impart knowledge in design of stator and rotor of synchronous machines.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Calculate the MMF for rotating machines based on the major considerations.
CO2 - Learn, understand and apply the design procedure for DC machines.
CO3 - Analyze and apply the design procedure for core, yoke, winding and cooling systems of transformer.
CO4 - Learn, understand and apply the design procedure for stator and rotor of induction machines.
CO5 - Analyze and apply the design procedure for stator and rotor of synchronous machines.
CO6 - Select optimized design based on the requirement.
- Teacher: Sivagami P
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Apply Vehicle concept to electric vehicle
CO2 - Analyze the power conversion technique of electric vehicle
CO3 - Examine the performance of different electric drive train
CO4 - Select the appropriate electric motor for electric propulsion system
CO5 - Select a suitable battery for electric vehicle
CO6 - Analyze the recent technique used in modern electric vehicle
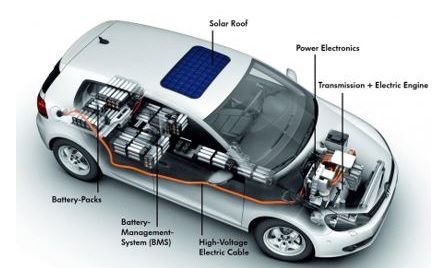
- Teacher: Regila Manohari M
- Teacher: Bharathi M L
- Teacher: Godwin Immanuel D
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide fundamental background for digital signal processing.
- To understand the basics of discrete time signals, systems and their classifications.
- To analyze the discrete time signals in both time and frequency domain.
- To design IIR filters and FIR filters using windowing techniques.

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To study the fundamental concepts of robotics and automation.
- To impart knowledge on various drive system, sensors & machine vision system.
- To learn the various manipulators, grippers as well as the various dynamic process.
- To acquire the concept of kinematics and inverse kinematics.
- To understand the programming and specific industrial applications.

- Teacher: Rajalakshmi G
To introduce basic concepts of various dynamics processes
To educate on the effect of various power sources and sensors.
To impart knowledge on the manipulators , grippers and robot dynamics
To introduce the evaluation criteria and tuning techniques of controllers
To introduce the concept of multi loop control techniques

- Teacher: Vedanarayanan V
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the electronics in automobiles.
CO2 - Explain the electronics in Ignition systems, Injection systems, Engine, Chassis and Safety systems.
CO3 - Understand the working of sensors, actuators in automobiles.
CO4 - Apply the knowledge of electronics in automobiles.
CO5 - Develop electronics in automobiles.
CO6 - Design a electronic system in automobiles.
- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
Business Economics integrated with Syllabus of CA Foundation - Business Economics and Business Commercial Knowledge
- Teacher: MUTHUVALAVAN R
This subject is part of Business Law and Business Correspondence & Reporting in CA Foundation, which is for 30 marks.
It is about general communication skills, comprehension and Passage writing.
Students to read newspapers, articles, talk and practice this language as an art.

- Teacher: AKHILA R
- Teacher: MUTHUVALAVAN R
Advanced Corporate Accounting Integrated with Syllabus of CA Intermediate Group Paper -5 Advanced Accounting
- Teacher: Murthy CMA
FASHION PSYCHOLOGY AND GROOMING
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To enable students to understand the trends in Clothing behavior
- Gain an insight into the planning process involved in Wardrobe Clothing selection.
UNIT I
Fashion flow chart - Fashion terminology - Cycle influences - Elements of fashion design - History of fashion. Introduction to Clothing, Understanding, and Purpose of clothing - Protection, Modesty, attraction. Social & Psychological aspects of fashion.
UNIT II
Clothing Values, Clothing Culture, Men and Women clothing and Ornamentation, Groups, Role & status of clothing. Clothing according to climatic conditions.
UNIT III
Selection of clothes, - Clothes for children, middle age, adults, types of clothes, according to human figure - Different material for different clothes - Color suitable for different garments.
UNIT IV
Modern Clothing-Youth style and fashion, Teddy boy, skins modes, hippies, punks, taste of youth and their life style. Ancient to modern clothing, minis maxis, unisex, fit women, glamorous woman. Casual and formal clothing. Fashion for all, ready to wear fashion, mass marketing of fashion.
UNIT V
Planning for clothing needs, Clothes for school, Clothes for parties, Clothes for sports, Clothes for resting Wardrobe Planning
COURSE OUTCOMES
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Understand terms involved in Fashion and Clothing .
CO2: Understand the selection of clothes for various age Groups .
CO3: Gain knowledge on Wardrobe Planning.
CO4: Planning for various clothing needs for different climatic conditions.
CO5: Know the Modern Clothing
TEXT/ REFERENCE BOOKS:
- ‘ A History of Fashion’ , Black A.J. (1985) , USA Orbits Publishing Ltd. Rouse E. (1989),
- ‘Understanding Fashion’,UK, Blackwell Science
- ‘The Dictionary of Costume’,Wilcox T. UK,- Bats ford Ltd.
- Fashion & color Mary Garthe, Rockport Publishers - Encyclopedia of fashion detail by Patric John, Ireland Batsford

- Teacher: SARANYA N
- Teacher: Krithika S
Researching the subject - Organizing matter - Structuring the report/presentation, Making Visual presentations
Presenting a Paper - Making a fully researched informative presentation - Official Correspondence- Letters- Memos- Emails - Notices- Public Announcements- Circulars.
Official Documentation - Agenda/Minutes of Meeting - Files and other Documents. Informative Communication – presentation skills - News Reports- Report Writing- Persuasive Communication - How to write Applications- letters- Articles persuasively- Meetings- Group Discussions- Interviews
The art of Negotiation and Persuasion- Writing a good CV/Resume- profile- Reviews (Film/Restaurant)- Articles- Creating Characters- Writing Stories- Exploring other forms- Writing for Print/Television/Films/Web- Role Play- Writing and Performing a Skit- Writing and Performing an Ad/Social Service Spot.
Final Presentation - complete presentation - with Performance.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to
CO 1: improve the skills in research techniques.
CO 2: Develop skills in Visual Presentations
CO 3. Develop the various Skills through Documentation and Negotiation.
CO 4: Understand the basics of communication and presentation

- Teacher: SARANYA N
- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
· To understand the basic principles of research and learn various methods available for collecting and analyzing data.
- To develop the ability to understand design strategies and plan design activities for women’s wear.
- To understand the application of various tools to fashion forecasting in Indian markets
- To comprehend fashion forecasting as a tool to understand consumer behavior in the Indian scenario.

- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
UPCYCLE FASHION
COURSE OBJECTIVES
ï To aim the hands-on foundation to reuse and recycle of various materials.
ï To generate the innovative ideas of new fashion products from Waste and alternatives to landfills, including reusing in creative ways.
ï To create self-awareness based on source reduction through efficient and effective usage of materials and energy.
LIST OF EXERCISES
Mind mapping, existing product research on reused and recycled materials in market, Designing, Product Making for
the followings:
1. Recycling of denim Products
2. Recycling of Saree
3. Recycling of Shirt
4. Recycling of T-Shirt
5. Recycling of Clothing fastenings

- Teacher: SOOSAI ANUGRAHA X
FASHION STYLING AND PHOTOGRAPHY
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To enable the students to identify areas of interest within the field of Fashion Styling and Image Design.
- To develop new fashion images through fashion photography to build new fashion trends.
- To develop the ability to create the complete look according to the theme, event, one’s personal style, ongoing trends, etc.
LIST OF EXERCISES:
- Introduction to styling, Understanding the dynamics of the Style look book, music, promos, advertising, e-commerce, digital video, and films.
- Photography Basics -Parts of a camera, Elements of photography, lighting, camera techniques, Depth of Field and Focus and framing.
- Styling for Men’s and Women’s Wear- Party Wear, Casual Wear, Sportswear, Formalwear.
- Preparation for The Shoot - Selection of location for an indoor/outdoor, Creation of a suitable ambiance/backdrop for the shoot, Sourcing, and coordination of clothes and accessories according to a theme/season, criteria and selection of model, Coordination of movement, mood, and image of model and apparel.
- Photo Shoot Styling for Men’s and Women’s Wear: Building effective wardrobes with balanced assortments using coordinated and mix-matched apparel Draping techniques using scarves and other apparel Accessorizing with jewelry, bags, belts, and other accessories. Accentuating attire using different techniques of make-up and hair-dos Styling for fashion shoots and fashion shows and its use in retailing
- Editorial -apparitional styling for magazines and designer’s look book and similar media in both printed and digital forms.
- Commercial -styling for advertisements, films, fashion shows, and other promotional platforms.

- Teacher: SARANYA N
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- The design portfolio is the expression of the graduating student’s creativity design technical expertise and illustration and presentation skills. It is a body of work that is the culmination of all previous semesters’ learning and a visual expression of integrative learning.
- The students document all their presentable work done through all semesters and those that portray the student’s areas of interest.
- The portfolio can be an effective means of communicating the capacities and capabilities of the students to anyone who seeks their skills and talents
COMPONENTS OF PORTFOLIO:
1. Individual design philosophy that manifests itself in all design projects
2. Design Projects: Industry–oriented: The projects should exhibit a thorough understanding of industry segmentation e.g. buying a house- export house- corporate house- in the house design team of brands/boutiques- designer unit both couture and RTW- Self – generated briefs as an expression of the student’s individual design aesthetics. Each project must be specifically geared and suitably edited and presented to best demonstrate both the creative and commercial orientation of the student.
The ability to integrate multi-pronged learning of the previous semesters with special aptitude research- historical referencing of fashion/ costume- assessment of fabric suitability to justify sourcing/development of surface design techniques- extended/edited range plan- illustrations both hand – done and on computers along with flat working drawings and specification sheets would be essential attributes.
3. Demonstrated awareness and competence in the latest design-oriented computer software as required intensively by the industry
4. Suitable presentation techniques and graphics
5. Marketing and Visual Merchandising of designs through logo design- packaging etc.
6. Catalogues and advertisements for line promotion may also be made

- Teacher: SARANYA N
- Teacher: Priyadarshini R
- Teacher: DEVI NANDANA
The course aims to develop working knowledge and understanding of the cultural and historical diversity of England in relation English language and literature so as to enable them to critically analyse the influence of history and cultural diversity on literature and language.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Kavipriya M

Course proposes
· To enable the students to understand the origin and development of English drama
· To critically appreciate the trends that influenced the theatre and drama.
· To provide an insight into popular culture and its dramatic expressions.
· To enhance the knowledge on various aspects of Drama.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
This course comprises novels of different types with a brief introduction to the techniques of fiction as a genre. The students would be able to distinct and analyse the literary characteristics of the novel. The students will be made aware of the social background, structure and theme of the prescribed novels and would be able to effectively communicate ideas related to the novel during class and group activities . They would be able to read, summarize, and evaluate critically the works suggested for the course. 📖 ☕

• The paper provides opportunities for students to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts
that present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative.
• To provide an opportunity to the students to improve their vocabulary
• To develop skills relating to creative writing.

This course familiarizes the students with the concepts and theories of translation and introduces them the art of translation. The students will be able to develop critical thinking on the connection between usage of language and translation and they will be able to implement the diverse approaches to translation prevalent within the theories and types of translation.

OBJECTIVE:
To enable students to achieve a high degree of fluency in English.
To enhance the effectiveness of oral and written communications
To equip learners with languages skills that could provide good career opportunities
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
At the end of the course, the students will be able to
• get knowledge on Communication and its types
• enjoy working in an online environment knowing the listening strategies
• learn how to face various audience
• learn how to impress the audience by communicating Effectively
• create PPT, Blogs and participate in online discussion

Objectives:
• Understanding the origins, structure and development of language and its application to other areas of humanistic and scientific knowledge.
• Understanding the general characteristic of the structure of language, its phonological sound system, word structure, and phrase and sentence patterns.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Grasp the complexity of language as a communication system shaped by cognitive, biological, cultural, and social factors. Demonstrate understanding of the concepts, theories, and methodologies used by linguists in qualitative and quantitative analyses of linguistic structure, and patterns of language use. Demonstrate understanding of processes of language change and variation, the role of language in reflecting and constructing social identities, and the distinctive properties of human language. Acquire the technical vocabulary and theoretical tools of the field, necessary to read published linguistic research. Apply their understanding of linguistic concepts, methods and approaches to the construction and analysis of meanings in different modes of communication. Are ready for significant scholarly participation in the field of linguistics.

- Teacher: Amutha Monica
To make the learners aware of the social, cultural and psychological implications of the literary
masterpieces of the Neo-classical and the Romantic ages of British Literature.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
Course Objectives:
· To make the learners aware of the social, a cultural and psychological implication of the modern age
· To familiarize the students with the evolution of the different genre in Britain.
· To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
· To provide knowledge on the Romantic age and Victorian Age of British Literature.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
COURSE OBJECTIVE
• To enable the students to read and respond to specialized (scientific) materials and to subject
areas included for their study.
• To provide an opportunity for students to comprehend and react in oral and written forms to the
specialized texts that they read in their respective courses so as to summarise and paraphrase
the texts presented in the class.
• To provide opportunities for students to respond to listening and writing tasks by using digital
tools
• To enhance 21st century skills like communication, collaboration, critical thinking and creativity
through blended learning contexts
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Classify technical words to use them in sentences framing, compose problem solving paragraphs in semi formal letters, use rubrics to self evaluate, listening to take linear notes, reading to infer, predict and to differentiate facts from opinions, guess contextual meaning of words, modify the verbs in present tense, use learnt language in role plays with 80% accuracy
CO2: Categorize information based on global understanding of reading materials to prepare notes in graphic format like tables, use cohesive words related to comparing and contrasting by writing short paragraphs based on visual inputs in the form of bar diagrams, pie chart etc; describe process by composing paragraphs, recognize topic sentences and identifying verbal phrases while reading, use prepositions and prepositional phrases, modify the verbs from one form to the other in past and future tenses with 80% accuracy
CO 3: Generate specific information by using scanning and skimming reading materials, Construct questionnaire to conduct class survey by framing open ended questions to generate data on current issues to make oral presentations and report in written format by using template provided, arrange sentences in the right order by using sentence linkers as clues, revise the written materials by identifying elements of editing, edit errors related to subject verb agreement, punctuation and spelling besides coherence with 70 % accuracy, use reported speech in spoken and written form in class room in reporting contexts, list paired words, word associations by recalling and identifying by noticing them while reading CO 4: Paraphrase based on reading to discuss and design products thereby to create and design user manual, identify technical words related to compound nouns to expand and to paraphrase, enact role plays to present the product, discuss facts and opinions of the product in pair and team work, read current topics to summarise in note form , listen to current issues to deduct meaning from the context, choose the right option, define technical words related to the reading materials.
CO 5: Summarise reading materials, use the ideas while writing essays, take, and differentiate meaning of homonyms and homophones
CO 6: Demonstrate the ability to work cooperatively in a small group environment, in activities developed for language learning in the classroom/ online for formative assessment purposes, use and develop rubrics for self reflection, apply elements of reasoning skills for critical reading, identify facts and opinions and make judgements independently, develop intellectual courage and perseverance in pair and group work.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Classify technical words to use them in sentences framing, compose problem solving paragraphs in semi formal letters, use rubrics to self evaluate, listening to take linear notes, reading to infer, predict and to differentiate facts from opinions, guess contextual meaning of words, modify the verbs in present tense, use learnt language in role plays with 80% accuracy
CO2: Categorize information based on global understanding of reading materials to prepare notes in graphic format like tables, use cohesive words related to comparing and contrasting by writing short paragraphs based on visual inputs in the form of bar diagrams, pie chart etc; describe process by composing paragraphs, recognize topic sentences and identifying verbal phrases while reading, use prepositions and prepositional phrases, modify the verbs from one form to the other in past and future tenses with 80% accuracy
CO 3: Generate specific information by using scanning and skimming reading materials, Construct questionnaire to conduct class survey by framing open ended questions to generate data on current issues to make oral presentations and report in written format by using template provided, arrange sentences in the right order by using sentence linkers as clues, revise the written materials by identifying elements of editing, edit errors related to subject verb agreement, punctuation and spelling besides coherence with 70 % accuracy, use reported speech in spoken and written form in class room in reporting contexts, list paired words, word associations by recalling and identifying by noticing them while reading
CO 4: Paraphrase based on reading to discuss and design products thereby to create and design user manual, identify technical words related to compound nouns to expand and to paraphrase, enact role plays to present the product, discuss facts and opinions of the product in pair and team work, read current topics to summarise in note form , listen to current issues to deduct meaning from the context, choose the right option, define technical words related to the reading materials.
CO 5: Summarise reading materials, use the ideas while writing essays, take, and differentiate meaning of homonyms and homophones
CO 6: Demonstrate the ability to work cooperatively in a small group environment, in activities developed for language learning in the classroom/ online for formative assessment purposes, use and develop rubrics for self reflection, apply elements of reasoning skills for critical reading, identify facts and opinions and make judgements independently, develop intellectual courage and perseverance in pair and group work.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To understand specialized subject areas and skills included for their study.
To comprehend and react in oral and written forms to the specialized texts
To respond to listening, reading and writing tasks by using digital tools
To enhance communication, collaboration and critical thinking skills
To explore creativity through blended learning contexts

- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: SUFINA K
- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: Berlin Mary S

Introduce the students to basic principles, theories and practices in ELT.
Enable students to identify changes that took place over a period of time in the area.
Analyze the teaching approaches and methods. Recall basic approaches for teaching language with four skills.

Course Objectives:
● To introduce the students to the body of literary writings that stands evergreen in the regions of Kenya, Africa,
Australia, Canada, New Zealand and Pakistan.
● To acquaint the students the various genres.
● To acquaint the students with different authors relating to different regions and literature.
● To make the students approach selected texts for their literary value and cultural importance.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
Course Objectives:
To make the learners aware of the social, cultural and psychological implications of the Neo-classical.
To familiarize the students with the evolution of the genre of fiction in Britain.
To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
To provide knowledge on the Romantic age of British Literature.
- Teacher: U S AKSHARA GOVIND
Course Objectives:
• To make the learners aware of the social, a cultural and psychological implication of the modern age
• To familiarize the students with the evolution of the different genre in Britain.
• To acquaint the students with different literary era, movements and authors relating to British history
• To provide knowledge on the Romantic age and Victorian Age of British Literature.

- Teacher: Sowmiya L.M.
- Teacher: MRITTIKA MAITRA
- Teacher: Srijothi Priya R T

- Teacher: Esther Rajathi D J B
- Teacher: Shamili Devi G
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: Sashtihasini M P
- Teacher: Srijothi Priya R T
- Teacher: Aishwarya S
- Teacher: Anurekha S
- Teacher: Anurekha S
- Teacher: VISHALI S
- Teacher: Esther Rajathi D J B
- Teacher: Shamili Devi G
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: Mr. L. J. Binovin Lal, M. A., M. Phil., (Ph.D).
- Teacher: Srijothi Priya R T
- Teacher: Aishwarya S
- Teacher: Malavika J
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
· To enhance student's critical and analytical reading and writing skills through women's literary works.
· To identify various critical theories, such as feminism, Eco feminism and new criticism.
· To generalize deconstruction, gynocriticism, reader response, psychoanalysis and several other relevant theories
· To apply these theories enhance the assigned texts.
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Swarnamughi K
- Teacher: Amutha Monica
- Teacher: Nithyasri S
- Teacher: VISHALI S
- Teacher: Senthil Kumar Sivamathiah
Course Objective:
To provide an exposure to the process and instrumentation & control applications in various industries like paper,
petrochemical, iron and steel, mining, pharmaceutical, nuclear and power plant industries.

To expose the students to the basic concepts of optical fibers and their properties.
To provide adequate knowledge about the Industrial applications of optical fibers.
To expose the students to the Laser fundamentals.
To provide adequate knowledge about Industrial application of lasers.
To provide adequate knowledge about holography and Medical applications of Lasers.

- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
COURSE OBJECTIVES
• To understand the basic concepts of signal and Image processing.
• To explore DFT for 1-D and 2-D signal
• To understand fundamentals of Image Processing
• To provide knowledge of the applications of the theories taught in Image Processing
• To apply digital image processing techniques for edge detection.
• To design and implement 1-D and 2-D Signal and Image Processing applications.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1-Understand the concept of DT Signal and DT Systems
CO2-Classify and analyze discrete time signals and systems
CO3-understand Basics of Image formation and transformation using sampling and quantization
CO4-Design and develop the enhancement techniques for digital Image Processing
Co5-To apply digital image processing techniques for edge detection.
CO5-Develop small projects of 1-D and 2-D Signal and Image Processing
- Teacher: Kanchana D
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: YOKESH V
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B
- Teacher: Inbathamizh L
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Dr. Mohmmad Ashaq Sofi
This effort on Universal Human Values (UHV) is in continuation with that tradition of self-enquiry, for the wellbeing of all :
It draws upon universal essence of these explorations.
It is put forth as proposals for self-exploration on one’s own right.
It is a systematic study of the harmony – from individual to family, society and nature/existence.
It is a proposal about the natural laws, about the reality, as it is – in a way that anyone can explore and understand it on their own right.
It follows a process of self verification, on the basis of one’s own Natural Acceptance, leading to self-confidence and self- evolution.
It encourages students to discover what they consider valuable. Accordingly, they are able to discriminate between valuable and the superficial in real situations in their life .
It enables the student to discover and understand the innate value of human being in every aspect of life (individual, family, society, nature/existence), reinforce the commitment and courage to live accordingly.
It facilitates discussion and self-exploration
Life goals, reflection on what they are and what they want to be :
Relationships in family
Relationships with society
Relationships with nature/existence
It provides a universal basis for human values
That supplements and can provide direction to the present educational and social systems.
The basic human values are fundamental to human nature and human existence.
These values are universal in nature, applicable to all human beings, in all places and all times, e.g. truth, love and compassion.

- Teacher: Viji Amutha Mary A
- Teacher: SUDHA D
- Teacher: Joshila Grace
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR K
- Teacher: Karunya K
- Teacher: Roobini M S
- Teacher: Asha P
- Teacher: Jeberson Retna Raj R
- Teacher: Ramya R
- Teacher: V SARANYA
- Teacher: Asha Judi V
- Teacher: DHARANI V
- Teacher: Sathish Jackson Putti Vincent
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To develop a holistic perspective based on self-exploration about themselves (human being), family, society and
- nature/existence
- To understand (or developing clarity) the harmony in the human being, family, society and nature/existence
- To strengthen self-reflection
- To develop commitment and courage to act
- Teacher: Dr.Divya A
- Teacher: Bhuvana B P
- Teacher: Sharanya C
- Teacher: RAJESWARI D
- Teacher: Dr Jayasudha F V
- Teacher: SOWMIYA G
- Teacher: Shamini G I
- Teacher: MUTHIAH M. A
- Teacher: Krishnamoorthy N R
- Teacher: Bharathi R
- Teacher: PURUSHOTHAMAN S
- Teacher: MALATHI T
- Teacher: YOKESH V
- Teacher: Mohammed Aneesh Y
COURSE OBJECTIVE’S
- To understand the network architecture and protocols supported for connecting devices in a network.
- To gain the knowledge of framing in data link layer.
- To learn the functions of network layer and the routing strategies with their associated protocols.
- To introduce the protocols used for end to end packet delivery in transport layer.
- To understand the application layer protocols.

- Teacher: Pushpavalli M
- To learn basics of Sensor and Network technology
- To learn key routing protocols for sensor networks and main design issues
- To learn transport layer protocols for sensor networks, and design requirements
- To understand the medium access control protocols and address physical layer issues
- To learn the security features in WSN

- Teacher: Anbuselvi G
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the technologies and business trends impacting mobile applications.
CO2 - Understand and remember the components of android, iOS and Windows mobile applications.
CO3 - Learn the programming languages and techniques for developing mobile applications.
CO4 - Develop mobile applications with compelling user interface and database connectivity for real time applications for iOS.
CO5 - Deploy mobile applications with compelling user interface and database connectivity for real time applications for Windows OS.
CO6 - Develop and deploy mobile applications using silverlight.
- Teacher: KALAIVANI A
- Teacher: Dr. S. Jancy
- Teacher: Aishwarya R
- Teacher: Ruby Angel
- Teacher: Joshila Grace

- Teacher: SATHIYARAJ A
- Teacher: Sivasangari A
- Teacher: SundaraVelarani K
- Teacher: Gomathi R M
- Teacher: Gowri S
S614BLH38 - CYBER FORENSICS
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To learn about the Cyber Crime and to Understand the concepts of open source tools
To learn about Cyber Forensics and to identify and report the forensic on disk level
To learn about Cyber Investigation and to Implement forensic concepts in network level
To learn about Evidence Management and to Analyze Virtual machine forensic
To learn about Cyber Laws and Authorities and Analyze various cloud forensic

- Teacher: Kiruthika Devi B.S
- Teacher: Alex Anand D
- Teacher: Anu Disney D
- Teacher: MANGAIRKARASI S

- Teacher: JESLIN SHANTHAMALAR JACOB SAMUEL
- Teacher: Dr.Sridevi N
- Teacher: POTHUMANI S
This course aims at understanding important medically important virus its mode of infection, pathogenesis prophylaxis and treatment.
Topic: 1
- General Concepts: Virus history,
- Diversity,
- shapes,
- sizes
- components of genomes.
- Isolation and purification of viruses and components.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 2
- Consequences of virus infection to animals
Consequences of virus infection to human.
- Viral infection: affect on host
macromolecules.
- Viral infection: establishment of the antiviral state.
- Viruses counter attack mechanisms.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 3
- Classification of viruses and nomenclatures.
- Positive strand RNA viruses- Picornaviruses. Flaviviruses
- West Nile virus and Dengue virus.
- Coronaviruses- SARS pathogenesis
- Negative strand RNA viruses Paramyxoviruses. Orthomyxoviruses
- Influenza pathogenesis and Bird flu.
- Rhabdoviruses: Rabies pathogenesis.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 4
- dsRNA viruses-
- Reoviruses: structure, classification,
- Reoviruses: life cycle; reverse
transcription.
- Retroviruses: HIV, viral pathogenesis and AIDS.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 5
- Small DNA viruses: parvo,
- polyomaviruses.
- Large DNA viruses: Herpes,
- adeno-,
- poxviruses.
- Miscellaneous viruses.
- Assignment
- Quiz
- Dr.S.SUDHA: Bavani latha Muthiah
Drug Regulatory Affairs gives awareness in the aspects of Regulatory and Quality Compliance in the pharmaceutical industry, National and International Drug Approvals & Bio-ethics, Research Methodology & Pharmacological Screening, Modern Analytical Techniques, Clinical Trials & Healthcare Policies, National Regulatory Affairs, International Regulatory Systems, Emerging Concept in Regulatory Affairs, GLP, GMP & Validation, Intellectual Property Rights & Bioethics. In an overall the basics principles of Regulatory Affairs, GLP, IPR and Bioethics in Clinical Research are covered.
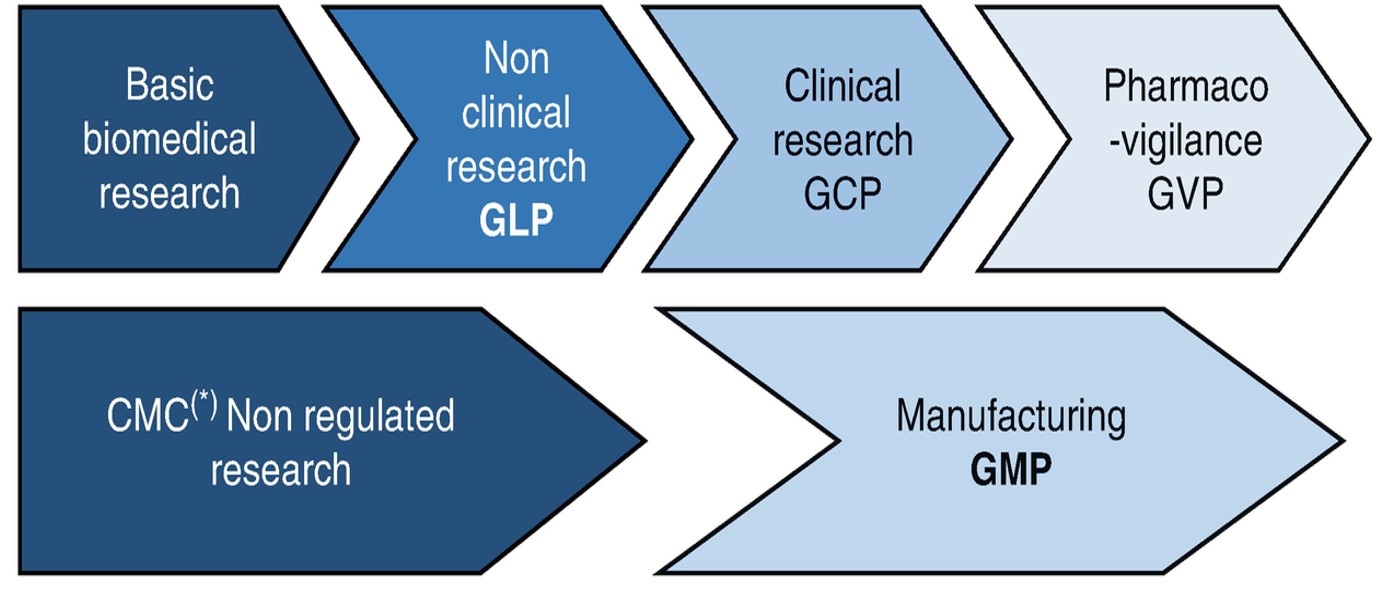
COURSE OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this course is to introduce students to scientific foundation of microorganisms and their
relationship to agriculture and environment. The course will appraise the students about application/control of
microbes for agriculture and how to design approaches to mitigate environmental pollutants
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
This course aimed to understand microbiology of marine environment with special emphasis on microbiological ecology, taxonomy, nutrient cycle, food microbiology and microbial biodegradation.

- Teacher: Jesia Persis Preethi
This course aims at understanding important medically important virus its mode of infection, pathogenesis prophylaxis and treatment.
Topic: 1
- General Concepts: Virus history,
- Diversity,
- shapes,
- sizes
- components of genomes.
- Isolation and purification of viruses and components.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 2
- Consequences of virus infection to animals
Consequences of virus infection to human.
- Viral infection: affect on host
macromolecules.
- Viral infection: establishment of the antiviral state.
- Viruses counter attack mechanisms.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 3
- Classification of viruses and nomenclatures.
- Positive strand RNA viruses- Picornaviruses. Flaviviruses
- West Nile virus and Dengue virus.
- Coronaviruses- SARS pathogenesis
- Negative strand RNA viruses Paramyxoviruses. Orthomyxoviruses
- Influenza pathogenesis and Bird flu.
- Rhabdoviruses: Rabies pathogenesis.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 4
- dsRNA viruses-
- Reoviruses: structure, classification,
- Reoviruses: life cycle; reverse
transcription.
- Retroviruses: HIV, viral pathogenesis and AIDS.
- Assignment
- Quiz
Topic: 5
- Small DNA viruses: parvo,
- polyomaviruses.
- Large DNA viruses: Herpes,
- adeno-,
- poxviruses.
- Miscellaneous viruses.
- Assignment
- Quiz
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø This course aims on studying interaction of microorganisms and food in relation to food-borne diseases, food spoilage and bioprocessing of food and dairy products.
Ø To make students learn about technologies to render foods and dairy products safe and analytical techniques for monitoring of food biological safety.

- Teacher: Usha Nandhini S
- Teacher: INDUMATHI S M
- Teacher: Kavi Prabha A
- Teacher: Dr. Saqib Hassan
- Teacher: Prakash P
Clinical Microbiology course will give us a comprehensive knowledge about the microbes.
With this we will get to know the classification, structure and function of the microbes.
Moreover, we will have a thorough idea about their role on human health.
Also we will come to know about different life threatening diseases caused by the microbes.
- Teacher: RoselinJenifer D
- Teacher: Jancy Mary E
Unit: 1 – CELLS AND CELLULAR METABOLISM 12 Hrs
Introduction to human anatomy and physiology – Basic elements of life, characteristics and maintenance of life – levels of organisms, structure of matter, chemical constituent of cell – movement through cell membrane, life cycle of cells and control of cell reproduction, metabolic process, control of energy and metabolic reactions, metabolic pathway - nucleic acids and protein synthesis – change in genetic information.
Unit: 2 – TISSUES AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM 12 Hrs
Tissues – epithelial, muscular and nervous tissues – integumentary system, types of membranes, skin – accessory organs, disorders, regulations of body temperature – Bone structure, development, function and organization of skeleton – joints, classification, structures and movements – muscle, structure and types, actions and responses.
Unit: 3 – BODY SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS 12 Hrs
Blood, circulation and function – lymphatic system-Endocrine system, endocrine glands, structure and function – respiratory system, structure and function – cardiac system, structure and function.
Unit:4 – NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND SENSES 12 Hrs
Nervous tissue, cell membrane potential, classification of neurons and nerve fibres – meninges, spinal cord, brain – peripheral and autonomic nervous system – somatic and special senses, receptors and sensations (smell, taste, hearing, equilibrium and sight).
Unit: 5 – METABOLISM AND NUTRITION 12 Hrs
Digestive system, structure and function – urinary system, kidney and nephron, structure and function – reproductive system – metabolism and nutrition.
Max. 60 Hours
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology, 11th Edition, 2011, Martini, Nath, and Bartholomew.
2. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology, 12th Edition, 2017, Elaine N. Marieb and Suzanne M. Keller.
- Teacher: Beryl Vedha Y
Thermal Engineering is the study of heating and cooling processes in open and closed environments. As an academic discipline, it involves the science of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To make the student understand the overall view of thermal engineering through topics such as Power cycles, IC Engines, Steam nozzles & turbine, air compressors and Refrigeration and Air conditioning.
- This subject enables the students to understand the principle of operation, construction and control of several thermal equipment's which find wide applications in a variety of fields like power generation, automobile industry, process industries, food preservation and human comfort.
- It provides the fundamentals for Power plant Engineering, Automobile Engineering, Turbo machinery and Refrigeration & Air conditioning (R&AC)

COURSE OBJECTIVES
· To understand the layout and working of conventional and non-conventional power plants
· To understand the working power plant equipment’s and instruments
· To understand the economics of power plants and environmental aspects
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Nagpal G.R., Power Plant Engineering - Khanna Publishers, 1996.
2. Domkundwar, Power Plant Engineering - Dhanpat Rai & Sons, Delhi, 1988.
3. Vopal and Stortzki,” Power Plant Engineering”, PHI, 2007.
4. El Wakil M.N., “Power Plant Technology”, McGraw Hill, 1985.
5. Joel Weisomon and Roy Eckart, “Modern Power Plant Engineering”, PHI, 1985.
6. Rai G.D., "Non conventional sources of Energy”, Khanna Publishers Delhi, 1994.
Time table: ODD SEM (2020-2021)| Time/Day order | 8.30- 9.30 | 9.30-10.30 | 10.30-11.00 | 11.00-12.00 | 12.00-1.00 |
| Monday | |||||
| Tuesday | SME1304 | ||||
| Wednesday | SME1304 | ||||
| Thursday | SME1304 | ||||
| Firday | SME1304 | ||||
| Saturday |

- Teacher: R Siva
Finite element analysis (FEA) is a computerized method for predicting how a product reacts to real-world forces, vibration, heat, fluid flow, and other physical effects. Finite element analysis shows whether a product will break, wear out, or work the way it was designed.
FEA enables you to predict potential design issues and therefore minimize risk to your product, profits, and your business. With FEA you can test the impact of varying conditions (stress, vibration, buckling, fatigue, creep, heat, etc.) on your design.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Understand the capabilities of FEM and its importance in Engineering.
To introduce the concepts of Mathematical Modeling of Engineering Problems.
COURSE OUTCOMES
|
CO1:Understand the Fundamental Theory of Finite Element Method. |
|
CO2: Select and interpret Finite Element analysis results for design and evaluation purposes. |
|
CO3:Solve plain elasticity problem using energy approach |
|
CO4:Solve one dimensional heat transfer problems and two dimensional scalar variable problem using ANSYS. |
|
CO5:Develop a basic understanding of the limitations of the Finite Element method and understand the possible error sources in its use. |
|
CO6:Examine the longitudinal vibration, transverse vibration of beams, Mesh Generation and Errors in the finite element method. |
UNIT 1 1D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 9 Hrs.
Historical Background -Basic concept of FEM- steps involved in FEA - Variational Formulation of Boundary value problem - Rayleigh Ritz Method - Weighted Residual methods-Finite Element Modeling - Element Equations - Shape functions -Bar, Beam Elements - stepped bar, tapered bar-simple problems
UNIT 2 2D FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 10 Hrs.
Basic Boundary Value Problems in 2 Dimensions - Triangular, quadrilateral, higher order elements - Poisson and Laplace Equations - Weak Formulation - Elements Matrices and Vectors -.Natural Co-ordinate System - Lagrangian Interpolation Polynomials - Iso-parametric Elements - Formulation -Numerical Integration -2D Triangular elements - rectangular elements - Illustrative Examples.
UNIT 3 SOLUTION TO PLANE ELASTICITY PROBLEMS 8 Hrs.
Introduction to Theory of Elasticity - Plane Stress - Plane Strain and Axisymmetric Formulation - Principle of virtual work - Element matrices using energy approach.
UNIT 4 APPLICATIONS IN HEAT TRANSFER & FLUID MECHANICS 9 Hrs.
One dimensional heat transfer element - application to one-dimensional heat transfer problems- scalar variable problems in 2-Dimensions - Applications to heat transfer in 2- Dimension - Application to problems in fluid mechanics in 2-D.
UNIT 5 SPECIAL TOPICS 9 Hrs.
Vibrational problems - equations of motion based on weak form -longitudinal vibration of bars - transverse vibration of beams Mesh Generation-Errors in the finite element method - various measures of errors- accuracy of the solution- Eigen value Problems - h & p elements- Applications of FEM software to solve simple problems, types of solver - a brief.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. J.N Reddy. “An Introduction to the Finite Element Method” , Mc Graw Hill, International Edition, 1993.
2. Seshu, P, “Text Book of Finite Element Analysis”, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi,2007.
3. Segerlind L.J,“Applied Finite Element Analysis”, John Wiley, 1984.
4. Rao. S.S, “Finite Element Method in Engineering” , Pergamon Press, 1989.
5. Chandrupatla & Belagundu , “Finite Elements in Engineering”, Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd., 1997.
6. Cook, Robert Davis et al, “Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis” , Wiley, John & Sons,1999.
7. George R Buchanan, “Schaum’s Outline of Finite Element Analysis”, McGraw Hill Company, 1994.
8. Taylor.C and Hughes.J.B. “Finite Element Programming of the Navier Stoke equation” Pineridge Press Limited, UK 1981
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the basic modes of heat transfer and Compute temperature distribution in steady-state
and unsteady-state heat conduction.
CO2 - Understand and analyze heat transfer through extended surfaces.
CO3 - Interpret and analyse forced and free convection heat transfer.
CO4 - Explore the real time applications of radiation mode of heat transfer.
CO5 - Design heat exchangers using LMTD and NTU methods.
CO6 - Relate the mass transfer concepts for various industrial applications
- Teacher: Anderson A
- Product Design as a design field involves designing or creating products that will be used by consumers. Thus, while designing anything, a product designer needs to ensure that the product being designed is easy and safe to use.
- Product Design is related to all the work that is done between an idea coming to mind and finally seeing the product in the hands of the customer
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
- Teacher: Venkatesh S
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF MATERIALS- Crystallography: Basics, Atomic radius and Atomic packing factor of BCC, FCC & HCP, Miller’s indices, Allotropy, Solid solutions and intermetallic compounds. Atomic Diffusion: Laws of diffusion, Factors affecting diffusion. Phase diagrams: Solidification of metals, Phase rules, Construction of phase diagram, Isomorphous diagram, Eutectic diagram showing partial solid solubility, Peritectic system.
UNIT 2 FERROUS AND NON-FERROUS ALLOYS- Ferrous alloys: Cooling curve of pure iron, Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagram, Critical points in Fe–Fe3C equilibrium diagrams, Classification of ferrous alloys, Influence of alloying elements, Designation systems, Types of steels and cast iron, Typical compositions, properties and applications of ferrous alloys. Non-ferrous alloys: Typical compositions, properties and applications of Aluminium and its alloys, Copper & its alloys, Ti & its alloys, and Nickel & its alloys.
UNIT 3 STRENGTHENING PROCESSES- Heat treatment of steel: TTT diagram and CCT diagram. Heat treatment processes: Annealing, Normalizing, Tempering and Quenching, Jominy quency test for hardenability. Case hardening: Carburizing, Nitriding, Cyaniding, Carbonitriding, Flame hardening and Induction hardening. Others: Dispersion strengthening & Precipitation hardening
UNIT 4 FAILURE OF MATERIALS AND TESTING- Tensile testing: Significance, Universal testing machine, Stress–strain curve for ductile & brittle material, Results. Hardness Testing: Significance, Rockwell harness test, Brinell’s hardness test and Vicker’s hardness test, Results. Impact testing – Significance, Charpy impact test and Izod impact test, Results. Failure of materials: Defects in materials, Deformation mechanisms, Failure mechanisms and influencing factors of ductile and brittle failures, fatigue failure, creep failure and impact failure.
UNIT 5 MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION AND SELECTION - X-ray diffraction (XRD): Bragg’s law of diffraction, Powder, rotating crystal and Laue methods to determine the crystal
structure. Optical microscopy: Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and Applications of optical
microscopes. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample preparation and
Applications of SEM. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM): Image formation techniques, Construction, Sample
preparation and Applications of TEM. Materials selection: Engineering materials and their properties, Materials selection
charts, Material selection strategy, Factors affecting materials selection, Case studies.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
- Teacher: JINO L
Mechanical engineering plays a dominant role in enhancing safety, economic vitality, enjoyment and overall quality of life throughout the world. Mechanical engineers are concerned with the principles of force, energy and motion. Mechanical engineering is a diverse subject that derives its breadth from the need to design and manufacture everything from small individual parts and devices (e.g. microscale sensors and inkjet printer nozzles) to large systems (e.g. spacecraft and machine tools).
The role of a mechanical engineer is to take a product from an idea to the marketplace. In order to accomplish this, a broad range of skills are needed. Since these skills are required for virtually everything that is made, mechanical engineering is perhaps the broadest and most diverse of engineering disciplines.

- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
Thermodynamics is a very important branch of science and engineering that studies the role of heat and its relation to energy and work. This course introduces you to the core concepts of thermodynamics such as the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature and how changes in one can affect the others. You will also look at examples and solve certain problems in order to help you better understand the concept of thermodynamics.

- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
SMEA1303 FLUID MECHANICS AND FLUID MACHINERY
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the fluid properties, flow characteristics and hydrostatic force on surfaces.
To study the equation of motions such as mass, momentum and energy equation and their practical applications.
To understand the functioning and characteristic curves of hydraulic machines.
UNIT 1 FLUID PROPERTIES 9 Hrs.
Fluid Properties: Density-Specific Weight-Specific Gravity-viscosity-surface tension-capillarity-Vapour pressure-compressibility. Fluid Static: Hydrostatic Law-Pressure Variation in static fluid-Hydrostatic force on a submerged plane surfaces-Location of hydrostatic force. Manometers-Simple, U tube and differential Manometers. Buoyancy-Meta centric height-determination of stability of floating bodies and submerged bodies.
UNIT 2 EQUATIONS OF MOTION 9 Hrs.
Types of fluid flow-Concept of Control Volume- Control Volume Analysis of mass, momentum and energy. Differential equation of continuity and momentum - Euler’s and Bernoulli’s Equation and its applications. Flow Measurement: Orifice meter, Venturi meter, Piezometer, Pitot tube.
UNIT 3 FLOW THROUGH ORIFICE, NOTCHES, WEIRS AND PIPES 9 Hrs.
Hydraulic co-efficient-Flow through orifice, Notches and weirs. Laminar and Turbulent flow-Reynolds experiment-laminar flow through circular pipe (Hagen poiseulle’s)-Major and minor losses in pipes-Darcy weisbach’s equation, chezy’s formula-friction factor- moody diagram-pipes in series and pipes in parallel-total energy line-hydraulic gradient line-Equivalent pipe. Concept of Boundary Layer-Types of boundary layer thickness-drag on flat plate.
UNIT 4 PUMPS 9 Hrs.
Centrifugal Pumps: Introduction-Definitions of heads and efficiencies-Operations-work done by the Impeller with Velocity triangles-Performance curves-Cavitations-Multi-staging: Pumps in Series and Parallel. Reciprocating Pumps: Operation–power required driving the pump-Slip-indicator Diagram–Separation-Air vessels.
UNIT 5 TURBINES AND DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 9 Hrs.
Hydraulic Turbines: Classification of hydraulic turbines-Working principle of Pelton wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines-velocity triangles-draft tube-hydraulic turbine characteristics. Governing of turbines. Dimensional Analysis: Needs and methods-Buckingham’s π Theorem, Non-Dimensional Numbers, Similarities of flow. Model studies. Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the different properties of fluids and compute the fluid pressure in a pipe & hydrostatic forces acting on different surfaces.
CO2 - Analyze the Bernoulli’s theorem and applies it in engineering application.
CO3 - Evaluate and compare (i) the hydraulic coefficients and (ii) the energy losses in pipes.
CO4 - Explain the principle, working and operating characteristic curves of different types of pumps and estimate the power required.
CO5 - Distinguish the principle, working and operating characteristic curves of different types of turbines and compute the power developed.
CO6 - Understand the methods of dimensional analysis and application in model analysis.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., "Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Machines", 9th Edition, Laxmi Publications, 2015.
2. Modi P.N., Seth S.M., "Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Including Hydraulic Machines", 21st Edition, Standard Book House, 2017.
3. Goyal, Manish Kumar, "Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines", PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 2015.
4. Kumar K.L., "Engineering Fluid Mechanics", 8th Edition, Eurasia Publication House (P) Ltd, 2014.
5. Rajput R.K., "Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Machines", 4th Edition, S. Chand Limited, 2008.
6. Yunus.A.Cengel, John.M.Cimbala, "Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Application", 3rd Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2013.
7. Robert W. Fox, Alan T. McDonald, Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell, "Fluid Mechanics", 9th Edition, Wiley India, 2016.
8. Franck M. White, "Fluid Mechanics", 8th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publication, 2015.
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To study the aspects of Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
To gain knowledge of different types of stresses, strain and deformation induced in the components due to external loads.
To study the distribution of various stresses in the elements such as beams, shafts etc.
To study the effect of component dimensions and shapes on the stresses and deformations.
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 9 Hrs.
Rigid and Deformable bodies – Strength, Stiffness and Stability – Stresses; Tensile, Compressive and Shear – Deformation of simple and compound bars under axial load – Thermal stresses and strains. Elastic constants – Relation between Elastic constans- Strain energy and unit strain energy – Strain energy in uniaxial loads.
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN TWO DIMENSIONS 9 Hrs.
Principal planes and stresses – Mohr’s circle for biaxial stresses – Maximum shear stress - simple problems- Stresses on inclined planeBiaxial state of stresses – Thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Deformation in thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Efficiency of joint- Effect of Internal Pressure.
UNIT 3 BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES 9 Hrs.
Types of beams - Supports and Loads – Shear force and Bending Moment in beams – Cantilever, Simply supported and Overhanging beams – SFD and BMD for inclined loads and couples.Stresses in beams – Theory of simple bending – Stress variation along the length and in the beam section – Effect of shape of beam section on stress induced.
UNIT 4 TORSION 9 Hrs.
Analysis of torsion of circular bars – Shear stress distribution – Bars of Solid and hollow circular section – Stepped shaft – Twist and torsion stiffness – Composite shafts Springs - Laminated springs, axial load and twisting moment acting simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs– Deflection of helical coil springs under axial loads – stresses in helical coil springs under torsion.
UNIT 5 BEAM DEFLECTION 9 Hrs.
Columns – End conditions – Equivalent length of a column – Euler equation – Slenderness ratio – Rankine Gordon formula for columns. Elastic curve of Neutral axis of the beam under normal loads – Evaluation of beam deflection and slope: Double integration method, Macaulay Method, and Moment-area Method.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the fundamentals of Stress and Elastic Constants.
CO2 - Understand the concept of Principal stresses and thin shells.
CO3 - Create Shear force & Bending moment diagram and Bending stress.
CO4 - Apply the Concept of Torsion for Circular Shafts and Understand the concept of Springs.
CO5 - Understand the theory of Column and Beam deflection.
CO6 - Analyze overall deflection aspects related to Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., "Strength of Materials", Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd., 5th Edition, 2012.
2. Punmia B.C. & Jain A.K., Mechanics of Materials, Laxmi Publications, 2001.
3. Ryder G.H., "Strength of Materials", Macmillan India Ltd., 3rd Edition, 2002.
4. Ray Hulse, Keith Sherwin & Jack Cain, "Solid Mechanics", Palgrave ANE Books, 2004. 5. Allan F. Bower, "Applied Mechanics of Solids", CRC Press, 2009.
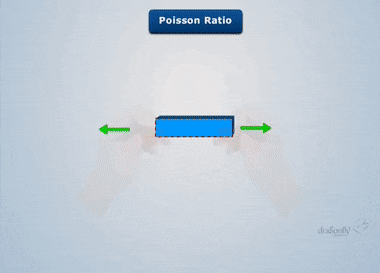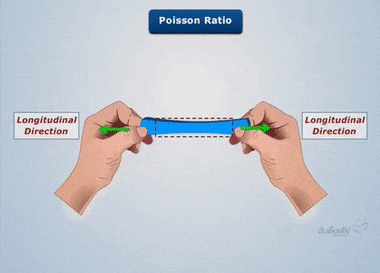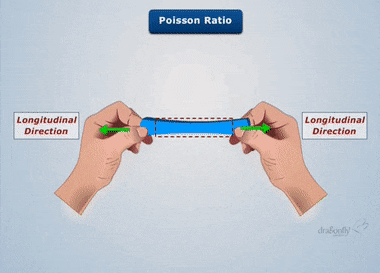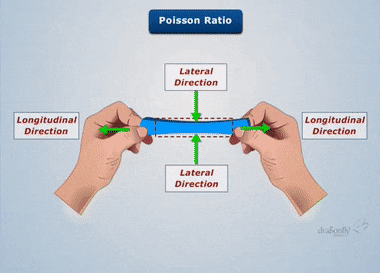
- Teacher: Madhan Kumar G
- Teacher: Senthilkumar J
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide essential knowledge of construction and working of various types of power plants.
To detail the role of Mechanical Engineers in their operation and maintenance

- Teacher: R Siva
Provide the insights of the fundamentals of Mechanisms and Cams.
Understand the basics of Flywheels, Balancing of Rotating and Reciprocating unbalance systems.
Enhance knowledge of Single degree - Free and Damped Vibrations.
Provide the detailed overview of Forced Vibrations.
Discuss the fundamentals of Gyroscopes and Governors.

- Teacher: RAM PRAKASH S
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Understand the basic modes of heat transfer and Compute temperature distribution in steady-state and
unsteady-state heat conduction.
CO2 - Understand and analyze heat transfer through extended surfaces.
CO3 - Interpret and analyze forced and free convection heat transfer.
CO4 - Explore the real time applications of radiation mode of heat transfer.
CO5 - Design heat exchangers using LMTD and NTU methods.
CO6 - Relate the mass transfer concepts for various industrial applications.
- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
To understand the concept and basic mechanics of metal cutting, working of standard machine tools such as
lathe, shaping and allied machines, milling, drilling and allied machines, grinding and allied machines and
broaching.
To understand the basic concepts of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) of machine tools and CNC
Programming.
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To discuss the concepts of compressible and Incompressible fluids.
To understand Mach number variation on area ratio.
To impart in depth knowledge on the flow characteristics through constant area duct.
UNIT 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPRESSIBLE FLUID FLOW 9 Hrs.
Concept of compressible flow, Energy and momentum equations, various regions of flow, fluid velocity, stagnation state, velocity of sound, critical states, Mach number, critical mach number, Crocco number, types of waves, mach cone, mach angle, effect of mach number on compressibility.
UNIT 2 FLOW THROUGH VARIABLE AREA DUCTS 9 Hrs.
Isentropic flow through variable area duct, T-S and h-s diagrams for nozzle and diffuser flows, area ratio as a function of Mach number, Mass flow rate through nozzles and diffusers, effect of friction in flow through nozzles.
UNIT 3 FANNO FLOW AND RAYLEIGH FLOW 9 Hrs.
Flow in constant area duct with friction - Fanno curves, and Fanno Flow equations, variation of flow properties, variation of Mach number with duct length. Flow in constant area duct with heat transfer, Rayleigh line and Rayleigh flow equations, variation of flow properties, maximum heat transfer.
UNIT 4 NORMAL SHOCK AND OBLIQUE SHOCKS 9 Hrs.
Governing equations, variation of flow parameters, static pressure, static temperature, density, stagnation pressure, entropy across normal shock and oblique shocks. Normal shocks - stationary and moving, applications. Prandtl Meyer equation, impossibility of shock in sub-sonic flows, flow in convergent and divergent nozzles with shock, Flows with oblique shock.
UNIT 5 JET AND SPACE PROPULSION 9 Hrs.
Aircraft propulsion, types and working of jet engines - energy transfer in jet engines, thrust, thrust power, propulsive and overall efficiencies, thrust augmentations in turbo jet engines, ram jet and pulse jet engines. Rocket propulsion, types of rocket engines, Liquid and solid fuel rocket engines, Introduction to Electrical and Nuclear rockets-Space Flights, Orbital and escape velocity.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Recall the fundamental concepts of compressible fluid flow.
CO2 - Demonstrate the significance of mach number on compressibility.
CO3 - Differentiate isothermal flow and isentropic flow.
CO4 - Apply the concept of normal shocks to different turbo machines.
CO5 - Estimate the heat transfer in flow through constant area ducts.
CO6 - Calculate the propulsive power in jet engines.

- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
Course objective:To understand the construction and working principle of various parts of an automobile
Course outcomes:
|
CO1: Explain the history of automobiles, classification, vehicle layout, various parts with their functions and environmental regulations. |
|
CO2: Describe the driveline fundamentals of vehicles, such as clutches, gear box, transmission system and differential. |
|
CO3: Explain the fundamentals of vehicles parts, such as steering system, front and rear axles, wheels and tyres. |
|
CO4: Examine the fundamentals of suspension systems and braking systems. |
|
CO5: Describe the fundamentals of electrical systems, such as battery, lighting, sound systems, etc. |
|
CO6: Apply the knowledge to electronic units, such as sensors, actuators, electronic control units etc. |
- Teacher: JAYAPRABAKAR J
- Teacher: PURUSOTHAMAN M
Model and End Semester Practicals Only
To draw complex geometries of machine components in sketcher mode.
To create complex engineering assemblies using appropriate assembly constraints.
To write programs to generate analytical and synthetic curves used in engineering practice.
To generate freeform shapes in part mode to visualize components.
To develop ‘G’ and ‘M’ codes for turning and milling components and to generate automated tool paths for a
given engineering component.
To generate automated tool paths for a given engineering component.
- Teacher: Sangeetha M
The course is consists of all non-conventional manufacturing processes. It starts with classification of manufacturing processes and necessity of non conventional manufacturing processes. This course dealt with details about the mechanism of material removal, sources of energy used for material removal, working principle, the set up or equipment and relative advantages and disadvantages. It gives a clear cut idea about the processes, its use in specific industrial application etc.

- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics.
To comprehend laws of thermodynamics and apply it to the related processes.
Perform thermal analysis on behavior and performance of systemsTime Table
Monday-12.00 to 1.00 pm
Wednesday-9.30 to 10.30
Friday-11.00 to 12.00 pm
Saturday 8.30 to 9.30
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
- Teacher: VENKATESAN S P
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To introduce the fundamentals of electric and hybrid vehicle technology
To understand the design and operation of electric and hybrid vehicle powertrains
To evaluate the performance and efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles
To analyze the environmental impact of electric and hybrid vehicles
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, students will be able to CO1 - Explain the basic principles and technologies used in electric and hybrid vehicles. CO2 - Analyze the design and operation of electric and hybrid vehicle powertrains. CO3 - Evaluate the performance and efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles. CO4 - Analyze the environmental impact of electric and hybrid vehicles. CO5 - Interpret the role of battery technology in electric and hybrid vehicles.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Huang, Y., & Ji, C. (2021). Advanced control of electric vehicles. Elsevier.
2. Zhu, X., Chen, Y., & Mi, C. (2021). Power electronics for electric vehicles: technology and design.
Springer.
3. Zhang, J., Liu, C., & Tang, T. (2018). Powertrain and Energy System Optimization for Hybrid
Vehicles. Springer.
4. Adachi, T., Kikuchi, K., & Kawamura, T. (2018). Electric Vehicles - Modelling and Simulations.
InTechOpen.
5. Li, J., Lu, X., & Yu, W. (2020). Battery Management System for Electric Vehicles: Theory and
Applications. Springer.
- Teacher: Bupesh Raja V.K
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To Understand the fundamentals of wind energy and its conversion system
To learn about solar radiation and solar collectors
- Teacher: Dr. Karthikeyan A
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To provide strong understanding of geometric modelling techniques used for creating the CAD models.
To make the awareness about the computer applications to the manufacturing and factory operations.
To offer the fundamental knowledge of the numerical methods to perform the design analysis.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to:
CO1 - Interpret how the geometric modelling techniques are applied to make the product designs.
CO2 - Create the CAD models using sketch tools, design features, assembly, and drawing annotations in a CAD package.
CO3 - Explain how the computer packages are employed in the direct and/or indirect manufacturing applications.
CO4 - Make a mechanical component using CNC machine/ 3D printer.
CO5 - Determine the nodal solutions to the one-dimensional element finite element problems.
CO6 - Perform the structural analyses of the stated 1D, 2D and 3D structural problems from solid mechanics.
COURSE CONTENT
UNIT 1 CAD FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.Computer graphics fundamentals, geometric transformation, viewing transformation, line generating algorithms, and hidden line removal algorithms.
UNIT 2 GEOMETRIC MODELING 6 Hrs.
Wireframe modelling: analytical curves and synthetic curves. Surface modelling: analytical surfaces and synthetic surfaces. Solid modelling: constructive solid geometry (CSG), boundary representation, parametric modelling. Assembly modelling.
UNIT 3 CAM APPLICATIONS IN FACTORY OPERATIONS 6 Hrs.
Indirect computer applications: Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Computer aided quality testing, Computer aided process monitoring, Computer integrated production system (CIPS), Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
UNIT 4 CNC PROGRAMMING 6 Hrs.
NC, DNC and CNC machine tools, rapid prototyping. NC Programming: point to point and continuous path machining approaches, G Codes, M Codes, Canned cycles, Manual NC programming for turning and milling operations.
UNIT 5 COMPUTER AIDED ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS 6 Hrs.
General form of finite element equation, Numerical solutions to one-dimensional problems from solid mechanics. Steps in finite element analysis.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 30 Hrs.
Activity 1: 2D Sketching using a CAD package.
Activity 2: 3D Part modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 3: 3D Assembly modelling using a CAD package.
Activity 4: Drawing a sheet with different model views, annotations and dimensions using a CAD package.
Activity 5: Apply rendering effects to the models using a CAD package.
Activity 6: NC Turning using an NC simulation software.
Activity 7: NC Machining using an NC simulation software.
Activity 8: Make a component using a CNC turning centre.
Activity 9: Make a component using a CNC machining centre.
Activity 10: Make a prototype using a 3D printing.
Activity 11: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (bar) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 12: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (beam) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 13: Structural analysis of one-dimensional element (truss) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 14: Structural analysis of two-dimensional element (plate) problems using an FEA package.
Activity 15: Structural analysis of three-dimensional element (solid component) problems using an FEA package.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Zhuming Bi and Xiaoqin Wang, "Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing", Wiley, 2020.2. Ibrahim Zeid and R. Sivasubramanian, "CAD/CAM: Theory and Practice: Special Indian Edition", 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2009, 828 Pages.
3. Sudip S. Bhattacharjee, "Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures", CRC Press, 2021.
4. Kuang-Hua Chang, "E-Design: Computer-Aided Engineering Design", Elsevier Science, 2016.
5. Donald D. Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, "Computer Graphics, C Version", 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, 2014, 660 pages.
6. Pawan Negi, Mangey Ram, Om Prakash Yadav, "Basics of CNC Programming", River Publishers, 2022.

- Teacher: JEYA JEEVAHAN J
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted.
This flexibility is generally considered to fall into two categories, which both contain numerous subcategories.The first category is called as Routing Flexibility which covers the system's ability to be changed to produce new product types, and ability to change the order of operations executed on a part.The second category is called Machine Flexibility which consists of the ability to use multiple machines to perform the same operation on a part, as well as the system's ability to absorb large-scale changes, such as in volume, capacity, or capability.
Most FMS consist of three main systems:
- The "Work Machines" which are often automated "CNC machines" are connected by
- By a "Material handling" system to optimize parts flow and
- The "Central Control Computer" which controls material movements and machine flow.
The main advantages of an FMS is its high flexibility in managing manufacturing resources like time and effort in order to manufacture a new product.
The best application of an FMS is found in the production of small sets of products like those from a mass production.

- Course Coordinator: ARUNKUMAR G
COURSE OBJECTIVES
Ø To understand and develop knowledge on the various flexible manufacturing systems and its applications.
Ø To get introduced to the simulation process and FMS database.
Ø To explore the future prospects of AI and Expert systems in FMS.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
FMS– development of manufacturing systems – benefits – major elements – types of flexibility-part selection problems– FMS application and flexibility –single product, single batch, N – batch scheduling problem – knowledge based scheduling system.
UNIT 2 COMPUTER CONTROL AND SOFTWARE FOR FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
Introduction – composition of FMS– hierarchy of computer control –computer control of work center and assembly lines – FMS supervisory computer control – types of software specification and selection – Object oriented control architecturetrends.
UNIT 3 FMS SIMULATION AND DATA BASE
Application of simulation–model of FMS–simulation software – limitation – manufacturing data systems–data flow–FMS database systems–planning for FMS database- predictive control algorithms for on line scheduling of FMS.
UNIT 4 GROUP TECHNOLOGY AND JUSTIFICATION OF FMS
Introduction – matrix formulation – mathematical programming formulation –graph formulation – knowledge based system for group technology – economic justification of FMS- application of possibility distributions in FMS systems justification- Measuring flexibility and performance of FMS.
UNIT 5 APPLICATIONS OF FMS AND FACTORY OF THE FUTURE
FMS application in machining, sheet metal fabrication, prismatic component production – aerospace application – Case
studies. FMS development towards factories of the future – artificial intelligence and expert systems in FMS – design philosophy and characteristics for future.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Identify the need and role of Flexible Manufacturing System in Industry.
CO2 - Assess the concepts and linkage of software in FMS.
CO3 - Demonstrate the simulation process involved and its data flow.
CO4 - Justify the importance of FMS and its importance in group technology.
CO5 - Compare and categorise the level of FMS needed in an manufacturing industry.
CO6 - Appreciate and explore the penetration of AI in FMS.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1 Jha, N.K. “Handbook of flexible manufacturing systems”, Academic Press Inc., 2012.
2 Radhakrishnan P. and Subramanyan S., “CAD/CAM/CIM”, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Age International Ltd., 2010.
3 Raouf, A. and Ben-Daya, M., Editors, “Flexible manufacturing systems: recent development”, Elsevier Science, 2015.
4 Jan Beier, “Simulation approach towards energy flexible manufacturing systems”, Springer Publications, 2017.
5 H.K. Shivanand, “Flexible Manufacturing System”, New Age International Publishers, 2011.
6 Taiichi Ohno, “Toyota production system: beyond large-scale production”, Productivity Press (India) Pvt. Ltd. 2013.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks : 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 Questions of 2 marks each-No choice 20 Marks
PART B: 2 Questions from each unit with internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks

- Teacher: RAM PRAKASH S
COURSE OUTCOME
CO1: Describe the architecture of the 8085 microprocessor.
CO2: Analyse assembly language programs for 8085, incorporating various addressing modes and instruction sets.
CO3: Explain the architecture and features of the 8051 microcontroller, including memory structure, timers, interrupts, and instruction sets.
CO4: Compare and contrast ARM Cortex and OMAP processors with traditional microprocessors and microcontrollers in terms of architecture and application suitability
CO5: Design and simulate applications using 8085/8051/ARM processors for controlling hardware CO6. Develop Embedded C programs to interface peripherals and implement real-time control logic communication protocols.
- Teacher: Aranganathan A
- Teacher: Dr. G D Anbarasi Jebaselvi
- Teacher: EBENEZAR JEBARANI M R
- Teacher: Dr.R Narmadha
- Teacher: Vijaya Baskar V
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. To learn fundamental concepts of Stress, Strain and deformation of solids with applications.
2. To know the method of finding slope and deflection of beams. ÿ To understand the effect of torsion on shafts.
3. To understand the basic properties of the fluid, fluid kinematics, fluid dynamics and to analyse and appreciate the complexities involved in solving the fluid flow problems.
4. To develop understanding about hydrostatic law, principle of buoyancy and stability of a floating body and application of mass, momentum and energy equation in fluid flow.
5. To understand bioelectric amplifiers.
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 9 Hrs.
Rigid bodies and deformable solids - stability, strength, stiffness - tension, compression and shear stresses - strain, elasticity, Hooke’s law, limit of proportionately, modules of elasticity, stress-strain curve, lateral strain - temperature stresses deformation of simple and compound bars - shear modulus, bulk modulus, relationship between elastic constants - bi axial state of stress - stress at a point - stress on inclined plane - principal stresses and principal planes - Mohr’s circle of stresses.
UNIT 2 BENDING MOMENT IN BEAMS AND TORSION OF SHAFTS 9 Hrs.
Introduction, Types of beams, loads and reactions, Shear force and bending moment in beams – Cantilevers – Simply supported beams. Numerical on Shear force and bending moment diagrams for Cantilevers – Simply supported beams subjected to various loading condition-SFD and BMD for uniformly Distributed load (UDL) and Point load. TorsionIntroduction, assumptions, derivation of torsional equations, torsional rigidity/stiffness of shafts. Power transmitted by solid and hollow circular shafts.
UNIT 3 FLUID PROPERTIES 9 Hrs.
Fluid Properties: Density - Specific Weight - Specific Gravity - Viscosity - Surface tension - Capillarity - compressibility. Fluid Statics: Hydrostatic Law - Pressure Variation in static fluid - Hydrostatic force on a submerged plane surface - Location of hydrostatic force. Manometers - Simple U tube and differential manometers - Buoyancy - Meta-centric height - determination of stability of floating bodies and submerged bodies.
UNIT 4 EQUATIONS OF MOTION 9 Hrs.
Basic equations of motion: Types of fluid flow-Concept of Control Volume- Control Volume Analysis of mass, momentum and energy. Differential equation of continuity and momentum - Euler’s and Bernoulli’s Equation and its applications. Flow Measurement: Orifice meter, Venturi meter, Piezometer.
UNIT 5 FLUID DYNAMICS AND FLOW THROUGH PIPES 9 Hrs.
Flow through orifices: Classification - Hydraulic co-efficient - Flow through rectangular orifice, Notches and weirs. Laminar and Turbulent flow: Reynolds experiment - Major and minor losses in pipes - Darcy Weisbach’s equation, Chezy’s formula - pipes in series and pipes in parallel - total energy line - hydraulic gradient line - Equivalent pipe.
Max. 45 Hrs.
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Analyze the state of stress and strain at any point in a member.
CO2 - Identify, formulate, and solve structural engineering problems.
CO3 - Calibrate flow discharge measuring device used in pipes channels and tanks.
CO4 - Apply Hagen Poisueille’s equation to solve numerical Problems.
CO5 - Characterize laminar and turbulent flows.
CO6 - Interpret different pipe fittings and evaluate the fluid velocity considering major and minor losses.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Rajput.R.K. “Strength of Materials” 4th Edition, S.Chand & Co., New Delhi, 2002.
2. Khurmi, R.S, “Strength of Materials“, 23rd Edition, S.Chand & Co., 2008.
3. Bansal.R.K., “Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Machines”, 9th Edition, Laxmi Publications, 2005.
4. Kumar K. L., “Engineering Fluid Mechanics”, 8th Edition, Eurasia Publication, 2009.

- Teacher: Dr. ANISH M
This course enable the students
- To understand the basic concepts of thermodynamics
- To understand the air standard cycles and working principles of four stroke and two stroke engines
- To familiarize with the types of air compressors and their working principle
- To understand the working principles of refrigeration and air conditioning systems
- Teacher: Kanimozhi B
- Teacher: SENTHILKUMAR G
At the end of the course Students will be able to form and solve the nth degree algebraic equations. Using the concept relation between roots and coefficients of equations the student will be able to find the roots of the equation. Reciprocal equations can be solved using the newton’s method. The student will be able to find rank and inverse of a matrix by elementary transformation. Students get a clear idea on finding the characteristic equation and roots of the characteristic equation of a given matrices. Cayley Hamilton theorem gives him a clear idea to find the inverse and higher powers of the given matrix. Student can solve the system of equations using matrix methods

- Teacher: KAVITHA C
- Teacher: MARY METILDA M I
- Teacher: Subhashini N
The ability to identify,reflect upon,evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements. Analytical,logical thinking and conclusions base<l on quantitative information willbe the mainobjective of learning this subject.
- Teacher: MOHAMED ISMAIL A
- Teacher: MAHESWARI S
To learn about division algorithm. To have knowledge about fundamental theorem of arithmetic. To be
familiar with linear congruences. To have knowledge in Mobius inversion formula and Euler’s theorem
- Teacher: FRANKLIN THAMIL SELVI M S
Understand the basic rules of logic, including the role of axioms or assumptions and appreciate the
role of mathematical proof in formal deductive reasoning and able to distinguish a coherent argument from a fallacious one, both
in mathematical reasoning and in everyday life.

- Teacher: FRANKLIN THAMIL SELVI M S
The ability to identify, reflect upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgments. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject.

Students can learn the basics of formal languages and Automata Theory and establish some of the properties of such systems. To
familiarize the theories of Mathematics in Computer Science
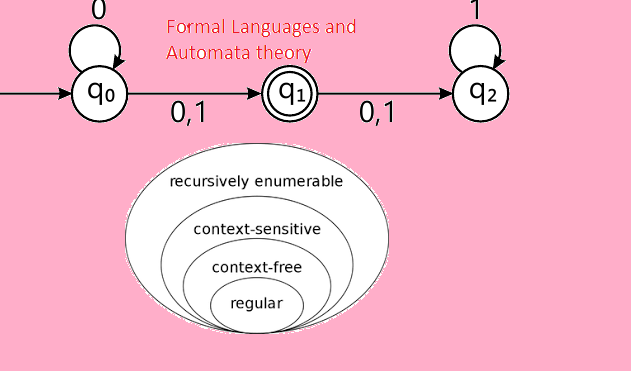
- Teacher: BHUVANESWARI K
To translate real life situations to diagrammatic representations and develop problem solving skills and thereby solve real life problems.
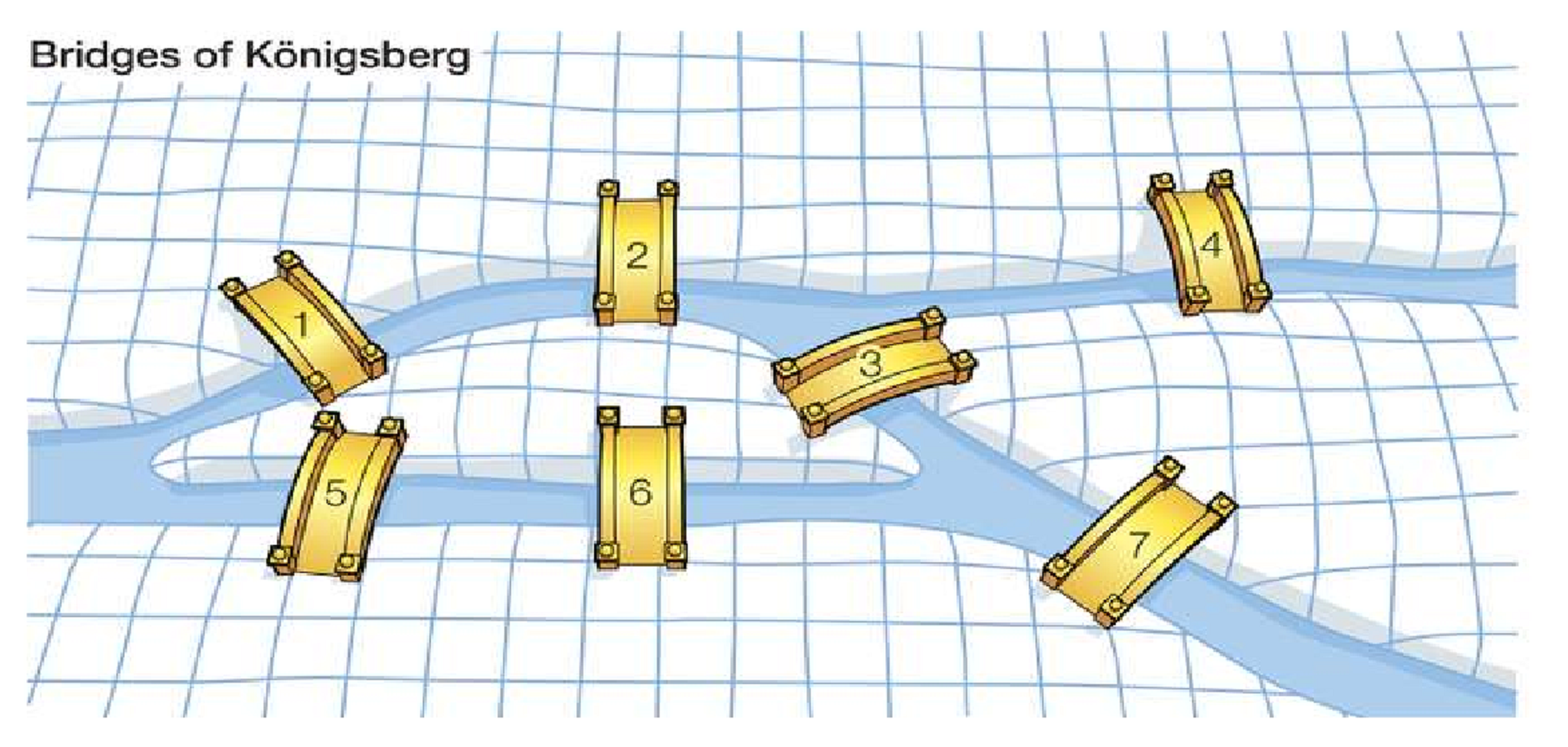
- Teacher: FRANKLIN THAMIL SELVI M S
To Provide an understanding for the graduate business student on Statistical concepts to include probability, probability distributions, sampling, estimation, hypothesis testing, regression and correlation analysis and business and economic forecasting.

- Teacher: Subhashini N
The ability to identify, reflect upon, evaluate
and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent
judgments. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative
information will be the main objective of learning this subject.

This course is useful in having hands-on experience in doing data analytics by using R programming language. Students will be able to use R as a calculator to evaluate vectors, matrices,etc.
- Teacher: PRIYADARSHINI E
This course is designed to provide knowledge to identify, reflect upon, evaluate and apply different types of information form independent judgements. The main objective of learning this course is to provide students with analytical, logical thinking and to derive conclusions based on quantitative information. This course in the first semester provides student an understanding of concepts of calculus and how they are applied to solve real life problems. Besides learning the basics of calculus, students completing this course gain a deeper level of learning of differential and integral calculus and its application.
Students successfully completing this course are familiar with the various rules of differentiation and know how to find the nth derivative of functions. They know to construct the circle of curvature, evolutes and envelopes of any curve. Also they know to find the Taylor series, Jacobians of function of two variables and analyze the maxima and minima of functions of several variables. Students are familiar with various integration techniques, evaluation of multiple integrals and know how to use these integration concepts to calculate the surface area and the volume of solids of revolution.

- Teacher: Logeshwari M
- Teacher: NIRMALA M
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
- Teacher: Subhashini N
- Teacher: MANOHARAN R
- Teacher: PRIYADARSHINI E
The Ability to identify, reflect upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject.

- Teacher: Anand V W J
The ability to identify, reflect upon, evaluate and apply different types of information and knowledge to form independent judgements. Analytical, logical thinking and conclusions based on quantitative information will be the main objective of learning this subject.

- Teacher: PREMKUMAR M
- This course provides the knowledge in formation of ordinary differential equations,partial differential equations and also in finding the solution to those equations.
- Numerical approach for solving algebraic equations,system of linear equations, ordinary differential equations and partial differential equations.
- Teacher: GANESH S
Linear algebra is the most important math skill in machine learning. A dataset is represented as a matrix. Linear algebra is used in data pre-processing, data transformation, and model evaluation.
Objectives:
- Construct, or give examples of, mathematical expressions that involve vectors, matrices, and linear systems of linear equations.
- Evaluate mathematical expressions to compute quantities that deal with linear systems and eigenvalue problems.
- Analyse mathematical statements and expressions (for example, to assess whether a particular statement is accurate, or to describe solutions of systems in terms of existence and uniqueness).
- Write logical progressions of precise mathematical statements to justify and communicate your reasoning.
- Apply linear algebra concepts to model, solve, and analyse real-world situations.

- Teacher: Lenin Sindhu S
Introduction to ordinary differential equations and their applications. Specific topics include first
order differential equations, linear differential equations with
constant coefficients and solution of partial differential
equations.
COURSE OUTCOMES
- Creating differential equations from word problems/application scenarios.
- Choosing the most appropriate method for solving a specific boundary value or initial value problem from among several different viable techniques.
- Generating general and particular solutions to differential equations using appropriate solving techniques.
- Verifying that an expression or function is actually a solution to a differential equation.
- Interpreting the results of a differential equation solution.

- Teacher: Dr. R. DELHI BABU

- Teacher: MOHAMED ISMAIL A
This lab provides online data analysis using the softwares SPSS for various statistical measures.It enhances the students knowledge in the applications of statistics.

- Teacher: PRIYADARSHINI E
Dear Learners,
As we are aware that many real life problems could be modelled into a differential equation, this course helps you to explore various methods of solving the differential equations and the characteristic properties of such solutions. At the end of the course one would gain
Expertise in applying various methods to obtain non-trivial solutions to second order linear complete and reduced differential equations.
Learner would be able to understand nature, Qualitative properties and Essential characterization of the solution of reduced second order linear differential equation by direct analysis of its equation. Learn the procedure to obtaining power series solution to first and second order ordinary differential equation.
A learner would gain proficiency in solving Gauss Hyper geometric equation, homogeneous differential equation for large values of the independent variable. Familiarize some special functions of Mathematical Physics and their properties. Acquaintance to system to first order linear differential equation, solution to homogeneous linear system with constant coefficients, Isoperimetric problems and method of successive approximation.
- Teacher: VELANKANNI A
- Teacher: RAHIM K.H.
- Teacher: LEEMA NIVETHINI R
- Teacher: Cynthiya Margaret Indirani S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To acquire basic knowledge of Python Programming .
- To educate the students about basics of data acquisition.
- To investigate Basic mathematical operations

- Teacher: ASWINI B
- Teacher: Dr.KARTHIKA J
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
- Teacher: PRASANNA JEYANTHI M
- Teacher: RAJAKUMAR R
- Teacher: Dr. D. Rajkumar
- Teacher: Lenin Sindhu S
NURSING RESEARCH AND STATISTICS
This course is designed to enable students to acquire understanding of basic concepts of research, research process and statistics. It is further, structured to conduct / participate in need based research bodies in various settings and utilize the research findings to provide quality nursing care. The hours for practical will be utilized for conducting individual / group research project.The learning objectives of are:
Ø To know the concept of research, terms, needs and areas of research in nursing
Ø The steps of research process
Ø To identify and state the research problem and objectives
Ø The review related literature
Ø The research approaches and designs
Ø To know the sampling process
Ø The methods of date collection
Ø To analyze, interpret and summarize the research data
Ø The use if statistics, scales of measurement and graphical presentation of data
Ø The measures of central tendency and variability and methods of correlation
Ø To communicate and utilize the research findings

- Teacher: KALAI LAKSHMI TR
Human Physiology is about learning the functions of all organs of the body and clinical conditions related to their malfunction.

- Teacher: ANURADHA NATARAJAN

COURSE OBJECTIVES:
• To understand how human behavior is influenced by social factors.
• To explore the psychological aspects of various social phenomena.
Unit I: Social Perception and Social Cognition (15 hours)
Nonverbal Communication- Facial Expressions of Emotion - The Covariation Model - The Fundamental Attribution Error - Self-Serving Attributions -The Bias Blind Spot- Confirmation bias. Social Cognition: Low-Effort Thinking - Types of Automatic Thinking- High-Effort Thinking - Errors in Social Cognition
Unit II: Social Influence (15 hours)
Conformity - Informational Social Influence - Normative Social Influence - Conformity and Social Approval - The Asch Line-Judgment Studies - Milgram’s Obedience Studies - Social Facilitation - Social Loafing - Group Polarization
Unit III: Attitudes (15 hours)
Attitude formation: How attitudes develop -Affective and Cognitive Bases of Attitudes - When and why do attitudes influence behavior - attitudes guide behavior - Change in attitudes toward the environment - The fine art of persuasion: Elements of persuasion - Resisting persuasion attempts - Cognitive dissonance - managing cognitive dissonance.
Unit IV: Prosocial Behavior (15 hours)
Positive Social Relations- Prosocial behavior: Basic Motives Underlying Prosocial Behavior: Personal Qualities and Prosocial Behavior Situational Determinants of Prosocial Behavior: – Helping influences – factors that increase and decrease Pro-social behaviour- Crowdfunding
Unit V: Stereotype, Prejudice and Discrimination (15 hours)
Stereotype: How members of different groups perceive inequality - The nature and origins of stereotyping - Prejudice and discrimination - Frustration and Aggression: The Scapegoat Theory - Social Identity Theory- The Self-Fulfilling Prophecy - Feelings and actions toward social groups - Why prejudice is not inevitable: Techniques for countering its effects.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will understand and apply theories and findings in social psychology.
2. Students will analyse the different methodologies in social psychology and their importance.
3. Students will evaluate and critique research in social psychology.
4. Students will create knowledge of social psychology with their own life experience.
5. Students will apply the knowledge of the psychological causes and consequences, towards the cure, for prejudice.
6. Students will remember the psychological aspects of various social phenomena.
References:
1. Baron, R. A., & Byrne, D. (2003). Social Psychology, 10th ed. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
2. Aronson, E., Wilson, T. D., & Akert, R. M. (2013). Social psychology.9th edition. Prentice Hall/Pearson Education.
3. Myers, D. G. (2002). Social Psychology, 7th ed. Int. Education: Mc Graw Hill.
4. Chaube, S. P., &Chaube, A. (2007). Ground Work for Social Psychology. New Delhi: Neelkamal.
5. Lindgren, Henry. C. (1973) An introduction to Social Psychology, John Wiley & Sons.
6. Kloos, B., Hill, j., Thomas, E., Wandersman, Elias, M. J., & Dalton, J.H. (2012). Community psychology: Linking individuals and communities. Wadsworth, Cengage.
7. Schneider, F.W., Gruman, A., Coults, L .M. (Eds.). (2012). Applied social psychology: Understanding and addressing social and practical problems. New Delhi: Sage publications.
- Teacher: Madhana B
To construct knowledge on the fundamentals of art and its reflection in culture, theories and solutions related to society and culture.
To understand the basic concepts / theories of formation of society, role of architecture in built environment and the relationship between man and the environment.
To familiarize the students with community, various factors influencing various communities in a society and its impact on environment.

- Teacher: SHOBANA SUBRAMANIAN
- Teacher: Jayashree S
- Teacher: Priyadharshini B
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To enable students to develop cognizance of the importance of human behavior.
To provide insight on individual and group behavior.
To familiarize with organizational culture, change and development processes.

- Teacher: Princy A.S
- Teacher: JAYASEELY M
- Teacher: Kaavya K
- Teacher: Soundarya M
- Teacher: MD DANISH RAZA
- Teacher: UMAMAHESWARI S
- Teacher: R BLESSIE PATHMU
To enable students opportunities to read and respond to representations of current issues through texts
To present themes and topics that are familiar, insightful and informative
To improve their vocabulary in various aspects
To develop LSRW skills and to focus on creative writing

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
Introduce the students to basic principles, theories and practices in ELT.
Enable students to identify changes that took place over a period of time in the area.
Analyze the teaching approaches and methods. Recall basic approaches for teaching language with four skills.

- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Soumya Susan John
- Teacher: EMALDA ROSLIN S
- Teacher: MISHA T.P
- Teacher: LIZY BOSCO
- Teacher: Esther Rajathi D J B
- Teacher: DEVA SHAILU P
- Teacher: Reegan Jebadass J
- Teacher: Dr. D. Rajkumar
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To understand the basic principles of molecular spectroscopy in terms of the quantization of molecular energy and transitions between molecular energy levels when matter interacts with radiation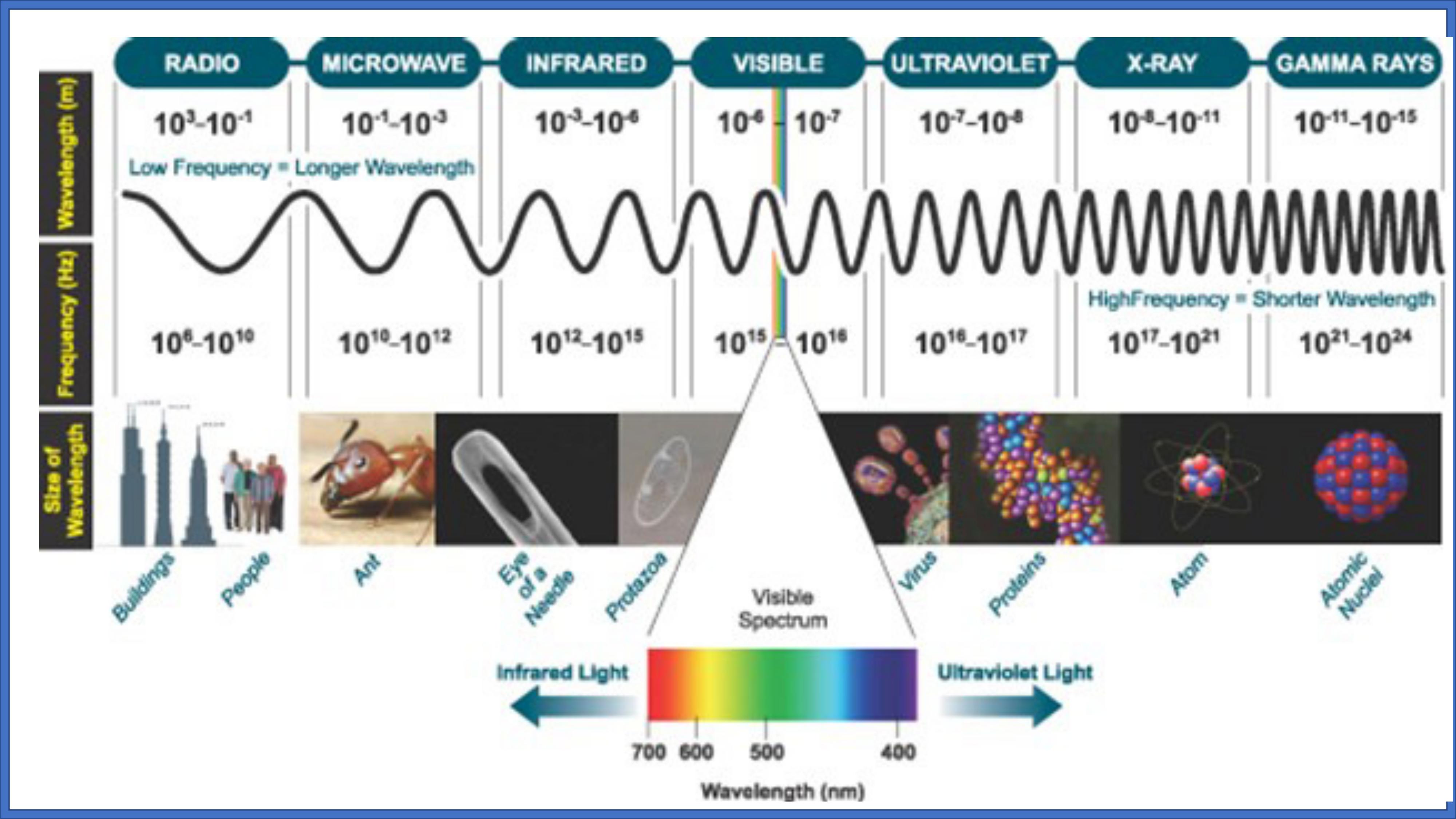
COURSE OBJECTIVE:
Unit 1: PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Unit 2: HEAT
Unit 3: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Unit 4: SOUND AND ACOUSTICS OF BUILDING
Unit 5: GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND PHYSICAL OPTICS
Course outcome:
CO1: Gain a basic knowledge of characterization of materials.
CO2: Explain statistical physics and thermodynamics as logical consequences of the postulates of statistical mechanics
CO3: Identify the Interaction of EM waves with matter in microscopic view given more values than previous.
CO4: Outline the importance of Acoustics and properties of sound in the modern society
CO5: Apply the principles and techniques of optics and defects in the selected problems.

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
Unit 1: Gravitation 10 Hrs
Keplers Laws- Newton’s law of gravitation, Determination of gravitational constant-Boy’s method, Poynting’s method-Gravitational field, Intensity of the field, Gravitational potential due to a spherical sphere, Escape velocity.

- Teacher: Malliga P
Course Name : Mechanics
Course Code: SPH1112
It consists five units.
Unit I : Dynamics
Unit II: statics and Hydrostatics
Unit III: Frame of Reference
Unit IV: Special Theory of Relativity
Unit V: Oscillations
- Teacher: Manjula M
The course is aimed
To acquire working knowledge of thermometry and calorimetry.
To acquire working knowledge of the zero-th, first and second law of thermodynamics.
To acquire basic understanding of liquid and solid cryogens working principle and their functionality
To understand conduction ,radiation and various law s such as Wien’s law, Planck’s law Rayleigh-Jean’s law
To link thermodynamics to the micro description used in Statistical Mechanics.
- Teacher: Helen Merina Albert
Course Outcomes
CO1: Understand the physical significance of Maxwell’s equations and hence estimate the speed of light.
CO2: Explain the basics and applications of LASER.
CO3: Explain the propagation mechanism of light through optical fiber.
CO4: Derive the relation between Numerical Aperture and Refractive indices.
CO5: Classify the types of optical fibers and attenuation mechanisms.
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
· It introduces to the fundamentals of diode theory, P.N junctions and bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
· It covers the basics and design of field effect transistors (FET) and transistors amplifiers.
· It explains the various feedback transistor and operational amplifiers.
· It deals with various number systems and Boolean algebra.
· It mainly focuses on the analysis and design of combinational logic systems.
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
COURSE OBJECTIVE
· To understand the basic architecture of 16 bit and 32-bit microprocessors.
· To understand interfacing of 16 bit microprocessor with memory and peripheral chips involving system design.
· To learn simple programs with 8085microprocessor.
· To learn the design aspects of I/O and Memory Interfacing circuits.
· To understand the concept of 8051 microcontroller
To provide the knowledge of different measurement techniques for different parameters to be measured in industries.
Choose the appropriate instrument based on the ranges of parameters to be measured.
Differentiate between different types of measuring technique for a parameter.

- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. To determine the refractive index of the given liquid forming liquid lens by parallax method
2. To determine the focal length and radius of curvatures of a convex lens.
3. To draw i-d curve and to determine the angle of minimum deviation and the angle of the prism from it and hence to calculate the refractive index of the material of the prism.
4. To determine the focal length and radius of curvatures of a concave lens by displacement method.
5. To standardize the diffraction grating and hence to determine the wavelength of mercury spectral lines by normal incidence method using spectrometer.
6. To determine the radius of curvature of a lenst by Newton’s rings method.
7. To determine the refractive index of the prominent spectral lines of mercury by spectrometer.
8. To determine the refractive index of a liquid using hollow prism.
9. To determine the dispersive power of the material of the prism by finding the refractive indices of different pairs of mercury spectral lines.
10. To determine the Cauchy’s Constant of a prism using spectrometer.
Learning Outcomes:
The student will be able to
CO1: Analyze the physical principle involved in the various instruments.
CO2: Analyze the physical principle involved in all related fundamental principles.
CO3: Nurture the students in all branches of Engineering.
CO4: Think innovatively and also improve the creative skills that are essential for engineering.
CO5: Apply for new application.

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
· It introduces to the fundamental and broad range of digital and analog experiments related to amplifiers, oscillators, timers, logic gates, multiplexers and demultiplexers
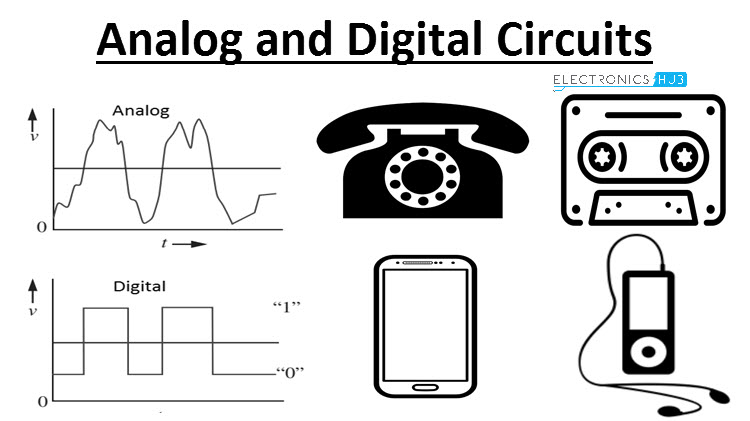
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
Course Objective:
➢ To enable students to understand the description of equations of motion of a system (using Lagrangian,
Hamiltonian mechanics and finally canonical transformation).
Course Outcomes:
Having successfully completed this course, students will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of
CO1: Derivation of Lagrange equation from D’Alembert principle
CO2: Apply the Lagrange equation to study the motion under central force problems
CO3: Apply the Lagrange equation to study the motion of rigid bodies.
CO4: Derivation of Hamilton equation of motion and apply the same for systems such as relativistic particles
and light rays.
CO5: Use of canonical transformation to find the constants of motion according to Hamilton-Jacobi theory

- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: Ravichandran S
COURSE OBJECTIVE
Ø To demonstrate how to differentiate a function of two variables.
Ø To describe smooth distribution of energy
Ø To understand the properties of a particle in universe.
Ø To introduce fourier series and its applications to the solution of partial differential equation.
Ø To describe differential equation through Frobenius Method and Integrals using Beta and Gamma functions.
Unit 1 Calculus of functions of more than one variable 9 Hrs
Partial derivatives, exact and inexact differentials. Integrating factor, with simple illustration. Constrained Maximization using Lagrange Multipliers.
Unit 2 Dirac Delta function and its properties: 9 Hrs
Definition of Dirac delta function.Representation as limit of a Gaussian function and rectangular function. Properties of Dirac delta function.
Unit 3 Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates: 9 Hrs
Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates.Derivation of Gradient, Divergence, Curl and Laplacian in Cartesian, Spherical and Cylindrical Coordinate Systems. Comparison of velocity and acceleration in cylindrical and spherical coordinate system.
Unit 4 Fourier Series 9 Hrs
Periodic functions. Orthogonality of sine and cosine functions, Dirichlet Conditions (Statement only).Expansion of periodic functions in a series of sine and cosine functions and determination of Fourier coefficients.Expansion of functions with arbitrary period.Expansion of non-periodic functions over an interval.Even and odd functions and their Fourier expansions.Application.Summing of Infinite Series.
Unit 5 Frobenius Method and Some Special Integrals 9 Hrs
Singular Points of Second Order Linear Differential Equations and their importance.Frobenius method and its applications to differential equations.Beta and Gamma Functions and Relation between them.Expression of Integrals in terms of Gamma Functions. Error Function (Probability Integral).
Max. 45 Hours
Learning Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to:
CO1: Know how to recognise and differentiate a function of two variables
CO2: Know distribution energy of the particles or materials.
CO3: Know the properties of a particle in universe using Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates
CO4: Know Fourier series representation of function of one variable to find solution of wave, diffusion and Laplace equations
CO5: Know how to handle differentiation using Frobenius Method and Integrals using Beta and Gamma functions.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
- Mathematical Methods for Physicists, G.B. Arfken, H.J. Weber, F.E. Harris, 2013,7thEdn., Elsevier.
2. Fourier analysis by M.R. Spiegel, 2004, Tata McGraw-Hill.
3. Mathematics for Physicists, Susan M. Lea, 2004, Thomson Brooks/Cole.
4. Mathematical Tools for Physics, James Nearing, 2010, Dover Publications.
5. Differential Equations, George F. Simmons, 2006, Tata McGraw-Hill.
6. Essential Mathematical Methods, K.F. Riley and M.P. Hobson, 2011, Cambridge University Press
7. Mathematical methods for Scientists and Engineers, D.A. McQuarrie, 2003, Viva Books.
8. Mathematical Method for Physical Sciences -- M. L. Boas (Wiley India) 2006.
END SEMESTER EXAM QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs.
PART A: 10 Questions of 2 mark each - No choice. 20 Marks
PART B: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice, each carrying 16 marks. 80 Marks
- Teacher: Sowbakkiyavathi E S
- Teacher: DAKSHANA MURUGAN
- Teacher: Malliga P
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
- Teacher: Jayalakshmi D.S
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
Ø To acquire basic understanding of laboratory techniques.
Ø To educate the basics of instrumentation, data acquisition and interpretation of results.
Ø To educate and motivate the students in the field of science.
Ø To allow the students to have a deep knowledge of fundamentals of optics.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
1. Determination of Young’s Modulus- Uniform bending Method.
2. Determination of Young’s Modulus- Non Uniform bending Method.
3. Determination of Rigidity Modulus of a wire – Torsional pendulum.
4. Determination of thermal conductivity of a bad conductor using Lee’s disc method.
5. Calibration of Voltmeter using potentiometer.
6. Calibration of Ammeter using potentiometer.
7. Determination of magnetic susceptibility using Quincke’s Method.
8. Determination of dispersive power of a prism using spectrometer.
9. Determination of Cauchy’s constant using spectrometer.
10. Determination of co-efficient of viscosity of a liquid by stokes method.
TEXT BOOKS
1. C.H. Bernard and C.D. Epp, John, Laboratory Experiments in College Physics
Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1995.
2. M.N. Srinivasan, A Textbook of Practical Physics, Sultan Chand & Sons, 1994.
REFERENCES
1. G. L. Squires, Practical Physics, 4th Edition, Cambridge University Press, 2001.
2. Geeta Sanon, B. Sc., Practical Physics, 1stEdition, S. Chand & Co, 2007.
3. Benenson, Walter, and Horst Stöcker, Handbook of Physics, Springer, 2002.
4. Chattopadhyay, Rakshit and Saha, An Advanced Course in Practical Physics, 8th
Edition, Books & Allied Ltd., 2007.
5. Indu Prakash and Ramakrishna, A Text Book of Practical Physics, 11th Edition, Kitab Mahal, 2011.
- S. MURUGESAN: Murugesan S
To study the thermal properties of materials by different methods.
To explain of the properties of macroscopic system.
Providing definitions of thermodynamic quantities and derivations of the laws of thermodynamics from the laws of quantum mechanics.

- Teacher: Murugesan S
COURSE OBJECTIVE
- To study the various types of communication techniques and their analysis based on Fourier transform and to provide fundamental knowledge of pulse modulation techniques and their types.
UNIT 1 SIGNAL ANALYSIS
Fourier transform of gate functions, delta functions at the origin – Two delta function and periodic delta function – properties of Fourier transform – Frequency shifting – Time shifting – Convolution theorem – Frequency convolution theorem – Sampling theorem.
UNIT 2 PULSE MODULATION AND COMMUNICATION
Pulse amplitude modulation – Natural sampling -Instantaneous sampling Transmission of PAM signals – Pulse width modulation – Time division multiplexing and frequency division multiplexing – Band width requirements for PAM signals – Pulse code modulation – Principles of PCU – Quantizing noise – Generation and demodulation of PCM – Effects of noise – Advantages and application of PCM – Differential PCM (DPCM) – Delta modulation.
UNIT 3 BROAD BAND COMMUNICATION
Coaxial cable circuit -Parallel wire line circuit – Computer communication – Digital data communication – Modems – Microwave communication links – LOS links – Tropospheric scatter microwave links – Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) – Architecture – Broadband ISDN – Local Area Network (LAN) – LAN topologies – Private Branch Exchange (PBX).
UNIT 4 SATELLITE COMMUNICATION
Introduction – Communication satellite systems – Transmitting and receiving earth station – Satellite orbits – Satellite frequency bands – Satellite multiple access formats – FDMA – CDMA – Satellite channel, Power flow – Polarization antenna gain – Parabolic dish antenna – Power loss – Rainfall effect – Receiver noise –satellite system power budget: EIRP, received power Carrier to noise ratio, G/T ratio. – Satellite link analysis – Up link – Down link – Cross link – Direct Home TV broadcasting – Satellite transponders.
UNIT 5 RADAR SYSTEMS AND OPTICAL FIBER
Introduction, Basic Radar systems, Radar systems – Radar range – Pulsed radar system – A Scope – Plan Position Indicator (PPI) – Search Radar – Tracking Radar – Moving Target Indicator (MTI) – Doppler Effect – MTI principle – Digital MTI – Radar Beacons. Optical Fiber: Introduction to light, optical fiber and fiber cables, optical fiber characteristics and classification, losses, Fiber optic components and systems, Installation, testing and repair.
Course Outcomes:
By the end of this course students will be able to
CO1: Design, operation, and troubleshoot of electronic systems
CO2: Solve electronic devices and systems using mathematical concepts.
CO3: Analyze electronics devices and circuits using computer simulations.
CO4: Analyze components associated with digital and analog electronic/communication systems.
CO5: Analyze basic wireless and communication circuits using computer simulations

- Teacher: JOANY R M
Course Objectives:
Ø The aim and objective of the course on Radiation Physics is to expose the students of M.Sc. class to the relatively advanced topics Radiation Physics and nuclear reactions.
Ø They understand the details of the underlying aspects and can use the techniques if they decide to be radiation or nuclear physicists in their career.
UNIT 1 INTERACTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATIONS WITH MATTER 12 Hrs.
Different photon interaction processes viz. photoelectric effect, Compton scattering and pair production. Minor interaction processes, Energy and Z dependence of partial photon interaction processes. Attenuation coefficients, Broad and narrow beam geometries. Multiple scattering.
UNIT 2 INTERACTION OF CHARGED PARTICLES WITH MATTER 12 Hrs.
Elastic and inelastic collisions with electrons and atomic nucleus. Energy loss of heavy charged particles. Range-energy relationships, Straggling. Radiative collisions of electrons with atomic nucleus.
UNIT 3 NUCLEAR DETECTORS AND SPECTROSCOPY 12 Hrs.
General characteristics of detectors, Gas filled detectors, Organic and inorganic scintillation detectors, Semi-conductor detectors [Si(Li), Ge(Li) HPGe]. Room temperature detectors, Gamma ray spectrometers. Gamma ray spectrometry with NaI(Tl) scintillation and semiconductor detectors.
UNIT 4 NUCLEAR SPECTROMETRY AND APPLICATIONS 12 Hrs.
Analysis of nuclear spectrometric data, Measurements of nuclear energy levels, spins, parities, moments, internal conversion coefficients, Angular correlation, Perturbed angular correlation, Measurement of g-factors and hyperfine fields.
UNIT 5 ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES 12 Hrs.
Principle, instrumentation and spectrum analysis of XRF, PIXE and neutron activation analysis (NAA) techniques. Theory, instrumentation and applications of electron spin resonance spectroscopy (ESR). Experimental techniques and applications of Mossbauer Effect, Rutherford backscattering. Applications of elemental analysis, Diagnostic nuclear medicine, Therapeutic nuclear medicine.
Max. 60 Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES:
CO1: Understand various modes of interaction of electromagnetic radiations and charged particles with matter.
CO2: Distinguish various types of radiations based on their interaction with matter.
CO3: Learn and understand about different detectors and their use for spectroscopy.
CO4: Use different analytical technique such as XRF, PIXE, neutron activation analysis and electron spin resonance spectroscopy.
CO5: Understand various analysis techniques and way to apply the materials in suitable manner
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. The Atomic Nucleus: R.D. Evans, Tata Mc Graw Hill, New Delhi.
2. Nuclear Radiation Detectors: S. S. Kapoor and V. S. Ramamurthy, New Age, International, New Delhi.
3. Radiation Detection and Measurements: G. F. Knoll, Wiley & Sons, New Delhi.
4. Introductory Nuclear Physics: K. S. Krane, Wiley & Sons, New Delhi.
5. An Introduction to X-ray Spectrometry: Ron Jenkin, Wiley.
6. Techniques for Nuclear and Particle Physics Experiments: W. R. Leo, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi.
7. Introduction to experimental Nuclear Physics: R.M. Singru, Wiley & Sons, New Delhi
- Teacher: Helen Merina Albert
- Teacher: Murugesan S
- Teacher: Dr. GOWTHAMARAJU SHANMUGAM
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To calculate youngs modulus of a materials
- To measure the thermal conductivity of a good and bad conductor.
- To understand the nature of waves

- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
Course Description for SPHB1104 – Physics
This course introduces engineering students to the fundamental principles of applied physics necessary for understanding materials, devices, and modern technologies. The curriculum covers:
-
Properties of Matter: Elasticity, stress–strain relations, bending of beams, and torsional oscillations.
-
Crystal Physics: Crystal systems, Bravais lattices, Miller indices, packing factors, and crystal growth techniques.
-
Semiconductors & Magnetism: Band theory, p–n junction devices, breakdown mechanisms, and classification of magnetic materials.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Wave–particle duality, Schrödinger’s equation, uncertainty principle, and applications like tunneling and STM.
-
Lasers & Applications: Principles of laser action, diode lasers, quantum cascade lasers, and applications in engineering and medicine.
The associated Physics Laboratory enables hands-on experience in optics, semiconductors, elasticity, fiber optics, and modern physics experiments. Students will gain skills in measurement, data analysis, and application of physical principles to engineering systems.
Learning Outcomes:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
-
Analyze the elastic properties of solids and determine material constants experimentally.
-
Interpret crystal structures, planes, and defects.
-
Explain semiconductor physics and magnetic materials with device-level applications.
-
Solve fundamental quantum mechanics problems and apply concepts to nanoscale systems.
-
Understand laser principles and evaluate their engineering/medical applications.
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
- Teacher: Murugesan S
Course Description for SPHB1104 – Physics
This course introduces engineering students to the fundamental principles of applied physics necessary for understanding materials, devices, and modern technologies. The curriculum covers:
-
Properties of Matter: Elasticity, stress–strain relations, bending of beams, and torsional oscillations.
-
Crystal Physics: Crystal systems, Bravais lattices, Miller indices, packing factors, and crystal growth techniques.
-
Semiconductors & Magnetism: Band theory, p–n junction devices, breakdown mechanisms, and classification of magnetic materials.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Wave–particle duality, Schrödinger’s equation, uncertainty principle, and applications like tunneling and STM.
-
Lasers & Applications: Principles of laser action, diode lasers, quantum cascade lasers, and applications in engineering and medicine.
The associated Physics Laboratory enables hands-on experience in optics, semiconductors, elasticity, fiber optics, and modern physics experiments. Students will gain skills in measurement, data analysis, and application of physical principles to engineering systems.
Learning Outcomes:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
-
Analyze the elastic properties of solids and determine material constants experimentally.
-
Interpret crystal structures, planes, and defects.
-
Explain semiconductor physics and magnetic materials with device-level applications.
-
Solve fundamental quantum mechanics problems and apply concepts to nanoscale systems.
-
Understand laser principles and evaluate their engineering/medical applications.
- Teacher: Lavanya J
To derive equations for current charges and its applications.
To know about the basic concepts of magnetism and basic laws.
To learn the properties of various circuits are going to be analysed.
To evaluate magnetic concepts and magnetic circuits

- Teacher: Jayalakshmi D.S
- Teacher: Malliga P
- Teacher: VIJAI ANAND K
- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
Course objective:
- To determine the rigidity modulus of wire
- To find the refractive index of prism
- To understand concept of string

- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
- Teacher: Anandhi S
- Teacher: Kanimozhi D
- Teacher: DAKSHANA MURUGAN
The purpose of research is to discover answers to questions through the application of scientific
procedures. The main aim of research is to find out the truth which is hidden and which has not been
discovered as yet. Though each research study has its own specific purpose, we may think of
research objectives as falling into a number of following broad groupings:
1. To gain familiarity with a phenomenon or to achieve new insights into it (studies with this
object in view are termed as exploratory or formulative research studies);
2. To portray accurately the characteristics of a particular individual, situation or a group
(studies with this object in view are known as descriptive research studies);
3. To determine the frequency with which something occurs or with which it is associated
with something else (studies with this object in view are known as diagnostic research
studies);
4. To test a hypothesis of a causal relationship between variables

- Teacher: PARASURAMAN K
To understand the static electric and magnetic fields in various aspects and relating them using Maxwell’s equations.
Also to study propagation of electromagnetic wave and its interaction with matter.

- Teacher: Rameshkumar C
- Teacher: Anita Lett J
The course is consists of all non-conventional manufacturing processes. It starts with classification of manufacturing processes and necessity of non conventional manufacturing processes. This course dealt with details about the mechanism of material removal, sources of energy used for material removal, working principle, the set up or equipment and relative advantages and disadvantages. It gives a clear cut idea about the processes, its use in specific industrial application etc.
- Teacher: ARUNKUMAR G
(i) to expose the student to the different types of manufacturing available today such as the Special Manufacturing System, the Manufacturing Cell, and the Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS)
UNIT 1 DESIGN FUNDAMENTAL- The design process – Considerations of good design - Morphology of Design – Design Drawings , Computer Aided Engineering – Designing of codes and standards – Concurrent Engineering – Product life cycle – Technological Forecasting – Market Identification– Competition Bench marking – Systems Engineering – Life Cycle Engineering – Human Factors in Design – Industrial Design.
UNIT 2 DESIGN METHODS- Creativity and Problem Solving – Creativity methods – Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) - product Design Specifications– Conceptual design – Decision Theory – Decision Tree – Evaluation methods - Embodiment Design – Product Architecture Configuration Design - Parametric Design – Role of models in designs - Mathematical Modeling – Simulation – Geometric Modeling – Finite Element Modeling – Optimization – Search Methods – Geometric Programming – Structural and Shape Optimization.
UNIT 3 MATERIAL SELECTION PROCESSING AND DESIGN- Material Selection Process – Economics – Cost Vs Performance – Weighted property Index – Value Analysis – Role of Processing in Design – Classification of Manufacturing Process – Design for Manufacture – Design for Assembly – Designing for castings, Forging, Metal Forming, Machining and Welding – Residual Stresses – Fatigue, Fracture and Failure.
UNIT 4 PROBABILITY CONCEPTS IN DESIGN FOR RELIABILITY- Probability – Distributions – Test of Hypothesis – Design of Experiments – Reliability Theory – Design for Reliability – Reliability centered Maintenance – Robust Design Failure mode Effect Analysis.
UNIT 5 LEGAL AND ETHICAL ISSUES IN DESIGN AND QUALITY ENGINEERING- Introduction – The origin of laws – Contracts – Liability – Tort law – Product liability – Protecting intellectual
property – Legal and ethical domains – Codes of ethics – Solving ethical conflicts– case studies. Total Quality Concept –
Quality Assurance – Statistics Process Control – Taguchi Methods – Robust Design – Failure Model Effect Analysis.
Max: 45 Hrs.
|
SPYS 1601 |
Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms. Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
Effective Leadership
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80Marks
|
SPYA 1404 |
Open Elective 4 – Effective Leadership |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT-I
Meaning -Purpose - Leader in Government -Inner Core of leader - Social Response - Essential Behaviours of Good leaders
UNIT-II -
Characterstis of Leader -Types of Leader -Assessment of Leader - Pros and Cons
UNIT-III
Aspiration of Good Leader, Ethics of Leader, Value, Skills
UNIT-IV
Information and Commetments of leader, Communication and Commetments of Leaders
UNIT-V
Sustainabilty of Good Leader - 360 tools - Educating and Developing leader.
References:
1. Svendsen, A., & Laberge, M. (2007). “FOSTERing” collaborative stakeholder relationships. Notes for Practitioners Series: CoreRelation Consulting, Inc. Retrieved from http://masterfulfacilitation.com/ articles/fostering.pdf
2. Tardanico, S. (2013, January 15) 10 Traits of courageous leaders. Forbes: Leadership. Retrieved from https:// www.forbes.com/sites/susantardanico/2013/01/15/10-traits-of-courageous-leaders/#7b075cbb4fc0
3. Th omas, K., & Kilmann, R. (2002). Confl ict mode instrument. USA: Xicom Inc., subsidiary of CPP, Inc. TNS Employee Insights. (2014). 8 Tips to engage your employees. Retrieved from http://tns.tnsemployeeinsights.com/acton/media/2055/employee-engagement-tips-for-managers
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
|
SPSY 1501 |
Core Theory 8 - Psychopathology II |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To explore abnormality and understand the nature and course of development of various psychological disorders.
· To familiarize with research, theory, and methods of practice in abnormal psychology.
Unit I: (15 hours)
Schizophrenia- Clinical description; schizoohrenia subtypes; Causes of schzophrenia - Biological dimensions, psychological And Social contributions; Treatment
Unit II: (15 hours)
Mood Disorders- Clinical descriptions of mood disorders; Depressive Disorders; bipolar disorders: Causes of Mood disorders; Treatment
Unit III: (15 hours)
Substance related disorders: alcohol abuse and dependence; drug Abuse and dependence; causes of substance related disorders; Treatment
Unit IV: (15 hours)
Sexual Disorders: Sexual dysfunctions - causal factors & Treatment Sexual variants - Paraphilias, Incest & rape; causes and treatment
Unit V(15 hours)
Behaviour Disorders Of childhood and adolescence: Hyperactivity, Conduct disorders, delinquent behaviour, eating disorders, autistic Disorder, elimination disorder Visit to mental health/de addiction centers must be arranged
REFERENCE
1 Barlow David H & Durand, V.Mark (1995) Abnormal
Psycholgy, Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.
2 Carson, Robert, Butcher, James V., Coleman,
James(1988): Abnormal Psychology and Modem Life, VIII edition, Scott.Frismand
& Co
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Students will apply the major concepts and theories of Abnormal Psychology
2. Students will create and explain the physiological, behavioural, and psychological correlates of abnormal behaviour.
3. Students will critically evaluate issues surrounding methods of assessing, diagnosing, and treating psychopathology.
4. Students will understand the historical foundations of current methods of assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of psychopathology.
- Teacher: Dr.Parveen Banu R
UNIT - I (15 hours)
Introduction of Human Resources Management: Definition, Importance of Human Resources, Objectives of Human Resources Management, Qualities of a good personnel manager – Need, type and scope – Advantage for a written policy - Human Resources policies and work Culture.
UNIT – II (15 hours)
Human Resource Planning: Human Resources Planning: Long and Short-term planning, Job. Recruitment and selection: Purposes, types and methods of recruitment and selection, Placement, Induction, Transfers, Promotions, Disciplinary actions, Termination of Services: Resignation, Dismissal, Retrenchment and Voluntary Retirement Schemes, Exit Interviews, Prevention of employee turnover.
UNIT - III (15 hours)
Performance Evaluation: Ranking, rating scales, critical incident method, Removing subjectivity from evaluation, MBO as a method of appraisal, Job evaluation, Criteria for Promotions and job enrichment.
UNIT - IV (15 hours)
Rewards Management: Wage and Salary Administration: Meanings, Calculation of Wage, Salary, Perquisites, Compensation Packages, Cost of Living Index and Calculation of Dearness Allowance, Rewards and Incentives: Financial and nonfinancial incentives, Productivity – linked Bonus, Compensation Criteria.
UNIT - V (15 hours)
HR Audit: Nature and Scope – Approaches to HR Audit Management of Differences: Grievance Handling – Discipline and Domestic Enquiry – Handling of Sexual Harassment in the Work Place – Introduction to Industrial Relations – Current Trends and Issues in HRM and Case Studies.
Reference Books:
1. Ashwathappa, K., Human Resource Management, 6th Edition, Tata McGrawHill Education Pvt. Ltd., 2010.
2. DeCenzo, D.A. and Robbins, S.P., Human Resource Management, 10th Edition, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd., 2011.
3. Dessler, G., Human Resource Management, 12th Edition, Pearson, 2011.
4. Ivanecevich, J.M., Human Resource Management, 10th Edition, Tata McGrawHill Education Pvt. Ltd., 2010. 5. Mamoria, C.B. and Gaonkar, S.V., Personnel Management, Himalaya Publishing House, 2011.
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks:100 ExamDuration:3Hrs.
PARTA: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PARTB: 2 Questions from each unit of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80Marks
|
SPYA 1602 |
Professional Core 10 – Rehabilitation Science |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
UNIT :I (15Hours)
Rehabilitation psychology: overview and concepts- Nature and scope of rehabilitation psychology- Concepts of ability and disability – Recovery - symptom control and rehabilitation - Establishment of division 22 of APA.
UNIT :II (15 Hours)
Importance and applications - Rehabilitation of addictions - drug and alcohol - Rehabilitation after abuse and violence - Palliative care and pain management - role of psychologists.
UNIT: III (15 Hours)
Rehabilitation of persons with physical disabilities – physical - psycho- social and vocational rehabilitation.
UNIT :IV (15 Hours)
Biopsychosocial and social model –Psychodynamic - behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counseling - Cognitive- behavioural approaches to rehabilitation counselling.
UNIT: V (15 Hours )
Parental care and support systems for persons with disabilities - Assessment of persons with disabilities - Legal issues in rehabilitation for persons with disabilities - overview of PWD act - RCI act - national trust act - United Nations convention on the rights of persons with disabilities.
Books for study
1. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company
2. Falvo, D.R. (2013). Medical and psychosocial aspects of Chronic Illness and disability (5th ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning
3. Frank, G.R., Rosenthal, M., Caplan, B. (2010). Handbook of Rehabilitation Psychology. American Psychological Association.
7. Chan, F., Berven, N.L., Thomas, K.R. (2004). Counselling Theories and Techniques for Rehabilitation Health Professionals. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
Books for reference
1. Federici, S. Scherer M.J. (2012). Assistive Technology Assessment Handbook (Eds.). Boca Raton, FL :Taylor and Francis Group.
2. Riggar, T.F. & Maki, D.R. (2004). Handbook of Rehabilitation Counselling (Eds). New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
3. Stuss, D.T., Winokur, G. & Robertson, I.H. (2008).Cognitive neurorehabilitation. UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
SPYS 1601 | Core Theory 10 – Counseling and Psychotherapy | L | T | P | Credits | Total Marks |
4 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To get acquainted with the nature, process, theories and techniques of counseling, guidance and psychotherapy and its application in therapeutic settings.
· To reflect on rehabilitation aspects.
Unit I–Introduction to Psychotherapy (15 hours)
Main features –Objectives of Psychotherapy – Therapeutic process – Therapist qualities- Effectiveness of Psychotherapy – Ethical issues in research and practice. Evidence-based psychotherapies.
Unit II - Psychodynamic therapies(15 hours)
Traditional psychoanalysis: Freud; free association; psychodynamic therapy: theoretical ground.Therapeutic factors: resistance, transference and counter transference, defense mechanisms.Adlerian therapy; Jungian therapy, Contemporary psychoanalytic therapies.Interpretation of dreams.Indian psyche
Unit III–Cognitive-Behavior therapies(15 hours)
Cognitive therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Cognitive conceptualization. Behavior therapy: Basic principles, theoretical background, history and development. Techniques of classical conditioning,operant conditioning.
Unit IV –Humanistic existential therapies(15 hours)
Humanistic therapy: client- centered therapy; meaning of existence and purpose in life, self-actualization, self-psychology. Existential therapy, logo therapy; Gestalt therapy, Group therapy.Humane approach.Spirituality
Unit V –Other forms of Psychotherapy(15 hours)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: Ellis. Couple therapy, marital and family therapy.Crisis Intervention.Positive Psychological interventions: mindfulness.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Remember professional standards of therapeutic counselling practice.
2. Understand the theory and practice of a relational approach to counselling.
3. Evaluate and integrate a range of theoretical approaches into a coherent model of practice.
4. Apply the knowledge, skills and understanding of the reflective practitioner.
5. Create an environment to work competently with diversity and with an anti-oppressive practice.
6. Analyse participation in and potential contribution to the changing (local and global) social, professional and organisational context for therapy.
References:
1.Hersen, M. & Sledge, W. (2002). Encyclopedia of psychotherapy.Academic Press.
2.Yalom, I. (2009). The Gift of Therapy. Harper Perennial: New York.
3.Gobbard, G. Beck, J. Holmes, J. (2007). Oxford Textbook of Psychotherapy. OUP: London.
4.Gerring, R.J. & Zimbardo, P.G. (2006). Psychology and Life. Pearson.
- Teacher: KINJARI K
- Teacher: Vinaya G
- Teacher: SHYAM SRINIVASAN K
|
SPYB1101 |
General Psychology I |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To generate interest in Psychology.
- To introduce the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behavior.
- To understand the various theories in Psychology.
- To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 12 Hrs
Psychology as a science – The History of Psychology – Schools - Modern Perspectives – Psychology in India- Methods: Introspection – Observation – Survey – Experiment – Case Study – Correlation Research - Scope of psychology. Fundamentals of Indian Psychology.
UNIT 2 SENSATION, PERCEPTION 12 Hrs
Sensation: Meaning –
Psychophysics -Thresholds – Weber’s Law – Adaptation – Basic sensation:
Vision – Hearing – Touch and other Skin senses – Olfaction- Gustation - Proprioception:
Kinesthetic sense – Vestibular sense Perceptual processing – Perception: Role
of attention in perception - Perceptual organization - Perceptual sets -
Perceptual constancies - Depth perception - Illusions - Extra Sensory
Perception. - Factors that influence perception – Depth perception.
UNIT 3 LEARNING 12 Hrs Definition – Nature- Principles of learning - Classical conditioning - Operant Conditioning - Principles of reinforcement – Punishment- Schedules of Reinforcement – Shaping – Learned Helplessness - Cognitive Learning - Latent Learning – Insight Learning – Observational Learning.
UNIT 4 MEMORY 12 Hrs
Memory: Definition - Processes of memory: Encoding – Storage – Retrieval – The information processing model - Stages of memory: Sensory memory – Short term memory – Long term memory – Forgetting: Meaning – Forgetting Curve-Theories of forgetting - Causes – Memory and Brain – Improving memory.
UNIT 5 THINKING AND LANGUAGE 12 Hrs
Thinking and language - Thinking process - Concepts - Problem-solving - Creative thinking - Reasoning – Inductive and Deductive reasoning, Language: Nature - Main Components of Language.
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO1: To understand the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behaviour.
CO2: To evaluate the various theories in Psychology.
CO3: To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
CO4: To remember the dynamics of the important cognitive processes.
CO5: To create and evaluate interventions and strategies and enhance the basic as well as higher-order cognitive functions.
CO6: Students will be able to identify the major fields of study and theoretical perspectives within psychology and analyse their similarities and differences.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Cicarelli, S. K. & White, J. N. (2021). Psychology 6th edition. Pearson India Education Services Pvt Ltd.
2. Kalat, J. W. (2021). Introduction to Psychology 12th edition. Cengage Learning.
3. Feldman, R. S. (2020). Understanding Psychology. 15th Edition. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
4. Morgan,C.T., King,R.A., Weisz, J.R., & Schopler,J. (2004). Introduction to Psychology. 7th Edition.NewDelhi:TataMcGraw-Hill.
5. Baron, R. A. (2010) Psychology (5th ed.). New Delhi, India: Pearson India Education Services Pvt Ltd.
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
Unit I: Motivation (15 hours)
Motivation – Meaning - Approaches-Instinct - Drive reduction - Arousal – Incentive -, Cognitive - Humanistic- Maslow’s Need hierarchy – Types-Physiological Motivation [Hunger, Thirst, Sex, Maternal drive] - Psychological motivation [Achievement, Affiliation, Power, Parenting.
Unit II: Intelligence and Assessments(15 Hours)
Concepts and nature of Individual differences – Intelligence - Theories of intelligence- factor and cognitive theories - Characteristics of Intelligence tests - Types of Intelligence tests - Determinants of Intelligence.
Unit III: Emotion (15 Hours)
Emotion - Meaning - Physiological basis of emotions – Theories-James Lange Theory - Cannon Bard Theory - Cognitive Theory.
Unit IV : Personality (15 Hours)
Definition - Approaches – Psychodynamic – Humanistic - Social – Cognitive approach - Assessment of Personality – Questionnaire - Rating Scales and Projective tests – Characteristics - Advantages and disadvantages.
Unit V: Altered States of Consciousness (15 Hours)
Consciousness – Nature – Waking - Sleep and Daydreaming - Biological Rhythms – Circadian - Stages - Dreams-Content, Links between dreams and waking .
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. To understand the concepts of basic psychological processes, systems and methods underlying human behaviour.
2. To evaluate the various theories in Psychology.
3. To apply the principles of psychology in day-to-day life for a better understanding of the self and others, particularly pertaining to the Indian context.
4. To remember the dynamics of the important cognitive processes.
5. To create and evaluate interventions and strategies and enhance the basic as well as higher-order cognitive functions.
6. Students will be able to identify the major fields of study and theoretical perspectives within psychology and analyse their similarities and differences.
References:
1.Morgan,C.T, King,R.A., Weisz,J.R., and Schopler,J. (2004). Introduction to Psychology, 7th
edition,24th reprint.NewDelhi:TataMcGraw-Hill.
2. Baron, R.A. (1996). Psychology. 3ed. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
3. Lahey, B. B. (1998). Psychology: An Introduction. New Delhi: Tata Mc Graw Hill.
4. Feldman, R. S. (2002). Understanding Psychology. New Delhi: Tata Mc Graw Hill.
5. Bootzin, R. R., Bower, G. H., Crocker, J., & Hall, E. (1991). Psychology Today. London: Mc Graw Hill.

- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
SPYA1302 - Life Span Development
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To explore the various influences on child and adolescent development processes.
· To explore the psychology of exceptional children.
· To explore the various influences on development processes concerning adulthood and aging, taking into consideration the individual, familial and societal contexts.
Unit I : INTRODUCTION (15 hours)
Developmental Psychology - Conception, Pregnancy,And Birth - Stages of Pregnancy –Conception –Implantation -The first trimester -The second trimester - The third trimester - Prenatal Care - Drug use during pregnancy - -Stages of Childbirth - The postpartum stage of childbirth
Unit II : INFANCY AND EARLY CHILDHOOD(15 hours)
Physical and cognitive development- Reflexes and motor skills -Sensation and perception- Psychosocial development – Family Relationships -Attachment – Parenting -Sexuality in Infancy and Toddlerhood - Gender Development - Gender identity -Psychological and social influences on gender identity - Gender roles early childhood: physical and Cognitive development –psychosocial development.
Unit III : MIDDLE CHILDHOOD and ADOLESCENCE(15 hours)
Physical And Congnitive Development –Physical Development in Middle Childhood and Adolescence- Physical changes - Brain and nervous system development - Motor skills – Health - Cognitive Development in Middle Childhood and Adolescence - Self-Concept - Social Cognition - Family Relationships - Peer Pressure - Sexuality in Middle Childhood
Unit IV : Early Adulthood and Middle Adulthood(15 hours)
Physical And Cognitive Development - Physical Development In Early Adulthood And Middle Adulthood – Health in Adulthood - Intellectual Development in Adulthood - Independence In Early Adulthood - Establishing A Career - Psychosocial Development - Crisis -Relationships In Middle Adulthood
Unit V :LATE ADULTHOOD (15 hours)
Physical Development in Late Adulthood - Health in Late Adulthood - Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease - Intelligence and Memory - Relationships - Late adulthood and sexuality - Relationships with adult children - Elderly abuse - Relationships with grandchildren .
COURSE OUTCOMES:
1. Understand theory and research in physical, cognitive, communication, emotional, and social development of the Child , Adolescence and adult.
2. Understand the physical, cognitive, communication, emotional, and social development of the infant and child..
3. Apply knowledge of infant and child development to facilitate and understanding of developmental outcomes.
References:
1.Papilla, Diane E, Olds, Sally Wendoks(1992): Human Development, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co
2.Shaffer, David R. (1996): Developmental Psychology, IV Edition, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company.
3.Hurlock, E.: Developmental Psychology (1980), Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co.
- Teacher: SATHISH KUMAR S
Unit I: Introduction to Statistics (15 hours)
Introduction to Statistics: the meaning of statistics - Need and importance of statistics in psychology - Prerequisites for studying statistics- Descriptive and inferential statistics - Frequency Distribution and Graphic representation of data: Histogram - Bar diagram - Pie Chart - Scatter Plot.
Unit II: Measures of Central Tendency and Variability (15 hours)
Computation of Mean, Median and Mode and their uses. Measures of variability: Computation of quartile and standard deviations - Cumulative distribution - Percentiles standard scores and their uses. Normal distribution curve: Characteristics and application - Kurtosis and Skewness.
Unit III: Parametric tests (15 hours)
Correlations: Meaning and methods – Characteristics - Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation - Point-Biserial Correlation and Phi - Biserial and Tetrachoric Correlation - Tests of Significance: t- test - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA): One way and Two way Analysis of Variance,
Unit IV: Non-parametric tests (15 hours)
Spearman’s Rank Correlation –Regression: Simple linear regression – Multiple Regression - Chi Square Test - Wilcoxon signed rank test - Mann- Whitney U test - Kruskal-Wallis (KW) test - Friedman's test
Unit V: Test construction and standardization (15 hours)
Characteristics of a good test - Steps in test construction: Item-analysis - determination of item difficulty - item discrimination - problems of item analysis - Introduction to SPSS: Meaning- Uses of SPSS in Statistics and Research.

- Teacher: KRISHNAPRIYA B
|
SPYB4001 |
Personality Development |
L |
T |
P |
EL |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
100 |
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
To enable the students to
· Understand the meaning and nature of personality
· Analyze their attitudes for personal enrichment
· Understand the concept of motivation and achievement motivation
· Maintain healthy relationships with others in turn developing personalities
UNIT – I: Meaning and Nature of Personality 15 Hours
Personality: Definitions, Meanings, Elements of personality, Types of Personality, Determinants of personality, Personality SWOT Analysis.
UNIT – II: Personality Enrichment 15 Hours
Self esteem, Self concept, Advantages of high self esteem, Characteristics of people with high and low self esteem, Steps to building positive self esteem, Attitude, Factors that determine our attitude., Benefits of a positive attitude and consequences of a negative attitude, Steps to building a positive attitude.
UNIT – III: Motivation 15 Hours
Motivation: Meaning and nature, The difference between inspiration and motivation, Motivation redefined, External motivation vs. Internal motivation, Achievement motivation
UNIT – IV: Success 15 Hours
Defining success-Real or imagined obstacles to success, Qualities that make a person successful, Reasons for failure – Interpersonal skills, Dealing with seniors, colleagues, juniors, customers, suppliers at the workplace.
UNIT – V: Positive Relationships & Personality 15 Hours
Positive Relationships – Factors that prevent building and maintaining positive relationships, the difference between ego and pride, the difference between selfishness and self interest, Steps for building a positive personality, Body language: understanding body language, Projecting positive body language.
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. To understand different elements of personality
2. They can able to know different types of Personality
3. Students can understand determinants of personality
4. To understand advantages of high self esteem
5. Students will be able to acquire the skills to manage time and relationship
6. Students can identify the factors that prevent building and maintaining positive relationships
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
- Nathan Dorman (2004) Personality Development Abishek Publication, New Delhi.
- Jafar Mahmud (2004) Introduction to Psychology APH Publishing Corporation, New Delhi.
- Zig Ziglar (2000) See You at the Top Magna Publishing Co. Ltd., Mumbai.
- Shiv Khera (1998) You can win MacMillan India Ltd., New Delhi.
- Walter Doyle Staples (2000) Think Like a Winner Magna Publishing co. Ltd., Mumbai\
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3Hrs.
PART - A: 10 Questions of 2 marks each – No choice 20 Marks
PART - B: 2 Questions from each UNIT of internal choice; each carrying 16 Marks 80 Marks
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
|
SPYA1604 |
Professional Elective II – Stress Management
|
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Total Marks |
|
3 |
1 |
|
4 |
100 |
Objectives
1. To understand how the stressors will change the Life events or life change events.
2. To know the different Theories of Stress.
3. To highlight the different types of relaxation technique to reduce stress.
Unit-I (15 hours)
Introduction: The science and sources of stress – Stress and health – Types of stress –concept of stress – Causes of stress –Theories of stress - Response-based concept of stress - Event-based concept of stress
Unit –II (15 hours)
Stressors -Life events or life change events -Chronic stressors -Effects of stress on the body -Enhancing awareness about managing stress - The health belief model and its application to stress management: an in -depth investigation.
Unit – III (15 hours)
Relaxation: Meaning – Sleep – Sleep related disorders - Relaxation techniques: yoga and meditation –Biofeedback -Progressive muscle relaxation - Autogenic training -Visual imagery - Self-hypnosis - Humor, stress, and relaxation - Mindfulness meditation.
Unit IV (15 hours)
Coping mechanisms: Method Based on Rational Emotive Therapy-Method Based on Simplified Kundalini Yoga -Method Based on Gestalt Therapy - Systematic Desensitization - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy -Regular physical activity and exercise.
Unit –V (15 hours)
Implementing a Stress Reduction Plan: Importance of implementing a plan - Stages of change - Determining goals, objectives, and targets: goal setting: Establishing objectives - Deciding targets -Social support.
- Teacher: Kalaivanan S
Unit I : Introduction (15 hours)
Positive psychology: Definition; goals and assumptions; Relationship with health psychology, developmental psychology, clinical psychology. Activities: Personal mini experiments; Collection of life stories from magazines, websites, films etc and discussion in the class.
Unit II: Positive emotions, Well-being and Happiness (15 hours)
Positive emotions: Broaden and build theory; Cultivating positive emotions; Happiness- hedonic and Euaimonic; Well- being: negative vs positive functions; Subjective well –being: Emotional, social and psychological well-being; Model of complete mental life. Test: The positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS-X); The satisfaction with life scale (Diener et al, 1985); Practice ‘Be happy’ attitude
Unit III :Self-control, Regulation and Personal goal setting (15 hours)
The value of self-control; Personal goals and self-regulation; Personal goal and well-being; goals that create self-regulation; everyday explanations for self-control failure problems. Activity: SWOT analysis
Unit IV: Positive Cognitive States and Processes (15 hours)
Resilience: Developmental and clinical perspectives; Sources of resilience in children; Sources of resilience in adulthood and later life; Hope. Optimism- How optimism works; variation of optimism and pessimism; Resilience. Spirituality: the search for meaning(Frankl); Spirituality and well-being; Forgiveness and gratitude. Test: Mental well-being assessment scale; Test: Signature strength
Unit V :Applications of Positive Psychology (15 hours)
Positive schooling: Components; Positive coping strategies; Gainful employment Mental health: Moving toward balanced conceptualization; Lack of a developmental perspectives. Activity: An action plan for coping. Test: Brief COPE assessment scale
References:
1.Snyder, C.R. & Lopez, S.J. (2002). Handbook of positive psychology.(eds.). New York:Oxford University Press.
2.Baumgardner, S.R & Crothers, M.K.(2009). Positive Psychology.U.P: Dorling KindersleyPvt Ltd.
3.Carr, A. (2004). Positive psychology, The science of happiness and human strengths.NewYork: Routledge.
- Teacher: SUBIKKSHA S
- Teacher: Dr. Gayathri P
This course is to familiarize students with fundamental process of human embryology and developmental biology, which provide solid foundation on stem cell biology, regulation of stem cells and human diseases connected to stem cell biology.
This course is to familiarize students with fundamental process of human embryology and developmental biology. This course will provide the solid foundation on stem cell biology, regulation of stem cells and human diseases connected to stem cell biology.
|
SMEB1303 |
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS |
L |
T |
P |
Credits |
Max.Marks 100 |
|
3 |
* |
0 |
3 |
OBJECTIVE:
- To study the aspects of Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
- To gain knowledge of different types of stresses, strain and deformation induced in the components due to external loads.
- To study the distribution of various stresses in the elements such as beams, shafts etc.
- To study the effect of component dimensions and shapes on the stresses and deformations.
UNIT 1: STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 9 Hrs
Rigid and Deformable bodies – Strength, Stiffness and Stability – Stresses; Tensile, Compressive and Shear –Deformation of simple and compound bars under axial load – Thermal stresses and strains. Elastic constants – Relation between Elastic constants - Strain energy and unit strain energy – Strain energy in uniaxial loads.
UNIT 2: ANALYSIS OF STRESSES IN TWO DIMENSIONS 9 Hrs
Principal planes and stresses – Mohr’s circle for biaxial stresses – Maximum shear stress - simple problems- Stresses on inclined plane. Biaxial state of stresses – Thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Deformation in thin cylindrical and spherical shells – Efficiency of joint- Effect of Internal Pressure.
UNIT 3: BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES 9 Hrs
Types of beams - Supports and Loads – Shear force and Bending Moment in beams – Cantilever, Simply supported andOverhanging beams – SFD and BMD for inclined loads and couples.Stresses in beams – Theory of simple bending – Stress variation along the length and in the beam section – Effect of shape of beam section on stress induced.
UNIT 4: TORSION 9 Hrs
Analysis of torsion of circular bars – Shear stress distribution – Bars of Solid and hollow circular section – Stepped shaft – Twist and torsion stiffness – Composite shafts Springs - Laminated springs, axial load and twisting moment acting simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs– Deflection of helical coil springs under axial loads – stresses in helical coil springs under torsion.
UNIT 5: BEAM DEFLECTION 9 Hrs
Columns – End conditions – Equivalent length of a column – Euler equation – Slenderness ratio – Rankine Gordon formula for columns.Elastic curve of Neutral axis of the beam under normal loads – Evaluation of beam deflection and slope: Double integration method, Macaulay Method, and Moment-area Method.
Max.45Hours
COURSE OUTCOMES:
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1: Understand the fundamentals of Stress and Elastic Constants.
CO2: Understand the concept of Principal stresses and thin shells.
CO3: Construct Shear force & Bending moment diagram and Bending stress.
CO4: Apply the Concept of Torsion for Circular Shafts and Understand the concept of Springs.
CO5: Understand the theory of Column and Beam deflection.
CO6: Analyze overall deflection aspects related to Strength, Stiffness and Stability.
TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Bansal R.K., “Strength of Materials”, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd.,Fifth Edition,2012
2. Punmia B.C. & Jain A.K., Mechanics of Materials, ,Laxmi Publications,2001
3. Ryder G.H, “Strength of Materials, Macmillan India Ltd”., Third Edition, 2002
4. Ray Hulse, Keith Sherwin & Jack Cain, “Solid Mechanics”, Palgrave ANE Books,2004.
5. Allan F. Bower, Applied Mechanics of Solids, CRC Press, 2009, 820 pages.
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER PATTERN
Max. Marks : 100 Exam Duration : 3 Hrs.
PART A : 2 Questions from each unit, each carrying 2 marks 20 Marks
PART B : 2 Questions from each unit with internal choice, each carrying 16 marks 80 Marks
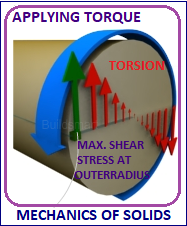
- Teacher: HEMANANDH J
- Teacher: LAKSHMI SANKAR S
Drawings on types of bolted joints designed bolted joint - Types of the weld and welded joint - Steel in the foundation, beams, and columns with column base. - Types of tubular Trusses, connections of various members of tubular truss - tubular constructions.
- Teacher: Dr.Annamalai S

- Teacher: Eshanthini P
To emphasize the importance of sustainable design practices and strategies in urban planning and settlement
design.

TV production involves various elements that come together to create a successful TV show. So, if you are enamored by large houses and the over-the-top look of the show, then read on to know what all goes into making these sets into a reality on TV. At the end of the course, you will be a multi-skilled, industry-ready practitioner. Employability is a core feature of this course.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
The Television production process refers to the stages (phases) required to complete a media product, from the idea to the final master copy. This process can apply to any type of media production including film, video, television and audio recording.
The three main stages of production are:
- Pre-production: Planning, scripting & story boarding, etc.
- Production: The actual shooting/recording.
- Post-production: Everything between production and creating the final master copy.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
- Media law presents a wonderful opportunity to explore the many competing rights and interests in society as the rights to free expression, information, and a free media compete with other important rights including reputation, a fair trial, privacy, confidentiality, intellectual property and national security, along with the right to be free from discrimination in all its forms.
- It affords us a superb showcase of the role of the news media in the varied political systems internationally as governments select different points where free expression should be curtailed. You learn that free expression is a continuum, with fewer restrictions in some nations and alarming censorship in others.

- Teacher: NAZINI N
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To help students learn and analyze the various content in media so that they are aware of the content produced in media.
To understand how media constructs reality and to choose right tool to analyze content provided in print and electronic medium.
UNIT 1 MEDIA CONTENT
Media Content - Media text as arrangements of signs – Narrative, genre - discourse analysis –Text, intertextuality & context - institutions & ways of seeing discourse analysis – sources - technologies of the gallery & museum
UNIT 2 MARXISM & IDEOLOGY
Media as Manipulators: Marxism & Ideology – culture industry as mass deception – ideological meanings –arguments and criticisms – communication flows & consumer resistance, Media & public sphere - nation as imagined community - digital dilution of nation
UNIT 3 PSYCHOANALYSIS
Psychoanalysis: visual culture, visual pleasure & visual disruption – subjectivity, sexuality & conscious Audience studies : audience, fans, users , ethnographies of visual objects
UNIT 4 COMPOSITIONAL INTERPRETATION
Critical study of visual methodology –production –image – compositional interpretation: technology & image production – media ,gender & sexuality : construction of femininity , patriarchal romance & domesticity – empowering – media & masculinities.
UNIT 5 SEMIOLOGY
From quality to quantity: content analysis : introduction - four steps to content analysis – semiological study – selecting images for study - sign making meaning processes – social semiotics

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
The Visual Narrative Method course provides a comprehensive introduction to the theories and concepts that shape storytelling through visual media. Students will begin by exploring visual semiotics, which involves understanding how signs, symbols, and images create meaning. The course then delves into the basic elements of narrative structure, such as plot, character, and setting, and how these are expressed visually. Key topics include the principles of composition, the use of perspective, and the way time and motion are depicted in visual storytelling.In addition, the course examines how different cultures and societies interpret visual narratives, highlighting the impact of cultural context on audience perception. Ethical considerations are also addressed, particularly in terms of how people, cultures, and events are represented in visual media. By studying a variety of genres and engaging with real-world examples, students will learn how visual narratives can both reflect and influence societal values and ideologies.Throughout the course, students will engage in critical analysis of visual narratives, applying theoretical frameworks to deepen their understanding. The course culminates in a final project where students will choose a visual narrative to analyze in detail, allowing them to apply their knowledge and develop strong analytical skills. This course is designed to prepare students for advanced studies or careers in fields like media studies, film theory, and visual communication.
- Teacher: Prasanna Lakshmi S
- Teacher: RAJA N
To impart basic concepts meaning and models of development
To make students aware about problems and issues of the development.
To Inculcate knowledge of development communication and relations with media and society.
To Know the functioning of media in development coverage.
5. Understanding the rural India and its problems.

- Teacher: SENTHIL KUMARAN E
- This course is to enable learners to understand the language of cinema and make them to recognize significant film movements and theories as well as filmmakers who have shaped the course of world cinema, along with a reading of key cinematic texts. It also covers the topics on recent trends and turning points in cinema. The course will motivate learners to approach and appreciate cinema in an academic way with the components of cinema.

- Teacher: YUVARAJ J
Social media advertising is a type of digital marketing that involves using paid ads on social media platforms to reach a target audience. It's a key component of a social media marketing strategy, along with social media marketing (SMM)
- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
Electronic field production (EFP) is a television industry term referring to a video production which takes place in the field, outside of a formal television studio, in a practical location or special venue. Zettl defines EFP as using "both ENG (electronic news gathering) and studio techniques. From ENG it borrows its mobility and flexiblity; from the studio it borrows its production care and quality control. EFP takes place on location (which may include shooting in someone's living room) and has to adapt to the location conditions... Good lighting and audio are always difficult to achieve in EFP, regardless of whether you are outdoors or indoors. Compared to ENG, in which you simply respond to a situation, EFP needs careful planning.

- Teacher: Dr. A R VIMAL RAJ
- Teacher: SHETTY DEEPA THANGAM GEETA
TEXTILE PROCESSING
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
- To enable the students to learn the preparatory steps of Textile wet processing
- To impart knowledge on various dyeing techniques.
- To provide the details printing and textile finishing.
UNIT I
Introduction - Wet processing- Areas and importance Production sequence of textile fabrics- flowchart. Process of removing impurities from fabrics – Singeing, Desizing, Scouring, Bleaching, Mercerizing.
UNIT II
Dyeing - Classification of dyes -Stages of dyeing - Different methods - Fiber dyeing - Stock Dyeing - Top Dyeing Yarn Dyeing - Methods – Skein Dyeing, Package dyeing, Warp beam Dyeing.Fabric Dyeing - Open Width Dyeing, Rope form Dyeing.Garment Dyeing - Methods – Exhaust Process, Continuous process.Colorfastness- Special dyeing effects cross dyeing- Union -Dyeing - tone on tone- Imperfections in dyeing.
Textile printing – Introduction - Method of printing - Block, Stencil, Hand -Screen, automatic Screen – Rotary- Screen, Roller, Ink -jet and Heat transfer Printing. Styles of printing - Direct Printing, Discharge Printing Resist Printing. Blotch Printing, Warp Printing - Burn- out Printing – Duplex Printing - Engineered print.
UNIT-IV
Fabric Printing - Fabric printing through vegetable blocks- Fabric resist-dyeing techniques. Silk painting using wax- urea and rock salt resists- Tie & Dye- Batik. Handmade Flock printing- Quilting by Hand, Imperfection in Printing. Fabric performance testing - Fabric test- Surface friction test- Appearance test- Functional test- Colorfastness.
UNIT V
Textile finishing - Classification of finishes- Aesthetic finishes and Functional finishes - Wrinkle-free finishes, Water repellent, Soil release finish, Special purpose finish, Anti-bacterial finish, Silicon finish, Denim finish. Fabric Care Labeling - Environmental Issues.

- Teacher: Savithiri S
- The studio aims at widening the avenues of creativity and allows inquiring more on lateral thinking.
- The emphasis is on understanding the process of design as a proactive and analytical tool toward generating alternatives which forms the foundation for future design by designing a meaningful space.
SKILL ENHANCEMENT COURSE – I
TRADITIONAL SURFACE ORNAMENTATIONEmbroidery is an art of decorating cloth with needlework using different types of thread to create fascinating designs. Embroidery can also be defined as an art of using stitches as an adorning feature by embellishing fabric or other material with designs, stitches in strands of threads on yarn using a needle. Embroidery may also include other materials like pearls, beads, sequins, etc. Embroidery is a craft of enhancing fabric with motifs, abstract design, patterns. Embroidery varies according to its underlying foundation fabric and whether the design is stitched on the top or through the base fabric.
Indian embroidery includes a wide variety of regional embroidery styles varying by different regions and materials used. Embroidery is India’s persistent eloquent tradition. Every state and region in India enjoys its own style. Needlework is not the only means of decorating the fabric but the fabrics are also embellished by stories of the community, with motifs emerging from natural surroundings, religious inscriptions, economic state, etc.
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
· To impart basic skills in hand embroider techniques, surface designing and other ornamentation techniques.
· To introduce the students to various traditional embroidery techniques of India.
· To create awareness on heritage of traditional embroideries of Indian culture.
LIST OF EXERCISES:
1. Hand embroidery – Outline stitches, Filling Stitches, Decorative Stitches.
2. Embroidery of North India – Chamba Rumal of Himachal Pradesh, Kashidha of Kashmir, Phulkari of Punjab.
3. Embroidery of Southern India - Kasuti of Karnataka.
4. Embroidery of Central India - Chikankari of Uttar Pradesh.
5. Embroidery of Eastern India- Kantha of West Bengal, Sujani of Bihar, Pipli appliqué of Orissa.
6. Embroidery of Western India- Kutch of Gujarat, Mirror work of Rajasthan.
7. Embroidery of Tribal India – Toda Embroidery of Tamilnadu .
COURSE OUTCOMES
Handmade items are recaptured as new personification and the manifestation of luxury. Many ancient embroidery styles are being reclaimed and popularized. These embroidery styles are not only gaining its acceptance among the Indian designers but are also very popular with the International labels. Mumbai is a trade hub for many luxury brands chasing Indian embroidery.
On successful completion of the course, the students will able to
CO1: Identification of regional embroideries developed by various communities
CO2: Understand the origin of technique and design with reference to colours, motifs, layouts of different
embroidered textiles.
CO3: Appreciate the finer nuances of embroideries.
CO4: learn about the evolution of embroidered textiles over a period of time

- Teacher: Krithika S
Traffic Characteristics and Forecasting
Traffic Surveys
Traffic Regulatory Measures
Traffic Safety and Environment
Traffic Management

- Teacher: Dr.V.Sampathkumar .
COURSE OBJECTIVES
To develop a holistic perspective based on self-exploration about themselves (human being), family, society and nature/existence
To understand (or developing clarity) the harmony in the human being, family, society and nature/existence
To strengthen self-reflection
To develop commitment and courage to act
Upcycling stops adding stuff to a world that is already overwhelmed with material things. It also reuses materials that may otherwise end up in the landfill in creative and innovative ways - producing original often one-of-a-kind items from what many consider to be waste.

OBJECTIVE: To expose the basic concepts/theories of psychology relevant to architecture and the relationship between man and the environment.
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
Different perspectives on Urban Society - The concept of community, function and types. History of Urban Communities, Development, The fall of Urban Society. Introduction to environmental psychology, its importance in the field of architecture, understanding the principles of psychology, the roots and edges of environmental psychology, theories and approaches in environmental psychology.
UNIT 2 URBAN METROPOLITAN SOCIETY
Development of Urban Metropolitan Society, Projections of Urban population, Growth of Urban Areas, Dynamics of Metropolitan population growth, Contemporary Urban location theories, Lifestyle in city and suburbs, Urban Politics. The city, urban morphology, movement as motivating factor in design, monuments and dwelling, genius loci, street and square, urban conservation, responsive environments, pedestrian spaces and plazas, the social life of small urban spaces, new urbanism, landscape urbanism, sustainable urban form.
UNIT 3 COMMUNAL FUNCTIONS - HOUSING, TRANSPORTATION AND HEALTH
Housing Need, Different Housing types, Supply, Demand. The problem of Slums and squatter settlements. The urban transportation system. Health of Urban Population. Water Pollution, Air Pollution, Garbage and solid waste management. Concept of perception, visual perception, theories on environmental perception-environmental perception and design. Concepts of cognition. Environmental cognition and design. Environment and human response in relation to different environmental variables.
UNIT 4 PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT AND HUMAN BEHAVIOUR
Concept of personal spaces, personal space and human behaviour. Personal space and environmental design.
Concept of territoriality, territoriality and human behaviour & territoriality and environmental design. Residential environment. Concept of Home. Neighbourhood concept & Neighborhood satisfaction. Place attachment theory, Workplace environment
and behaviour. Application of the knowledge in the design of a residence, community neighbourhood and other built
environments.

- Teacher: Yusuf Chiniwala
- Teacher: Michael Rahul Soosai
- Teacher: Venkatesan D
- Teacher: Sathish S
- Teacher: oviya R.P
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To develop knowledge in design of vehicle body to give maximum comfort for the passengers
To develop skills in the areas of car body design, bus body design, active and passive safety.
To understand different types of bodies and ergonomics of the vehicle
COURSE OUTCOMES
On completion of the course, student will be able to
CO1 - Discuss the different types of car body design and its safety features.
CO2 - Select a suitable body optimization techniques to minimize drag and able to describe the wind tunnel testing procedure.
CO3 - Classify the various types of bus body construction and able to identify the body layout.
CO4 - Describe the different types of commercial vehicles and its design.
CO5 - Explain the various types of materials and painting techniques used in automobiles.
CO6 - Acquire knowledge about the corrosion coating methods
Drawing from Observation is an all levels course focused on developing drawing skills in black and white. This course will help to get familiar with drawing tools and techniques while developing visual literacy by drawing from life.

- Teacher: Krithika S
- Teacher: Savithiri S
- Teacher: MRITTIKA MAITRA
This course introduced to the special technique of writing for mass media. And to help students write for different medium so that they know to incorporate the various principles of each medium. The course content will make to understand the nuances of writing for all media and thus help students cope with the modern journalistic skills. The outcome of the course is to Understand of Broadcast News Writing, Special News Story coverage. it also included to Interpret and demonstrate the viability of the current news according to the signs of the times in the Radio. And the Ability to create Radio News & Radio Programme Script, Web Publishing & online Advertising, copy writing. Also this course design to Ability to create: Press Release (Event, Movie, Audio launch), Organizational & Promotion Writing.

- Teacher: NAZINI N
அலகு - ஒன்று
சிற்றிலக்கியங்கள் தோற்றம் வளர்ச்சி குறித்தும் அவற்றுள் பரணி இலக்கியங்களில் முதன்மையான கலிங்கத்துபரணியையும் குறவஞ்சி இலக்கியங்களில் திருக்குற்றாலக் குறவஞ்சியையும் மாணவர்கள் இவ்வலகின் மூலம் அறிந்து கொள்வர்.
அலகு – இரண்டு
புதுக்கவிதை தோற்றம் வளர்ச்சி குறித்தும் புதுக்கவிதைகளின் முன்னோடிகளான பாதியாா், பாரதிதாசன், நா.காமராசன், இன்குலாப், பாரதிபுத்தின் ஆகியோர் தம் கவிதைகள் குறித்து மாணவர்கள் அறிந்து கொள்வர்.

- Teacher: Shanmugam V